Cancer Unit Study Guide
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
What takes place in Gap 1?
the cell grows and synthesizes proteins.
What takes place in S?
chromosomes replicate and divide to form identical sister chromatids.
What takes place in Gap 2?
cells continue to grow and produce the proteins necessary for cell division.
What is the purpose of Mitosis?
The purpose of mitosis is the division of the nucleus, making two identical nuclei, each with the same number of chromosomes.
Metaphase
Chromosomes line up in the center/middle of the cell.
Anaphase
Chromosomes are separated/pulled apart at their centromeres.
Telophase
Spindle fibers break down and two new nuclei form.
Prophase
Chromosomes become visible, nucleus breaks down.
What is the purpose of Cytokinesis?
The purpose of cytokinesis is to divide the cytoplasm.
What is the difference between cytokinesis in plants and animals?
Plant- From cell plate
Animal- pinches using cleavage furrow
What happens if a cancer cell evades destruction?
Continue to divide by mitosis and form tumors
What is the difference between benign and malignant tumor?
Benign: Mass of abnormal cells that remains at the original site
Malignant: Mass of cells that invades and impairs the functions of one or more organs
What is cell differentiation and what initiates this process?
A process through which a cell becomes specialized in order to perform a specific function. Only specific parts of the DNA activate to determine the function and specialized structure of a cell
What are the two types of cell division?
Meiosis and Mitosis
Mitosis- # of cells produced?
2
Meiosis- # of cells produced?
4
Mitosis- Type of cells?
Somatic
Meiosis- Type of cells?
Gamete
Mitosis- Chromosome #?
Diploid
Meiosis- Chromosome #?
Haploid
Mitosis- Reproduction type?
Asexual
Meiosis- Reproduction type?
Sexual
Indicate whether the statement below is about mitosis (MI) or meiosis (ME):
Daughter cells are identical to parent cell.
MI
Indicate whether the statement below is about mitosis (MI) or meiosis (ME):
Chromosome number is maintained.
MI
Indicate whether the statement below is about mitosis (MI) or meiosis (ME):
The chromosome number is halved.
ME
Indicate whether the statement below is about mitosis (MI) or meiosis (ME):
Occurs throughout an organism’s lifetime.
MI
Indicate whether the statement below is about mitosis (MI) or meiosis (ME):
Occurs only during certain times in an organism’s life.
ME
Indicate whether the statement below is about mitosis (MI) or meiosis (ME):
Produces gametes.
ME
What is the difference between a somatic cell and gamete?
Somatic Cell – is also considered a body cell
Gamete – Sex Cell
Which sex chromosomes do you have if you are a female and male?
XX__F____
XY__M____
What are homologous chromosomes?
Have the same genes in the same locations
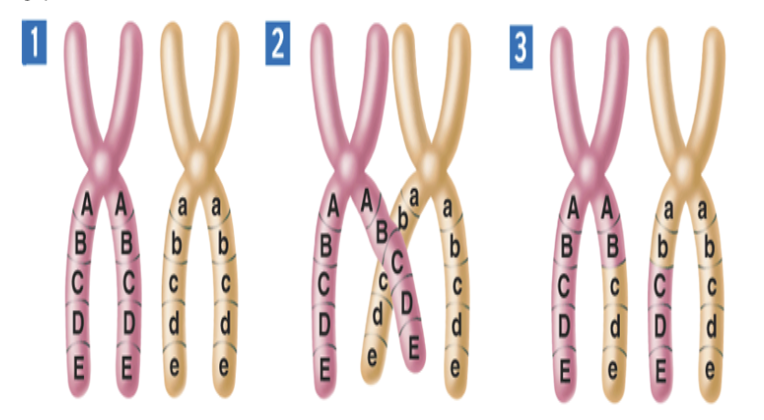
Use the diagram to the right to describe what is taking place.
Crossing Over
What is Crossing Over?
The exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes during meiosis.
Explain the difference between dominant and recessive alleles.
Dominant alleles will be expressed. Recessive is only shown when dominant is not present
What is the difference between a genotype and a phenotype?
Genotype: The genetic makeup
Phenotype: The physical description
What are Multiple alleles?
Multiple alleles can exist for a particular trait even though only two alleles are inherited.
Type A
IAIA or IAi.
Type B
IBIB or IBi.
Type AB
IAIB.
Type O
ii.
Cross a heterozygous type A blood type person with a homozygous type B person.
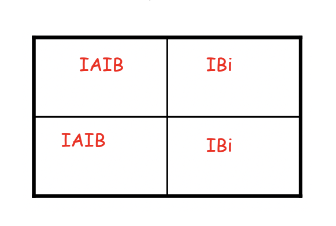
What is the probability that an offspring with Type A blood is produced if the parents have type O blood and Type AB blood? Show your work.
50%
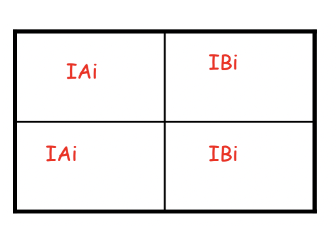
What are polygenic traits? Give an example.
Traits that are controlled by two or more Genes;
Skin, Eye color
What are sex-linked traits?
Traits that are the result of genes that are carried on sex chromosomes.
Why are sex-linked traits more common in males than females?
Males will inherit the gene on the X chromosome, but not the Y
XRXr.
Female Red (Carrier)
XRY.
Male red
XrXr.
Female white
XRXR.
Female red
XrY.
Male white
Nitrogen Base
Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, Thymine, Uracil.
Show the cross of a white-eyed female with a red eyed male.
Parental genotypes: ___XrXr________ x ____XRY______
Phenotype: 50% red eyed F, 50% white eyed M
Genotypes: 50% XRXr (2), 50% XrY (2)
Show the cross of a heterozygous red eyed female and a white eyed male.
Parental genotypes: ___XRXr________ x ____XrY______
Phenotype: 25% red-eyed F, 25% white-eyed F, 25% white-eyed M, 25% red-eyed M
Genotypes: 25% XRXr, 25% XrY, 25% XrXr, 25% XRY
Name the three components of a nucleotide.
Nitrogen Base, Sugar, Phosphate Group
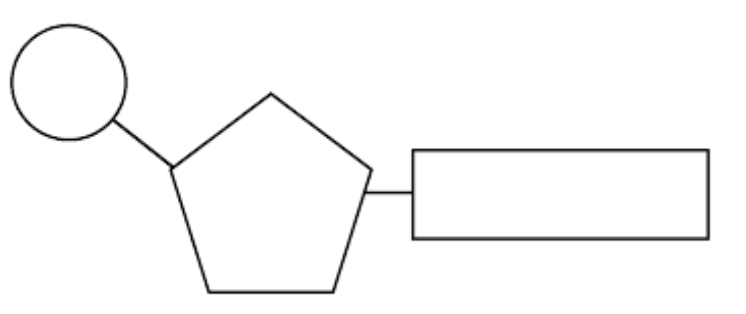
Label the parts of this model
Left- Phosphate Group
Middle- Sugar
Right- Nitrogen Base
Sugar in DNA
Deoxyribose
Sugar in RNA
Ribose (RNA).
Nitrogenous Bases in DNA
A-T C-G
Nitrogenous Bases in RNA
A-U C-G
DNA molecule structure/shape.
Double Helix
RNA molecule structure/shape.
Single Strand
Name the complementary base for each nucleic acid below.
Adenine
Thymine (DNA), Uracil (RNA).
Name the complementary base for each nucleic acid below.
Guanine
Cytosine.
Name the complementary base for each nucleic acid below.
Cytosine
Guanine.
Name the complementary base for each nucleic acid below.
Thymine
Adenine.
Name the complementary base for each nucleic acid below.
Uracil (RNA)
Adenine.
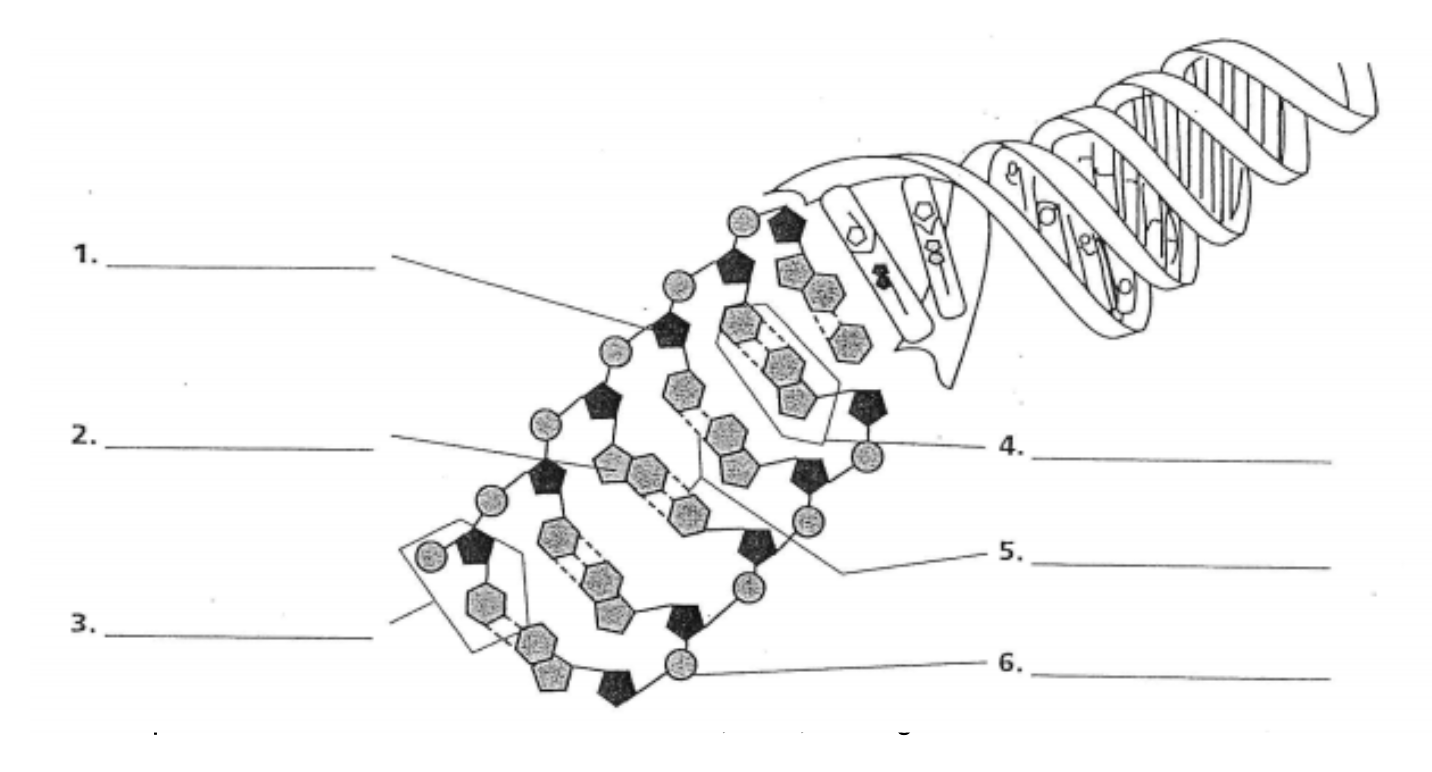
Label the Diagram with these terms: Sugar, Phosphate Group, Nitrogenous Base, Nucleotide, Nitrogenous Base Pairs, Bond.
1. Sugar, 6. Phosphate Group, 2. Nitrogenous Base, 3. Nucleotide, 4. Nitrogenous Base Pairs, 5. Bond.
Explain the difference between a chromosome, DNA, and a gene.
Chromosome: One long molecule of DNA that is tightly coiled. here are 46 chromosomes in the human cell.
DNA: The DNA is made up of organic molecules that transmit the genetic information for the organism.
Gene: A gene is a specific location of a chromosome that codes for specific proteins.
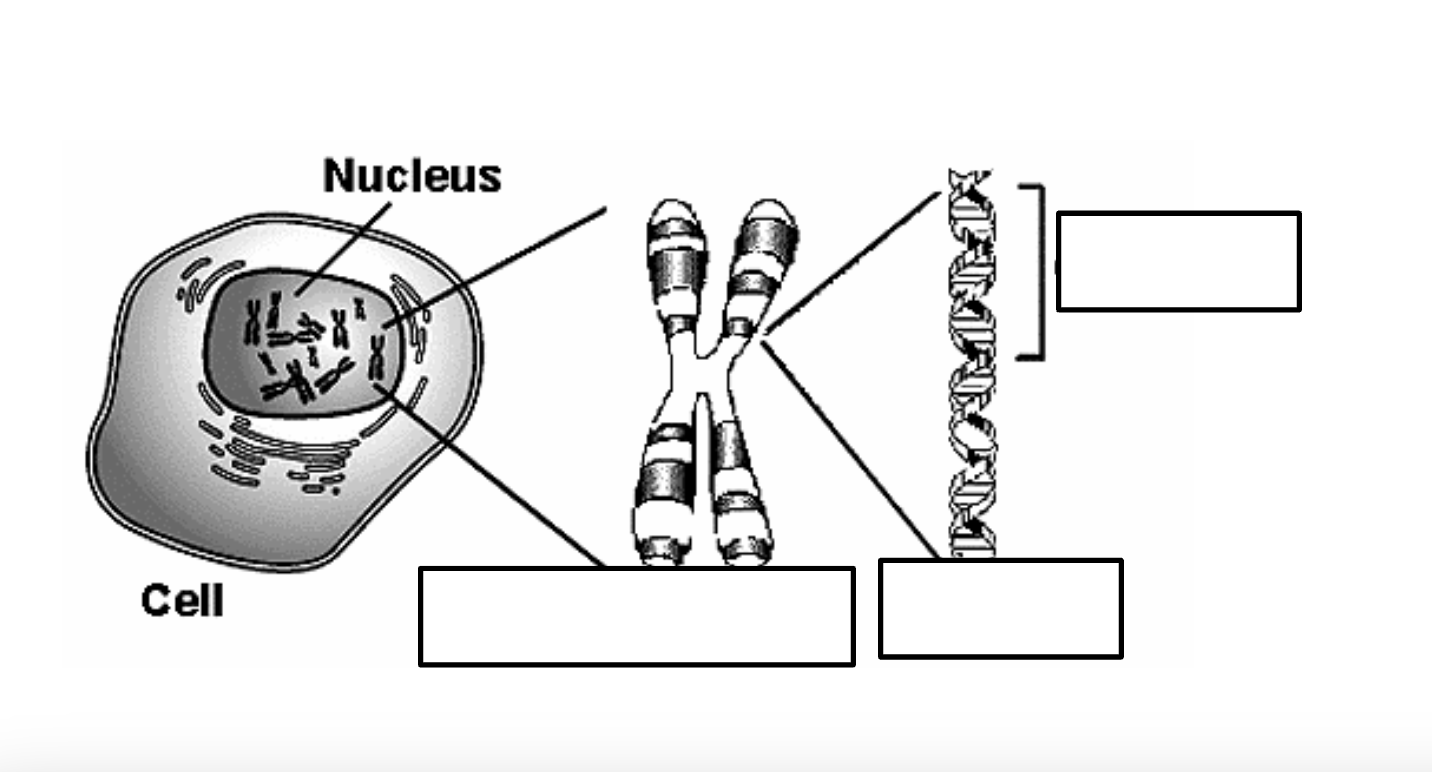
Label this diagram using the terms: Gene, DNA, Nucleus, and Chromosome.
4. Gene, 3. DNA, 1. Nucleus, 2. Chromosome.
Why is DNA considered the “code of life” (genetic code)?
The molecule that contains the instructions for building proteins
How many chromosomes are in each cell?
Each cell typically has 46 chromosomes, in 23 pairs.
Name the two types of chromosomes in a cell and the numbers
a. Somatic (Body), numbered 1-22
b. Gamete (Sex), numbered 1-23
What is DNA Replication? Why is it important?
DNA Replication is copying DNA during the S-stage of Interphase so that each new daughter cell has an identical copy of the DNA.
Where does DNA replication take place?
Nucleus
Briefly explain the process of DNA replication.
An enzyme unzips the DNA. Another enzyme will go along each single strand of DNA and attach the appropriate nitrogenous base. The bases will bond together completing replication.
What is the purpose of protein synthesis?
To take the genetic information in DNA and make proteins for the organisms’ functions.
Name the two steps of protein synthesis and where they take place.
Transcription- Nucleus
Translation - Ribosome
What is the purpose of transcription?
Copy the DNA to mRNA. This happens because the DNA cannot leave the nucleus
What is the purpose of translation?
Translation takes the mRNA and uses the codons to bring amino acids to the ribosome. The ribosome bonds the amino acids with a peptide bond forming proteins.
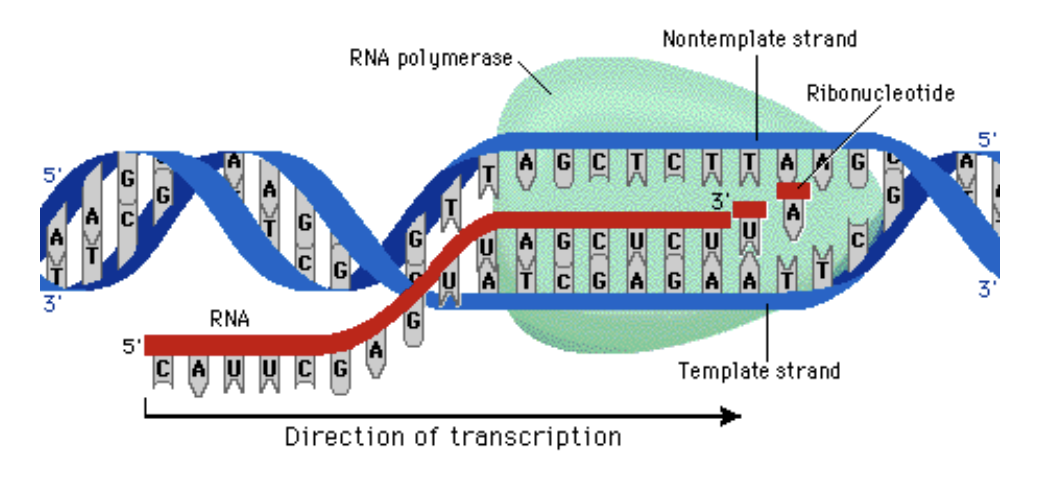
The process illustrated below is:
Transcription
What is mRNA and why is it created
mRNA carries the message of DNA to the ribosome, created because the DNA can not leave the nucleus
Translation
What is the difference between a codon and an anticodon?
Codon: 3 bases on the mRNA
Anticodon: 3 bases on the tRNA
What is the name of the bond that holds the amino acids together?
Peptide Bond
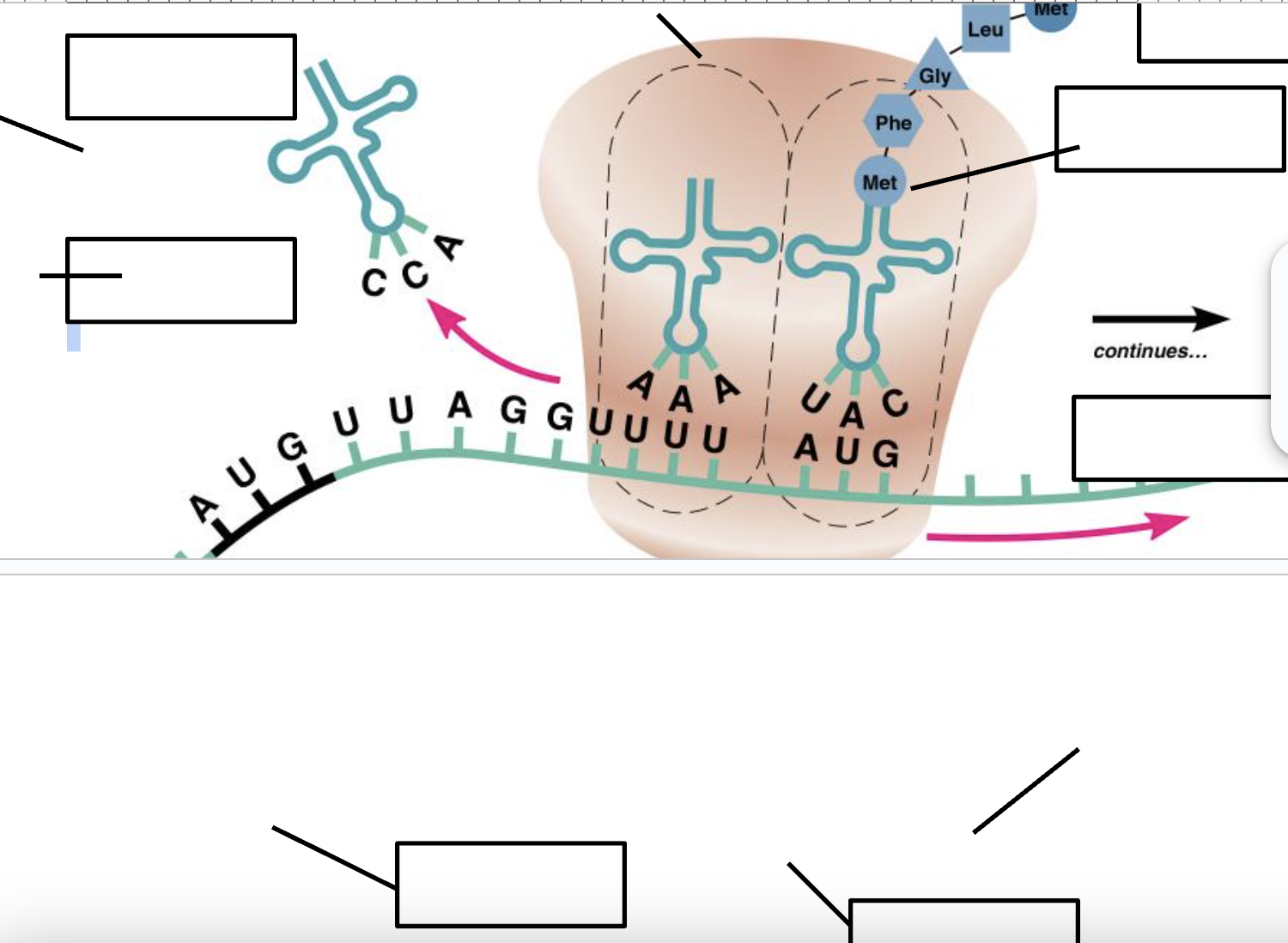
Label the diagram below using the terms: mRNA, peptide bond, tRNA, codon, anticodon, amino acid, ribosome, and polypeptide chain.
7. mRNA, 2. peptide bond, 1. tRNA, 5. codon, 4. anticodon, amino acid, 6. ribosome, 3. polypeptide chain.
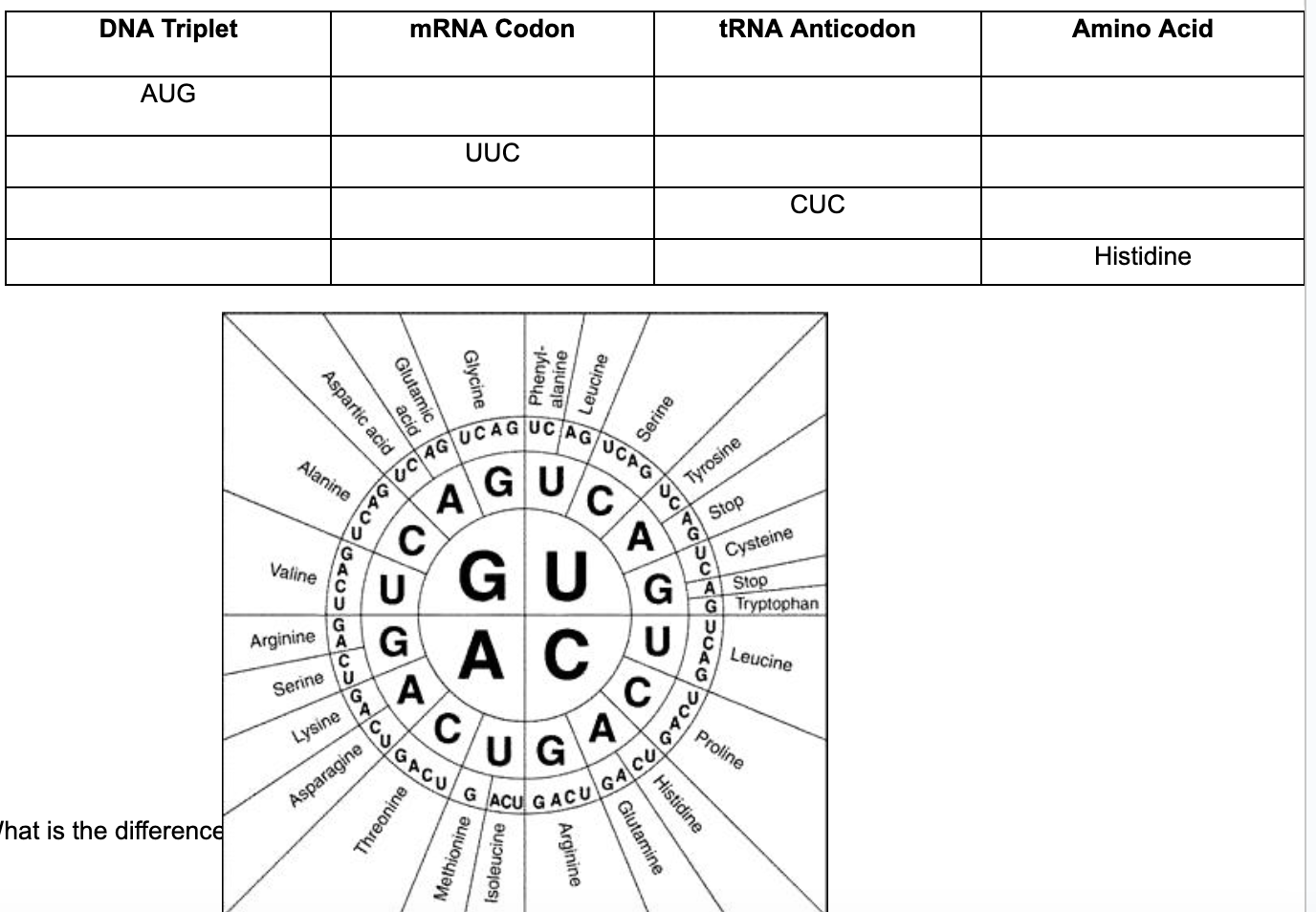
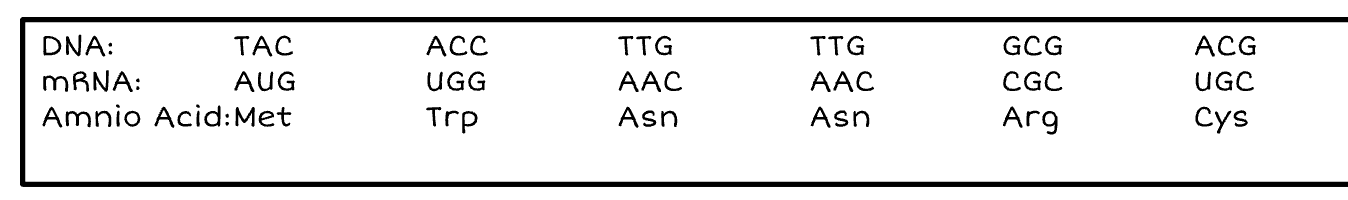
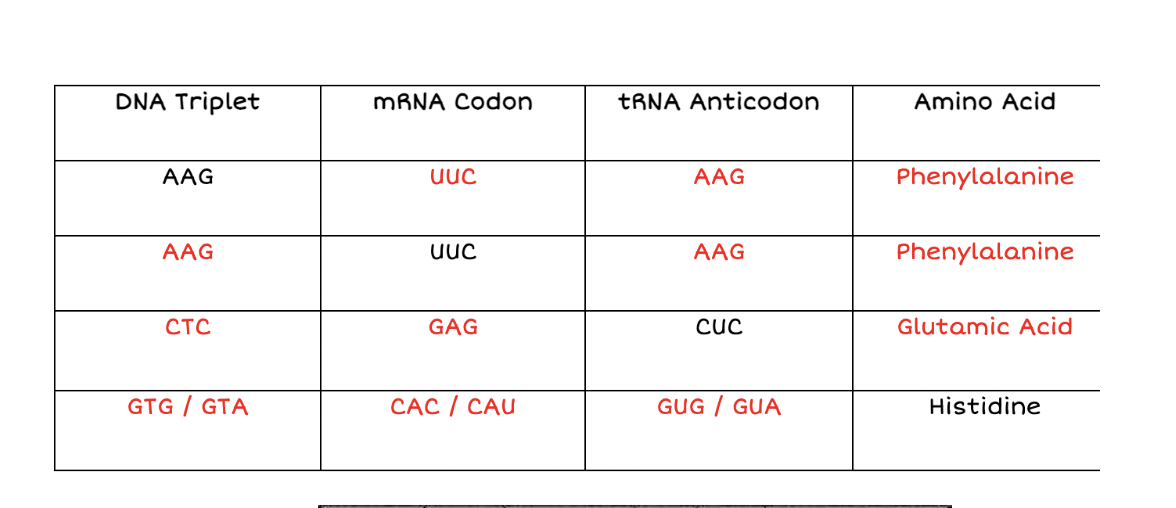
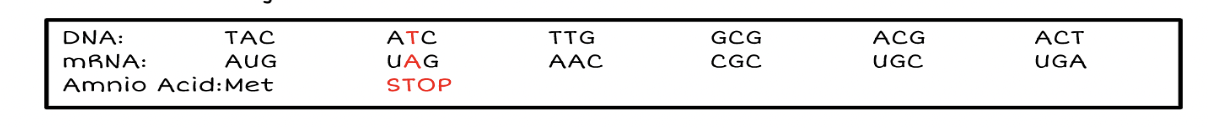
Complete the chart below
answers
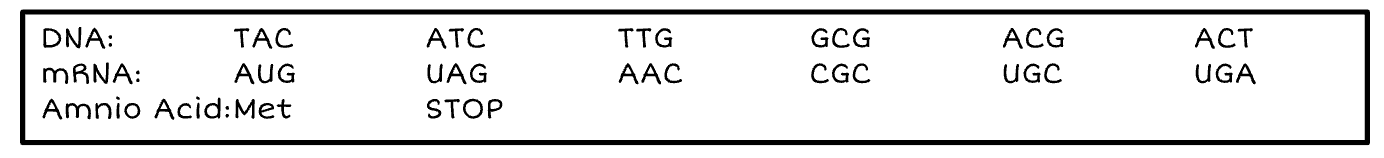
What is the difference between a gene and a chromosomal mutation?
Gene mutation occurs in a single gene. Chromosomal mutation occurs in multiple genes or the entire chromosome.
Circle the change in the DNA.
Change in Mutation: Point
Circle the change in the DNA.
Name of Mutation: Fr