AQA GCSE physics: Atomic structure
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
What did JJ Thomson discover?
electrons
What did JJ Thompson's modle prove?
Atoms weren't the fundamentals of elements and that atoms are neutral
Plum Pudding Model
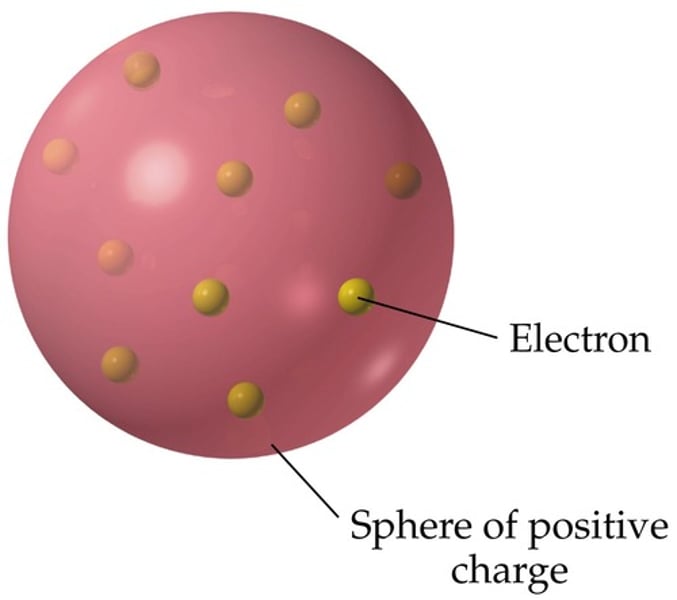
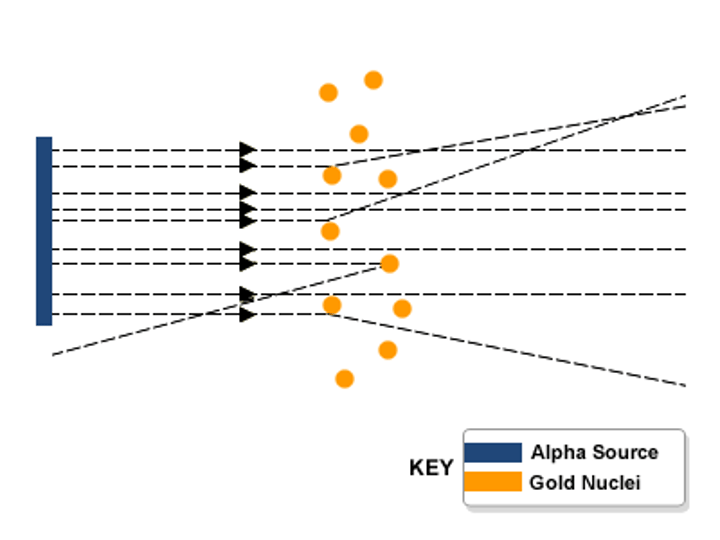
What was the alpha scattering experiment?
Rutherford fired alpha particles at a surface expecting them to pass right throug, alot did but some refracted and some didn't pass through at all
Why did the alpha particles refract?
The alpha particles that got close to the nucleus refracted due to them being a helium atom
Why did some alpha particles bounce back the way they had came in the alpha scattering experiment?
They hit the nucleus and couldn't penetrate
Alpha scattering experiment
What was Rutherford's model?
Nuclear model
What did Rutherford's model prove?
Their are also positively charged protons and electronically charged neutrons that make up the nucleus
Rutherford model

Elements
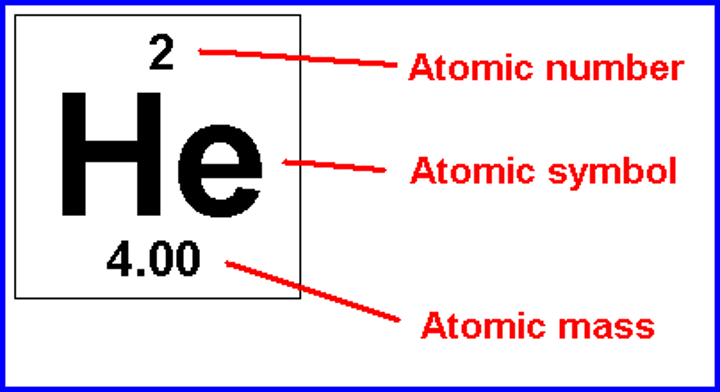
What is the atomic number?
number of protons
What is the mass number?
Number of protons and neutrons
What are isotopes?
atoms with the same number of protons but different number of neutrons
What makes an atom stable?
A full outer layer of electrons
What makes an atom radioactive?
Atoms with unstable nuclei are said to be radioactive. Sooner or later, they break down and eject energetic particles and emit electromagnetic radiation.
What is a half-life?
length of time required for the radioactive atoms in a sample to decay by 50%
How do you calculate half-life?
A=A^o(0.5)^t/h
volume of distribution and clearance
What is half-life measured in?
Becquerels (Bq)
What is nuclear fission?
a process that releases energy by splitting nuclei apart
How does nuclear fission work?
uranium atoms split by shooting neutrons at them
positives - high energy yield
negatives - produces radioactive waste
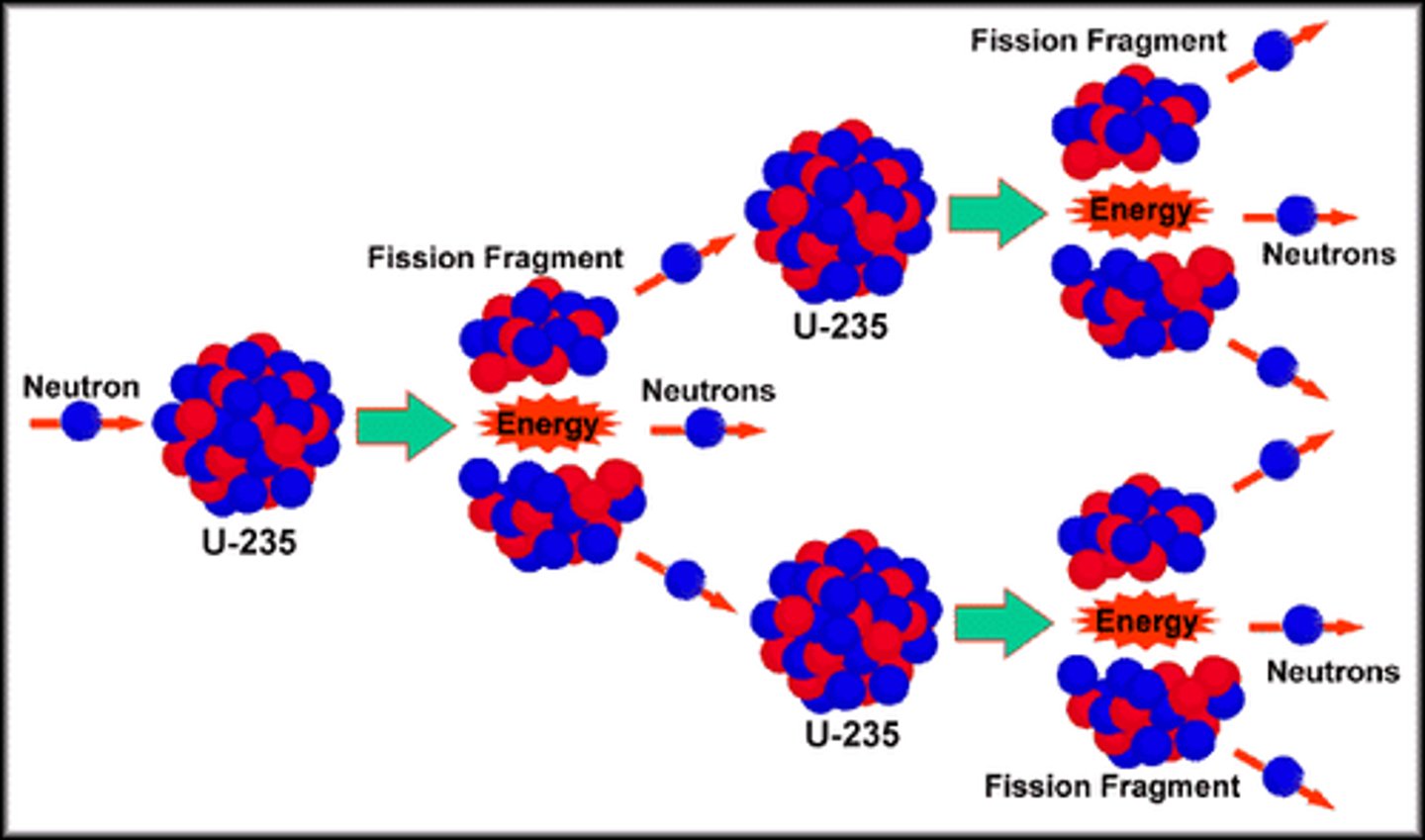
How is fission used?
The nuclear reaction releases energy in the form of heat which is used in nuclear power stations to boil the water which is then used to drive a turbine with the steam
Fission in use in nuclear power stations
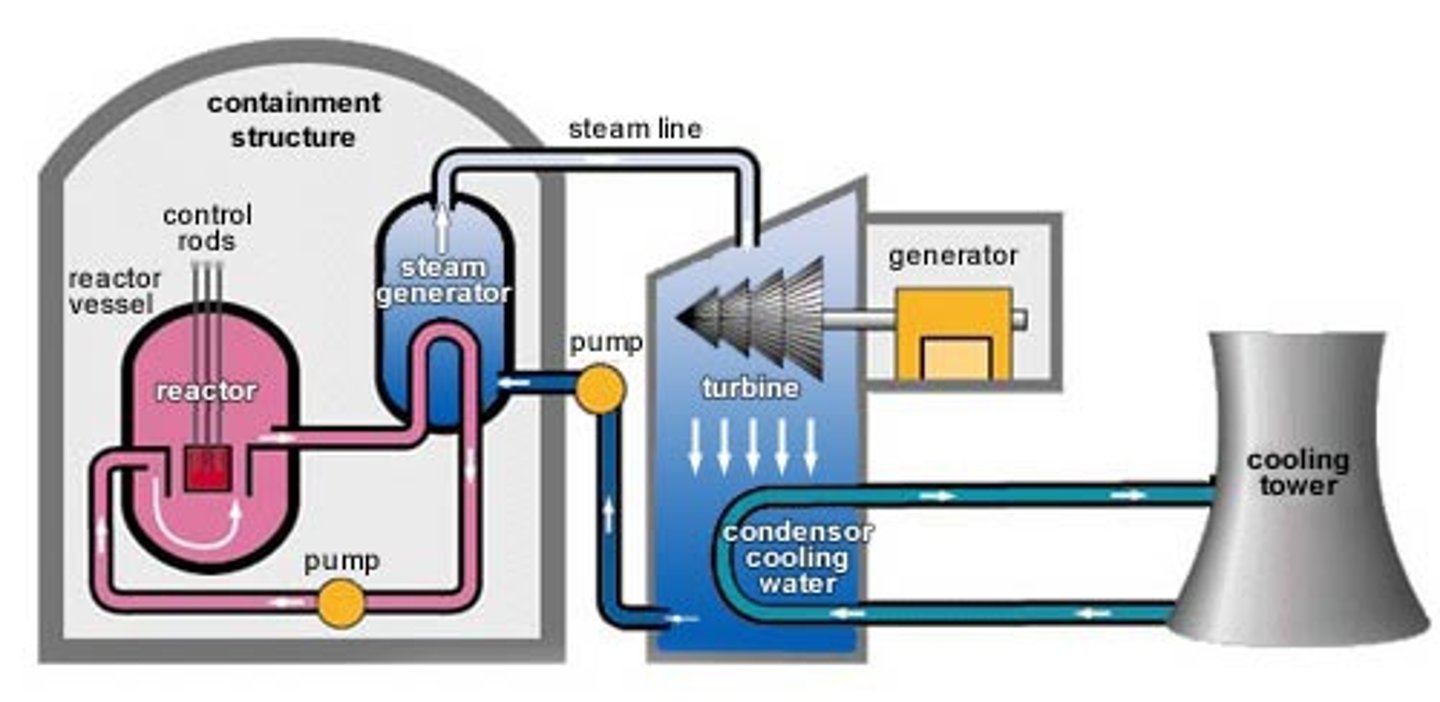
How is fission used in nuclear power stations?
Chain reactions are started and neutron is fired from uranium into another uranium atom
Nuclear fission begins
Heat given off is used to boil water
Steam produced is used to turns a turbine
This turns a generator
This produces electricity
What are the advantages of using nuclear fission to produce electricity?
Cheap to run
Conserves energy
No CO2 emissions
Less transport needed
Safe under normal conditions
What are the disadvantages of using nuclear fission to produce electricity?
Expensive to build
Expensive to decomission
Produces radioactive waste
Carcinogenic
Non-renewable
Risk of nuclear disaster
What is alpha radiation?
helium nucleus: 2 protons and 2 neutrons
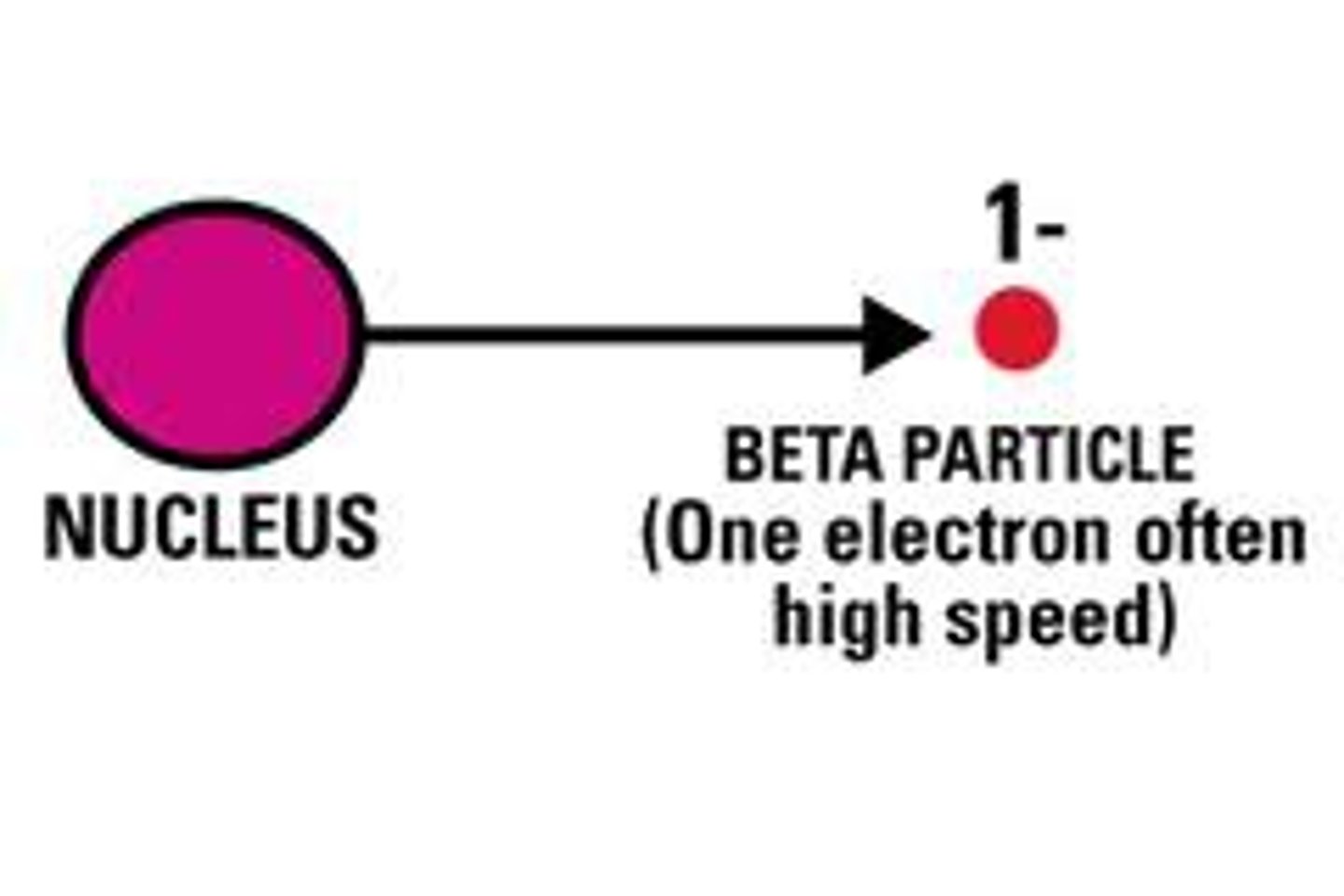
What is beta radiation?
The product of the decomposition of a neutron and is composed of high energy high-speed electrons
What is gamma radiation?
an electromagnetic wave
What equation represents alpha radiation?
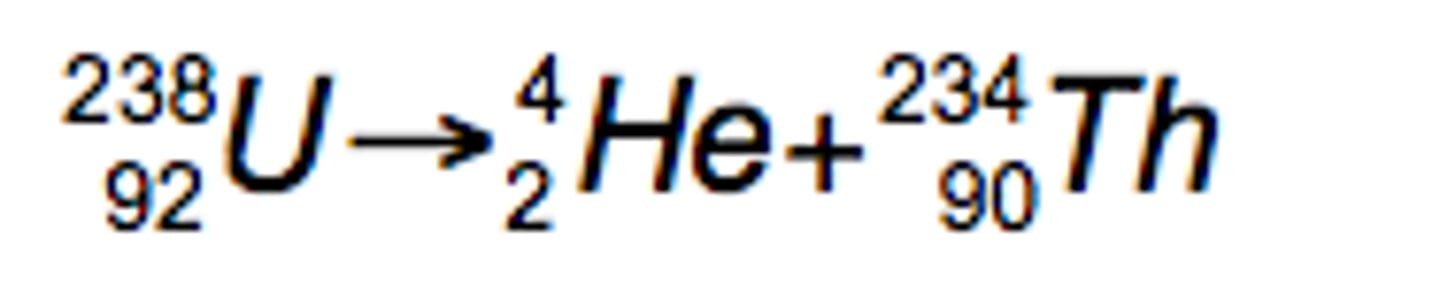
What equation represents beta radiation?
0/-1
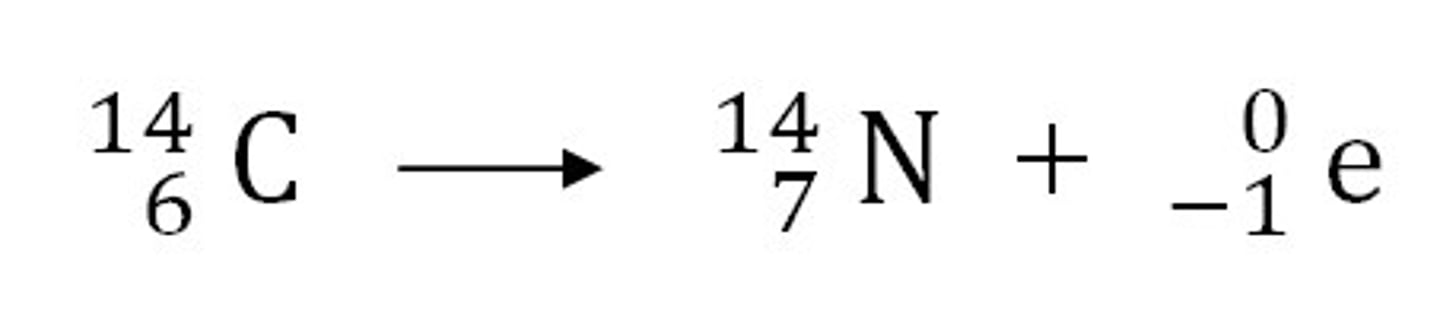
What is alpha radiation stopped by?
5cm of air, paper, skin etc.
What is beta radiation stopped by?
A few mm of aluminium
What is gamma radiation stopped by?
Thick lead absorbs most but not all of the radiation
Is alpha affected by magnetic or electric fields?
Deflected by both and it deflects upwards due to positive charge
Is beta affected by magnetic or electric fields?
Deflected by both and deflects downwards due to negative charge
Is gamma affected by magnetic or electric fields?
No as it travels in waves and has no charge
How ionising and pentetrating are alpha particles?
Very ionising but not very penetrating
How ionising and pentetrating are beta particles?
Quite ionising and penetrating
How ionising and pentetrating are gamma particles?
Not very ionising but most penetrating
Alpha particle
Beta particle
Gamma wave
0/0
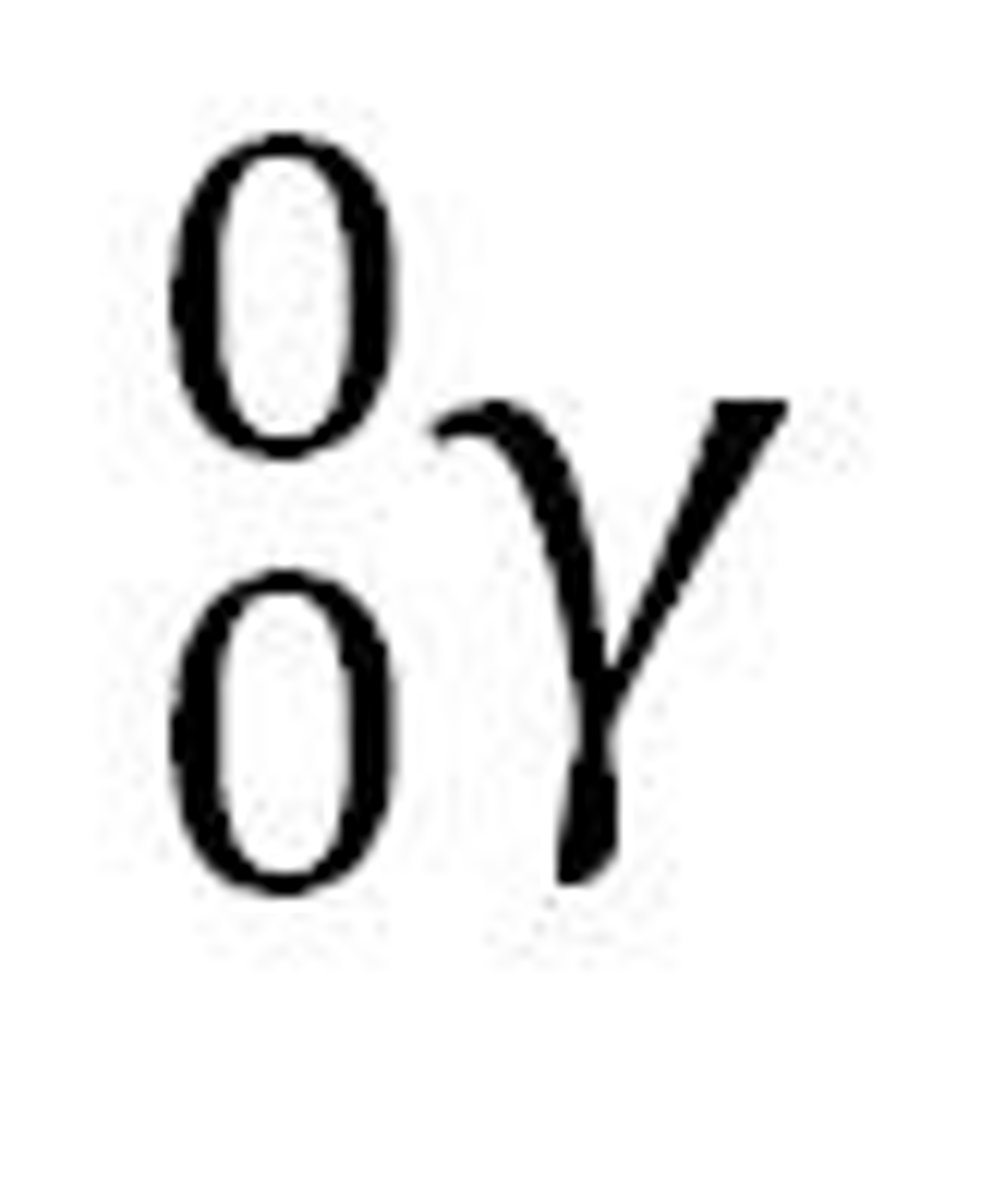
What is carbon dating?
a way to measure the age of dead organisms by comparing the amount of carbon-14 from the dead organism to a living one
Uses beta radiation as all living things take in carbon-14
What are tracers?
radioactive isotopes that can be followed through the steps of a chemical reaction or industrial process to test for blockage
If there is a blockage, they build up and can be detected
Uses gamma radiation as they have shortest half life and least ionising
How is radiation used in smoke alarms?
There is a gap the supplies alpha particles through it, if there is smoke, the supply is cut off and the alarm sounds
Alpha particles are used a sthey ahve a long half life an dleats penetrating hence can't pass through the smoke
How is radiation used as a metal thickness tracker?
Beta particles are fired at alluminium an dif they can no longer be detected, the metal is too thick
Beta particles ara used as they are stopped by thick alluminium
What is nuclear fusion?
the process of combining lightweight nuclei to make heavier nuclei