PMT 2.2 - Group 2 Flashcards
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Write an equation for the first ionisation energy of magnesium
Write an equation for the first ionisation energy of magnesium
Mg (g) → Mg+ (g) + e-
Explain the first Ionisation energy across period 3
increases across period 3 because of:
increased nuclear charge,
decreased atomic radius and
same electron shielding means more energy is needs to remove the first electron.
Dips at Al because: outer electron is in a 3p orbital, higher energy than 3s orbital → less energy needed to remove electron
Dips at S because one 3p orbital contains two electrons → repulsion between paired electrons → less energy needed to remove one
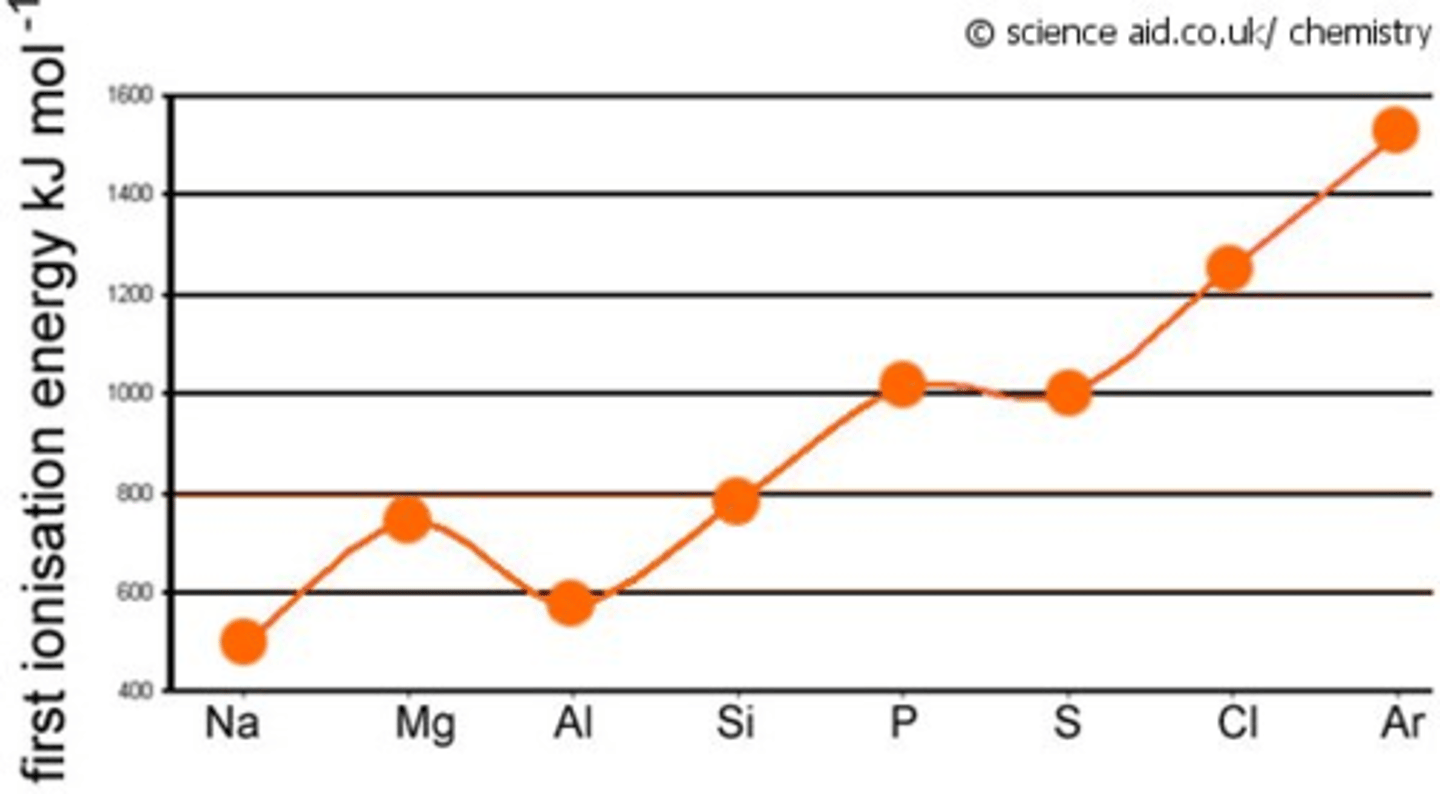
What happens to the first ionisation energy as you go down group 2? Why?
What happens to the first ionisation energy as you go down group 2? Why?
Decreases because: number of filled electron shells increases down the group → increased shielding, increased atomic radius → weaker force between outer electron and nucleus → less energy needed to remove electron
How does reactivity with water change as you go down group 2?
How does reactivity with water change as you go down group 2?
Increases (Mg least → Ba most)
Because outer electrons further from nucleus and more electron shielding, so electrons are lost more easily
Write an equation for the reaction of Barium and water
Write an equation for the reaction of Barium and water
Ba (s) + 2H2O (l) → Ba(OH)₂ (aq) + H₂ (g)
Write an equation for the reaction of Magnesium and steam.
Write an equation for the reaction of Magnesium and steam.
Mg (s) + H₂O (g) → MgO (s) + H₂ (g)
What is the trend in hydroxide solubility down group 2?
What is the trend in hydroxide solubility down group 2?
Increases down the group
Mg(OH)₂ is almost insoluble
Ba(OH)₂ creates a strong alkaline solution
What is the trend in sulphate solubility down group 2?
What is the trend in sulphate solubility down group 2?
Decreases down group
MgSO₄ is soluble
BaSO₄ is insoluble
What is the trend in melting point down group 2? Why?
What is the trend in melting point down group 2? Why?
Decreases down group
Because sea of delocalised electrons is further from the positive charge of the nucleus → weaker metallic bonds / forces of attraction which take less energy to weaken
What is the trend in atomic radius down group 2?
What is the trend in atomic radius down group 2?
Increases as there are more occupied electron shells down the group
Write the equations for the extraction of Titanium using Magnesium.
Write the equations for the extraction of Titanium using Magnesium.
TiO₂ + 2Cl₂ + C → TiCl₄ + CO₂
TiCl₄ (l) + 2Mg (s) → 2MgCl₂ (s) + Ti (s)
What are flue gases?
What are flue gases?
Gases produced by power stations which are harmful to the environment
How can CaO or CaCO3 be used to remove flue gases? Write equations
How can CaO or CaCO3 be used to remove flue gases? Write equations
CaCO₃ (s) + SO₂ (g) → CaSO₃ (s) + CO₂ (g)
CaO (s) + SO₂ (g) → CaSO₃ (s)
What is Ca(OH)2 used for? Write an equation related to one of its uses
What is Ca(OH)2 used for? Write an equation related to one of its uses
Used to neutralise soil
Ca(OH)₂ (aq) +2HCl (aq) → 2H₂O (l) + CaCl₂ (aq)
What is Mg(OH)2 used for?
What is Mg(OH)2 used for?
Milk of magnesia - antacid to treat indigestion, heartburn, wind etc.
What is a use of BaSO4? Why is this safe?
What is a use of BaSO4? Why is this safe?
In barium meals to outline gut in X-rays
Ba²+ is toxic but is fine as barium sulphate is insoluble
How can BaCl2 be used to test for sulfate ions?
How can BaCl2 be used to test for sulfate ions?
Add to sample with HCl, white ppt will form if sulfate ions present
Ba2+ + SO42- -> BaSO4