cognitive-perceptual impacts on motor control
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
perception
integration of sensory impressions (peripheral sensory/afferent info) into psychologically meaningful info (higher level processing at cortex, interpretation and meaning to incoming afferent info)
cognition
ability to process, sort, retrieve and manipulate info
orientation & memory
attention, reasoning, planning, problem solving
motivation, emotional aspects
critical for goal directed movements
perception and cognition
both are required for successful movement within the environment
deficits in either=often major barrier/s to successful rehabilitation
information processing
the CNS must identify and perceive sensory inputs contribution to
individual must determine useful actions
individual must execute action w/ correct movement sequencing, timing, coordination
executive function
a variety of higher cognitive processes that use and modify information from many cortical sensory systems to modulate and produce behavior
necessary for effective, goal directed actions and for the control of attentional resources
3 core components of executive function
behavioral inhibition (self control), working memory, cognitive flexibility (set shifting)
together they allow for reasoning, problem solving, and planning
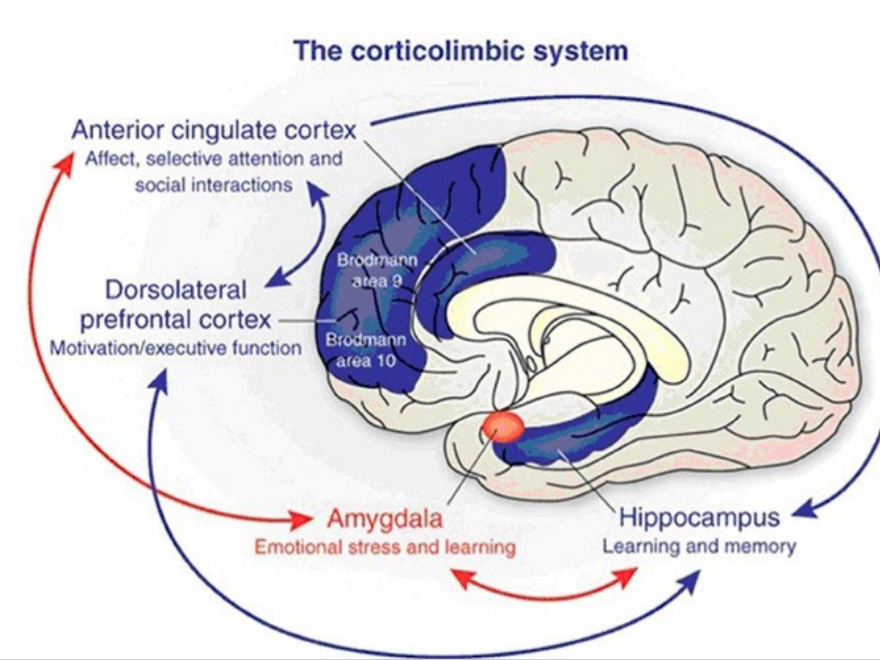
executive functioning areas of the brain
frontal lobe and related networks play critical role
DLPFC: dorsolateral prefrontal cortex
cingulate cortex
limbic system
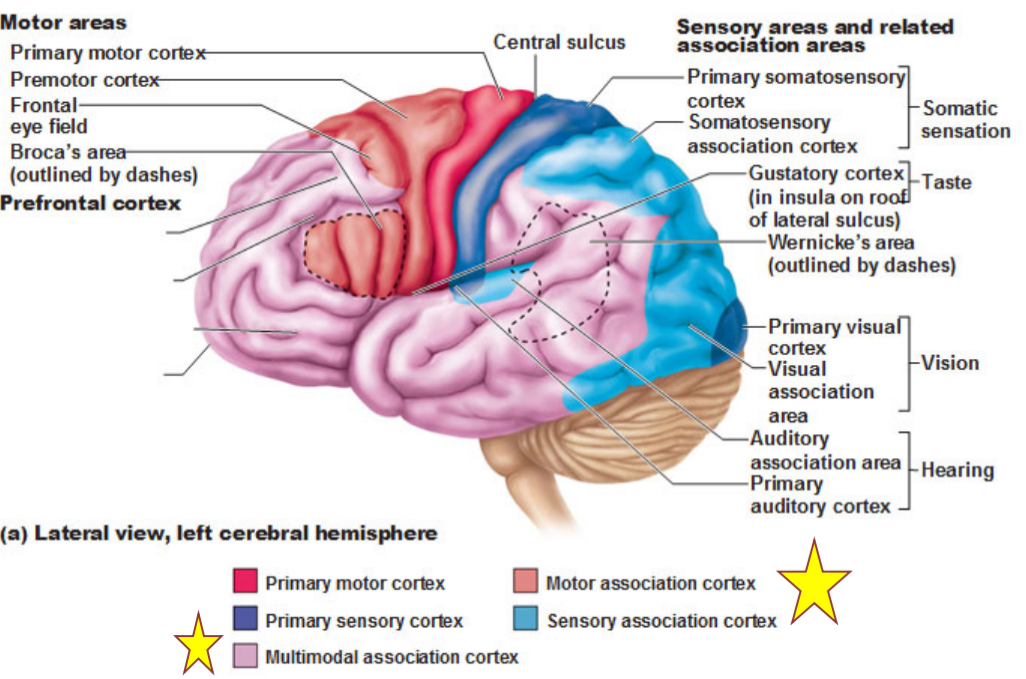
association areas
association areas
multimodal, motor, and sensory
parts of cognition
processes that contribute to establishing goals or intent of movement
orientation
memory
attention
reasoning
problem solving
planning
motivation
emotional aspects
types of attention
focused, selective, sustained, alternating, divided
focused attention
the ability to respond discretely to specific visual, auditory, or tactile stimuli
selective attention
the ability to maintain a behavioral or cognitive set in the face of distracting or competing stimuli
sustained attention
the ability to maintain a consistent behavioral response during continuous and repetitive activity
alternating attention
shift focus of attention and move btwn tasks having different cognitive requirements
divided attention
highest level of attention and refers to ability to respond simultaneously to multiple tasks or multiple task demands
attention impairment
inability to follow directions
orientation impairment
disoriented
memory impairment
appears disoriented, wil forget names, schedules, etc. and decr ability to learn
problem solving impairments
difficulty with ADLs, sociallly inappropriate, inability to recognize threats to safety
higher level processing
receiving info about the environment and state of the body through somatosensation, visual, vestibular system (peripheral sensory mechanisms from the environment)
perceptual impairments
body scheme: awareness of body parts, position of body
R/L discrimination: ability to understand R/L
body part indentification: ability to identify body parts
anosognosia: unawareness or denial of deficits
unilateral neglect: neglect of 1 side of body/space
position in space: ability to understand concepts like over, under, around, above , below
spatial relations: ability to perceive self in relation to other objects
topographic orientation: ability to find one’s way from one place to another
figure ground perception: ability to distinguish foreground from background
limb apraxia: inability to carry out purposeful movement in the presence of intact sensation
constructional apraxia: deficits in constructional activities
dressing apraxia: inability to dress oneself
praxis
ability to perform a learned skilled movement
apraxia
inability to perform a learned movement that cannot be accounted for by weakness, in coordination, sensory loss or incomprehension or inattention
agnosia
inability to recognize and identify objects, persons, or sounds using one or more of their senses despite otherwise normally functioning senses
deficit cannot be explained by memory, attention, language problems or unfamiliarity to the stimuli
perceptual deficit
damage typically to post parietal and occipital temporal cortex
perception, avoidance, confidence
perception infl how individuals conceptualize their movement
perception infl what activities individuals participate in
all congruent with actual abilities normally
standardized outcome measures for cognition
mini-mental state exam (MMSE) C&P
slu mental status exam (SLUMS)
montreal cognitive assessment (MOCA)
minicog P
clock drawing test
quick assessment of cognition (executive function)/perception (visuospatial relationships)
screens for attentional and executive dysfunctions (cognition) and apraxia or neglect (perception)
instruct pt to draw numbers to make circle look like face of clock, then draw the hands of the clock to read 10 after 11
score 1-6 with 1=perfect and 6=no representation of a clock
avoidance measures
fear avoidance beliefs questionnaire (FABQ): impact on PA & work
fear of falling avoidance behavior question (FFABQ)
activities specific balance confidence scale (ABC)
kinesiophobia scales
pt specific functional scale with avoidance