biotechnolgy and GMO
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
What is a GMO?
A GMO (Genetically Modified Organism) is an organism whose DNA has been changed using biotechnology, often by adding a gene from another species.

What does “transgenic” mean?
Transgenic means an organism has DNA from another species.
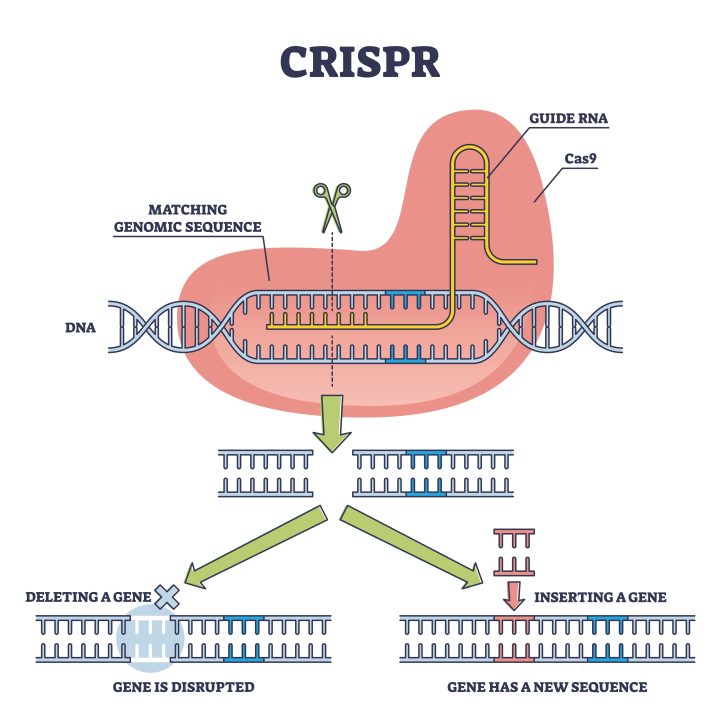
What is CRISPR?
Scientists identify the gene that needs to be changed.
They design a guide RNA that matches that exact DNA sequence.
The guide RNA is attached to the Cas enzyme.
The CRISPR–Cas complex is delivered into the cell.
Guide RNA finds and binds to the target DNA.
Cas enzyme cuts the DNA at that exact spot.
The cell detects the damage and starts repair.
Scientists add new DNA (if needed).
The cell repairs itself using this new DNA.
CRISPR can:
Fix broken genes
Add genes
Change genes
. What is the difference between knockout and CRISPR?
Knockout = a gene is destroyed or turned off.
CRISPR = a gene is cut and repaired or changed.
Why is gene editing risky?
Gene editing is risky because the molecular scissors can cut the DNA in the wrong place. This may damage an essential gene that the cell needs to survive. If important genes are harmed, cells may stop working properly, which can cause serious harm or even death.
What are knockout mice?
Knockout mice are genetically modified mice where one specific gene is turned off to learn what that gene does.
Why do scientists use knockout mice?
Humans have ~20,000 genes.
By removing one gene and observing changes, scientists learn its function.
Helps understand human diseases.
Why do we care about DNA sequences?
Humans share 99.9% of DNA.
The 0.1% difference makes you unique.
Used for paternity tests, crime solving, and identification.
How does DNA profiling work?
DNA is separated using gel electrophoresis.
Small fragments move faster, large ones slower.
Matching band patterns = same person.
What is PCR?
PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) is a technology that makes millions of copies of DNA quickly.
Why do we need PCR?
To get enough DNA to study
For forensics
For medical tests
For sequencing DNA
How do we clone a gene?
Cut the human gene with a restriction enzyme.
Cut a plasmid with the same enzyme.
Sticky ends match.
DNA ligase glues them together.
Put plasmid into bacteria.
Bacteria copy the gene and make the protein.
What is recombinant DNA?
DNA made from different sources combined into one molecule.
What is a vector?
A vector is a vehicle that carries DNA into a cell, such as a plasmid or virus.
Give an example of gene cloning.
The human insulin gene is inserted into bacteria.
Bacteria produce human insulin for diabetics.
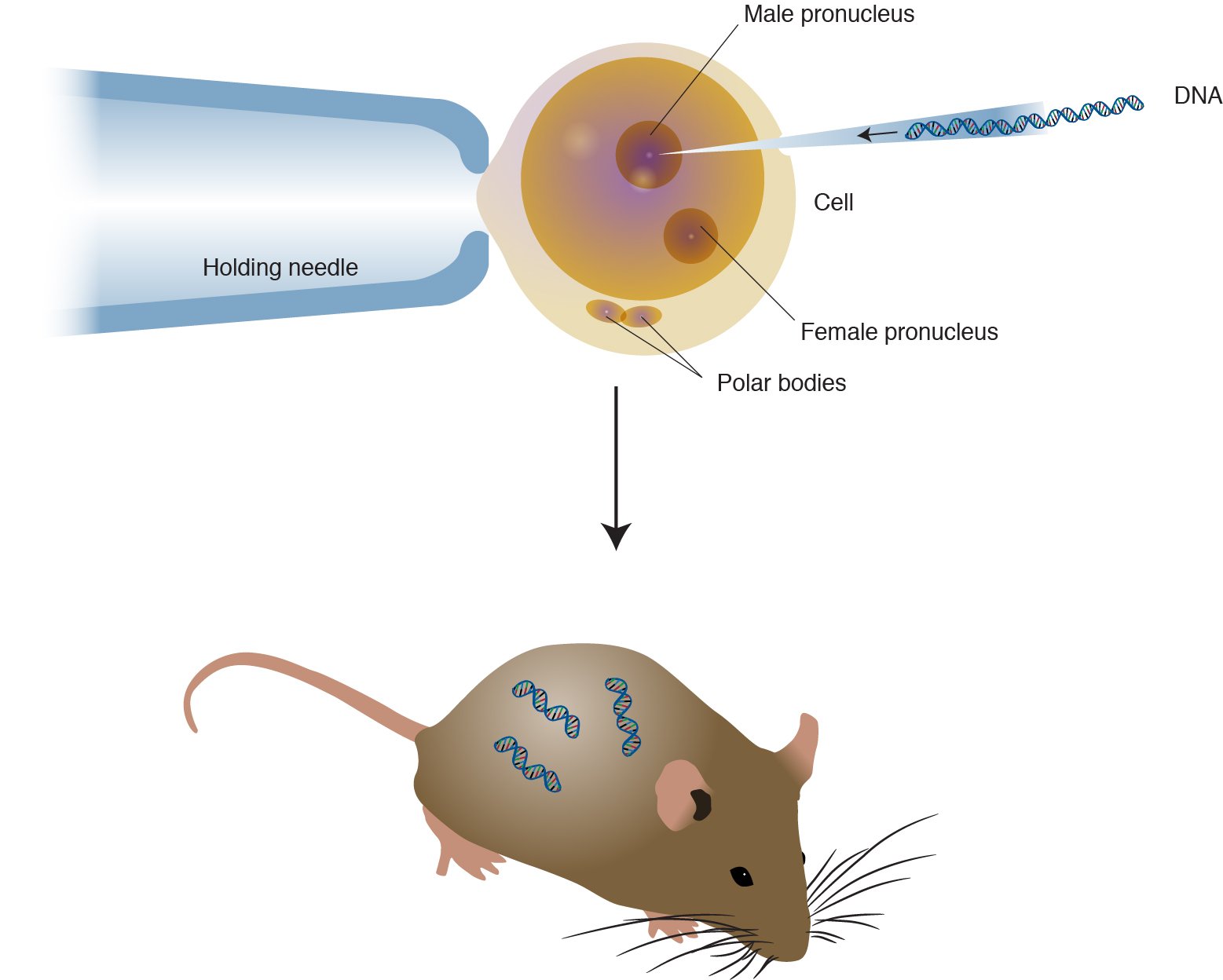
How are animals cloned?
Take a body cell and remove its nucleus.
Take an egg cell and remove its nucleus.
Insert the first nucleus into the egg.
Let it grow into an embryo.
Place it in a surrogate mother.
Result: a genetic copy (clone).
What problems exist with animal cloning?
Expensive
Inefficient
Many clones are unhealthy
Shorter lifespans
Human cloning is illegal.
What is gene therapy?
Gene therapy treats genetic diseases by:
Adding a working gene
Fixing a faulty gene
Turning off a harmful gene
What are the two types of gene therapy?
In vivo: genes are delivered inside the body.
Ex vivo: cells are removed, edited, and returned (e;
Why are viruses used in gene therapy?
They are good at entering cells
Their own genes are removed
A healthy gene is inserted
They deliver the gene to target cells
. Why does genetic engineering matter?
Genetic engineering helps solve global problems like food shortages, population growth, and climate change.
It is a powerful tool that can be used for good or bad, so it must be understood and controlled.
How common are GMOs in everyday life?
GMOs are very common, especially in the USA.
Most people eat GMOs indirectly through corn, soy, sugar beets, and animal feed.
So far, most GMOs are plants, but GM animals may appear in the future.
What is the difference between traditional breeding and GMOs?
Traditional breeding (artificial selection) has been used for thousands of years.
Example: broccoli, cabbage, and cauliflower all come from wild cabbage.
Modern GMOs usually use transgenesis, not breeding.
What is transgenesis?
Transgenesis is inserting a gene from one species into another species.
What is the history of genetic engineering?
1920s: mutation breeding using radiation and chemicals
1983: first successful gene transfer between species
1994: first GM food sold (Flavr Savr tomato)
Public debate about GMOs started and still continues
. What types of GM crops are most common?
Over 90% of GM crops are commodity crops such as:
Corn
Soy
Sugar beets
They are usually modified to resist insects or herbicides.
What are Roundup Ready crops?
Roundup Ready crops are genetically engineered to survive the herbicide glyphosate.
This allows farmers to kill weeds without damaging crops.
They are made by inserting bacterial genes into plants.
How are genes inserted into plants?
Gene gun: shoots DNA-coated gold particles into plant cells
Agrobacterium: a bacterium that naturally transfers DNA into plants
After insertion, GM plants are bred into crop varieties using back-crossbreeding.
Why do GM crops take a long time to develop?
Development can take up to 15 years
Testing for safety and effectiveness is required
It is very expensive, so companies patent and control seeds
What are the main concerns about GMOs?
Corporate control of the food supply
Farmers cannot save patented seeds
Risk of cross-pollination with non-GM crops
Possible environmental effects on insects and ecosystems
GMO Biotechnology Benefits
Helps solve food shortages and population growth
Crops can resist insects and herbicides
Higher yields and more reliable food supply
Can reduce the need for pesticides
Important for adapting agriculture to climate change
GMO Biotechnology Problems:
Corporate control of seeds and food supply
Farmers cannot save patented seeds
Risk of cross-pollination with non-GM crops
Possible long-term environmental effects
Ethical concerns and unequal access
Conclusion:
GMOs are powerful and useful, but they must be carefully regulated and used responsibly.
What is food chemistry and why is it important?
Food chemistry studies what food is made of and how its chemical components provide energy and building materials for the body. It helps explain how diet affects health, stamina, and how well the body functions.
why are nutrients essential for the human body?
Nutrients are needed to supply energy for the brain and muscles, support growth and repair of cells, and regulate important body processes so the body can function properly during daily activities.
What are the main chemical classes of nutrients in food and their roles?
Carbohydrates: main energy source
Fats: long-term energy storage and insulation
Proteins: building and repairing tissues, enzymes
Vitamins & minerals: regulate body processes
Nucleic acids: broken down and reused by the body
Why is vitamin B12 considered a unique and essential nutrient?
Vitamin B12 is needed in extremely small amounts but is essential for life. Humans cannot make it, and it is only produced by bacteria and Archaea. Despite being rare in cells, it is crucial for nerve function and red blood cell formation.
How do carbohydrates provide energy to the body?
Carbohydrates are broken down during digestion into glucose, which is used by cells for energy, especially by the brain and muscles.
What is the difference between sugars, starch, and fiber?
Sugars: simple carbohydrates that give quick energy
Starch: long chains of glucose that provide slower, long-lasting energy
Fiber: cannot be digested but supports gut health and digestion
Why are proteins important, and why do some amino acids need to come from food?
: Proteins are needed to build and repair tissues and make enzymes. Nine amino acids are essential because the body cannot produce them and must get them from the diet.