urinary
1/417
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
418 Terms
In utero, the kidneys develop in what?
The pelvis.
In utero, when the kidneys develop into the pelvis, where would they ascend to after?
What weeks?
Abdomen
12 - 15
What are the main functioning units of the kidneys?
Nephrons.
When do the nephrons begin functioning?
8 weeks.
When are the kidneys completely formed?
36 weeks.
What other structure forms at the same time as the kidneys?
The genitals.
Variations in fusion account for (1)___________________, (2)_______________, and other anomalies.
Junctional parenchymal defect
Column of Bertin
Where does the left kidney lie to the spleen?
Inferior
Medial
Where are the adrenal glands located in relation to the kidney?
Anterior
Medial
Superior
Where is the right adrenal gland located in relation to the kidneys?
Superior.
Where is the left adrenal gland located in relation to the kidneys?
Medial.
Where does the tail of the pancreas lie to the upper pole of the left kidney?
Anterior.
The left renal artery goes directly into what structure?
The left kidney
The left renal vein goes to what structure?
The left kidney
The left or right renal vein is longer?
Left renal vein
Where does the right renal vein flow from?
The right kidney
What are the 2 main functions of a nephron?
Excrete waste
Regulate the composition of blood
The nephron consists of what 2 main structures?
Renal corpuscle
Renal tubule
What is another term for renal corpuscle?
Malpighian body.
What is another term for Malpighian body?
Renal corpuscle.
What does the renal corpuscle do?
Filters the blood in the glomerulus.
The glomerulus consists of a network of (1)_________ surrounded by (2)_________ capsule.
Capillaries
Bowman’s
Blood is filtered,
When needed substances are returned to the _______
Any _______ product and excess water pass into the collecting systems as ______
Blood
Waste, Urine
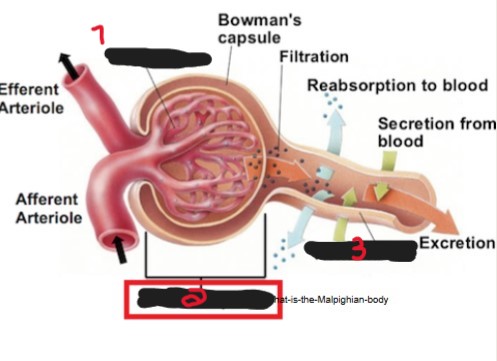
On the image, what is the name of the structure labeled ‘1’?
Glomerulus.
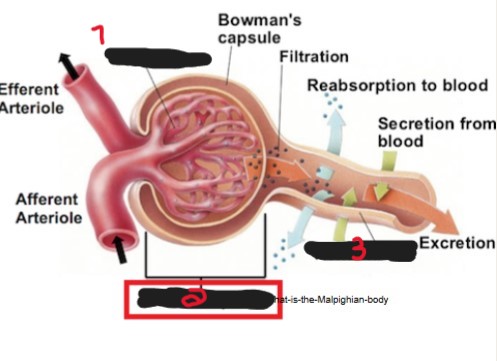
On the image, what is the name of the structure labeled ‘2’?
Renal corpuscle/Malpighian body.
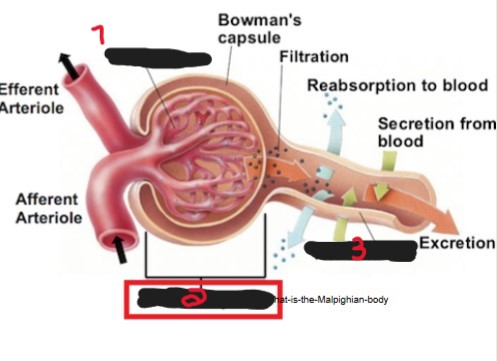
On the image, what is the name of the structure labeled ‘3’?
Renal tubule.
Inside the renal tubule; once blood is filtered, where does it flow from there?
→ Proximal convoluted tubule
→ Loop of Henle
→ Distal convoluted tubule
What is another name for loop of Henle?
Nephron loop.
What is another name for nephron loop?
Loop of Henle.
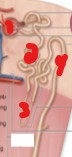
On the image, what is the name of the structure labeled number 1? (The outer part, not the inner)
Renal corpuscle.
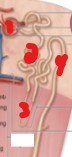
On the image, what is the name of the structure labeled number 2?
Proximal convoluted tubule.
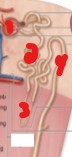
On the image, what is the name of the structure labeled number 3?
Loop of Henle/Nephron loop.
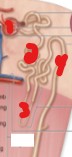
On the image, what is the name of the structure labeled number 4?
Distal convoluted tubule.
In the distal convoluted tubule,
Substances needed by the body are returned to the _______
Waste products not needed are passed into the ducts as ______
Blood
Urine
What is the juxtaglomerular apparatus made up of?
Proximal convoluted tubule
Nephron loop
Distal convoluted tubule
What does the juxtaglomerular apparatus regulate?
Function of each nephron
Blood pressure
What is another term for gerota’s fascia?
Renal fascia.
What is another term for renal fascia?
Gerota’s fascia.
Gerota’s fascia is a layer of (1)________ tissue that surrounds the (2)__________ and _______________.
Connective
Kidneys, Adrenal glands
Gerota’s fascia provides what 2 things?
Support
Protection
What is the echogenicity of the renal fascia?
Hyperechoic
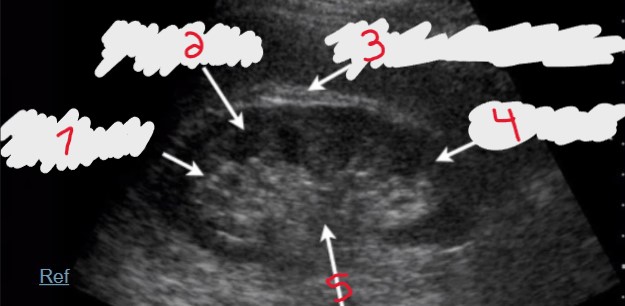
Which number would be the correct structure for Gerota’s fascia?
3
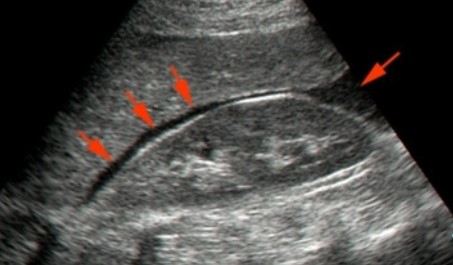
The red arrows point to what area?
Morrison’s pouch
What is Morrison’s pouch?
A space that separates the liver from the right kidney
Can fluid accumulate in Morrison’s pouch?
Yes, and from a wide range of causes.
The renal capsule has what echogenicity to the cortex?
Hyperechoic
The renal cortex extends from where to where?
Renal capsule to medullary pyramids.
What is the normal measurement for the renal cortex?
Greater than 1 cm
What should the renal cortex echogenicity be to the liver?
Isoechoic
Slightly hypoechoic
What does the renal medulla contain?
Medullary pyramids
Medullary pyramids can be confused with what pathologies?
Mass
Cysts
What is the appearance of a medullary pyramid on US?
Hypoechoic
Equally spaced triangular or round areas
The medullary pyramids lie between which 2 structures?
Cortex
Sinus
On a medullary pyramid, where does the base lie?
Next to the renal cortex
On a medullary pyramid, where does the apex lie?
Towards the renal sinus
What is the echogenicity of the renal sinus?
Hyperechoic
The echogenicity of the renal sinus is hyperechoic due to what?
Various interfaces between fat, vessels, and fibrous tissue
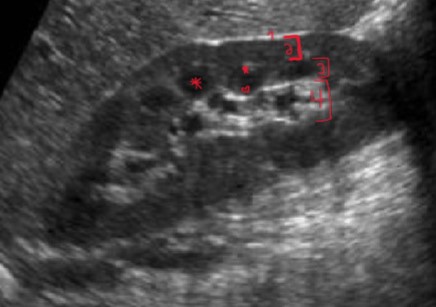
What are the names of the layers that are numbered? (#3 is LAYER name, not the structures inside)
Renal capsule
Renal cortex
Renal medulla
Renal sinus
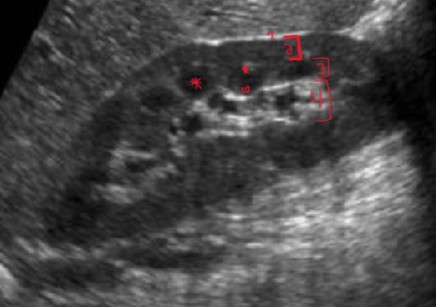
What is the name of the structure labeled with an * ?
Medullary pyramid
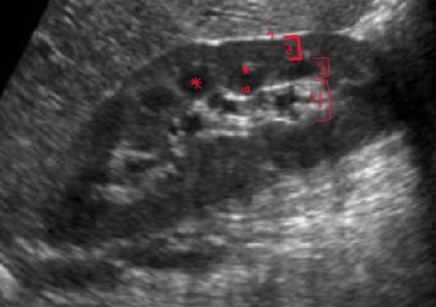
What are the names of the areas labeled with a star and heart on a medullary pyramid?
Star = base
Heart = apex
The renal hilum is the (1)______ opening for which 3 structures?
Medial
Renal vein, renal artery, and ureter
List the structures in the renal hilum from anterior to posterior.
Renal vein
Renal artery
Ureter
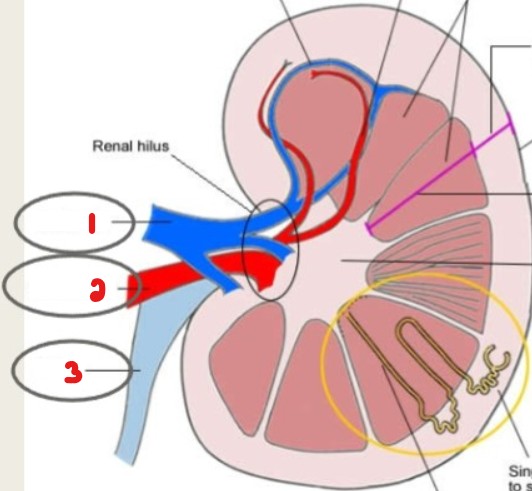
Label these structures seen at the renal hilum.
Renal vein
Renal artery
Ureter
What is the mnemonic for remembering the renal hilum order from anterior to posterior?
It’s Very Annoying that it’s Unclear.
Each ureter has a renal ______.
Pelvis
The renal pelvis is the _______ shaped upper end.
Funnel
The renal pelvis branches into (1))______ calyces and then (2)______ calyces.
Major
Minor
What does the renal parenchyma consist of?
Renal cortex
Renal medulla
What structure is crossed out in this image?
Psoas major muscle
Where does urine go AFTER the nephrons?
(List step by step)
Through the minor and major calyces
Then the renal pelvis
Then the ureter
Into the bladder
The bladder stores (1)______ until it is passed via the (2)_________.
Urine
Urethra
What shape do the paired, kidneys take on?
They lie in the (intra/retro)peritoneal.
They lie against the deep muscles of the _____.
Bean shaped
Retroperitoneal
Back
What is the difference in placement of the right and left kidney?
Why is this?
The right kidney is slightly more inferior than the left kidney
Due to the liver
Which can sometimes be larger, left kidney or right kidney?
Left kidney
How does a normal adult kidney appear on an US?
Heterogenous
Smooth contour
Why does the kidney appear heterogenous?
Due to the combination of medullary pyramids and renal parenchyma
How does hydronephrosis appear on a US?
Anechoic at renal pelvis
Can sometimes branch into major calyces
In severe cases of hydronephrosis, fluid can branch into the…
Minor calyces
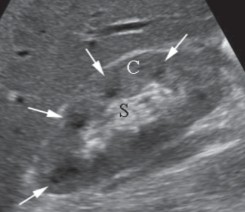
Label the ‘C’ and ‘S’ on the image.
C = Renal cortex
S = Renal sinus
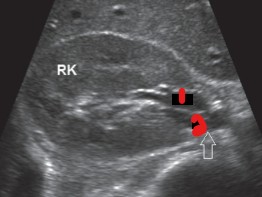
Label the structures at the renal hilum.
(HINT: The structure at the 2 did not have color)
Right renal vein
Ureter
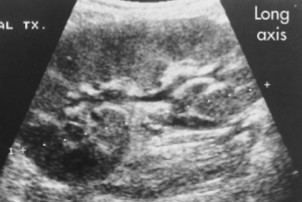
What plane/position was this image captured in?
Coronal
Out of these 3 planes/positions: Coronal, Sagittal, and Prone
Which provides the most detail?
Coronal
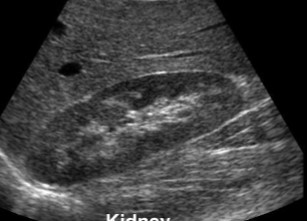
What plane/position was this image captured in?
Sagittal
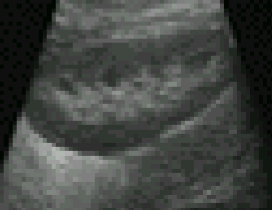
What position could this image have been taken in?
Prone
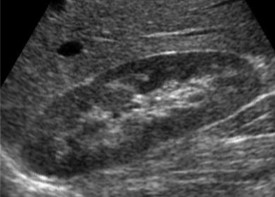
Is the kidney imaged from an adult, child, neonate, or fetus?
Adult
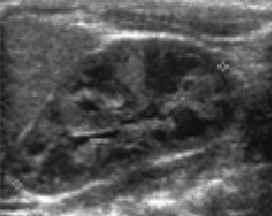
Is the kidney imaged from an adult, child, neonate, or fetus?
Child
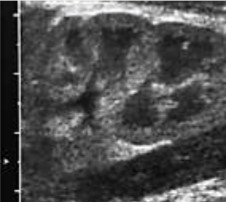
Is the kidney imaged from an adult, child, neonate, or fetus?
Neonate
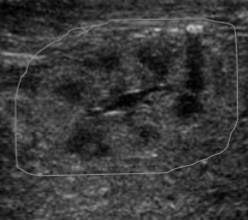
Is the kidney imaged from an adult, child, neonate, or fetus?
Fetus
What do child, neonate, and fetal kidneys all have in common on US?
The medullary pyramids are more anechoic
Which renal measurement is most important to watch for?
Length
What is the normal measurement range for renal length?
9 - 12 cm
What is the normal measurement range for renal AP?
2.4 - 4 cm
What is the normal measurement range for renal width?
4 - 6 cm
In a sagittal scan of the kidney, what measurements are taken?
Length and AP (Height)
In a transverse scan of the kidney, what measurements are taken?
Width
What would consider the kidney measurements to be abnormal?
There is a difference >2 cm between 2 kidneys
What is the formula for calculating renal volume?
Length x AP x Width x .49
In the absence/nonfunction of one kidney, what can occur?
Describe what question 1’s answer is.
Compensatory hypertrophy
The other kidney increases in size
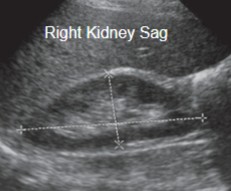
What measurements are taken here?
Length
Height (AP)
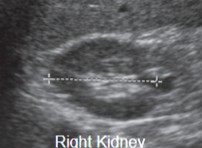
What measurements are taken here?
Width