stereochem & bromination
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
what happens to esters in a cis orientation?
the esters are close to one another in space, electrons that make up the lone pairs and bonds in the esters repel one another
two broad classifications of stereoisomers that are of importance in organic chemistry
conformational and configurational
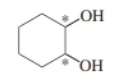
1,2-cyclohexanediol
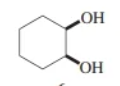
cis-1,2-cyclohexanediol
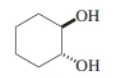
trans-1,2-cyclohexanediol
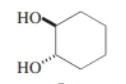
trans-1,2-cyclohexanediol
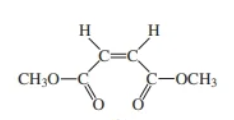
dimethyl maleate
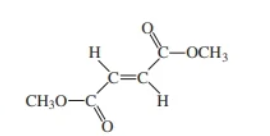
dimethyl fumarate
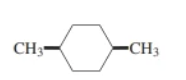
cis-1,4-dimethylcyclohexane
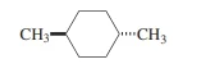
trans-1,4-dimethylcyclohexane
example of geometric isomers
dimethyl maleate & dimethyl fumarate
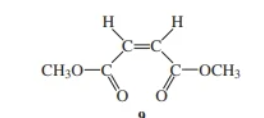
dimethyl maleate
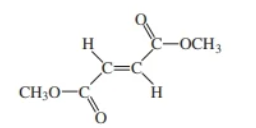
dimethyl fumarte
what to clean bromine with
sodium thiosulfate
do not wash glassware that contained bromine with_
acetone
bromine carciogenicity
not a know carcinogen
bromine mutagenicity
not a known mutagen
dochloromethane carciogenicity
known carcinogen
dochloromethane mutagenicity
possible mutagen
d,l-stilbene dibromide carciogenicity
not a known carcinogen
(E)-stilebene carciogenicity
not a known carcinogen
(E)-stilebene mutagenicity
possible mutagen
meso-Stilbene dibromide carcinogenicity
not a known carcinogen
cyclohexene mutagenicity
not a known mutagen
cyclohexene carcinogenicity
not a known carcinogen
dimethyl fumarate carcinogenicity
not a known carcinogen
dimethyl fumarate mutagenicity
not a known mutagen
dimethyl maleate carcinogenicity
not a known carcinogen
dimethyl maleate mutagenicity
not a known mutagen
ethanol carcinogenicity
not a known carcinogen
ethanol mutagenicity
possible mutagen
what are the two extremes for an even distribution
1:1:1, 1:0:0
the results will be mostly ___
meso
what can explain why it is mostly meso
there is a mixture of cations in solution and if the cyclic cation is favored this can explain why we are getting mostly meso
enantiomers
non-superimposable, mirror images, almost identical
diasteriomers
not superimposible, non-mirror image, different properties
energy for single c-c bond
83
energy for a double c-c bond
146
what energy do we need?
either the full single bond or the difference between the two (70-80)
what is the source of energy in the lab?
lab
energy needed to break c-c in this lab
right at the end of the visible spectrum and lightly moving into UV spectrum
energy much to break br-br
46
light for br is __ nm; which is __ on the visible spectrum
600; in the middle
what can we assume about the breaking of bonds in this lab?
because light has a role we can guess homolytic cleavage
major assumption with radicals
unstable/reactive due to unpaired electrons
how do we minimize pressure?
lightly resting stopper in round-bottom flask and balanced in the Keck Clamp
color change throughout lab
orange color disappears and solution becomes colorless
bromination of alkene is a ___ rxn
oxidation
Markovnikov’s Rule
hydrogen atom in an electrophilic addition reaction to an alkene adds to the cation of the double bond that already has more hydrogen atoms, resulting in the halide attaching to the more substituted carbon
cyclic cation results in__
100% meso
intermediate cation results in ___
50/50 L/D and meso
when to stop bromination rxn
after 10-15 min or until most of the orange color disappears and a white solid has formed
how much cyclohexane to add
one drop
eutectic point
substance A and B melt at constant ration
cis-trans isomers are ___ isomers
geometric
stereocenter of l isomer
1R,2R
stereocenter of d isomer
1S, 2S
racemate quality
will not rotate plane polarized light
meso compound characteristics
optically inactive and achiral. they have two or more stereocenters and a superimposable mirror image
dimethyl fumarate is a _ at room temp
solid
dimethyl maleate is a _ at room temp
liquid
cyclohexan and br rxn
cyclohexane reacts with Br to create a dibromide which serves to destory residual bromide
alkenes
organic compounds with a polarizable c-c double bond
most common way to produce c-c doubl ebond
elimination rxn
functional group of alkyl halide
carbon halogen single bond
dehydrohalogenation
carbon-hydrogen bond converted to carbon-carbon pi bond
dehydration
double bond formed by removing elements of water from alcohol
adding a reagent across a double bond is __
exothermic
most common mode of addition reaction
ionic stepwise mechanism where E+ first attacks the pi-bond and the nucleophile attacks the carbocation aka electrophilic addition
concerted mechanism
each new sigma bond is formed simultaneously on the same face of the pi bond
bromine fire hazard
negligible
bromine inhalation
irritation, mucous secretion, coughing, nosebleed, headache, delayed nausea, diarrhea & abdominal pains, pulmonary edema, pneumonia
bromine skin contact
cooling/burning sensation, redness, pain, discoloration, blisters, pustules, burns, ulcers
bromine eye contact
redness, pain, blurred vision, loss of vision, lacrimation, photophobia
bromine ingestion
burns of mouth, throat, stomach, brown discoloration/corrosion of tongue and mucous membrane, sore throat and vomiting
cyclohexane fire hazard
severe fire hazard
cyclohexane inhalation
irritation, cns depression, headache, dizziness, drowsiness, labored breathing, kidney/liver damage
cyclohexane skin contct
defatting, redness, burning
cyclohexane eye contact
redness and irritation
cyclohexane ingestion
nausea, labored breathing, cns involvement, aspiration, pneumonia
dichloromethane fire hazard
slight fire hazard
dichloromethane inhalation
irritation, lightheadedness, dizziness, tingling, numb extremes, heat, full head, confusion, nausea, headache, fatigue
dichloromethane skin
irritation, possible burns, skin absorption may cause inhalation-like effects
dichloromethane eye contact
pain and extreme irritation
dichloromethane ingestion
rapid then slowed respiration, GI ulceration and hemorrhage, unconsciousness, cns depression, liver/kidney damage
dimethyl fumarate fire hazard
slight fire hazard
dimethyl fumarate inhalation
irritation, coughing, dryness
dimethyl fumarate skin contact
irritation and redness
dimethyl fumarate eye contact
irritation
dimethyl fumarate ingestion
relatively non-toxic, large amounts may cause sore throat, vomiting, abdominal pain
dimethyl maleate fire hazard
moderate fire hazard
dimethyl maleate inhalation
irritation, coughing, dyspnea
dimethyl maleate skin contact
irritation, redness, pain
dimethyl maleate eye contact
irritation, redness, pain, corneal erosion
dimethyl maleate ingestion
sore throat, abdominal pain, vomting
ethanol fire hazard
severe fire hazard
ethanol inhalation
irritation, cns depression with headache, stupor, fatigue, dizziness, drowsiness, dullness, lassitude, loss of appetite
ethanol skin contact
redness, burning, contact dermatitis, possible skiin absorption
ethanol eye contact
immediate burning, stinging, reflex closure of lids, tearing, and temporary injury of corneal epithelium
ethanol ingestion
emotional lability, decreased inhibitions, exhiliration, boastfulness, beligerance, visual impairment, muscular incoordination, sensory disturbances, dilated pupuls, rapid pulse, nausea, vomiting, sweating, drowsiness, stupor