AP Psych - Semester 1 Review
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/288
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 10:41 PM on 1/15/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
289 Terms
1
New cards
structuralism
* early school of psychology that used **introspection** to explore the structural elements of the human mind
* introduced by **Edward Bradford Titchener**
* introduced by **Edward Bradford Titchener**
2
New cards
Gestalt psychology
school of thought that emphasizes the whole is __different__ than the sum of its parts (you can’t deduce attributes of the whole from analyzing the parts in isolation)
3
New cards
functionalism
school of psychology hat focused on how our mental and behavioral processes function (how they enable us to adapt, survive, and flourish)
4
New cards
behaviorism
the view that psychology (1) should be an objective science that (2) studies behavior __without__ reference to mental processes
5
New cards
humanistic psychology
* rebelled against determinism of **Freudian** psychology and **behaviorism**
* emphasized an individual’s potential for personal growth
* emphasized an individual’s potential for personal growth
6
New cards
cognitive neuroscience
interdisciplinary study of the brain activity linked w/ cognition (including perception, thinking, memory, and language)
7
New cards
psychology
the science of behavior and mental processes
8
New cards
nature-nurture issue
longstanding controversy over the relative contributions that genes and experience make to the development of psychological traits
9
New cards
natural selection
the principle that, among the range of inherited trait variations, those contributing to reproduction and survival will most likely be passed on to succeeding generations
10
New cards
levels of analysis
differing views (biological, psychological, social-cultural) for analyzing a given phenomenon
11
New cards
biopsychosocial approach
an integrated approach that incorporates biological, psychological, and social-cultural levels of analysis
12
New cards
psychology’s current perspectives
\
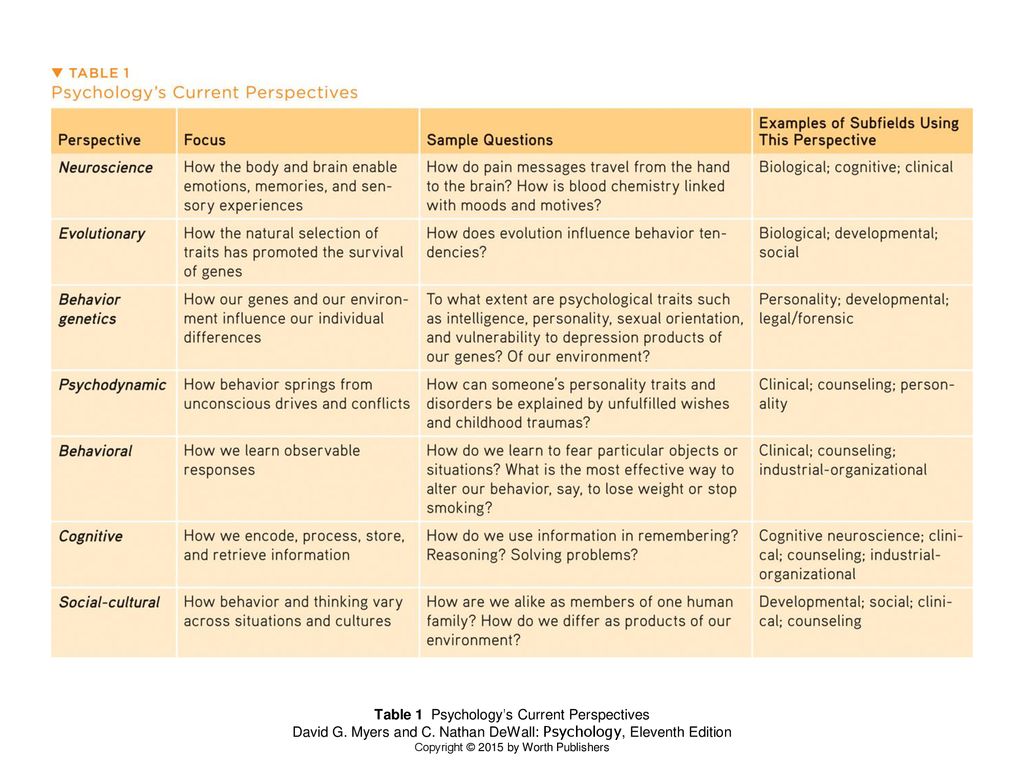
13
New cards
basic research
pure science that aims to increase the scientific knowledge base
14
New cards
applied research
scientific study that aims to solve practical problems
15
New cards
counseling psychology
a branch of psychology that assists people with problems in living (often related to school, work, or marriage)
16
New cards
clinical psychology
a branch of psychology that studies, assesses, and treats people with psychological disorders
17
New cards
psychiatry
a branch of medicine dealing with psychological disorders, practiced by physicians who sometimes provide medical treatments
18
New cards
SQ3R
* study method
* Survey, Question, Read, Rehearse, Review
* Survey, Question, Read, Rehearse, Review
19
New cards
Plato
believed in __innate__ ideas, suggested that the __brain__ is the seat of mental processes
20
New cards
Aristotle
denied the existence of innate ideas, suggested that the __heart__ is the seat of mental processes
21
New cards
Renee Descartes
French philosopher who proposed mind-body interaction and believed in the concept of __innate__ ideas
22
New cards
John Locke
British philosopher who rejected Descartes’ notion of innate ideas and insisted the mind at birth is a __“blank slate” (____*tabula rasa*____)__
23
New cards
Charles Darwin
* scientist
* theory of evolution, **natural selection**
* theory of evolution, **natural selection**
24
New cards
Dorothea Dix
activist who played a role in the founding/expansion of hospitals for the treatment of the mentally ill
25
New cards
Wilhelm Wundt
established the first psychology laboratory
26
New cards
Edward Titchener
used introspection to search for the mind’s structural elements
27
New cards
William James
* **functionalist**
* invited **Mary Calkins** into his graduate seminar
* invited **Mary Calkins** into his graduate seminar
28
New cards
Edward Thorndike
* puzzle boxes + cats
* **law of effect**
* **law of effect**
29
New cards
Jean Piaget
psychologist who studied child development
30
New cards
Mary Whiton Calkins
first woman elected to membership in the APA
31
New cards
Margaret Floy Washburn
first woman to get a Ph.D. in psychlogy
32
New cards
hindsight bias
the tendency to believe, after learning an outcome, that one would have foreseen it
33
New cards
confirmation bias
the tendency to look for information that confirms or strengthens beliefs, rather than evidence to the contrary
34
New cards
critical thinking
thinking that examines assumptions, evaluates evidence, and assesses conclusions
35
New cards
culture
the enduring behaviors, ideas, attitudes, and traditions shared by a group of people and transmitted from one generation to the next
36
New cards
theory
an explanation that organizes observations and predicts behaviors or events
37
New cards
hypothesis
a testable prediction
38
New cards
operational definition
a clear, measurable, definition of a variable
39
New cards
replication
repeating the essence of a research study to see whether he basic findings extend to other participants and circumstances
40
New cards
case study
and observation technique in which one person is studied in depth
41
New cards
survey
a technique for ascertaining the self-reported attitudes or behaviors of a particular group
42
New cards
random sample
a sample that fairly represents a population bc each member has an equal chance of inclusion
43
New cards
naturalistic observation
observing and recording behavior in naturally occurring situations without trying to manipulate and control the situation
44
New cards
correlation
the interdependence between variable quantities
45
New cards
correlation coefficient
a statistical index of the relationship btwn two things (from -1 to +1)
46
New cards
illusory correlation
the perception of a relationship where none exists
47
New cards
random assignment
assigning participants to experimental and control groups by chance, thus minimizing preexisting differences bwtn those assigned to different groups
48
New cards
comparing research methods
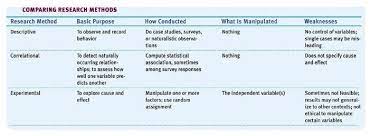
49
New cards
measures of variation
mode - most frequently occurring score in a distribution
mean - the arithmetic average of a distribution
median - the middle score in a distribution
range - the difference btwn the highest and lowest scores
standard deviation - a measure of how much scores vary around the mean
mean - the arithmetic average of a distribution
median - the middle score in a distribution
range - the difference btwn the highest and lowest scores
standard deviation - a measure of how much scores vary around the mean
50
New cards
normal curve
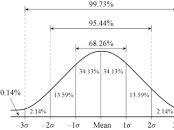
51
New cards
skewed curve
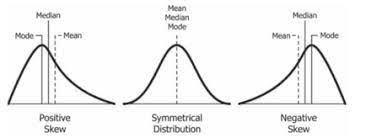
52
New cards
cognition
the mental activities associated w/ thinking, knowing, remembering, and communicating
53
New cards
statistical significance
a statistical statement of how likely it is that an obtained result occurred by chance
54
New cards
concept
mental grouping of similar objects, events, ideas, or people
55
New cards
prototype
a mental image or best example of a catagory
56
New cards
algorithm
a methodical, logical rule or procedure that guarantees solving a particular problem
57
New cards
heuristic
a strategy that allows us to make judgements and solve problems efficiently, usually speedier but also more error-prone than **algorithms**
58
New cards
insight
a sudden and often novel realization of the solution to a problem
59
New cards
mental set
a tendency to approach a problem in a particular way, often one that has been successful in the past
60
New cards
functional fixedness
the tendency to think of things only in terms of their usual functions
61
New cards
representative heuristic
judging the likelihood of things in terms of how well they seem to represent, or match, particular prototypes
62
New cards
availability heuristic
estimating the likelihood of events based on their availability in memory
63
New cards
framing
the was an issue is raised
64
New cards
language
our spoken, written, or signed words, and the ways we combine them to communicate meaning
65
New cards
phoneme
* the smallest distinctive sound unit
* *cats* has 4 (c, a, t, s)
* *cats* has 4 (c, a, t, s)
66
New cards
morpheme
* the smallest unit that carries meaning
* *cats* has 2 (cat, s)
* *cats* has 2 (cat, s)
67
New cards
grammer
system of rules that enables us to communicate with and understand others
68
New cards
semantics
the set of rules by which we derive meaning from **morphemes**, words, and sentences
69
New cards
syntax
* the rules for combining words into grammatically sensible sentences
* ex. *red* __ball__ vs. __pelota__ *roja*
* ex. *red* __ball__ vs. __pelota__ *roja*
70
New cards
language development
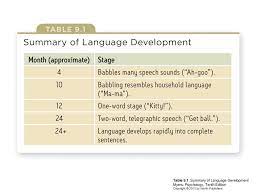
71
New cards
aphasia
impairment of language, usually caused by left hemisphere damage either to **Broca’s area** (impairing speaking) or **Wernicke’s area** (impairing understanding)
72
New cards
linguistic determinism
**Benjamin Whorf’s** hypothesis that language determines the way we think
73
New cards
universal grammar
* theory by **Noam Chomsky**
* human brain contains a predefined mechanism that is the basis for the acquisition of all language.
* human brain contains a predefined mechanism that is the basis for the acquisition of all language.
74
New cards
Wolfgang Kohler
* studied chimpanzee problem solving
* **insight**
* **insight**
75
New cards
Beatrix and Allen Gardner
* taught ASL to Washoe the chimpanzee
76
New cards
Sue Savage-Rumbaugh
known for her work w bonobos Kanzi and Panbanisha, used keyboards to communicate
77
New cards
Neuron
nerve cell, building block of the nervous system
78
New cards
sensory neurons (afferent)
carry incoming information from sensory receptors to brain and spinal cord
79
New cards
motor neurons (efferent)
carry outgoing information from brain and spinal cord to muscles and glands
80
New cards
interneurons
only in brain and spinal cord, communicate internally between sensory inputs and motor outputs
81
New cards
diagram of a neuron
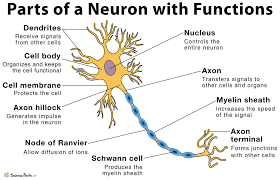
82
New cards
dendrites
receive information and conduct it towards cell body
83
New cards
soma (cell body)
contains nucleus
84
New cards
nucleus
has genetic material
85
New cards
axon
transfers electrochemical messages
86
New cards
myelin sheath
layer of fat that speeds up transmission
87
New cards
node of ranvier
gaps in myelin sheath that sped up transmission
88
New cards
schwann cell
produce myelin sheath
89
New cards
axon terminal (synaptic knobs, etc.)
very end of axon
90
New cards
synapse
allow for communication between nerve cells
91
New cards
action potential
neural impulse, brief electrical charge that travels down the axon
92
New cards
resting potential
* outside has more positive (sodium) ions, inside has more negative ions
* polarized
* polarized
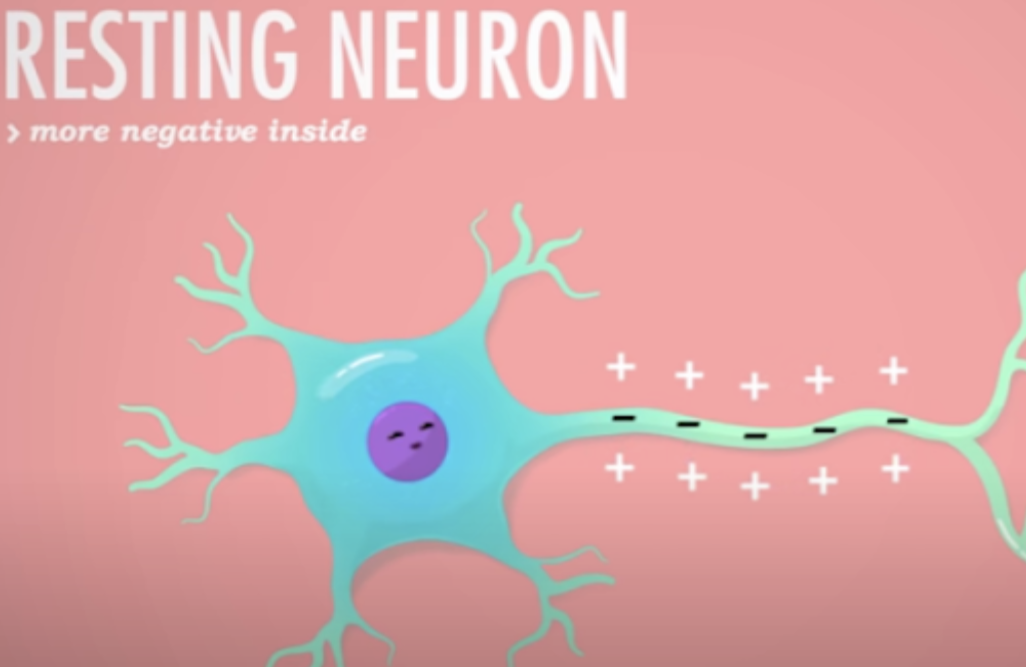
93
New cards
depolarization
positive Na+ ions enter cell
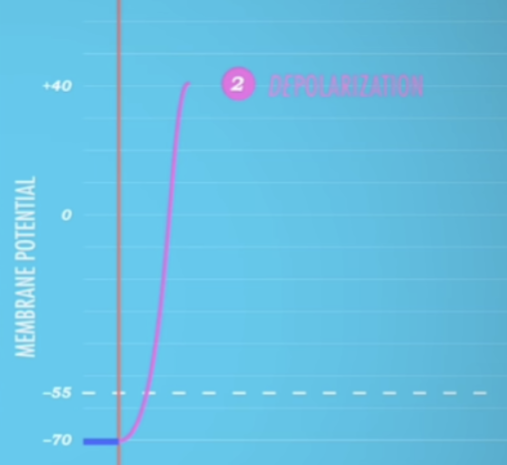
94
New cards
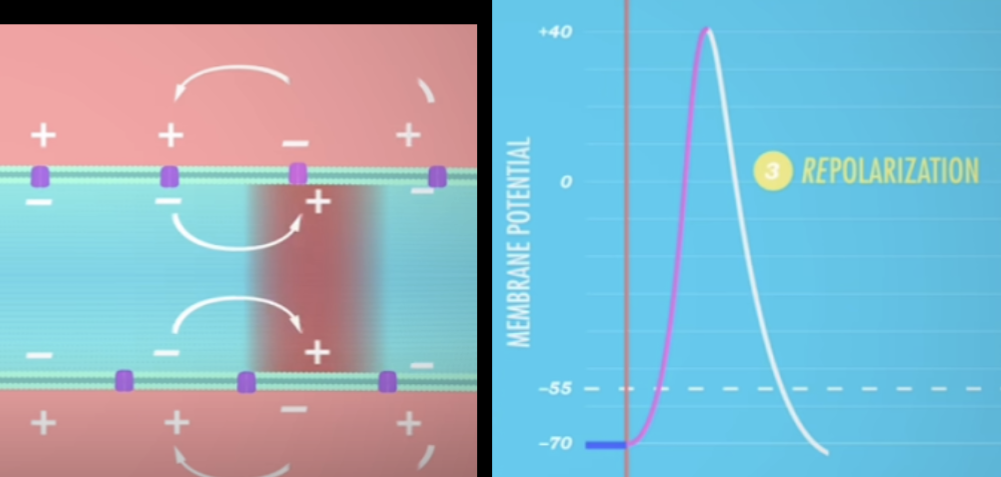
repolarization
return of + outside, - inside
95
New cards
excitatory signals
push charge above -70mv
96
New cards
inhibitory signals
push charge below -70mv
97
New cards
refractory period
the time in which a nerve cell is unable to fire an action potential (nerve impulse)
98
New cards
threshold
about -55 mv
99
New cards
"all or none" phenomenon
action potential either fires or it doesn't, no middle ground
100
New cards
When action potential reaches knoblike terminals at end of axion, triggers release of...
chemical messages called neurotransmitters