Chapter 26: Phylogeny and the Tree of Life
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
BIOL 1030
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
Biodiversity
the variety of life on Earth
Taxonomy
the naming and grouping of organisms
Systematics
the science of figuring out relationships between organisms
form biogenetic trees
Phylogeny
the evolutionary history itself
Taxon
The named group at ANY level
Ex: Mammalia at taxon level or Panthera at genus level
Clade
A special group
Ancestors plus all its descendants
Binomial Nomenclature
Two part naming system
Genus (always capitalized)
species epithet (always lowercase)
if typed, italicize
if written, underline
Carl Linnaeus
Father of modern taxonomy
Linnaean Classification (Hierarchy)
Domain → Kingdom → Phylum → Class → Order → Family → Genus → Spain
Domain
Most inclusive group of hierarchy
Species
Most exclusive group in hierarchy
Nested hierarchy
Lower, simpler levels are contained within higher, more complex levels
“Russian Doll” formation
Ex: Species are more nested than Order
Broader traits
More inclusive
Narrower traits
less inclusive
Bacteria
Prokaryotes, diverse
Archaea
Prokaryotes, extremophiles, closer to Eukarya
Eukarya
Nucleus; protists, fungi, plants, animals
All life comes from a
Single common ancestor
Linnaean System
based on physical characteristics only
does not always reflect evolutionary relationships
Groups become static (don’t account for change over time)
resulted in misclassification
Static
Groups are not accounted for changes over time
Modern taxonomy is based on…
Phylogeny (evolutionary relationships) rather than just physical similarities
Phylogenetic Trees
Shows a branching pattern that matches how systematists classify groups or organisms nested within more inclusive groups
Systematics go hand in hand with ___
Phylogeny
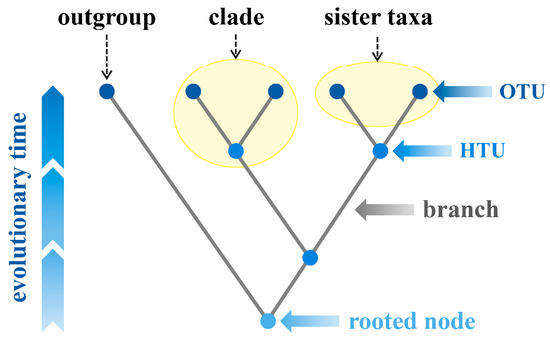
Root of a Phylogenetic Tree
“origin”
ancestral population from which all the other species originate
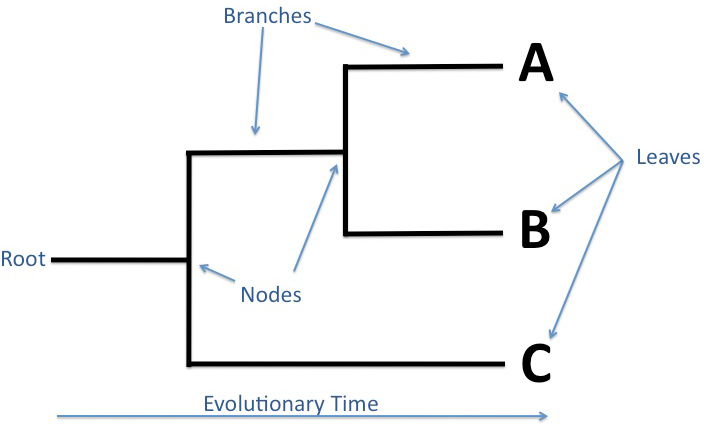
Node of Phylogenetic Tree
Common ancestor
a branching point form the ancestral population
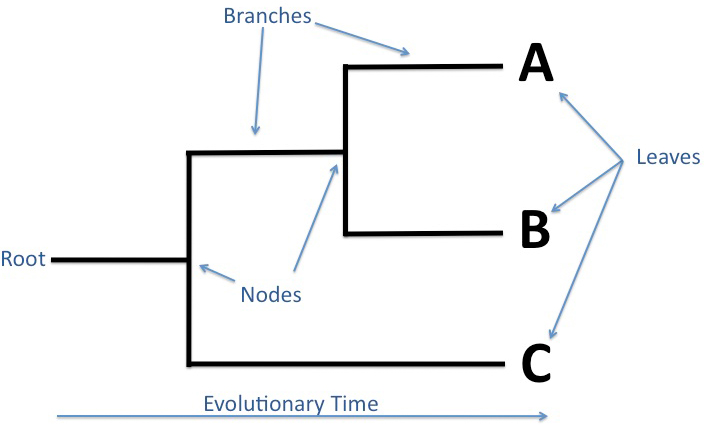
Branch of Phylogenetic Tree
Lineage
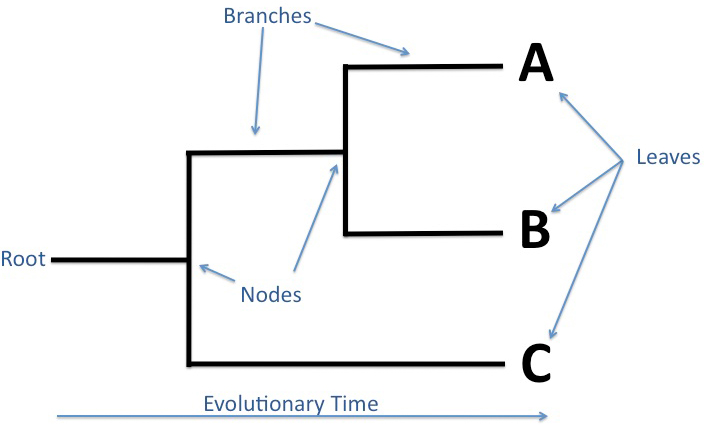
Clade of Phylogenetic Tree
A piece of phylogeny that includes an ancestral lineage and ALL the decendants of that ancestor
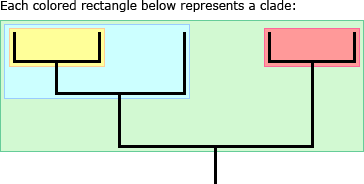
Sister Taxa
Groups of organisms that share a common ancestor that is not share by any other group
members of a sister group are each other’s closest relatives
Trees show__
Relationships, NOT progress
they serve as testable scientific hypotheses
Can make predictions that are close to the facts
Morphology
The study of the form and structures of plants and animals
fossils, anatomy
Homologies
Phenotypic and genetic similarities due to shared ancestry
Similar morphologies____
Doesn’t always mean organisms will look similar
Analogies
Similarities between organisms that are due to convergent evolution
Ex: bats, birds, and butterflies all have wings BUT have different reasons for developing them
Convergent Evolution
Occurs when similar environmental pressures and natural selection produce similar (analogous) adaptations in organisms from different lineages
No common ancestor
Morphology alone is____
misleading
Cladistics
Method of classification based on ancestry
Biologists attempt to place species into groups called clades
Clades are nested within larger clades
Systematics relies on cladistics
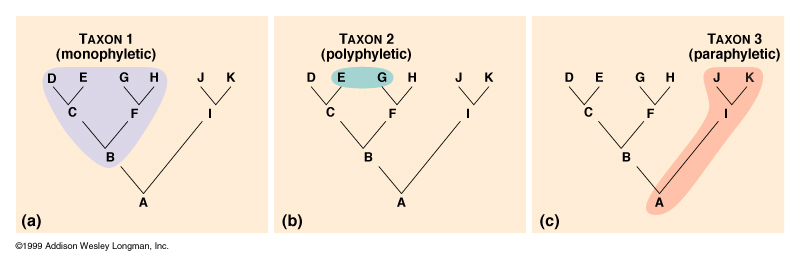
Monophyletic
True clade
Ancestor + ALL descendants
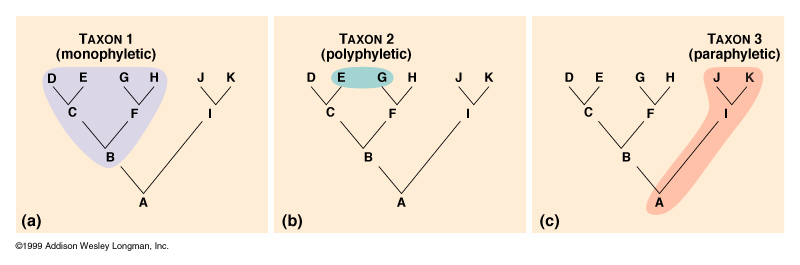
Polyphyletic
groups of organisms form MULTIPLE ancestors
Do not share a common ancestor
Not a clade
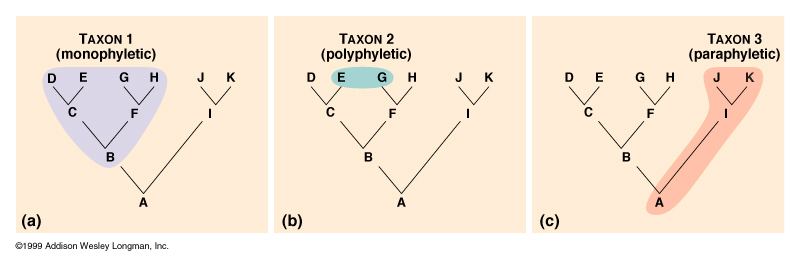
Paraphyletic
Includes an ancestor but NOT ALL its descendants
Not a clade
Ancestral Characters
A character that originated in an ancestor of the taxon
Derived Characters
New traits that are unique to a clade
most useful in building trees
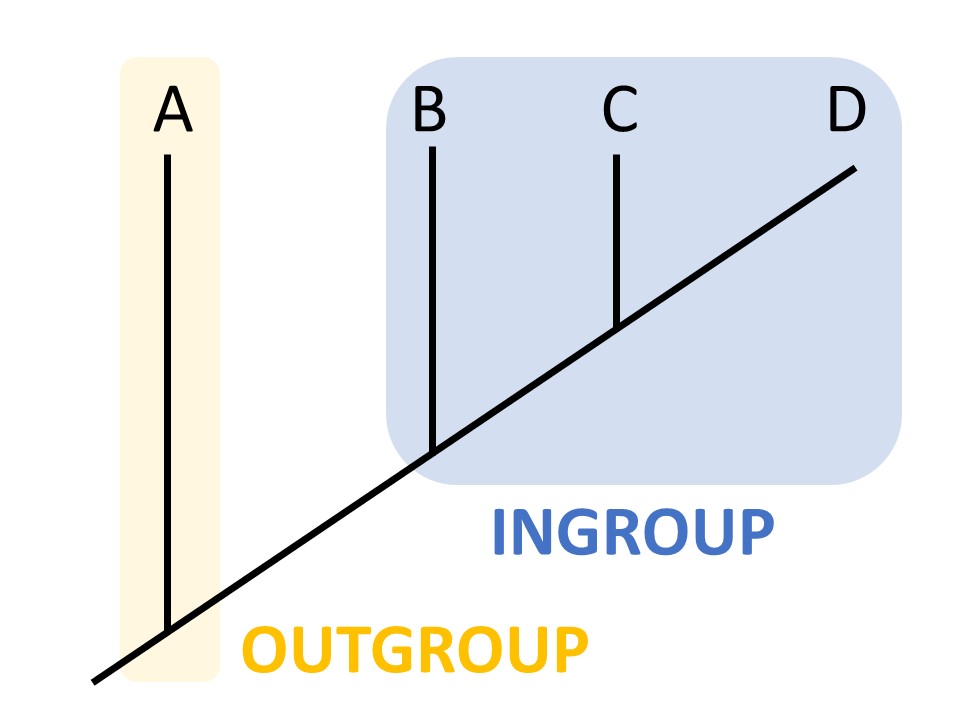
Outgroup
Lineage that diverged earlier
a species or group of species that is closely related to but not part of the group of species of interest (ingroup)
Longer branches mean___
A species has evolved more rapidly
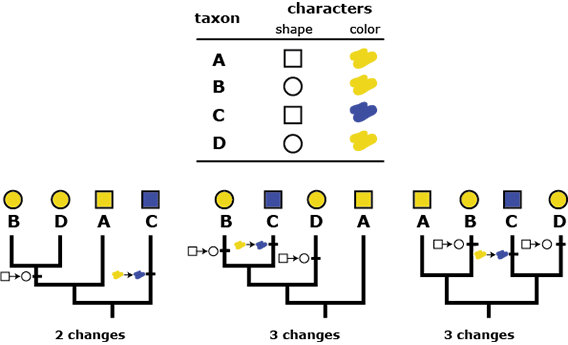
Maximumm Parsimony
Seeks to investigate the simplest explanation that is consistent with the facts
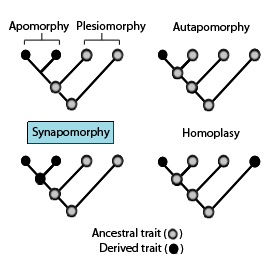
Apomorphy
new (derived) trait that evolved in a group, different from the ancestral condition
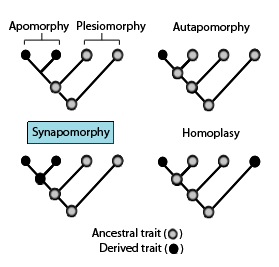
Plesiomorphy
old (ancestral trait) found in earlier ancestors
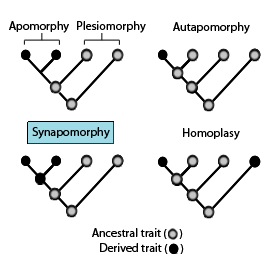
Synapomorphy
Share new (derived) trait that two or more groups have
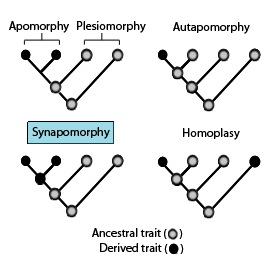
Autapomorphy
unique (derived) trait found in one lineage, not shared
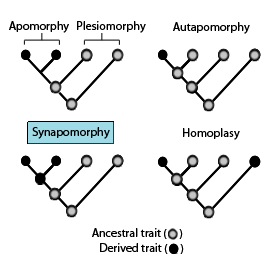
Homoplasy
“false similarity” (similar trait not due to share ancestry)