Assisting with Mobility
0.0(0)Studied by 0 people
Card Sorting
1/106
Last updated 2:12 AM on 2/3/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
1
New cards
contracture
a condition characterized by the tightening or shortening of a body part, such as muscle, tendon, or skin, due to lack of movement
2
New cards
atony
lack of sufficient muscular tone
3
New cards
atrophy
a decrease in size or wasting away of a body part tissue
4
New cards
thrombus
a blood clot that forms in a blood vessel and remains at the site of formation
5
New cards
embolus
a mass, most commonly a blood clot, that become lodged in a blood vessel and obstructs the flow of blood
6
New cards
Activity of daily living (ADL)
any basic self-care task, including prooming, bathing, and eating
7
New cards
posture
position of the body when sitting or standing
8
New cards
body alignment
the optimal placement of body parts so that bones are used efficiently and muscles have to do less work to get the same effect
9
New cards
ambulation
the ability to walk from one place to another
10
New cards
gait belt
a device made of canvas, nylon, or leather that is used by healthccare workers to safely move patients to a standing position of to assist them during walking
11
New cards
ankylosis
the stiffening or immobility of a joint resulting from disease, trauma, surgery, or bone fusion
12
New cards
foot drop
a condition characterized by the inability to lift the front part of one or both feet due to weakness or paralysis of the muscles in the foot; causes the toes to drag on the ground while walking
13
New cards
immobility
a condition charaxterized by a limited, or complete lack of, ability to move
14
New cards
traction
the use of a pulling force to treat muscle and skeletal
15
New cards
decubitus ulcer
a skin sore that is a result of lying in one position too long; caused by pressure that interferes with blood circulation to the skin
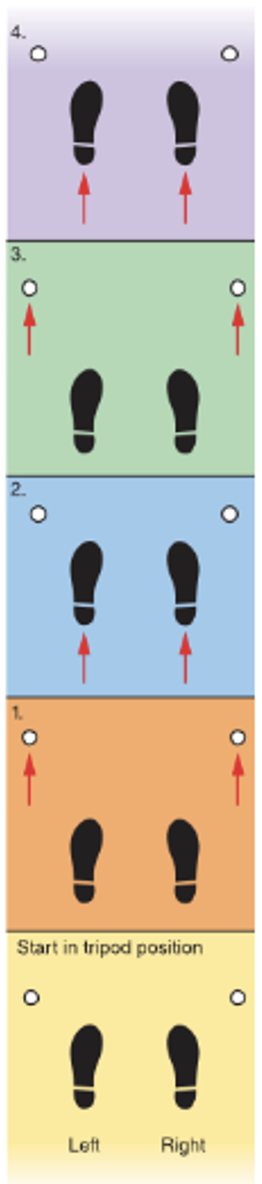
16
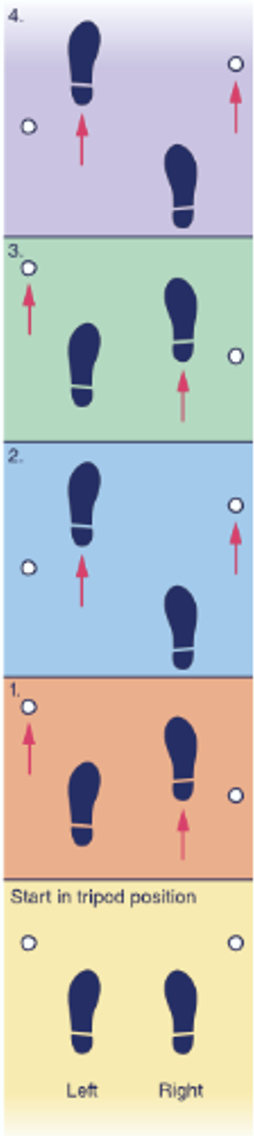
New cards
necrotic
term that describes dead cells or tissues
17
New cards
trochanter roll
a rolled towel or blanket placed along the hip that prevents the hips from rotating externally
18
New cards
contraindicated
term that describes any situation or condition that causes a particular type of treatment to be improper or undesirable
19
New cards
AAROM
Active Assistive Range of Motion
20
New cards
ABD
Abduction
21
New cards
ADL
Activites of daily living
22
New cards
amb
abulation
23
New cards
BR
Bedrest
24
New cards
BRP
Bathroom privileges
25
New cards
CPM
Continuous passive motion
26
New cards
HOB
Head of bed
27
New cards
OOB
Out of bed
28
New cards
ROM
Range of motion
29
New cards
Up ad lib
Up as desired
30
New cards
W/C
Wheelchair
31
New cards
First Pendulum
Leg leaves the ground, swinging forward from the ihp
32
New cards
second pendulum
Movement of the two legs is coordinated so that one foot is always in contact with the ground
33
New cards
How does walking differ from running?
When walking, one leg is always in contact with the ground, while the other is swinging. When running, there is a ballistic phase that occurs when both feet are off the ground at the same time
34
New cards
Stage 1 of Ambulation
Assit the patient to lift his body from lying in bed to stiing on the side of the bed in a dangling position.
35
New cards
Orthostatic hyptension
Dizziness and possibly fainting when standing
36
New cards
Step 2 of ambulation
After putting on a gait belt assist the patient to stand
37
New cards
Step 3 of ambulation
Patient begins ambulating
38
New cards
What should you not do if your patient is collapsing
You should not try to carry, hold up, or catch her
39
New cards
What should you do if your patient is falling
Assume a broad stance with your preferred foot slightly ahead of the other and between the patient’s legs. Grasp the patient’s body firmly at the waist or under the axilla, and allow her to slide down against your leg.
40
New cards
Can family members or friends availalbe assist
Yes, however, the appropriate provider has to have given persmiision and each person understands and is comfortalbe with the preocedure. Family members and friends must know how to avoid any risks or harm to themselves and the patient as described.
41
New cards
What is useful for those who may have had surgery and are not yet able to maintain balance or need extra stability
Canes
42
New cards
Used often for short-term conditions such as a sprained ankle or broken leg
Crutches
43
New cards
What is helpful for people who may have had surgery on their lower limbs, such as a hip or knee replacement
Walkers
44
New cards
How do the elderly use canes
use a cane if they have recovered from a stroke and are not yet able to fully ambulate, or if they have arthritis that has resulted in restricted movement.
45
New cards
How are walkers used by the elderly
When they begin to lose their balance and stability and need extra assistance.
46
New cards
Cane that has a single shaft and resemble a candy cane
C canes
47
New cards
Has a straight handle for a steadier grip
functional grip cane
48
New cards
Quad cane
base with four prongs, each with a skid resistant tip
49
New cards
Which type of cane assists best with balance
Quad cane
50
New cards
How do you know that a cane is the best fit for you
The top of the cane is in line with the patient’s wrist crease when she stands up straight and her arms are hanging loosely at her sides. The patient should be able to slightly bend her elbow
51
New cards
Which side should the patient hold their cane
Should hold the cane on their stronger side
52
New cards
How far foward should the cane move
6-10 inches
53
New cards
Which leg should the patient ambulate with when using a cane
Weak leg
54
New cards
With what grip should you grip the gait belt
underhand grip
55
New cards
When using a cane to climb stairs which foot should you start with
Stronger foot; then put cane on step and lift weak leg
56
New cards
When coming down the stairs which foot should you lead with
Should put your cane on the first step and follow with the weak foot
57
New cards
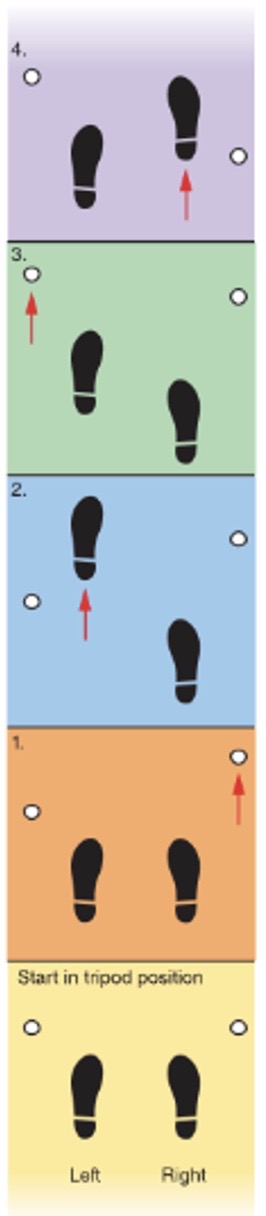
What gait is this
Four-point gait
58
New cards
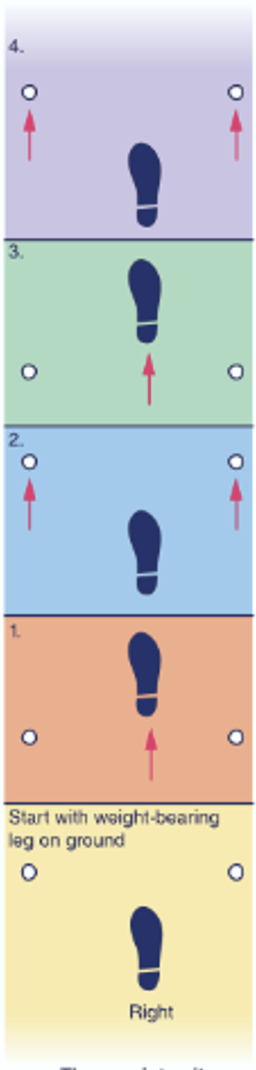
What gait is this
three-point gait
59
New cards
what gait is this
Two point gait
60
New cards
What gait is this
Swing through gait
61
New cards
Standard underarm/ acillary crutches
Generally made of wood or aluminum and can be adjusted fro height. They have padding on the underarms and also have hand holds. These crutches are usually for short-term use.
62
New cards
Strutter crutches
have a u-shaped underarm support that distributes weight over a larger area of the skin surface and also has a larger base. This provides better balance and helps alleviate any possible injury of nerves and blood vessels in the axilla
63
New cards
Platform crutches
Feature a horizontal, padded armrest. Patient using these crutches straps his arms onto each armrest and is then able to maneuver the crutches
64
New cards
Forearm crutches
Typically used for patients with disabilites. Are often selected for long-term use.
65
New cards
How do you know which crutch is right for you?
The tops of the crutches should be about one and a half inches below the acilla, while the patient is standing up straight and shoulders are relaxed adn the hand grips of the crutches should be even with the hips.
66
New cards
What can damge nerves in the axilla
When the crutches are presssing into the axilla
67
New cards
What is tripod position
The crutch tips are placed about four to six inches to the side and slightly in front of each foot. The strong foot bears weight of the body
68
New cards
When is a four point gait used
Used when there is some weight bearing ability on both legs
69
New cards
When is a three-point gait used
When there should be no weight bearing on the affected, or injured leg
70
New cards
When is a two-point gait used
when both legs can bear some weight
71
New cards
When is a swing-through gait used
When legs are paralyzed and in braces
72
New cards
What is one of the ways that patients can go down and up the stairs with crutches
Tucking both crutches under the opposite axilla. When going up stairs, have the patient lead with the strong foot keeping the weak foot raised behind. When going down stairs, the patient should hold the weak foot up and in front of the body, hopping down each stair on the strong foot, taking if one step at a time.
73
New cards
What is another way to go down stairs with crtuches
Patients sit on the stairs and inch up or down each step. The patient should hold the weak leg out in front of her body, and carry both crutches flat against the stairs the hand opposice of the railing. She should scoot her bottum up or down to the next step, using the free hand and strong leg for support
74
New cards
Standard walker
Lightweight metal and has four solid legs with rubber tips on the bottoms of legs. This type of walker is used when the patient is able to pick up the walker while ambulating
75
New cards
Rolling walker (rollator)
Has wheels or casters on the end of each of the four legs so the walker rolls during ambulation. To proivde stability, some walkers have two wheels on the front two legs and no wheels on the back two legs.
76
New cards
How do you know that a walker height is best for you?
The handles or tops of the walker should be at height even with the patients’s wrist when she is standing in an upright position with arms relaxed at her sides. When holding a walker a patients arms should be comfortably bent
77
New cards
How much space should you keep when you have a gait belt on
3 fingers
78
New cards
Which leg should you step with first when using a walker
Take first step with weakest leg. The heel of the foot should touch the ground first and the foot should flatten.
79
New cards
After how many hours should a patitent be repositioned
2 hours
80
New cards
Stage 1
The skin is not open but is discolored, turning red on people with light complexions and blue or purple on those who have darker complexion; Skin does not turn white when pressed.
81
New cards
Stage 2
Decubitus ulcer is still considered superficial but the skin is now open. A blister filled with fluid, an abrasion, or a shalow sore that looks like a crater can be seen, and the surrounding area may be irritated and red in color
82
New cards
Stage 3
The ulcer is much deeper and may affect the underlying connective tissue. The sore looks more like a crater and may ooxe, blled, or contain pus
83
New cards
stage 4
The damage is deep and may reach the muscle, tendons, ligaments, joints, and bone. The uclcer will bleed and the skin and tissue become necrotic
84
New cards
How many body positions should patients be rotated through?
4 body positions
85
New cards
Fowler’s position
* The patient is seated in bed and the head of the bed is raised to 45º
* The patient’s knees may be elevated by placing a pillow under the knees
\
* The patient’s knees may be elevated by placing a pillow under the knees
\
86
New cards
Semi-Fowler’s Position
* The patient is seated in bed and the head of the bed is raised to a 30º
* Support the patient’s head with a pillow
* The patient’s knees may be elevated by placing a pillow under the knees
* Use a foot support such as a foot board to prevent foot drop.
\
* Support the patient’s head with a pillow
* The patient’s knees may be elevated by placing a pillow under the knees
* Use a foot support such as a foot board to prevent foot drop.
\
87
New cards
Supine Postion
* The patient is lying face up, flat of her back
* The bed is flat and both of the patient’s arms and legs are extended.
* Support the patient’s head with a pillow
* Support the patient’s arms and hands with pillows
* Support the small of the patient’s back with a small rolled towel or blanket.
* The bed is flat and both of the patient’s arms and legs are extended.
* Support the patient’s head with a pillow
* Support the patient’s arms and hands with pillows
* Support the small of the patient’s back with a small rolled towel or blanket.
88
New cards
Prone
* The patient is lying face down, flat on the abdomen
* The patient’s legs are extended and his head is to one side
* The patient’s arms are bent upwards at the elbows or extended down at the sides.
* The patient’s head and abdomen may be supported with pillows, if preferred
* The patient’s legs are extended and his head is to one side
* The patient’s arms are bent upwards at the elbows or extended down at the sides.
* The patient’s head and abdomen may be supported with pillows, if preferred
89
New cards
Lateral Position
The patient is lying of her left side, called left lateral, or right side, called right lateral
90
New cards
Sims’ position
is a partly left-side lygin and partly prone-lying position
91
New cards
Active motion
used when there is a full range of motion of one or more parts of the body and the patient does not require physical help to perform exercises. Healthcare workers may need to remind or observe the patient to make sure exercises are being done correctly.
92
New cards
Active-assistive range of motion
Used when the patient needs help with a full range of motion for one or more body parts because the muscles are too weak or stiff. Healthcare workers help with reange of motion by encouraging normal muscle function
93
New cards
Passive range of motion
used when a patient cannot move one or more body parts. healthcare workers perform the full range of motion wihtout any help from the patient. Keeps joint flexible; will not preserve muscle mass
94
New cards
On whom do you not perform ROM exercises
Those with heart and respiratory diseases and conditions
95
New cards
Flexion
The act of bending a joint
96
New cards
Extension
The act of straightening a joint
97
New cards
Hyperextension
An exaggerated, or extreme, extension
98
New cards
Abduction
Lateral movement away from the midline
99
New cards
adduction
lateral movement toward the midline of the body
100
New cards
Rotation
turning of a body part around an axis or fixed point