204 Lungs and the Pleural Cavaity
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
right lung
which lung has a superior, middle and inferior lobe?
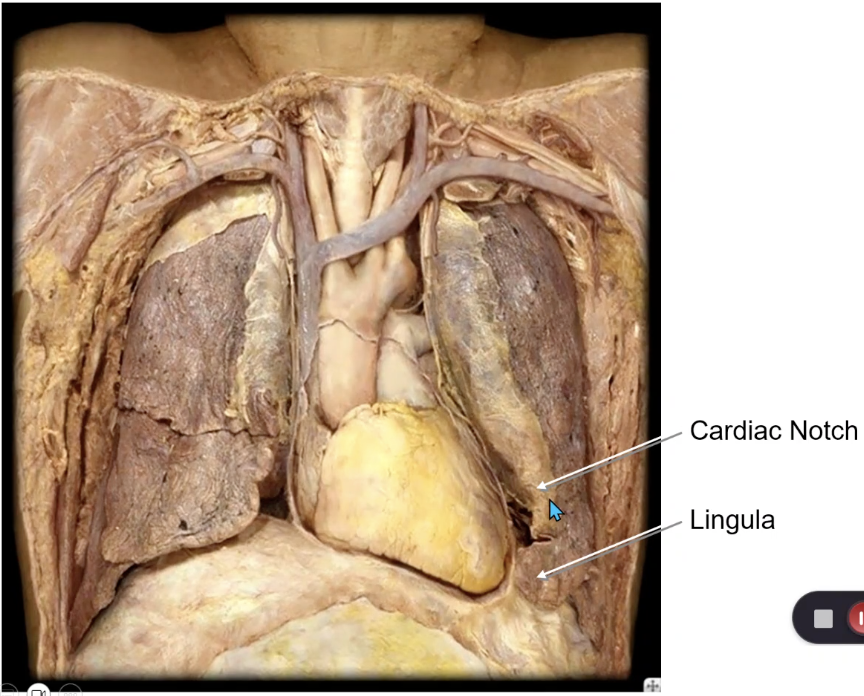
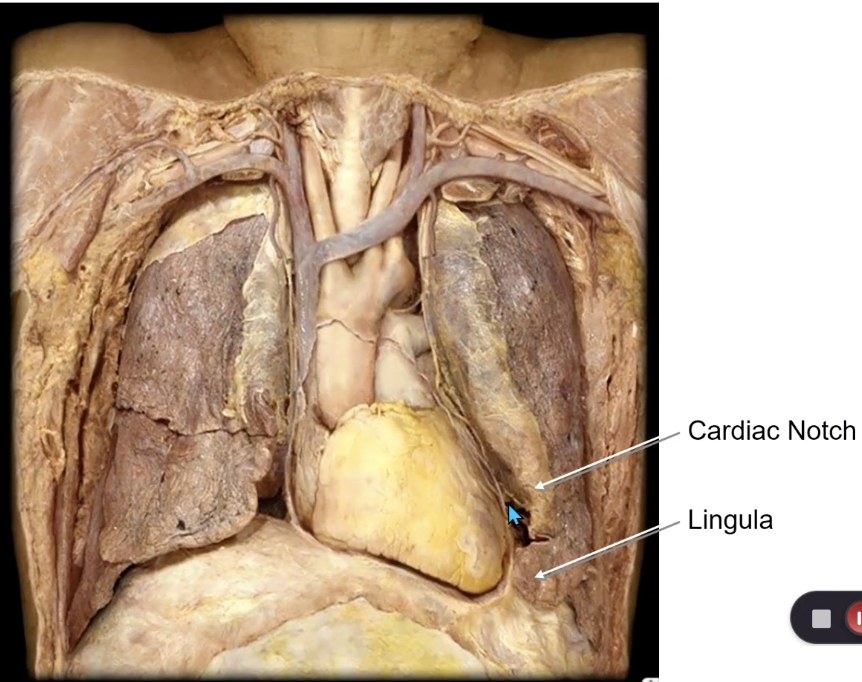
left lung
which lung has a cardiac notch?
left lung
which lung has a lingula?
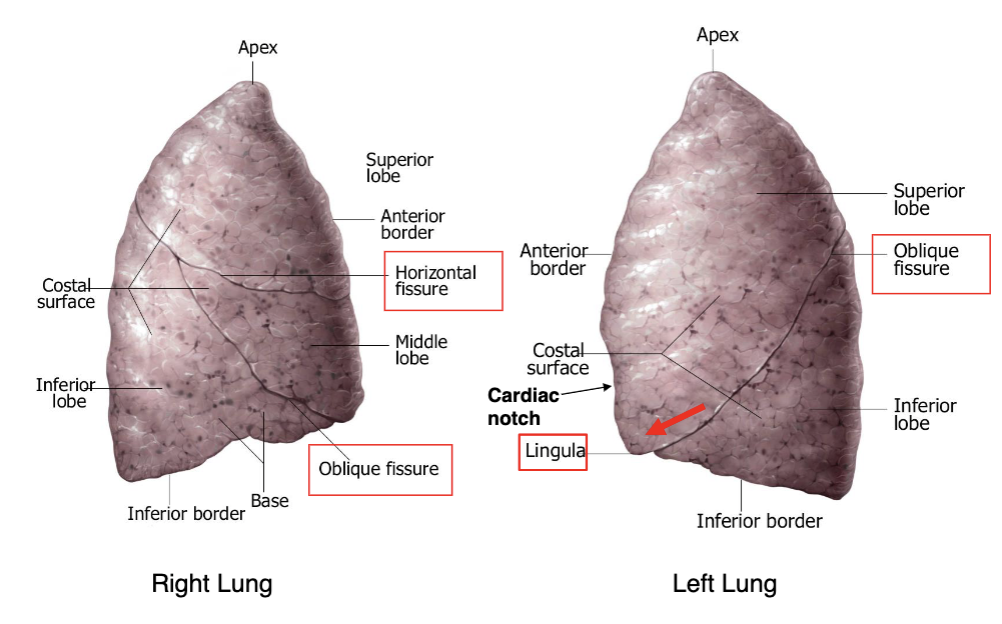
right lung
which lung has a horizontal fissure?
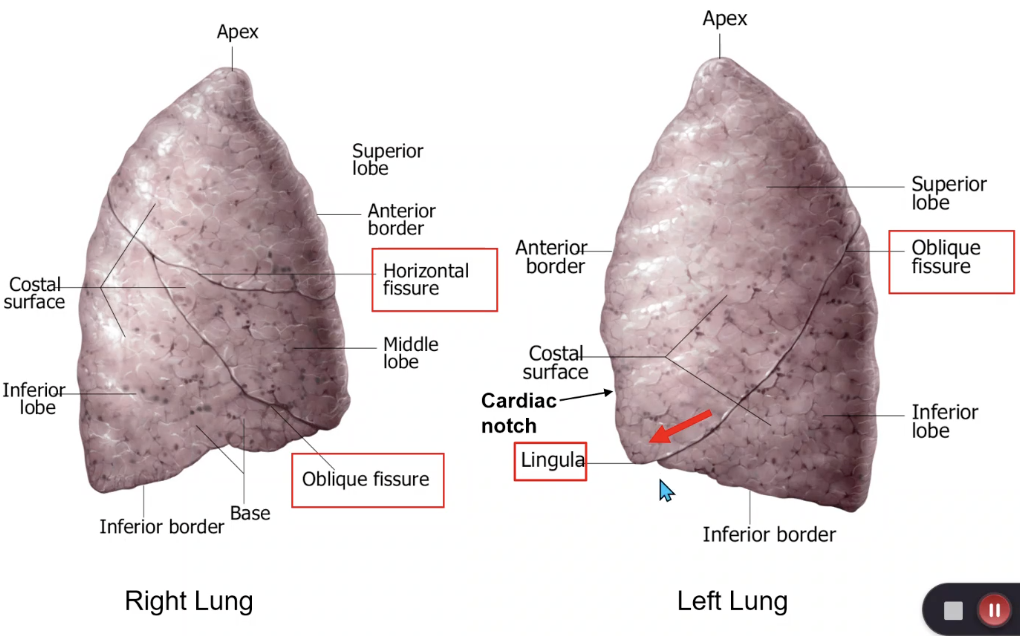
left and right lung
which lung has an oblique fissue?
superior lobe of left lung
the lingula is located on which lobe?
superior lobe of left lung
the cardiac notch is located on which lobe?
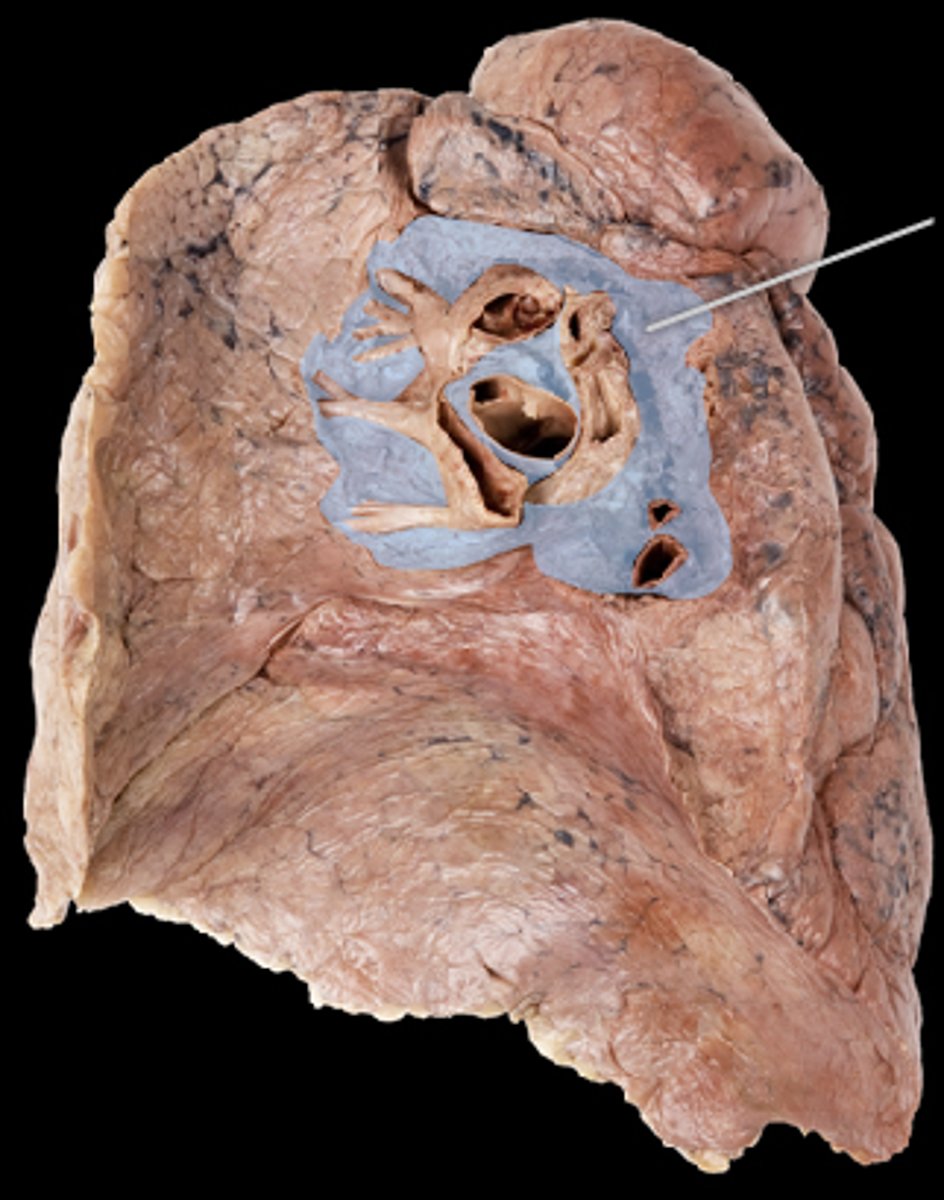
hilum of lung
Identify this structure
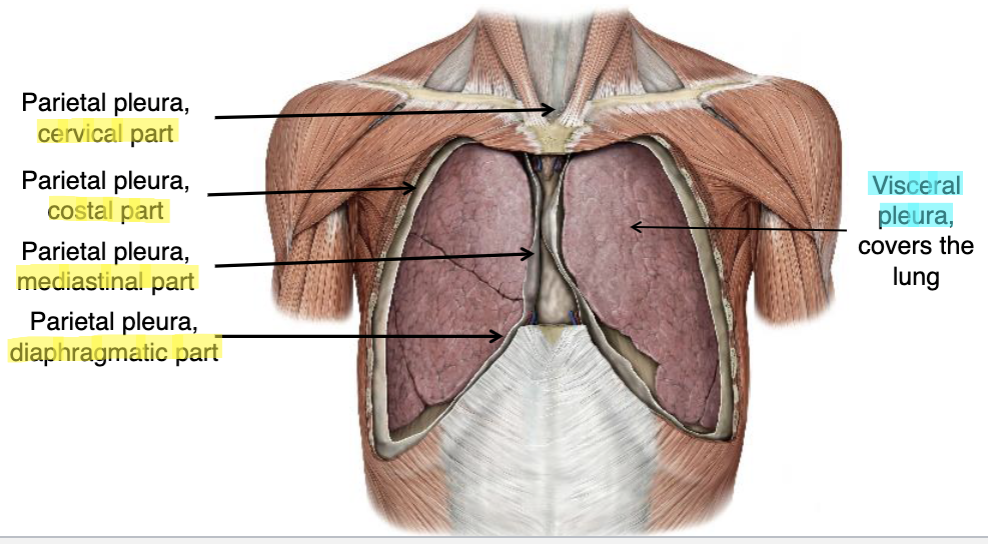
parietal pleura
lines the thoracic cavity and covers the diaphragm encasing the lungs:
visceral pleura
covers surface of lungs:
cervical pleura
which lung pleura extends above the 1st rib?
costal pleura
which part of the parietal pleura lines boarders the ribs?
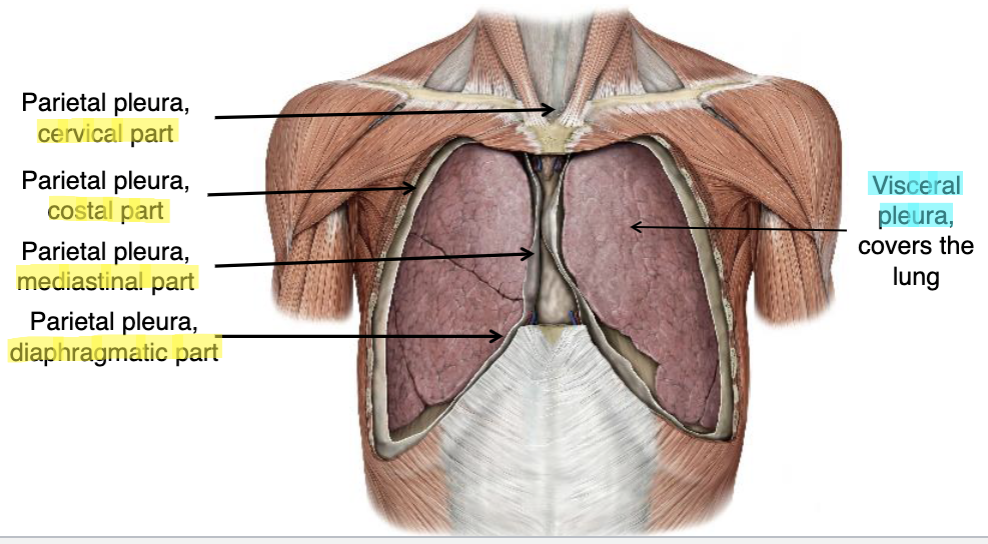
mediastinal pleura
which part of the parietal pleura lines boarders the heart?
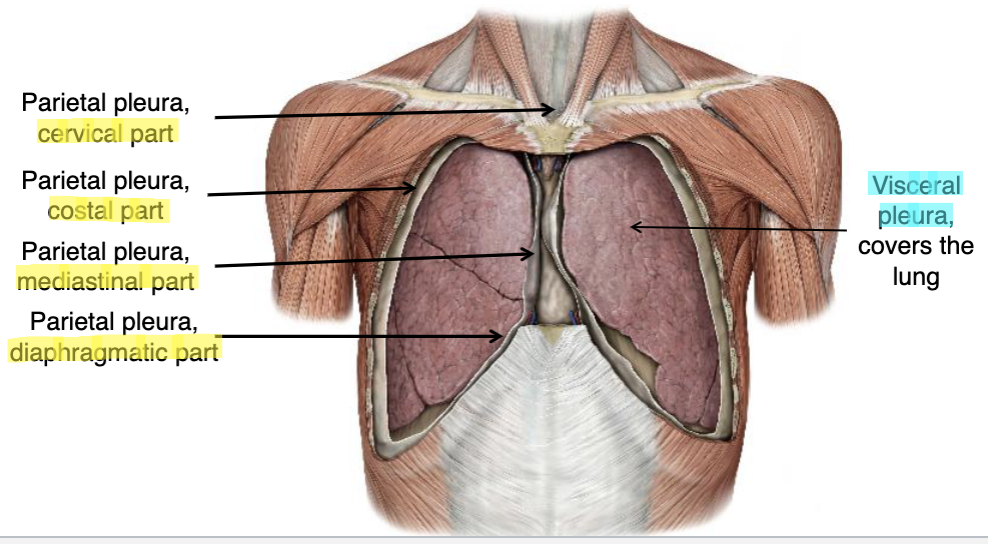
diaphragmatic pleura
which part of the parietal pleura lines boarders the diaphragm?
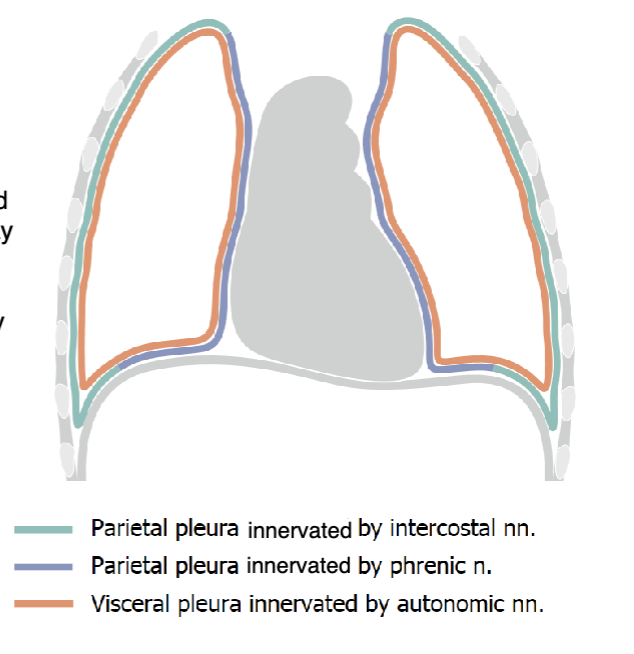
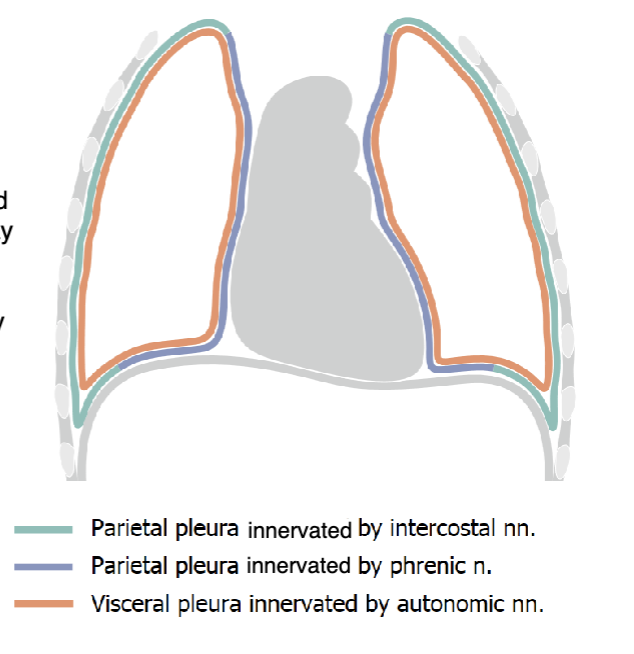
intercostal nn.
cervical and costal pleura are innervated by:
phrenic n.
mediastinal and diaphragmatic pleura are innervated by:
shoulders (C3-4 dermatomes)
pain in the mediastinal and diaphragmatic pleura will be referred to what dermatome?
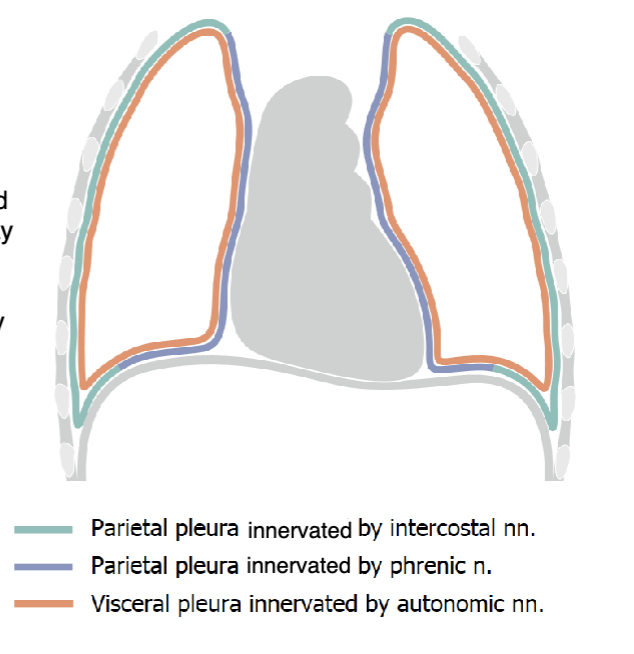
autonomic nn.
the visceral pleura is innervated by:
pleurisy
Inflamed visceral and parietal pleura rub against each other causing sharp pain during breathing, coughing and sneezing:
somatic pain
the parietal pleura is sensitive to _____ pain
visceral pain
the visceral pleura is sensitive to _____ pain
bronchial aa.
blood supply for the visceral pleura comes from:
intercostal aa.
musculophrenic aa.
blood supply for the parietal pleura comes from:
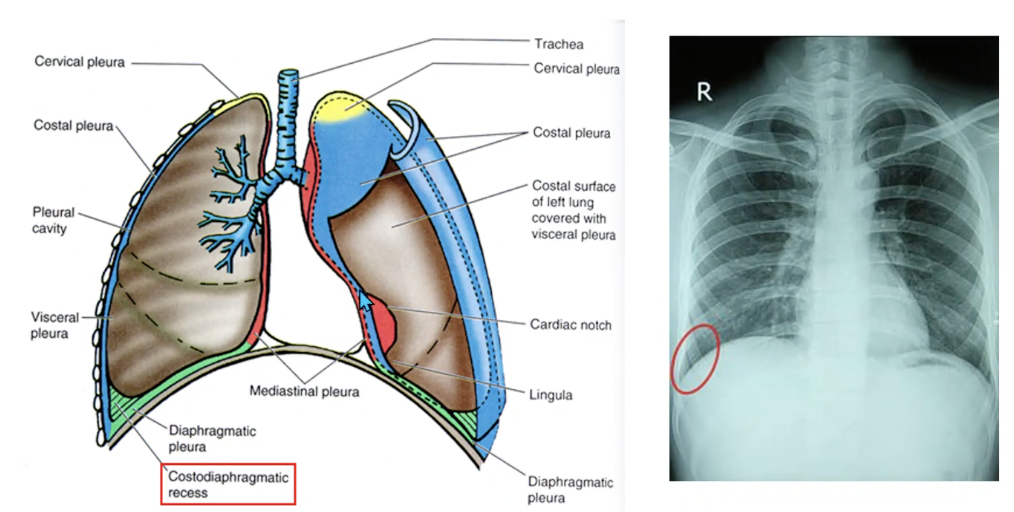
pleural effusion
build-up of fluid in pleural space and particularly in the costodiaphragmatic recess
costodiaphragmatic recess
space in lowest part of the thoracic cavity where the costal and diaphragmatic pleurae join
potential space into which the lung can expand during full inspiration and where excess fluids may accumulate when the person is standing upright
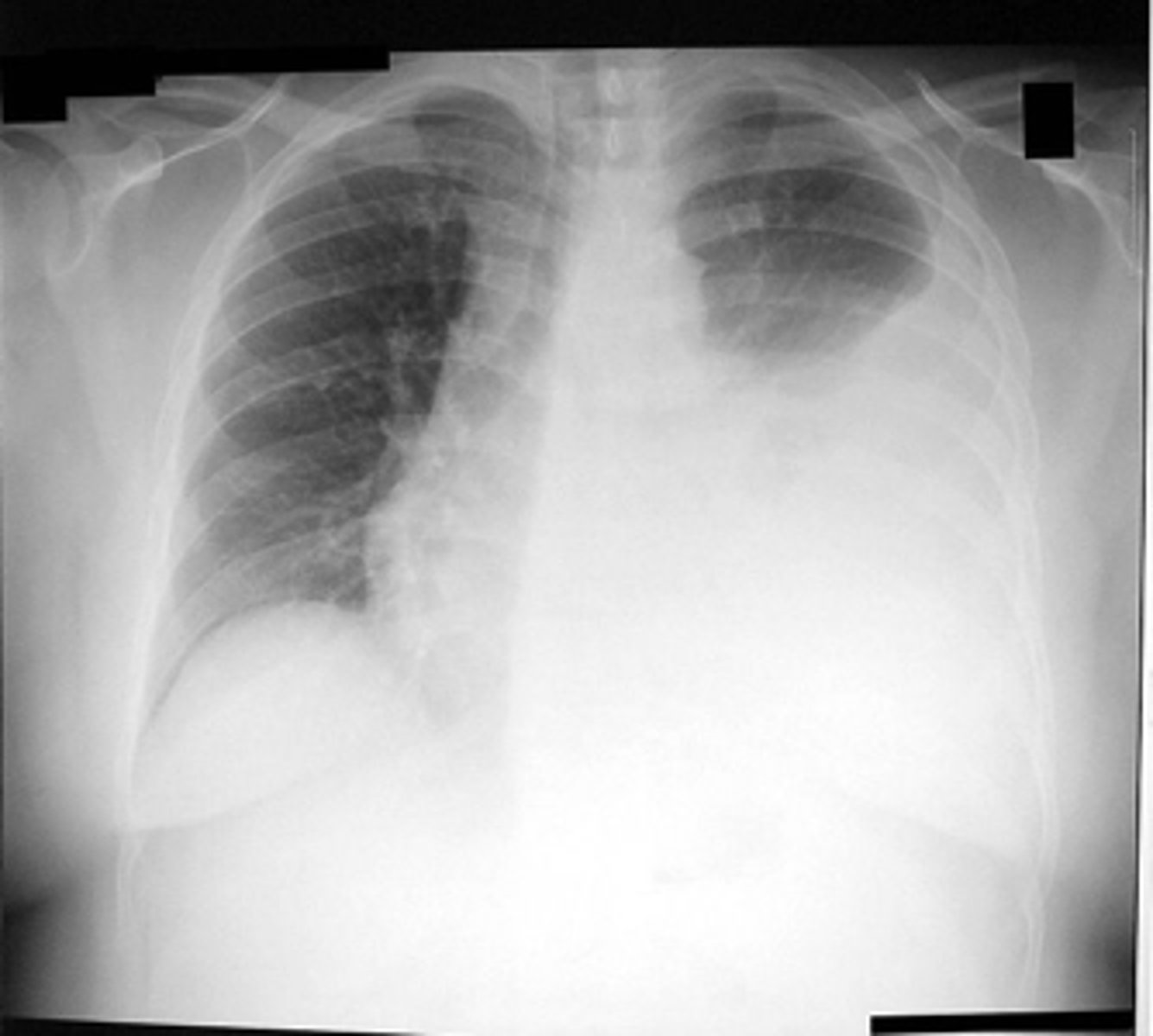
pleural effusion
what is the diagnosis?
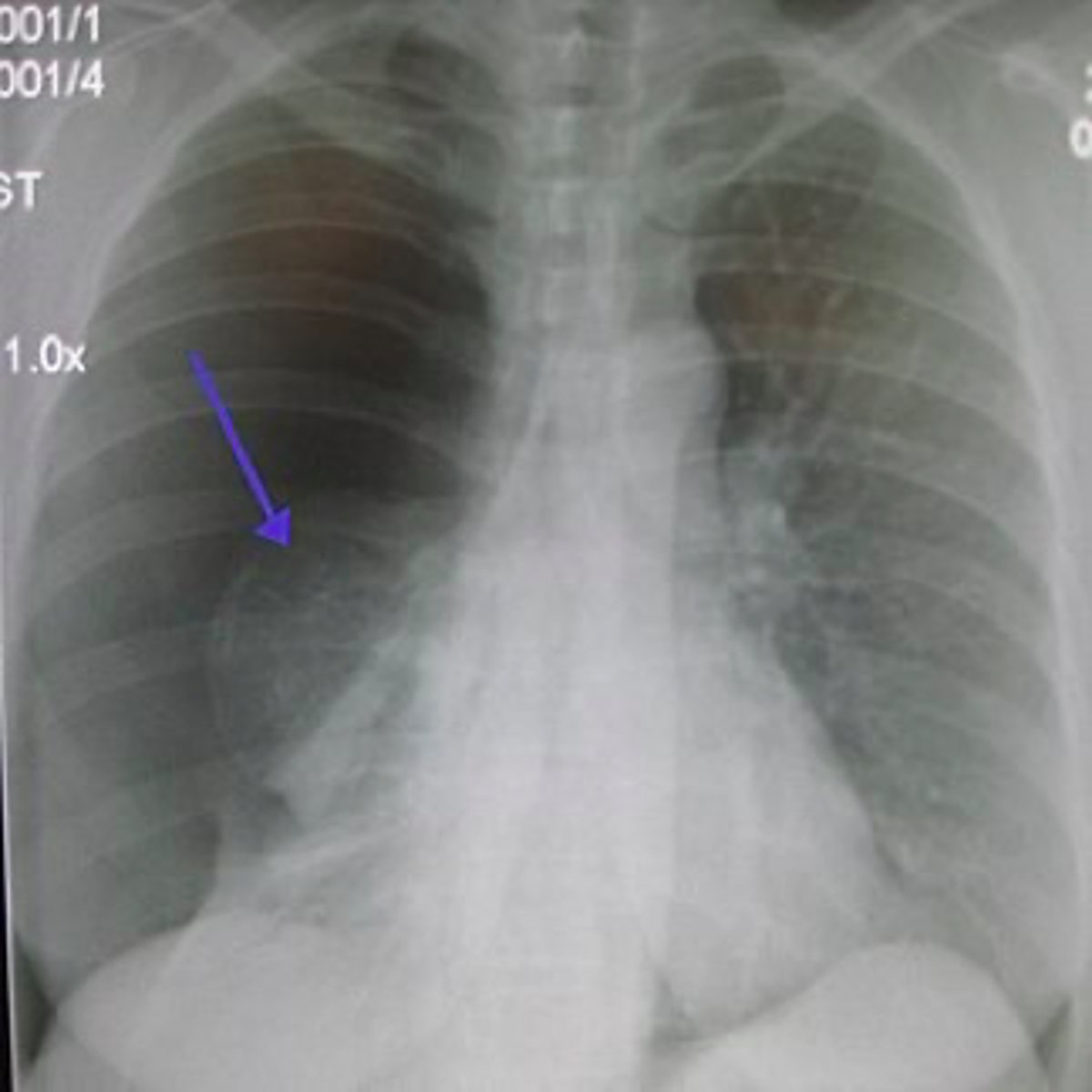
pneumothorax
what is the diagnosis?
serous (hydrothorax, pleural effusion)
blood (hemothorax)
lymph (chylothorax)
pus (pyothorax or empyema)
air (pneumothorax)
when 4 types of fluid can accumulates in the pleural space?
hemothorax
when blood accumulates in the pleural space:
pyothorax, empyema
when pus accumulates in the pleural space:
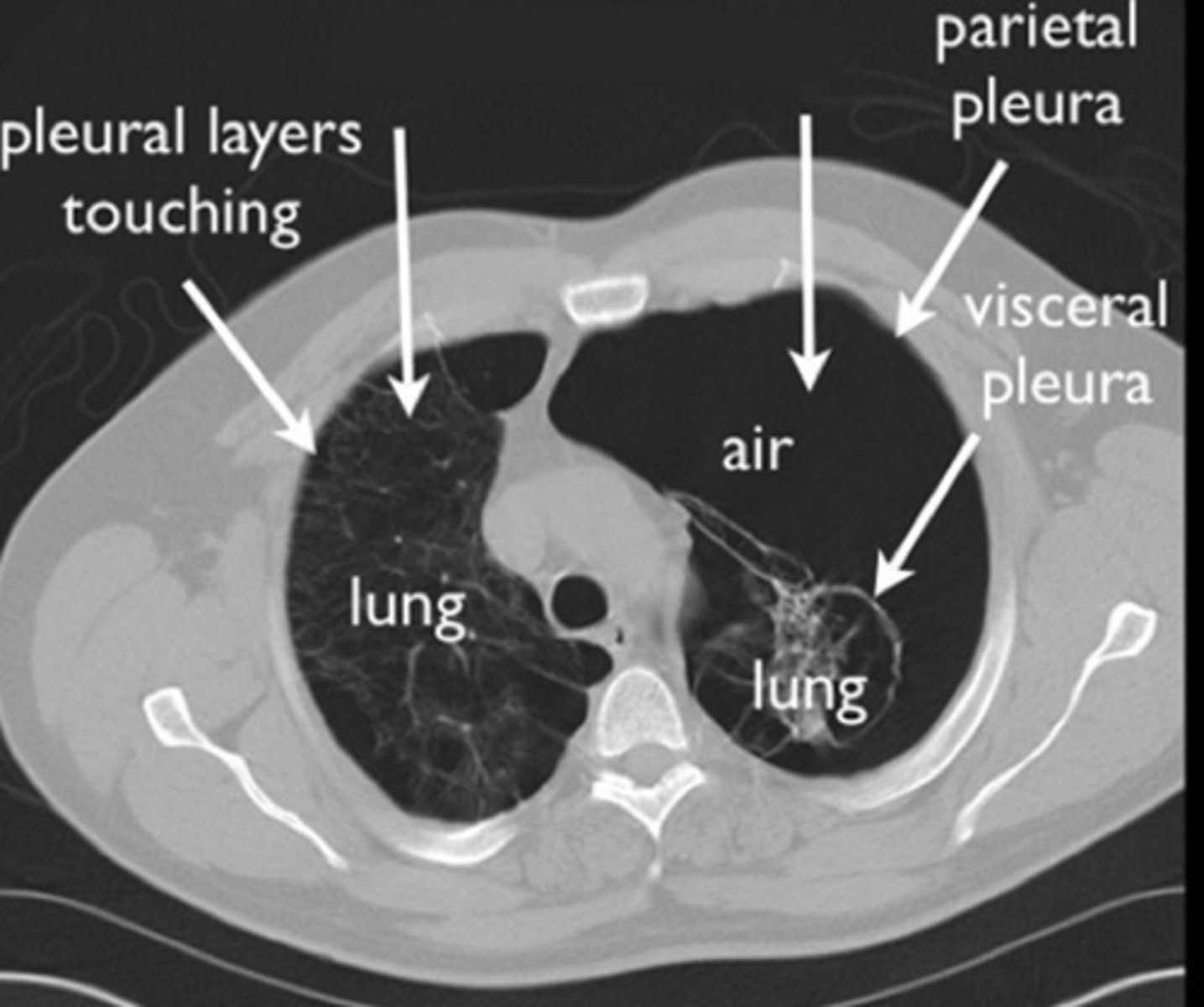
pneumothorax
when air accumulates in the pleural space, lung collapses:
tension pneumothorax
patient presents with gun shot to the lungs. Patient has chest pain and respiratory distress, an increased heart rate and rapid breathing. What is the patient suffering from?
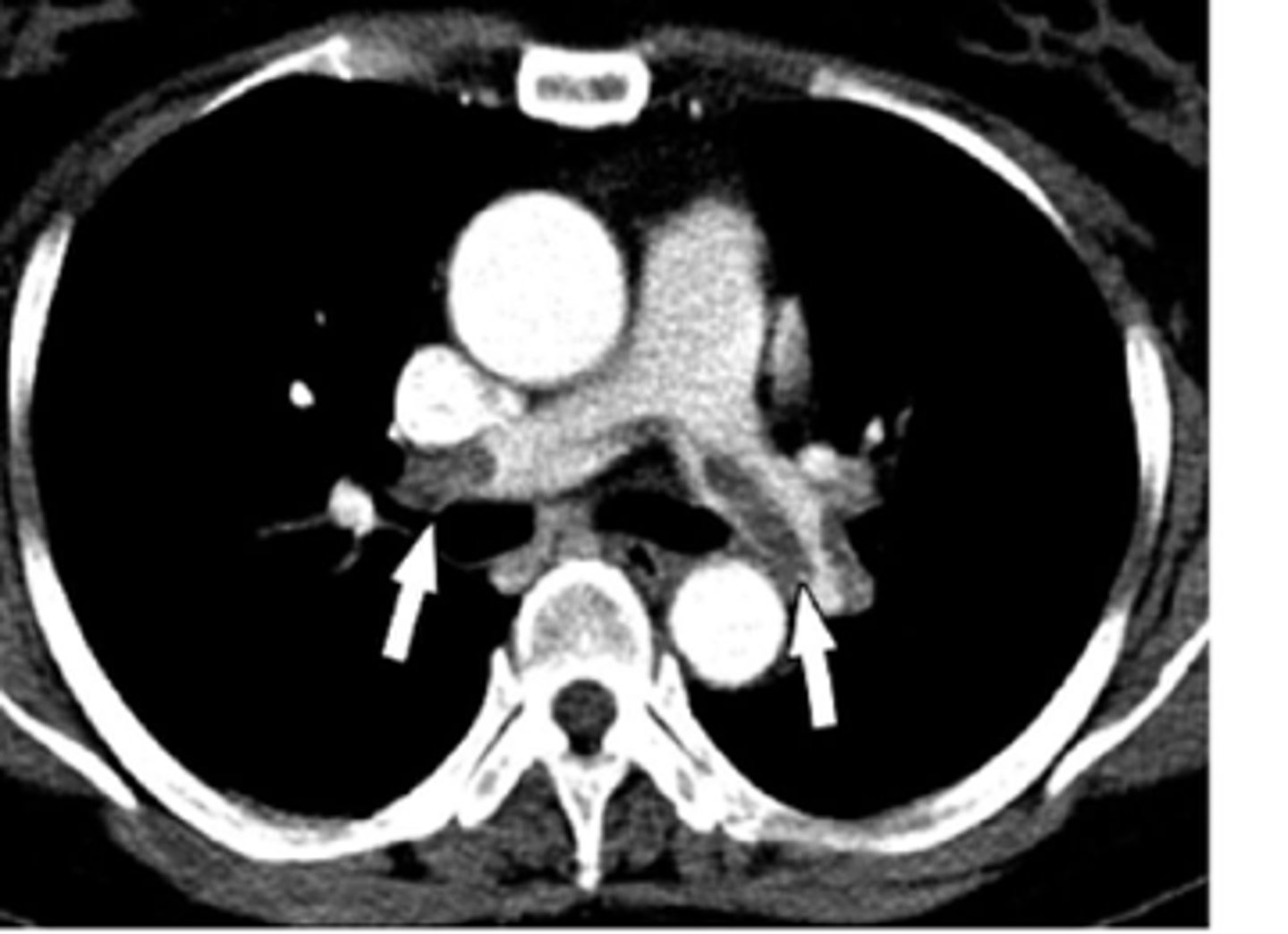
tension pneumothorax
identify the pathology:
pulmonary embolism
identify the pathology:
left
if a patient is shot and the bullet pierces the right lung, which direction will the heart be shifted?
right main bronchus
if a patient inhales a piece of amalgam, which main bronchi is it most likely to be stuck in?
trachialis m.
in the trachea, what muscle replaces the posterior portion of the cartilage?
T4/T5
at what level does the trachea divide into left and right main bronchi?
intermediate bronchi
moving distally, the main bronchi will transition into:
lobar bronchi
moving distally, the intermediate bronchi will transition into:
segmental bronchi
moving distally, the lobar bronchi will transition into:
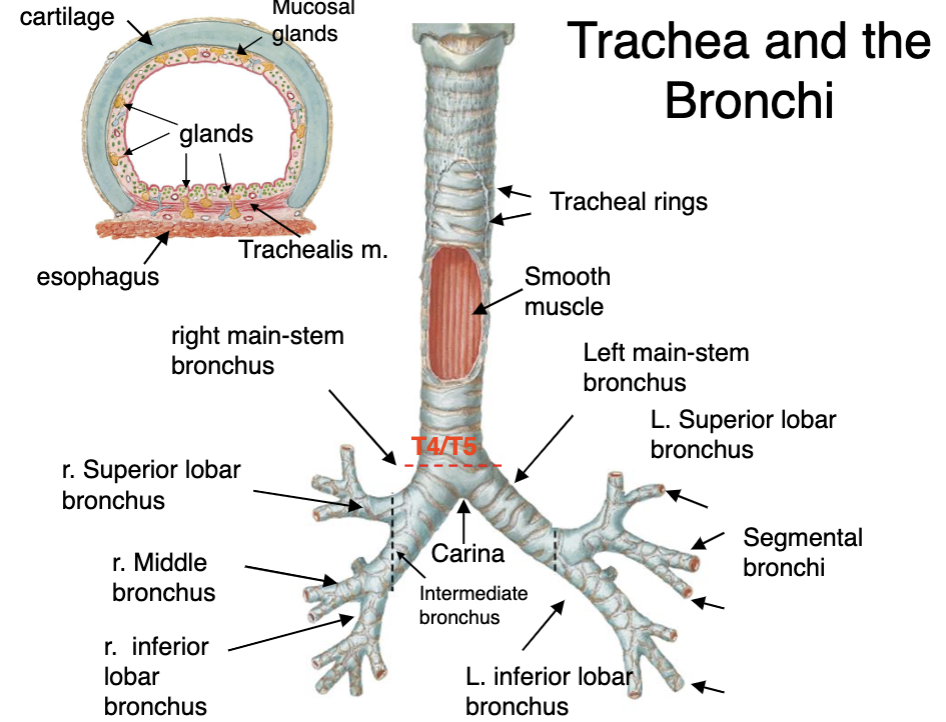
carina
ridge-like structure that divides lower part of trachea into right and left main-stem bronchi
pulmonary a.
which lung vessels carry deoxygenated blood to the lungs?
pulmonary v.
which lung vessels carry oxygenated blood from the lungs?
pulmonary a.
which lung vessels run within(inside) the lung segments?
pulmonary v.
which lung vessels run between(outside) the lung segments?
pulmonary embolism
Blockage of the pulmonary artery or one of its branches by a substance (e.g. blood clot) that has travelled from elsewhere in the body through the bloodstream
pulmonary a.
in a pulmonary embolism, what structure suffers the blockage?
autonomic nervous system
Smooth muscle, glands and blood vessels in the bronchi are innervated by the:
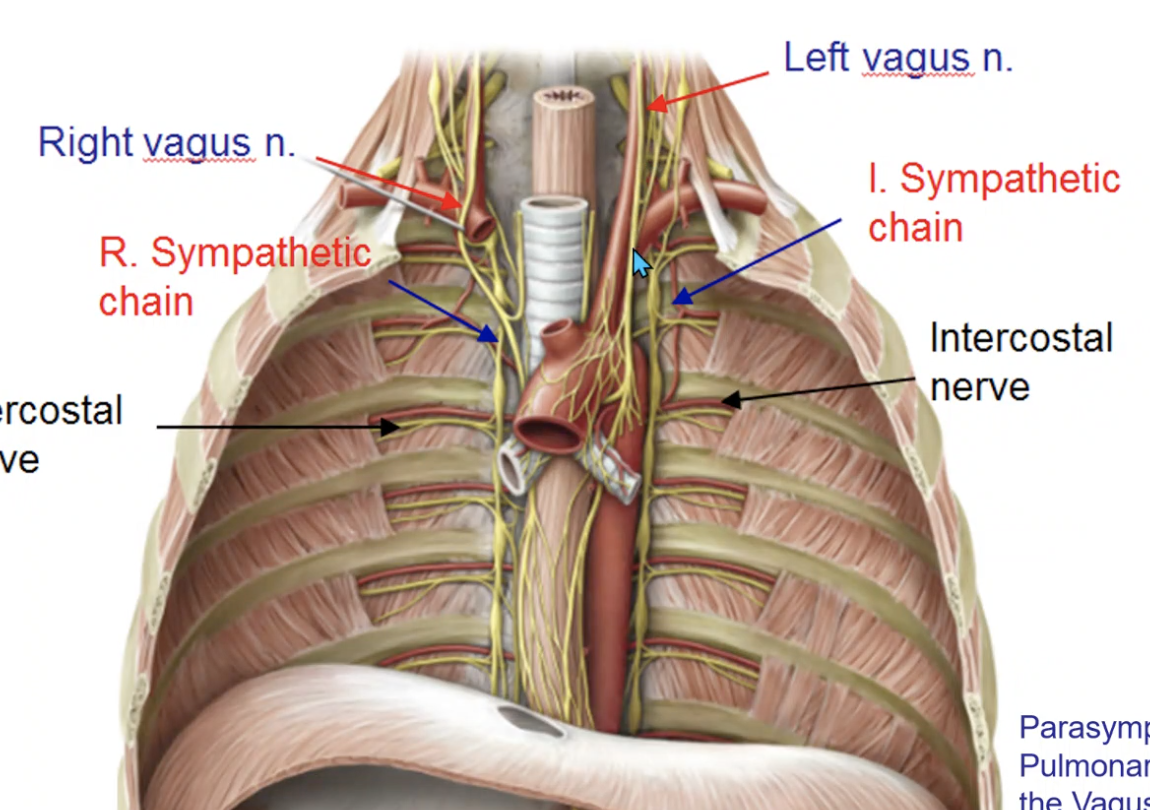
vagus n.
what nerve supplies parasympathetic innervation to the pulmonary plexus?
sympathetic trunk
what nerve supplies sympathetic innervation to the pulmonary plexus?
parasympathetic division (vagus CNX)
Constricts smooth muscle in bronchi:
parasympathetic division (vagus CNX)
Promotes secretion of mucous glands:
parasympathetic division (vagus CNX)
Relaxes blood vessels:
sympathetic division
Relax smooth muscle in bronchi:
sympathetic division
Inhibit secretion of mucous:
sympathetic division
Constrict blood vessels:
sympathomimetic
patients with asthma will use albuterol for ______ stimulation over the bronchi
pulmonary nodes
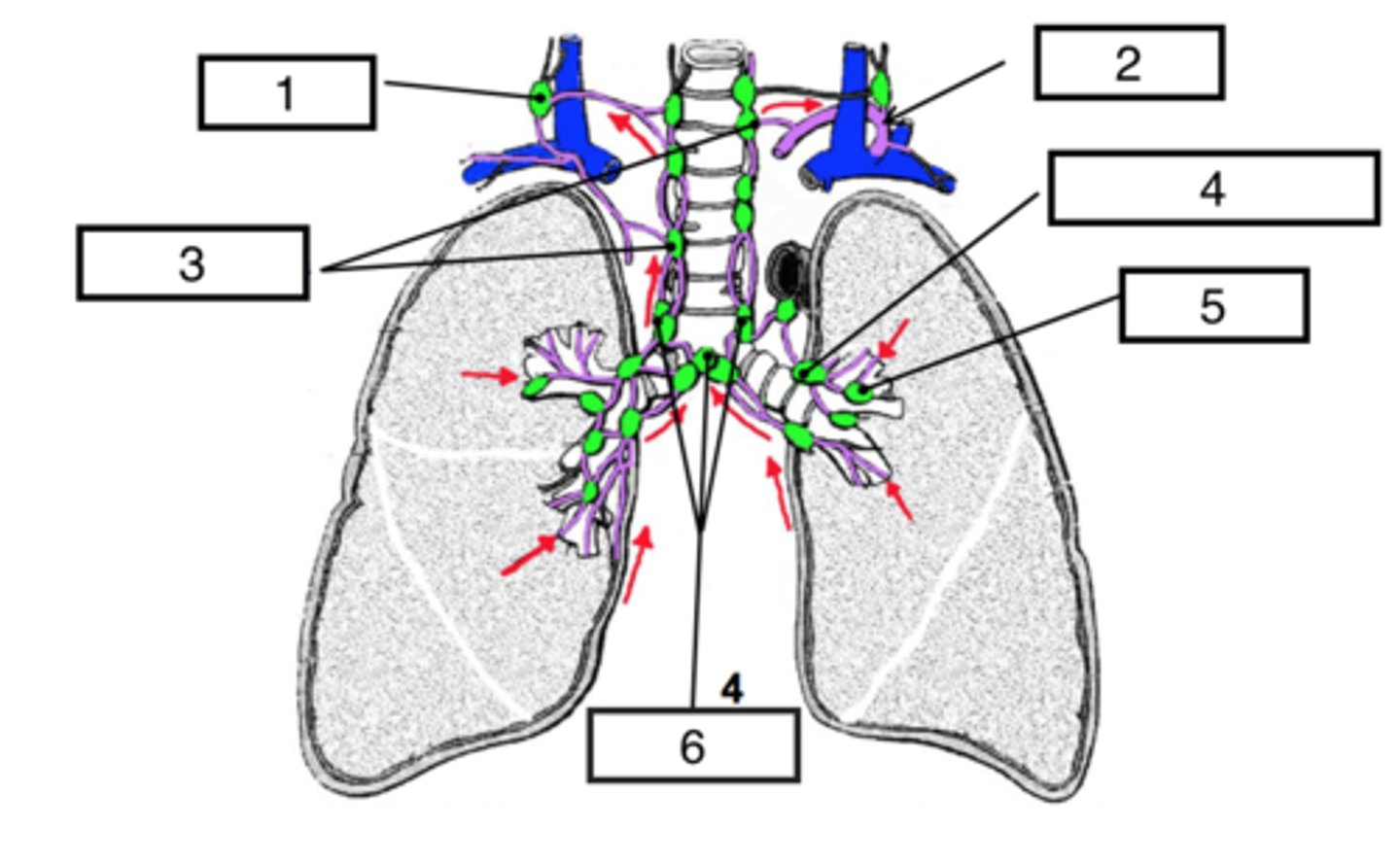
identify #5
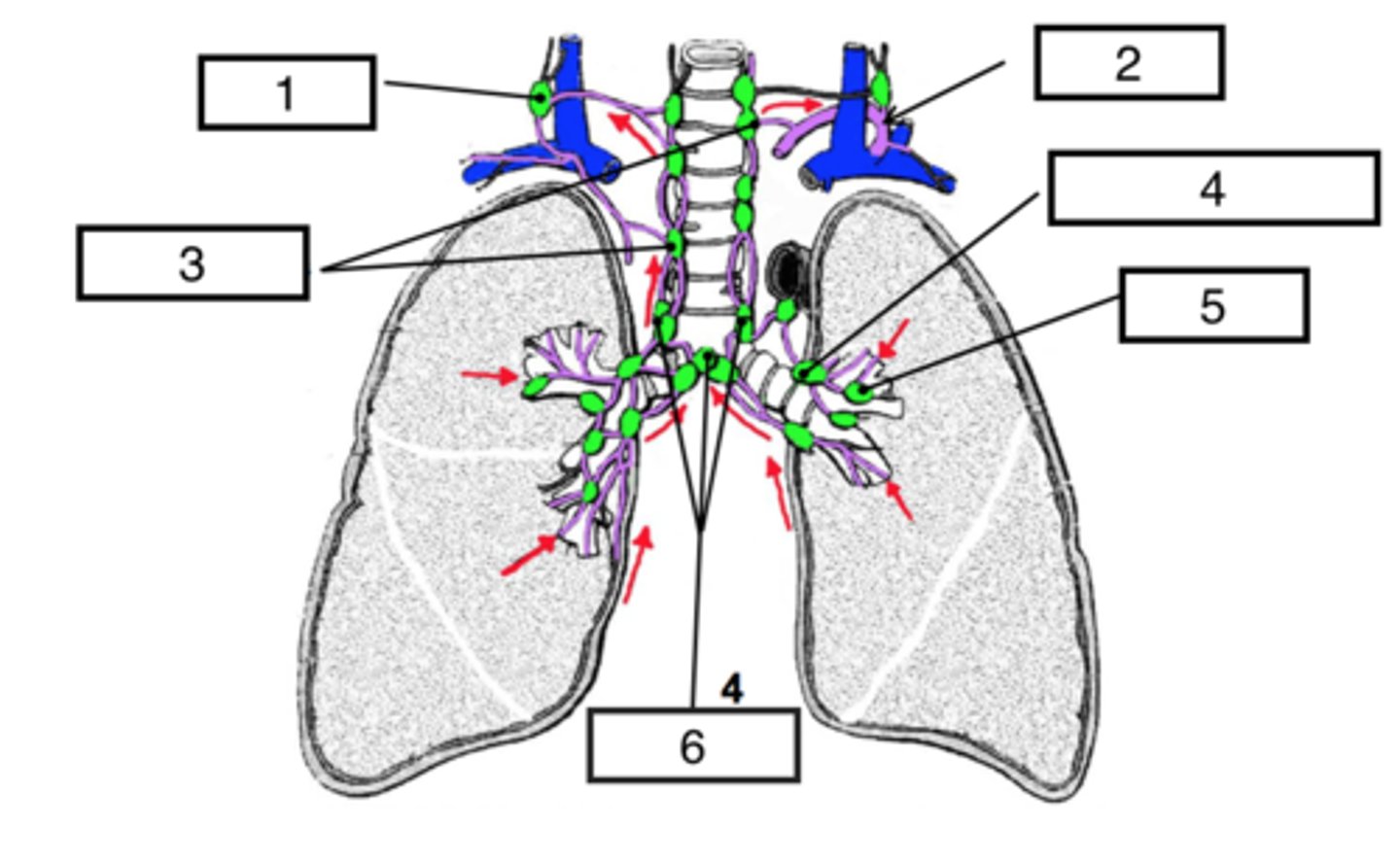
bronchomediastinal (hilar) nodes
identify #4
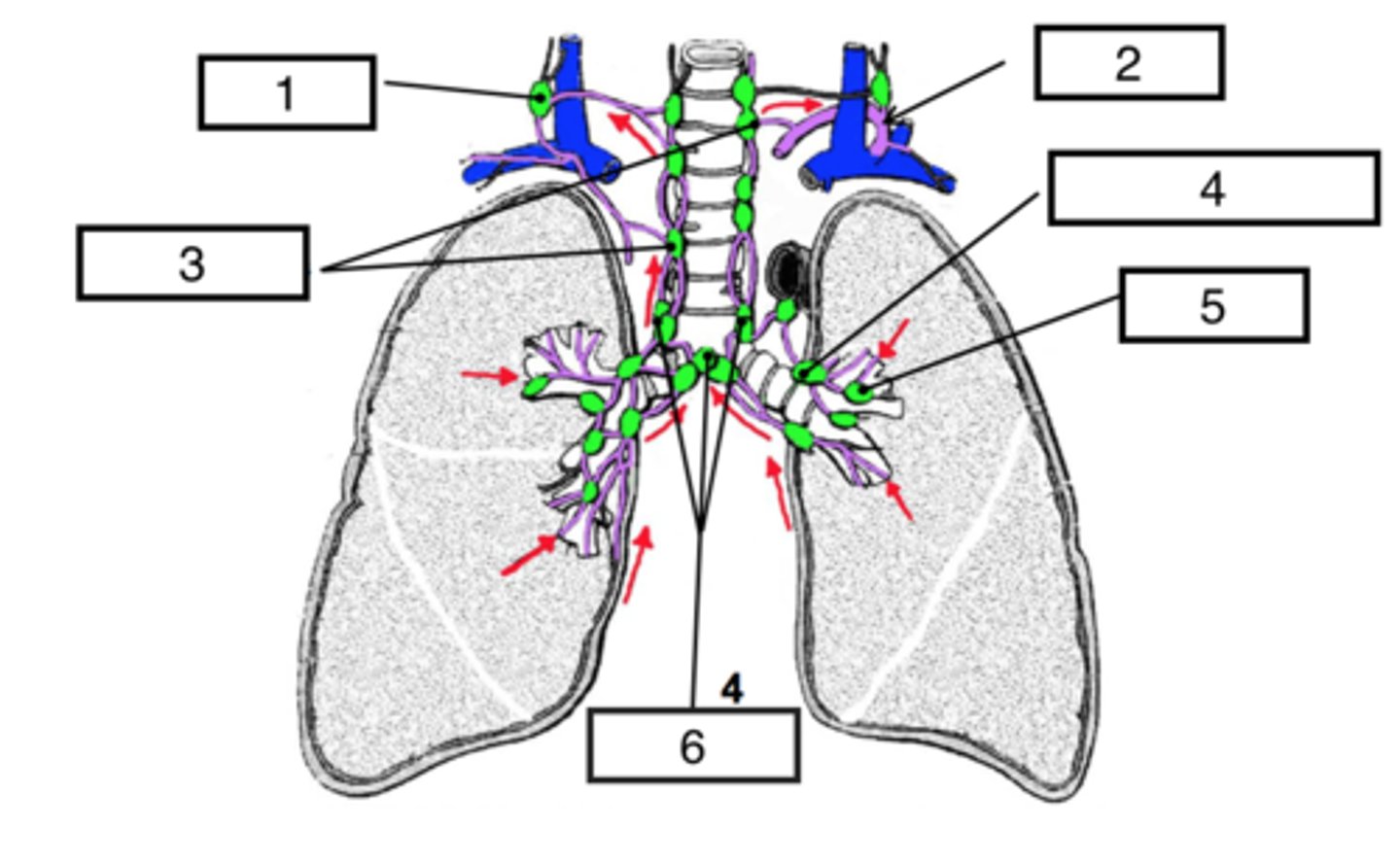
superior tracheobronchial nodes
identify #6
Paratracheal nodes
identify #3
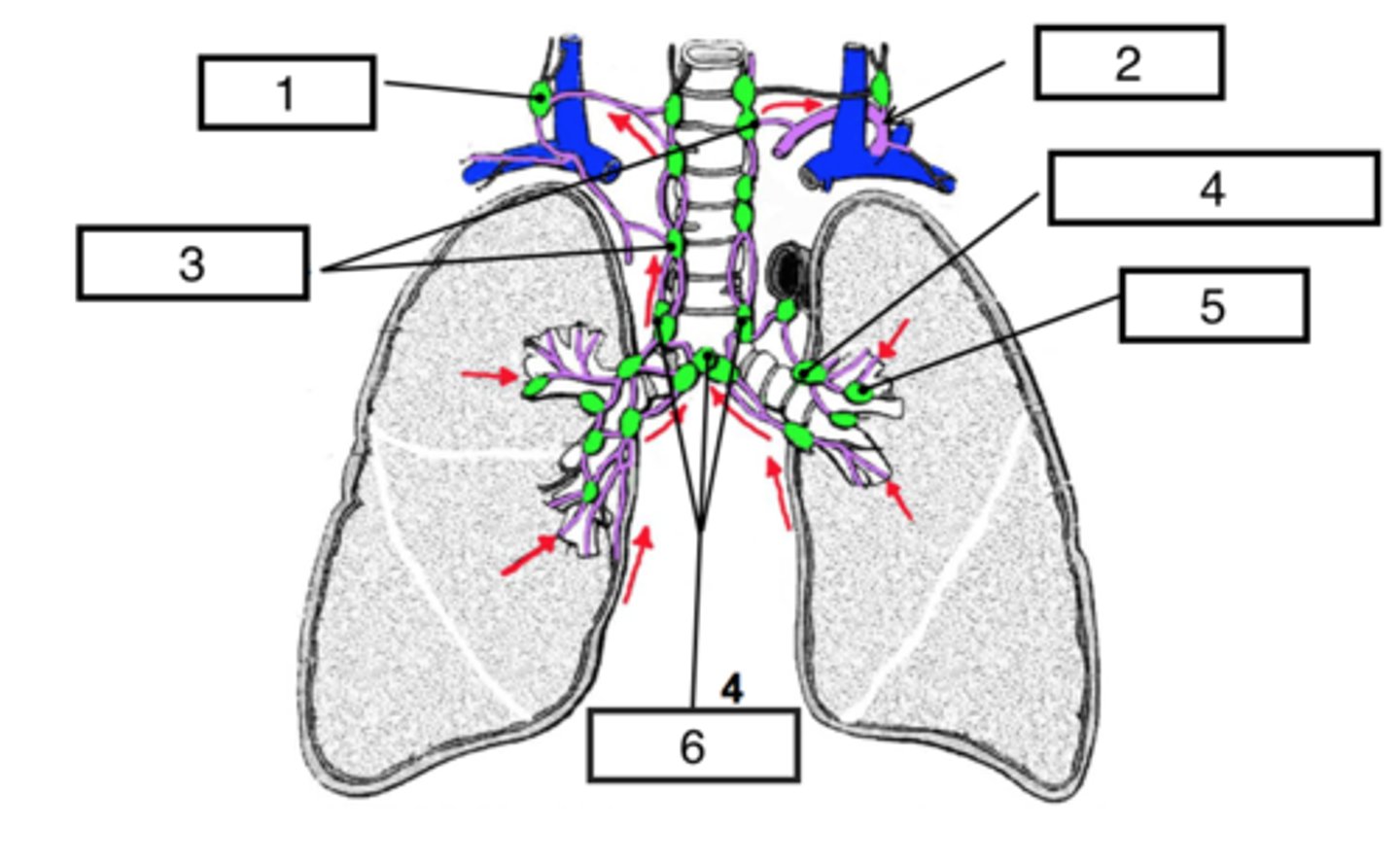
right lymphatic duct
lymph from the left lower lobe drains into which lymphatic collecting duct?
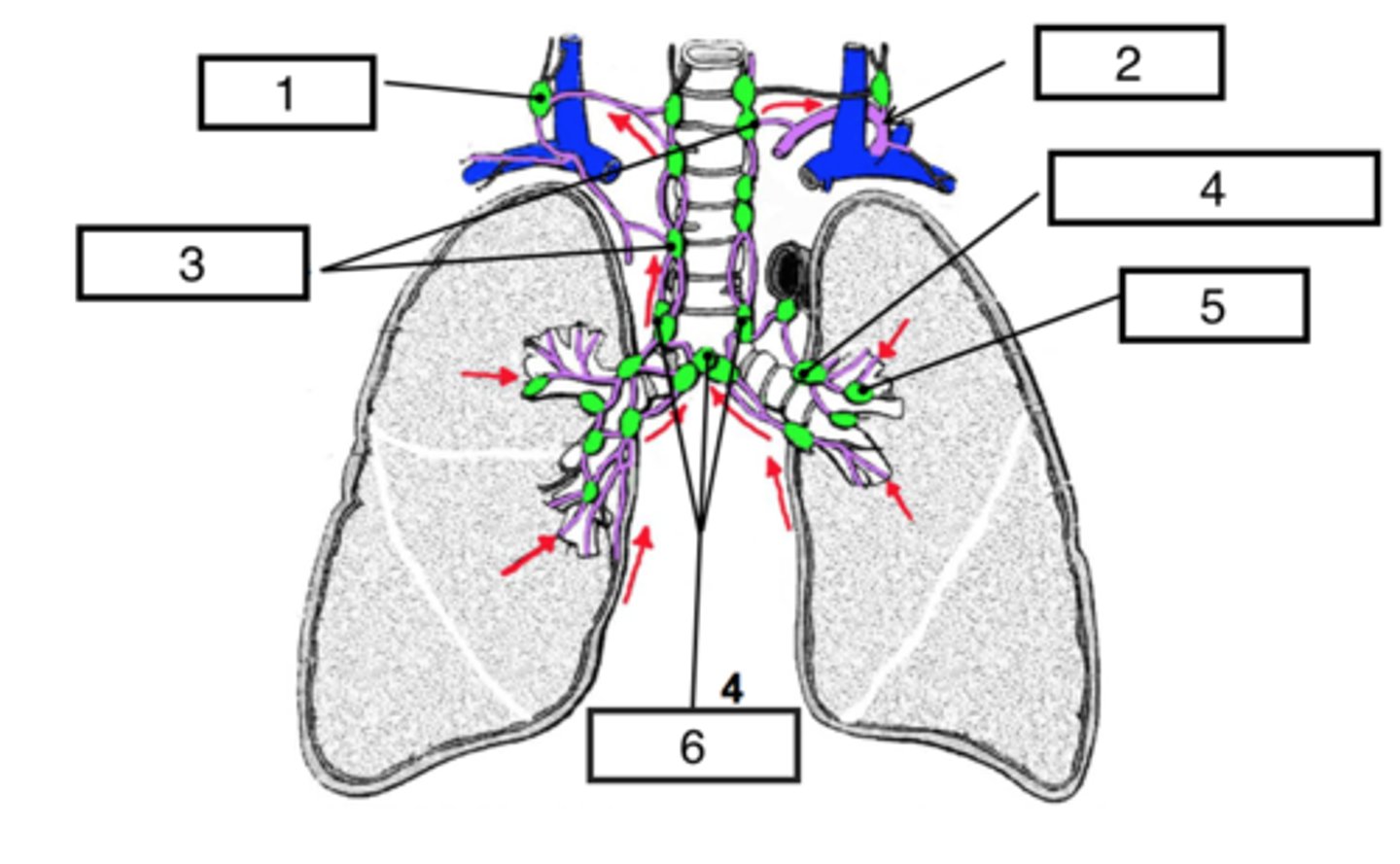
thoracic duct
lymph from the left upper lobe drains into which lymphatic collecting duct?
2 pulmonary cavities (lungs and pleurae)
mediastinum (central compartment including heart, great vessels, trachea, esophagus)
what are the 3 compartments of the thoracic cavity and lungs?
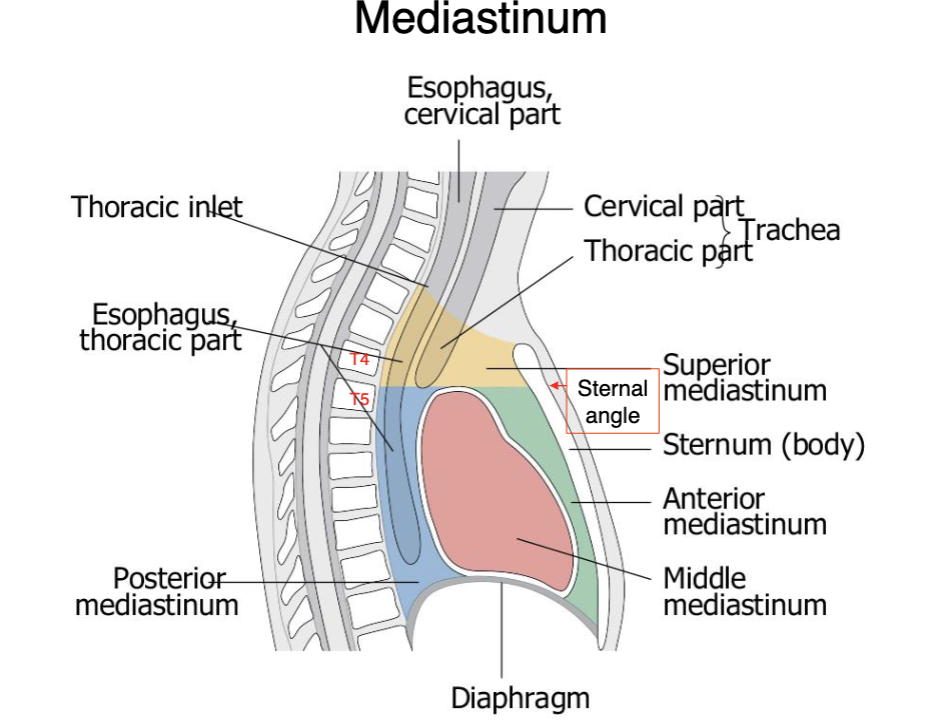
sternal angle (T4-T5 level)
the superior and anterior mediastinum is separated by what landmark?
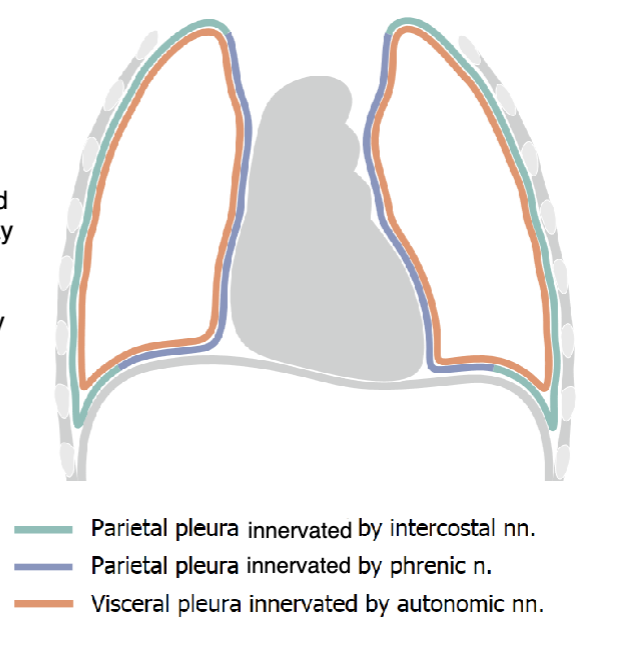
intercostal n. and phrenic n.
parietal pleura is innervated by
lubrication (allows movement within pleural cavity during respiration)
surface tension (keeps visceral and parietal pleurae in contact w thoracic wall and diaphragm)
pleurae (serous membranes) produce small amounts of pleural fluid which provides:
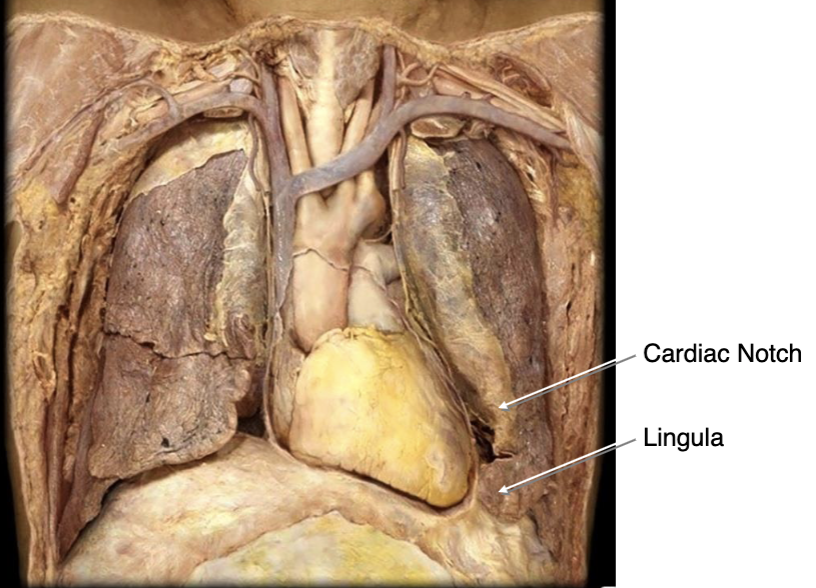
we can take sample from pericardial space or directly access heart through cardiac notch (without damaging lung or pleural space)
clinical significance of cardiac notch?
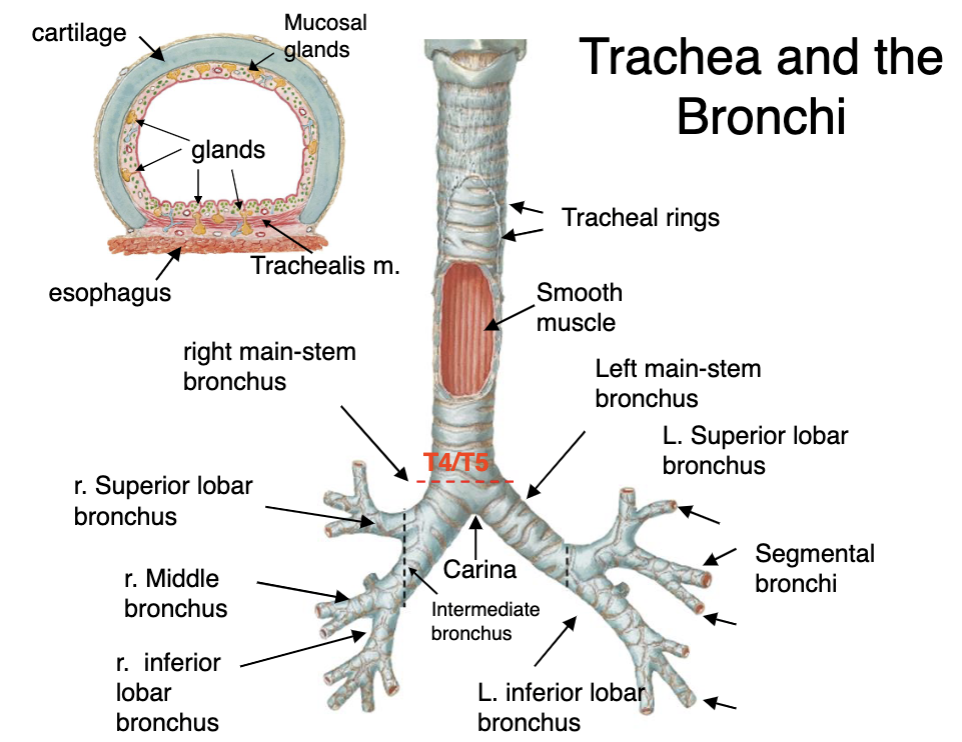
T4/5 (sternal angle)
bifurcation of the trachea into left and right bronchi occurs at which vertebrae/landmark?
right is thicker and more directly under trachea
why would foreign objects aspirated into the trachea usually enter the right main bronchus?
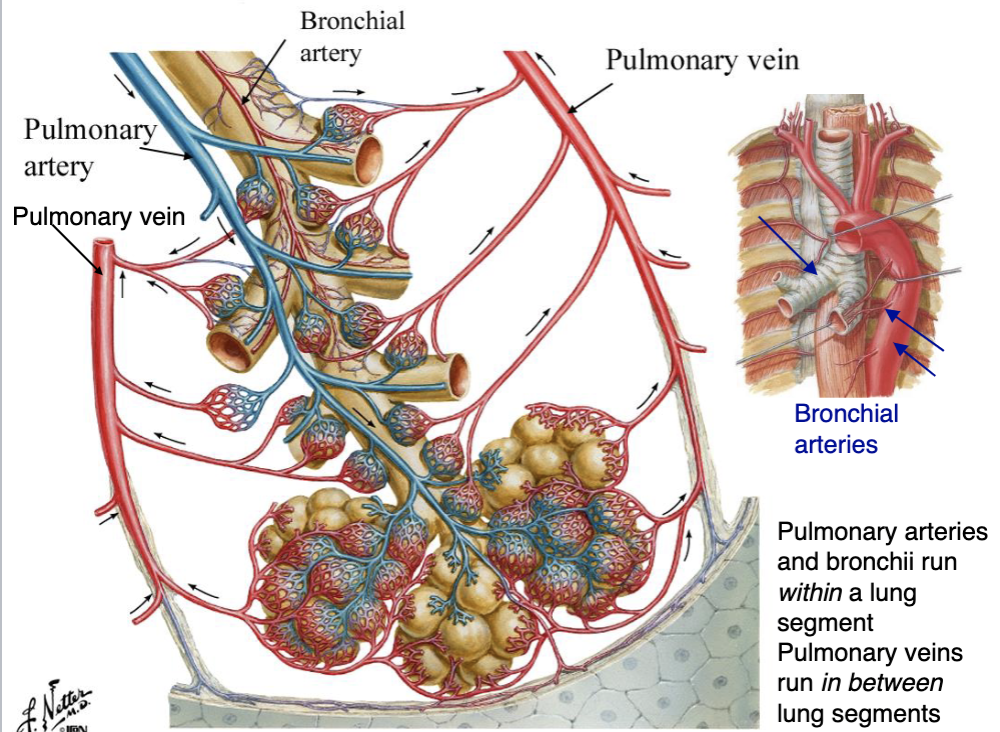
center; edges
pulmonary arteries (carrying unoxygenated blood) are always entering _____ of segment while pulmonary veins (carrying oxygenated blood) always collected at _____ of segment.
the interstitial structure of lung
bronchial artery do not participate in exchange. they are exclusively to supply
network of autonomic nerves that innervate smooth muscle, glands, blood vessels in bronchi
pulmonary plexus
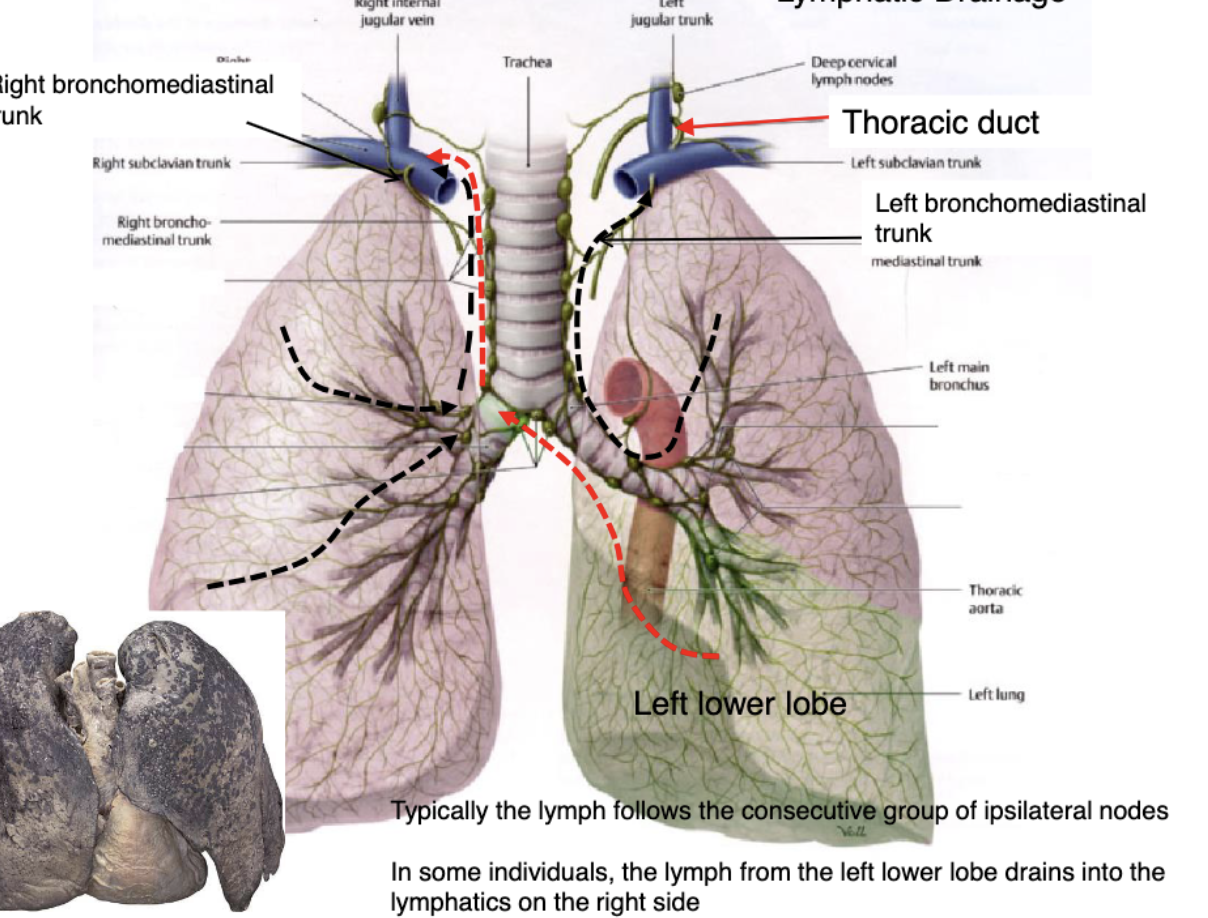
right side
in some individuals, the lymph from the left lower lobe drains into the lymphatics on the