[DCN] Number Systems, Data Link Layer and Ethernet Switching FC
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
Binary Number System
Consists of 1s and 0s, called bits.
Decimal Number System
Uses digits from 0 to 9 for representation.
Binary Addressing
Identifies hosts using 32-bit addresses.
Octet
8 bits in a binary address.
Dotted Decimal
Human-readable format of binary addresses.
Positional Notation
Value depends on digit's position in sequence.
IPv4 Addresses
32-bit binary addresses for network devices.
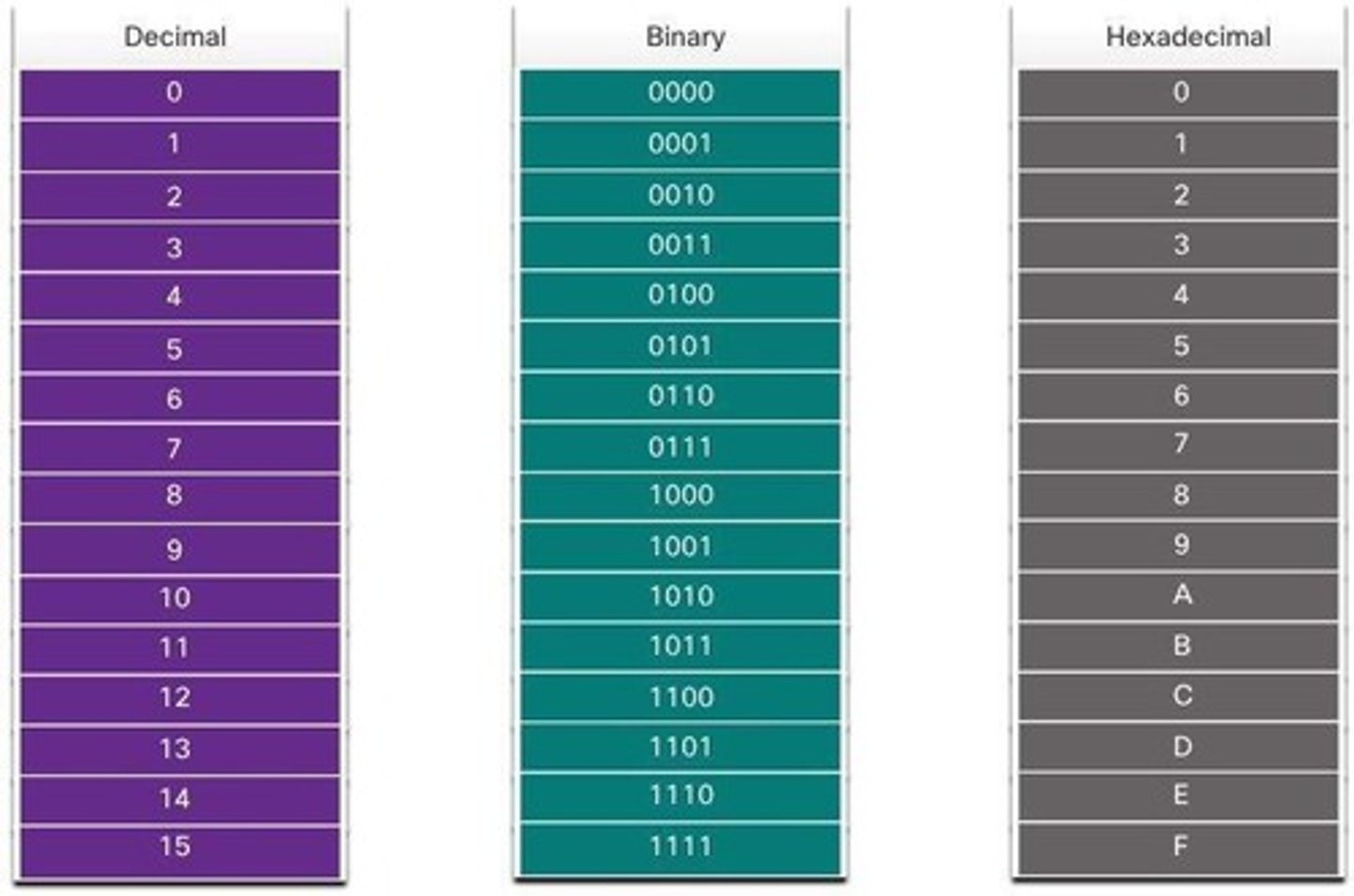
Hexadecimal Number System
Base 16 system using 0-9 and A-F.
IPv6 Addresses
128-bit addresses using hexadecimal representation.
Hextet
Group of four hexadecimal characters in IPv6.
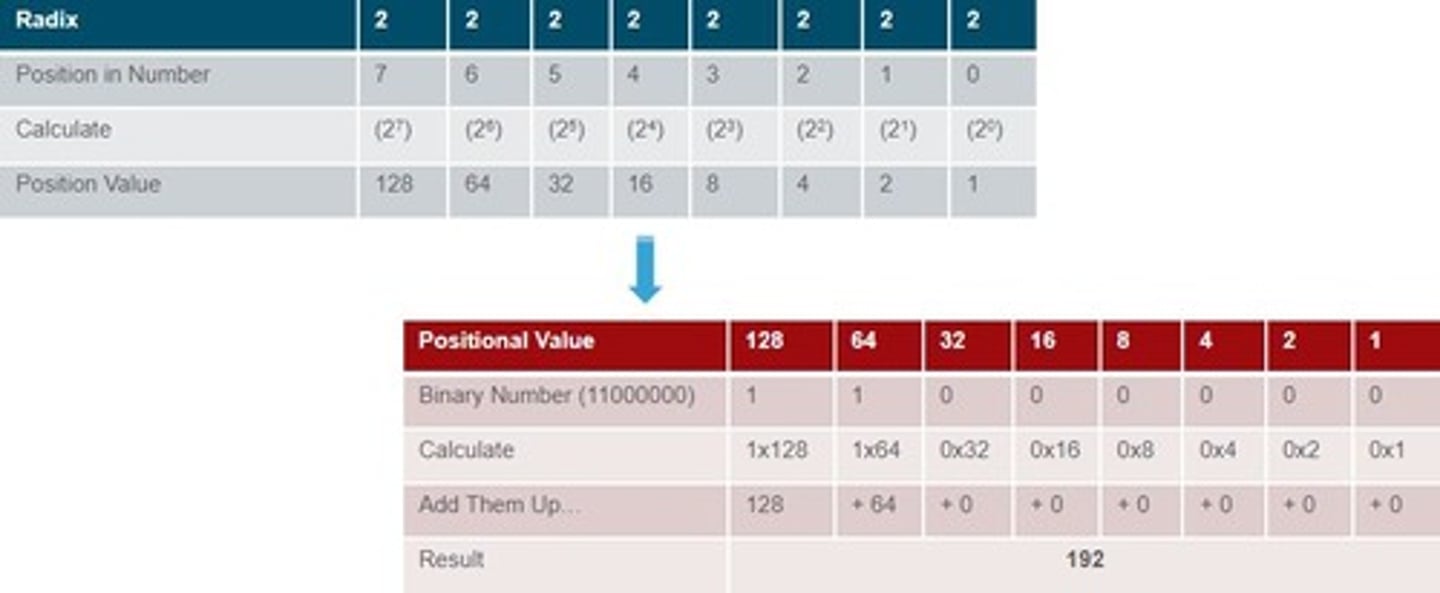
Conversion Binary to Decimal
Process of translating binary to decimal values.
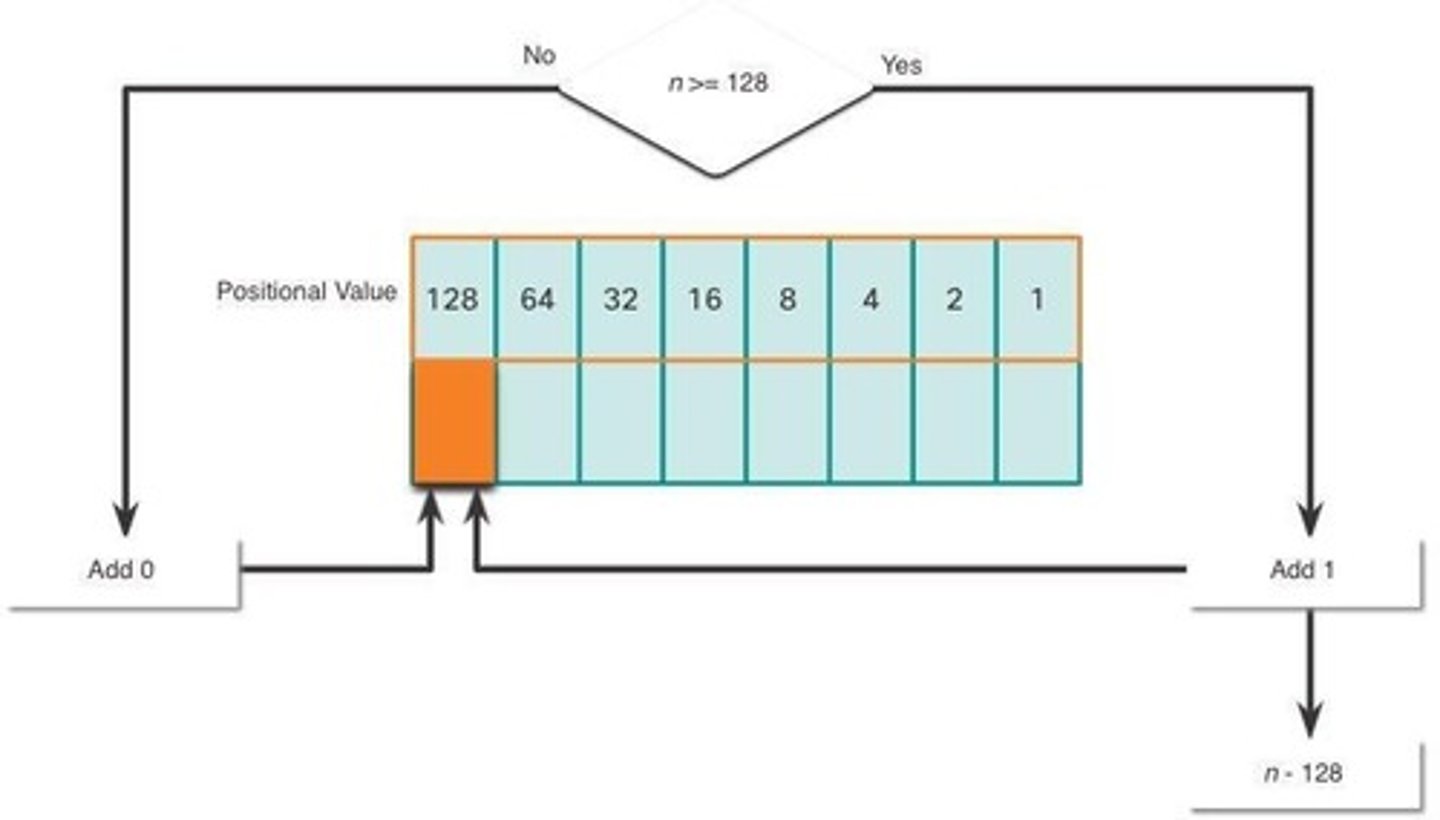
Conversion Decimal to Binary
Method to convert decimal to binary format.

Data Link Layer
Facilitates communication between network interface cards.
Layer 2 Frames
Encapsulates Layer 3 packets for transmission.
Error Detection
Identifies and rejects corrupt data frames.
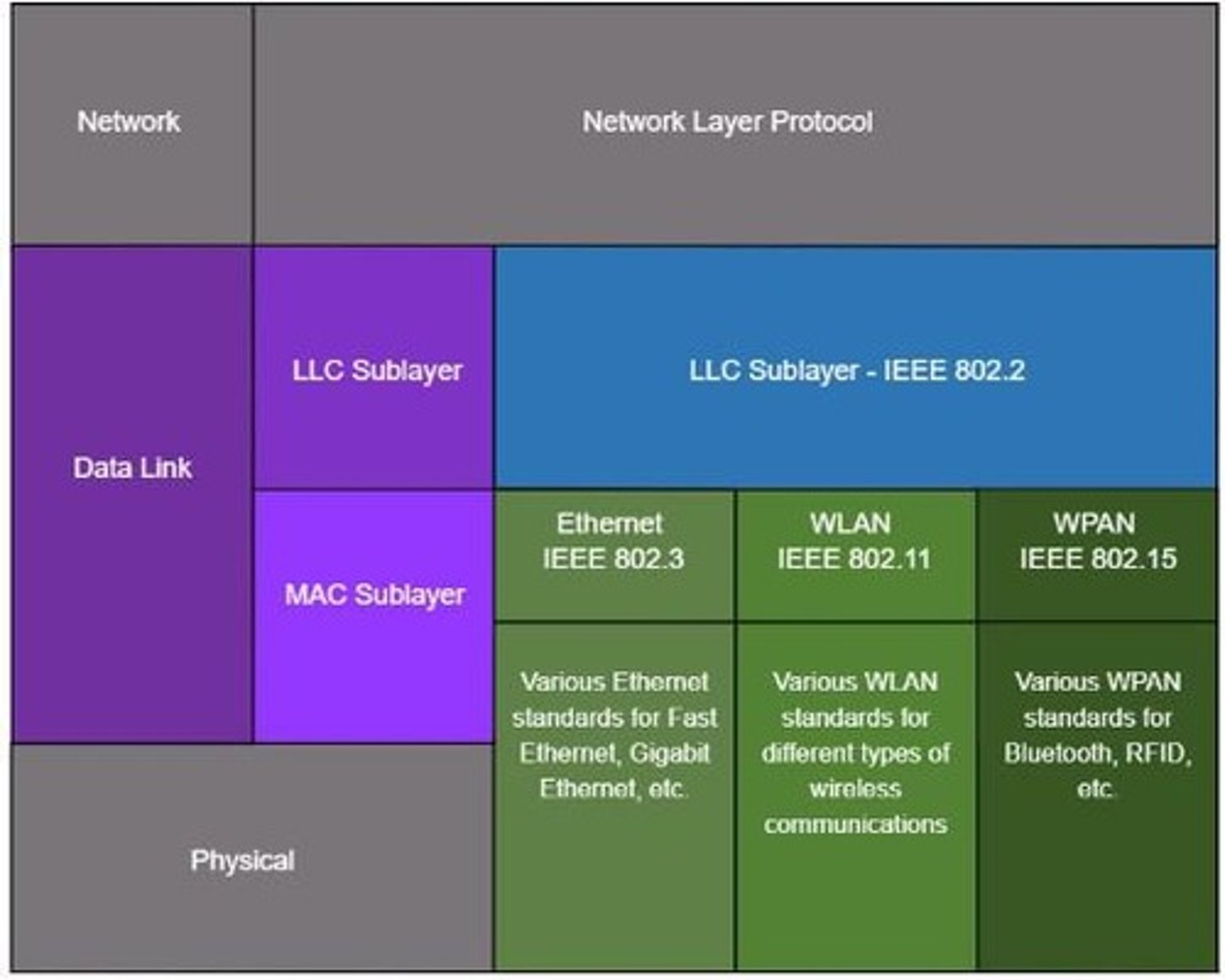
IEEE 802 Standards
Defines LAN/MAN data link layer protocols.
Logical Link Control (LLC)
Communicates between software and hardware layers.
Media Access Control (MAC)
Controls data encapsulation and access to media.
Frame De-encapsulation
Process of exposing encapsulated packets from frames.
Frame Re-encapsulation
Encapsulating packets into new frames for forwarding.
Data Link Layer Functions
Four basic functions performed by routers.
Binary to Hexadecimal Conversion
Translates binary strings into hexadecimal digits.
Hexadecimal to Decimal Conversion
Converts hexadecimal numbers into decimal values.
IEEE
Institute for Electrical and Electronic Engineers organization.
ITU
International Telecommunications Union for global standards.
ISO
International Organization for Standardization, develops standards.
ANSI
American National Standards Institute, coordinates US standards.
Physical Topology
Shows actual physical connections between devices.
Logical Topology
Defines virtual connections using IP addressing schemes.
Point-to-Point Topology
Direct link between two endpoints in WAN.
Hub and Spoke Topology
Central site connects branch sites via links.
Mesh Topology
Every system connects to every other system.
Star Topology
Devices connected to a central hub.
Extended Star Topology
A star topology with additional hubs.
Bus Topology
All systems chained and terminated at ends.
Ring Topology
Each system connects to two neighbors forming a ring.
Half-Duplex Communication
One device sends or receives at a time.
Full-Duplex Communication
Devices transmit and receive simultaneously.
Contention-Based Access
Nodes compete for medium access in half-duplex.
Controlled Access
Deterministic access with scheduled time for nodes.
CSMA/CD
Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection.
CSMA/CA
Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance.
Data Link Frame
Encapsulates data with header and trailer.
Layer 2 Addresses
Physical addresses used for local frame delivery.
Data Link Protocol
Protocol determined by logical topology and physical media.
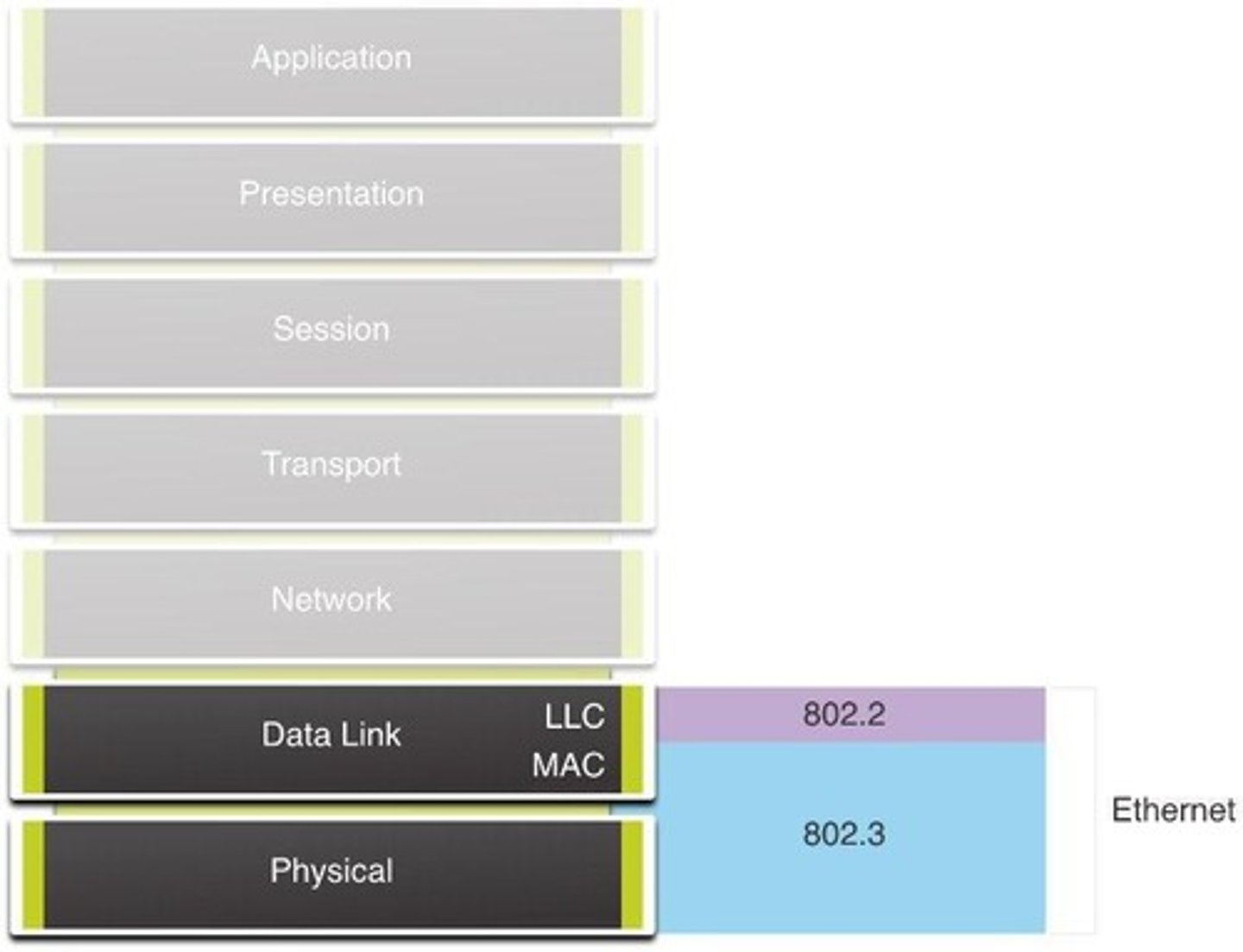
Ethernet
Common data link protocol for local area networks.
802.11 Wireless
Wireless networking standard for local area networks.
Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP)
Protocol for direct connection between two nodes.
High-Level Data Link Control (HDLC)
Bit-oriented protocol for point-to-point and multipoint links.
Frame-Relay
Packet-switching protocol for connecting local area networks.
LLC Sublayer
Identifies network layer protocol for data frames.
MAC Sublayer
Handles data encapsulation and media access control.
Ethernet Frame
Structure used to encapsulate data in Ethernet.
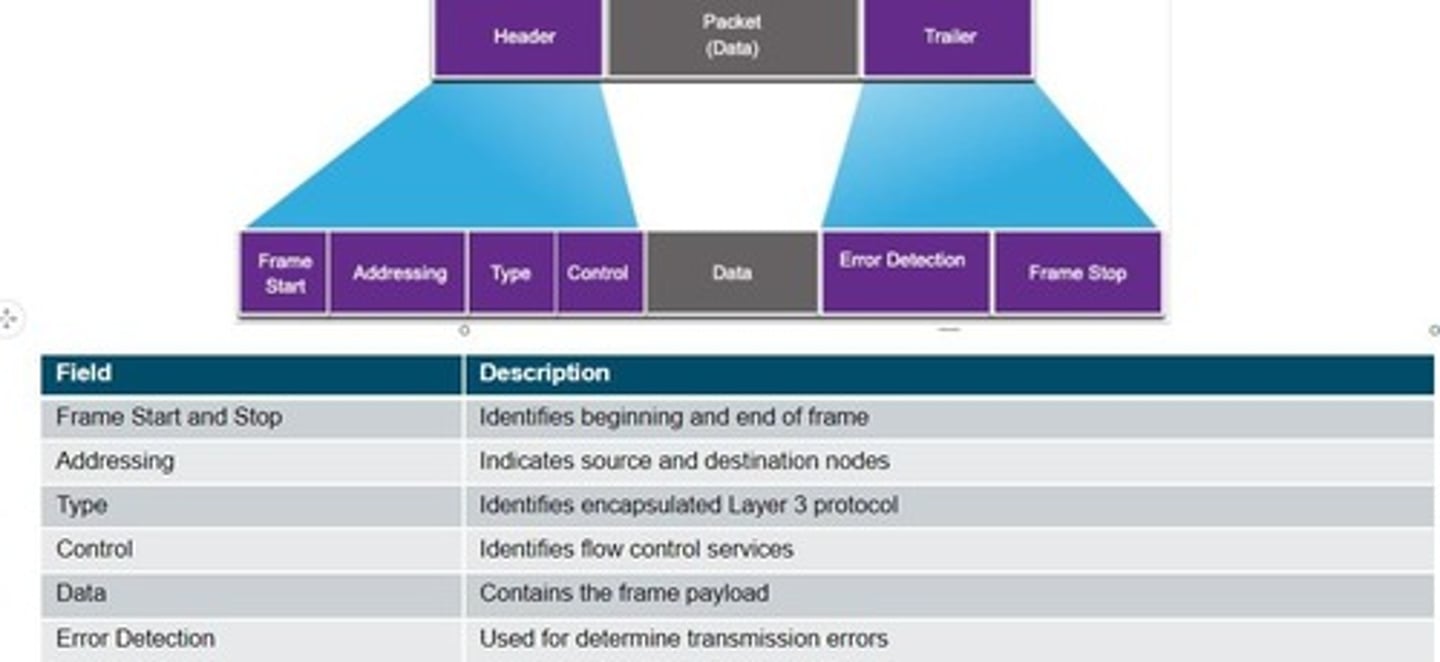
Ethernet Addressing
Includes source and destination MAC addresses.
Frame Check Sequence (FCS)
Trailer used for error detection in Ethernet frames.
IEEE 802.3 MAC
Specifications for Ethernet communications standards.
Half-Duplex Medium
Shared medium allowing one-way data transmission at a time.
CSMA/CD
Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection method.
Full-Duplex Communication
Simultaneous two-way data transmission using Ethernet switches.
Minimum Ethernet Frame Size
64 bytes; frames below this are discarded.
Maximum Ethernet Frame Size
1518 bytes; frames above this are jumbo frames.
Jumbo Frames
Frames larger than 1500 bytes, supported by modern switches.
Ethernet MAC Address
48-bit address for device identification in Ethernet.
Hexadecimal Representation
MAC addresses expressed using 12 hexadecimal digits.
OUI Code
Organizationally Unique Identifier in MAC addresses.
Frame Processing
Examining MAC addresses for frame forwarding decisions.
Broadcast MAC Address
Address allowing frame delivery to all devices in LAN.
Unicast MAC Address
Unique address for single device communication.
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)
Determines destination MAC for IPv4 addresses.
Neighbor Discovery (ND)
Determines destination MAC for IPv6 addresses.
Broadcast MAC Address
Address for sending frames to all devices.
FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF
Hexadecimal for Ethernet broadcast MAC address.
Multicast MAC Address
Address for communication with a group of devices.
01-00-5E
MAC address for IPv4 multicast packets.
33-33
MAC address for IPv6 multicast packets.
MAC Address Table
Stores MAC addresses for forwarding decisions.
Content Addressable Memory (CAM)
Another term for MAC address table.
Layer 2 Ethernet Switch
Uses MAC addresses for frame forwarding.
Ethernet Hub
Repeats bits to all ports except incoming.
Source MAC Address Learning
Switch learns addresses from incoming frames.
Refresh Timer
Default 5 minutes for MAC address entries.
Unknown Unicast
Forwarding when destination MAC is not in table.
Filtering Frames
Switch forwards frames based on MAC address table.
Store-and-Forward Switching
Receives entire frame, checks CRC before forwarding.
Cut-Through Switching
Forwards frame before complete reception.
Frame Forwarding Methods
Techniques for processing and sending frames.
Destination MAC Address Match
Switch forwards frame if address is in table.
Incoming Port
Port where a frame enters the switch.
Encapsulated Data
Data contained within a network frame.
Cut-through switching
Switch forwards data after reading destination MAC address.
Fast-forward switching
Lowest latency; forwards immediately after destination read.
Fragment-free switching
Checks first 64 bytes for errors before forwarding.
Memory buffering
Stores frames before forwarding during congestion.
Duplex settings
Configuration for simultaneous data transmission capabilities.
Full-duplex
Both ends can send and receive simultaneously.
Half-duplex
Only one end can send at a time.
Autonegotiation
Automatically negotiates speed and duplex settings between devices.
Auto-MDIX
Automatically detects cable type for device connections.
Ethernet switch
Device that forwards frames based on MAC addresses.
Destination MAC address
Unique identifier for network interface in a frame.