DC Drives
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards for all of DC Machine Drives- Prof Crabtree
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Motor
Converts electrical energy to mechanical energy
Generator
Converts mechanical energy to electrical energy
Electrical Machine
A device for electromechanical energy conversion (can be classified as a motor or a generator)
What can electrical machine be grouped into
DC machines, AC machines and Special Machines
Types of DC Machines
Wound field DC machines: Separately-excited, series-excited or shunt-excited (and sometimes ‘universal)
Permanent magnet DC Machines: Brushed or Brushless
Types of AC Machines
Synchronous generators
Synchronous motors
Induction generators
Induction motors
Synchronous generators
Primarily for power generation (hence calling them ‘generator’ when they can be either)
Wound field: Conventional (coal, gas, nuclear) generation (usually around 1000-3000 rpm); low speed generation (wind turbines at <20 rpm)
Permanent magnet: wind and other renewables; usually medium to high speed (200-2000 rpm) but very flexible
Synchronous motors: Limited applications for high power loads (but they could be generators too…)
Induction generators: Limited applications and functionality; typically used in older fixed-speed wind turbines at 1000-1500 rpm
Induction motors: Still referred to as “the workhorse of industry” and with good reason; around 80-90%of all industrial loads are induction motors; highly robust
Special Machines
Stepper motors: Fine positioning and control
Switched reluctance motors
Synchronous reluctance motors: Harsh or extreme environments (interestingly never really investigated as generators so there is your PhD topic)
Universal motors (e.g. power tools)
motor drive
a system that controls how a motor works — like how fast it spins or how much power it uses.
Electric Drives
A collection of electrical machines together with their power supplies and control equipment
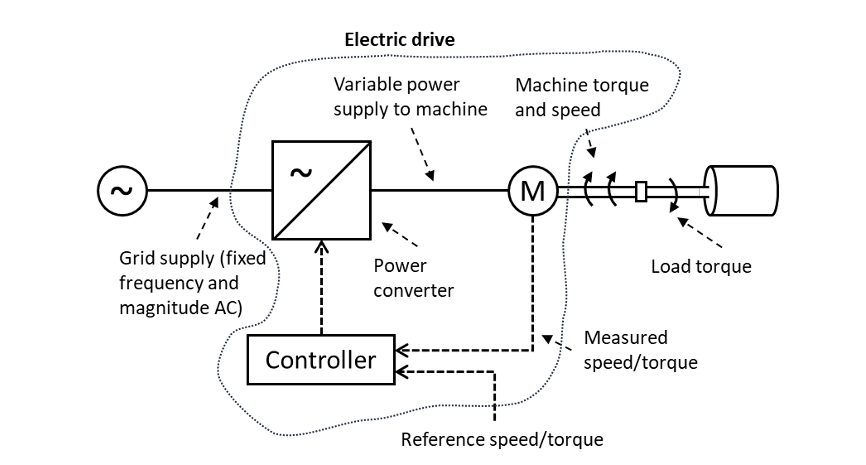
What can a power converter do
It can perform various functions, the most common of which are rectifier and inverter
Rectifier
Converts AC to DC
Inverter
Converts DC to AC
Power Converter
A catch-all term but which usually refers to a system to convert fixed frequency AC (such as from the power grid) to variable frequency AC (to control a machine) or vice versa. Such a converter will usually convert AC to DC and then DC to AC, meaning it combines both a rectifier and inverter with a ‘DC link’ between the two AC sides
What can drives control?
The speed and torque of an electrical machine. This could be a motor driving a water pump
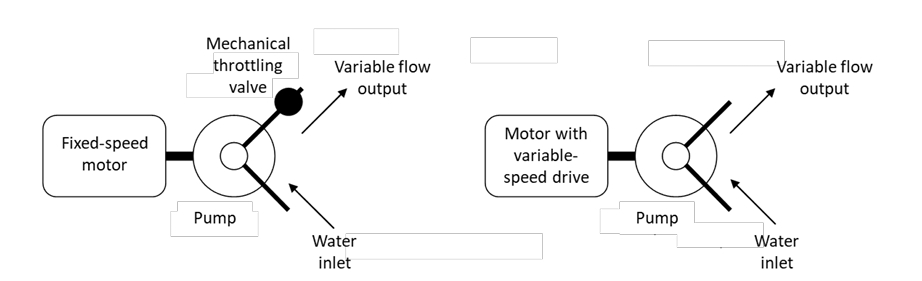
What is a major advantage of using a power converter to create electric drive systems?
The increased controllability generally allows for increased system efficiency.
How can you describe the drive quadrants in relation to motor operation?
Q1: Forward motoring (speed and torque are both positive)
Q2: Backward braking (positive torque and negative speed)
Q3: Backward motoring (speed and torque are both negative)
Q4: Forward braking (positive speed and negative torque)
What happens in Quadrant 1?
Torque is developed in the direction of the machine’s rotation, hence electrical power is converted into mechanical power and the machine operates as a motor trying to accelerate a load
What happens in Quadrant 4?
The torque opposes the direction of rotation of the machine hence the machine absorbs mechanical power from the load. The system is now a generator. In this quadrant, power is fed back to the electrical supply and the machine is under regenerative braking.
What happens in Quadrant 3?
As in Q1, the torque and speed act in the same direction. The difference is that the direction of rotation is reversed. this is the motor driving backwards, attempting to accelerate the load.
What happens in Quadrant 2?
As in Q4, torque acts in the opposite direction of rotation, extracting energy from the load (braking and generating)
What is an example of four-quadrant operation?
A train traction system where an electric drive provides forward and backwards motion plus braking in both directions.
What is a DC machine made up of?
Two main electromagnetic elements
Armature winding (usually on the rotor)
Field winding (usually on the stator) or permanent magnets
What do the commutators and brushes in the DC machine do?
Commutators are formed of insulated copper segments connected to the armature coil and rotating with it. The commutators carry the armature current and, together with the stationary carbon brushes, form a mechanical inverter (motor operation) or rectifier (generator operation)
Brushes are mounted in the stationary frame and rub over the commutator segment as they rotate. They allow us to have electrical contact with a moving circuit (the rotating armature)
What is the equation for Lorentz Force
F= B x Il (B(Tesla, T) is the flux density, l(metres) is the axial length of conductor within the field, I (amperes, A) is the armature winding current and N is the number of turns in the armature winding)
Back electromotive force (back EMF)
Induced voltage due to armature rotation
What does a separately-excited DC machine look like?
see image
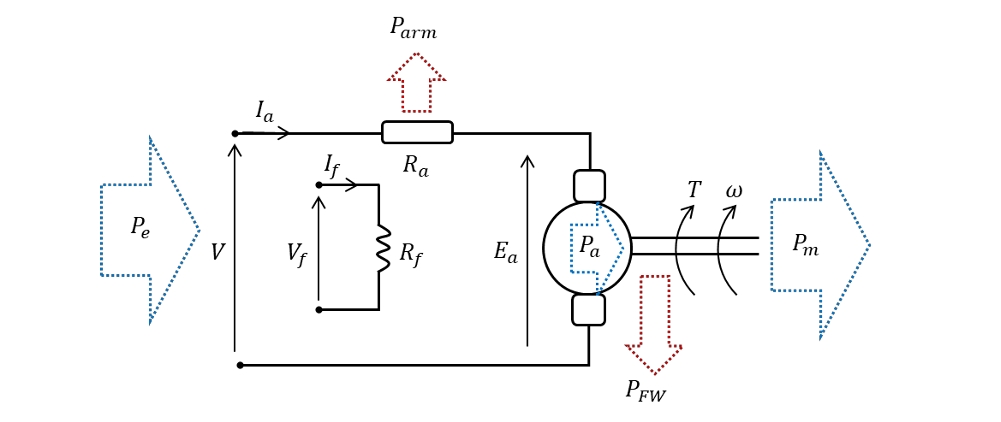
What does 𝐸𝑎 =𝑘𝜑𝜔 state?
The magnitude of the induced EMF is proportional to the speed as well as the strength of the magnetic field linking the armature coils
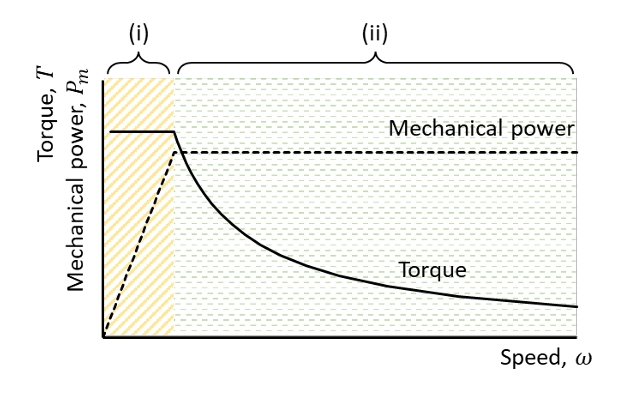
What do the two regions signify?
DC machine speed and torque depend on both the armature and the field voltages but that the two are, ultimately, not completely independent
Region (i): Maintaining a constant field current and increasing the armature voltage can achieve constant torque operation as show in region (i) of the torque-speed characteristic. the machine reaches its rated speed at rated armature voltage
Region (ii): Speed can be increased beyond rated by decreasing the field current. This is a constant power region and torque decreases as speed increases. This is field weakening control.
What happens when a diode is forward biased?
When forward biased, the ideal diode behaves exactly as a short circuit with zero voltage drop and a current which is determined by other circuit elements
What happens when a diode is reverse biased?
When reverse biased, the ideal diode becomes an open circuit, blocking the flow of current whilst maintaining a voltage drop across itself
1-quadrant buck converter DC motor drive
A circuit that reduces voltage from a DC supply to control the speed of a motor in one direction, allowing current and voltage to flow in only one quadrant (positive voltage and positive current)
What are two key differences of a boost converter when compared to the buck converter
The inductor is towards the input side of the circuit
The transistor (IGBT) is in parallel rather than series
What does a 1Q buck converter do in terms of power?
Transfers power from a higher voltage source to a lower voltage sink (i.e. stepping down voltage in the direction of power flow)
What does a 1Q boost converter do in terms of power?
Transfers power from a lower voltage source to a higher voltage sink (i.e. stepping up voltage in the direction of power flow)
Rectifier
When it converts AC voltage/current/power to DC