FSM - ENGR110 flashcards
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What is a Finite State Machine (FSM) in simple terms?
A model for a program or system that can be in only one of a finite number of states at a time. It changes states based on inputs according to a set of rules called transitions.
What are the three core components of an FSM?
States: The possible situations (e.g., Open, Closed).
Inputs: The signals that trigger change (e.g., push, pull).
Transitions: The rules that define how inputs change the state.
What is the main purpose of an Acceptor FSM?
To decide whether to "accept" or "reject" an input string. If the FSM ends in a special accepting state (often marked with a double circle), the input is valid.
What is the main purpose of a Transducer FSM?
To generate an output based on the current state and the input. It's used for systems that need to do something, like a vending machine dispensing a drink.
What is the difference between a Moore Machine and a Mealy Machine?
Moore: Output depends only on the current state.
Mealy: Output depends on the current state AND the input.
What is a common, simple way to code an FSM in a language like C++ or Java?
Using a variable to track the current_state and a series of if-else or switch statements to check the state and input to decide the next state.
What is the "alphabet" (Σ) in an FSM?
The set of all possible, valid input symbols. For example, for a door, the alphabet could be Σ = {push, pull}.
What is one major limitation of a "pure" FSM (without enhancements)?
It has no memory or variables. All information must be stored in the states themselves, which can lead to a "state explosion" (needing thousands of states) for complex problems like counting.
What is an "Extended FSM"?
An FSM that is enhanced with variables. This allows the transitions to have guards (conditions), making the FSM much more powerful without needing an infinite number of states.
What is a "State Diagram"?
A visual way to represent an FSM, where circles are states and arrows between them are transitions, labeled with the input that causes that transition.
what are the benefits of using an FSM as a basis for writing code?
It provides a clear outline for the code's structure.
It helps create well-organized and less error-prone programs.
It forces you to think about the design before jumping into coding.
What is "FSM explosion"?
It's when a "pure" FSM (without variables) requires a huge number of states to represent a simple concept, making the design unmanageable. (Example: A microwave timer FSM needing a separate state for every possible second).
What is the core difference between an "acceptor" and a "transducer" FSM?
Acceptor: Decides if an input string is valid. It has accepting states and answers "yes" or "no".
Transducer: Converts an input sequence into an output sequence. Its purpose is to generate output, not just accept/reject.
How do you represent an "accepting state" in a state diagram?
With a double circle.
What does it mean for a transducer FSM to "squeeze" substrings? (e.g., 000100110 -> 01010)
It means it outputs a symbol only when the input changes from one type to the other. It ignores consecutive repeated symbols.
How do you read an FSM state transition table/matrix?
The rows are the Inputs. The columns are the Current States. The cell where a row and column meet tells you the Next State.
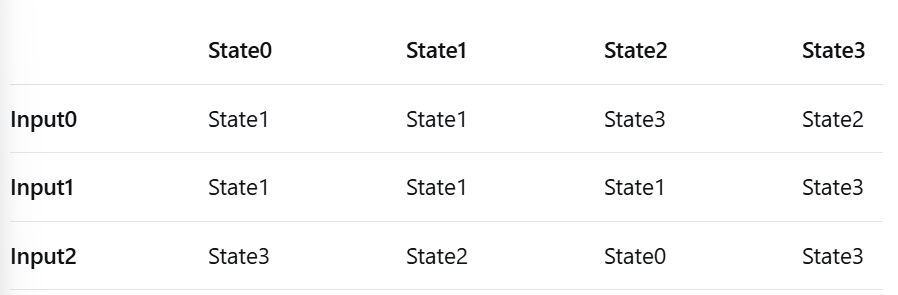
Given this transition table and starting state State0, what is the state sequence for inputs Input0?
State0 + Input0 -> State1
State1 + Input2 -> State2
State2 + Input0 -> State3
State3 + Input0 -> State2
State2 + Input1 -> State1
Sequence: State0 -> State1 -> State2 -> State3 -> State2 -> State1
What is Q?
Q is the set of all states
What is Σ (sigma)?
Sigma is the inputs
What is q0?
q0 is the starting state (initial state)
What is F?
F is the set of final states (it is a set because there can be more than one final state)
What is ∂?
It is a transition function that maps Q x Σ —> Q