A&P of the Eye Wishlist
1/32
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
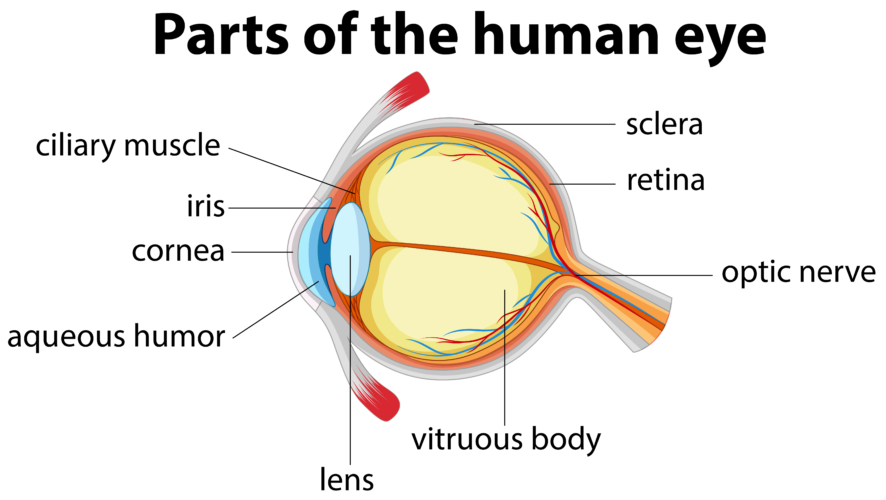
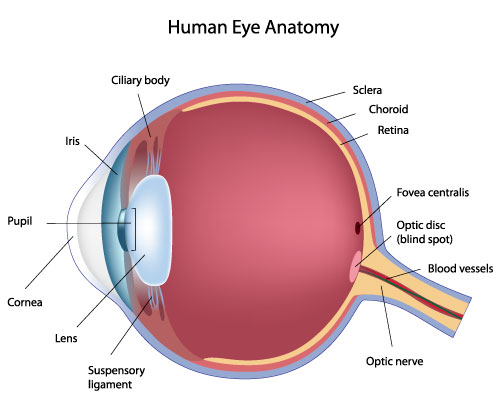
Palpebrae
eyelid; layers structure containing skin, orbicularis oculi muscle, tarsal plates, a vascular layer, eyelashes, meibomian glands and the conjunctiva.
lacrimal gland
tear-shaped gland located above each eye that produces the aqueous portion of the tear film.
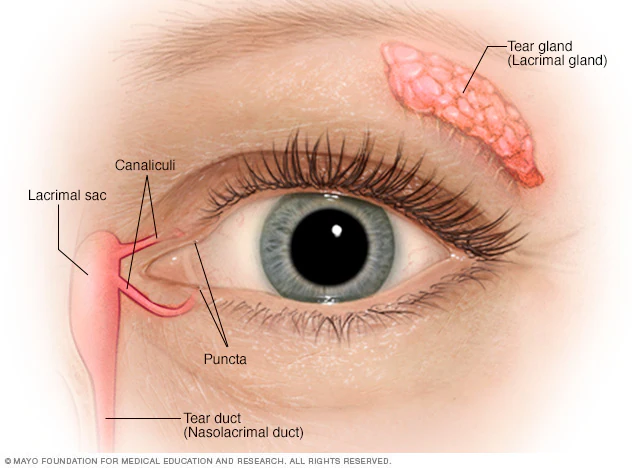
lacrimal gland duct
a system of tubes that transport tears from the lacrimal gland to the eye surface
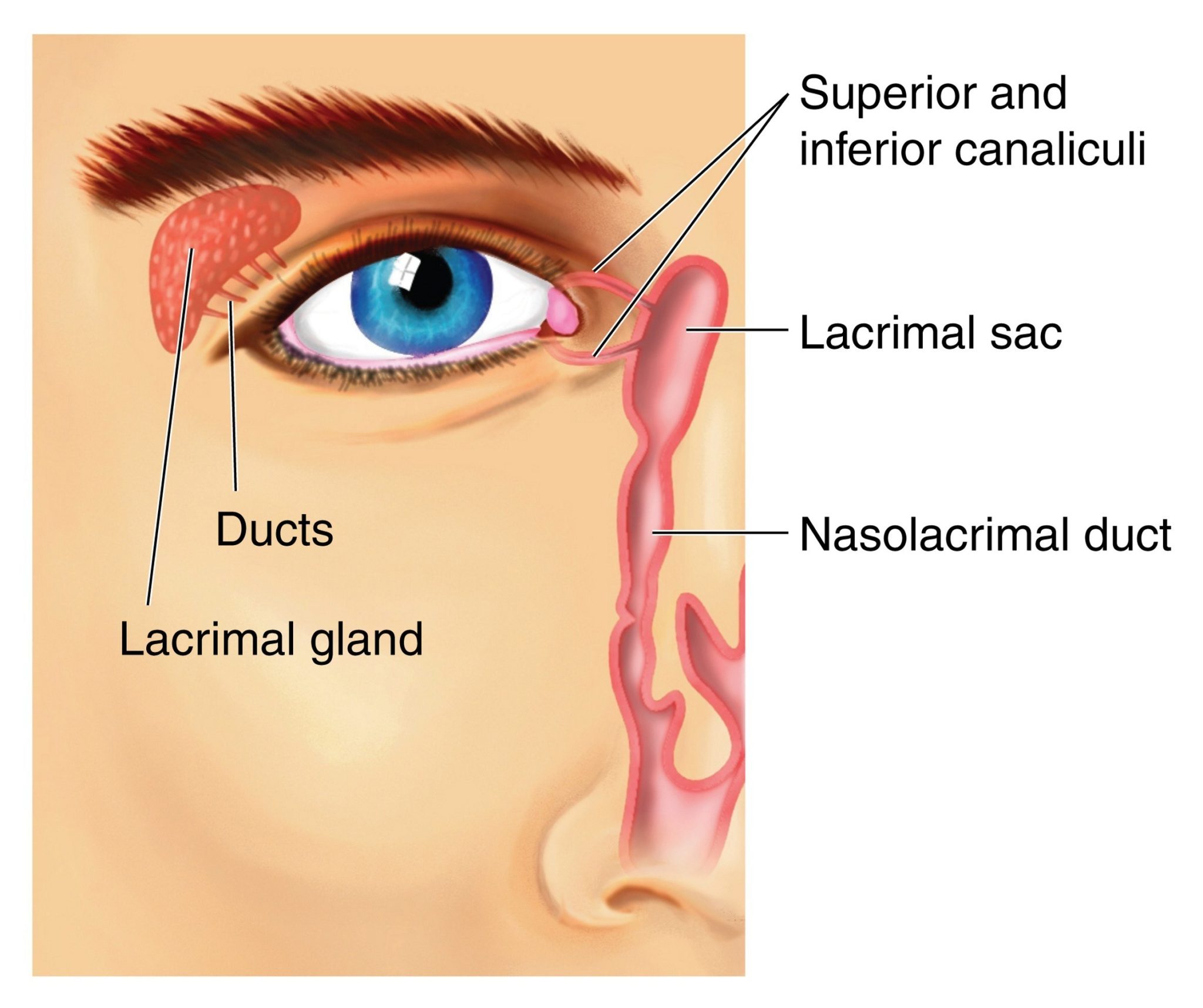
lacrimal sac
a small, dilated structure in the inside corner of the eyes tear duct system that collects tears after they have drained from the eye’s surface through the puncta and canaliculi.
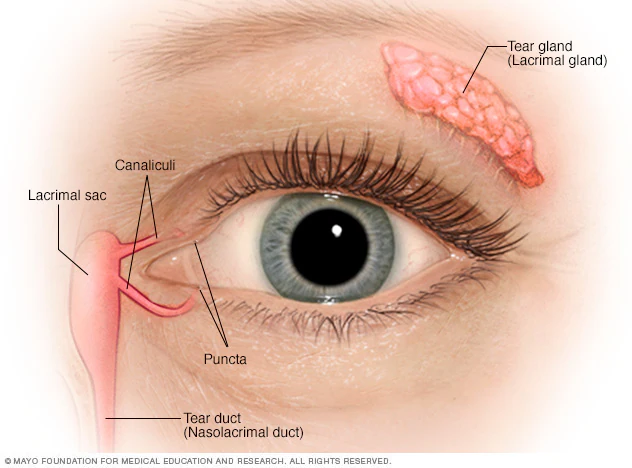
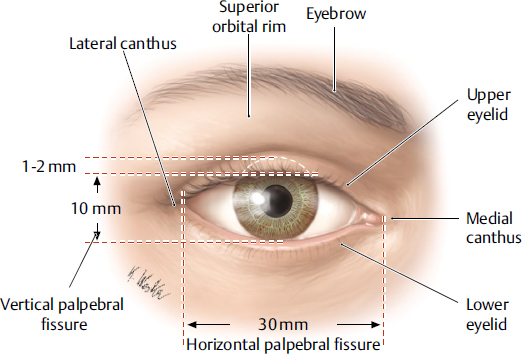
medial canthus
the medial corner of the eye where the upper and lower eyelids meet; collects tears and form the entry point into the lacrimal drainage system.
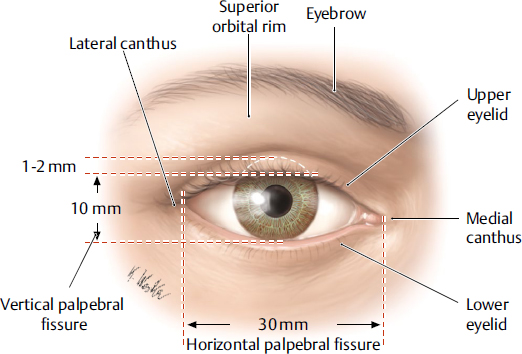
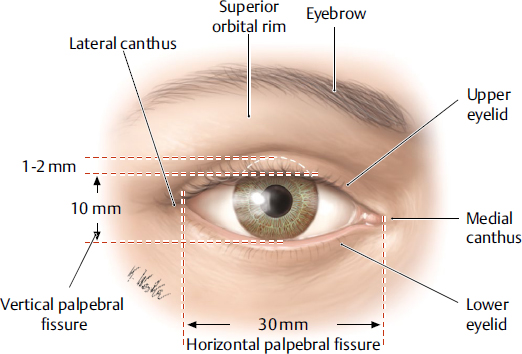
lateral canthus
the lateral corner of the eye where the upper and lower eyelids meet; provides structural support for the lower eyelid, preventing its displacement and contributing to the overall contour and health of the eye.
fibrous tunic
the eye’s tough, outermost layer; composed of the cornea and the sclera.
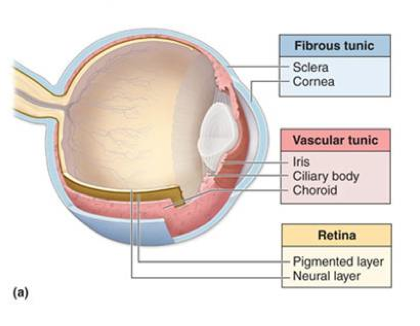
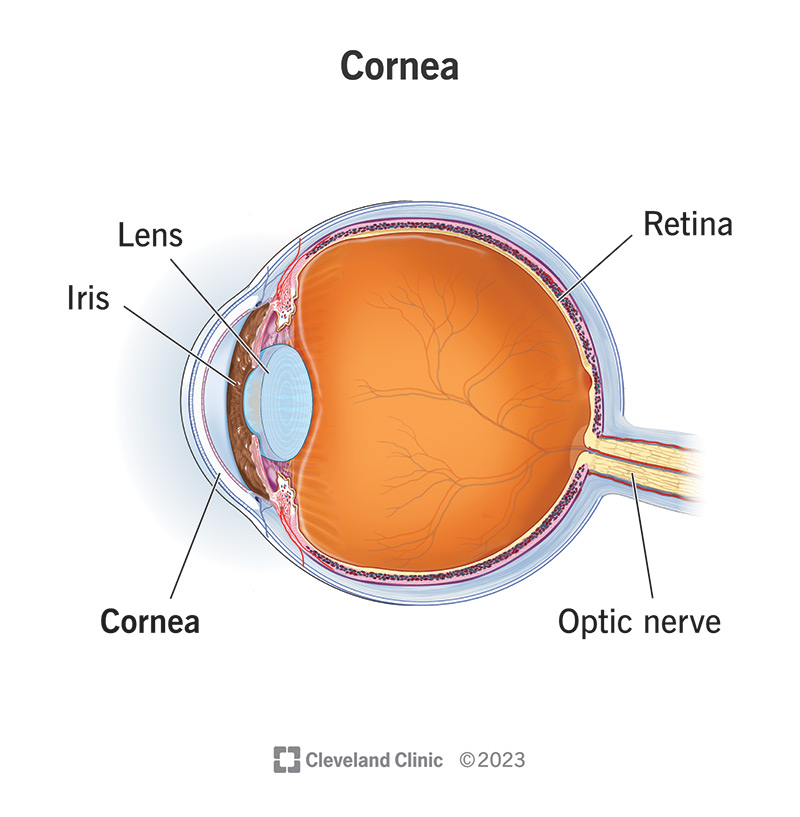
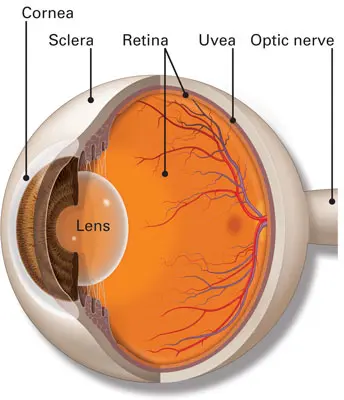
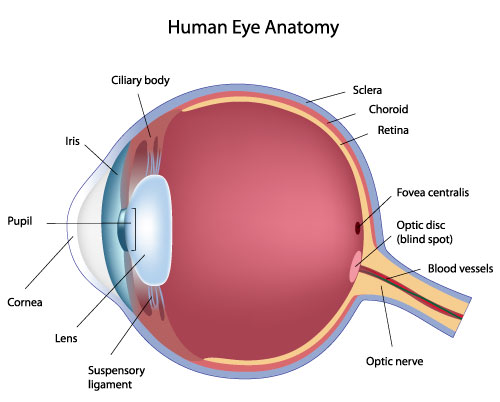
cornea
transparent, dome-shaped front layer of the eye that protects and focuses light into the retina; parting of the fibrous tunic
sclera
the white outer layer of the eyeball; at the front of the eye it is continuous with the cornea; part of the fibrous tunic
vascular tunic
the middle layer of the eye; composed of the choroid, the ciliary body and the iris; plays a crucial role in providing blood supply to the eye, supporting the retina, and regulating light entry.
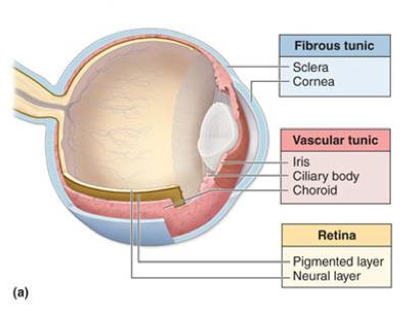
choroid
the pigmented vascular layer of the eyeball between the retina and sclera; part of the vascular tunic
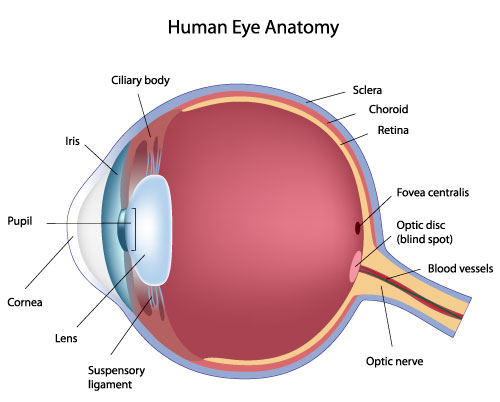
ciliary body
a ring- shaped structure located in the eye, behind the iris; maintains the shape of the lens and producing aqueous humor; part of the vascular tunic
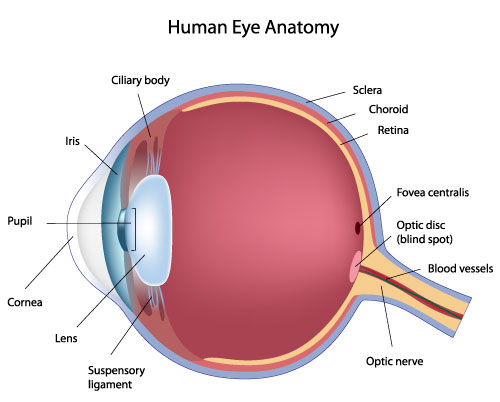
suspensory ligament
zone of zinc; a ring of fibrous strands connecting the ciliary body to the eyes crystalline lens, holding it in place and adjusting its shape for focusing; can also be Lockwood’s ligament — hammock-like structure of tenon’s capsule that supports the eyeball in the orbit and prevents it from sagging.
lens
a transparent, curved structure located posterior to the pupil that focuses light onto the retina to create a clear image.
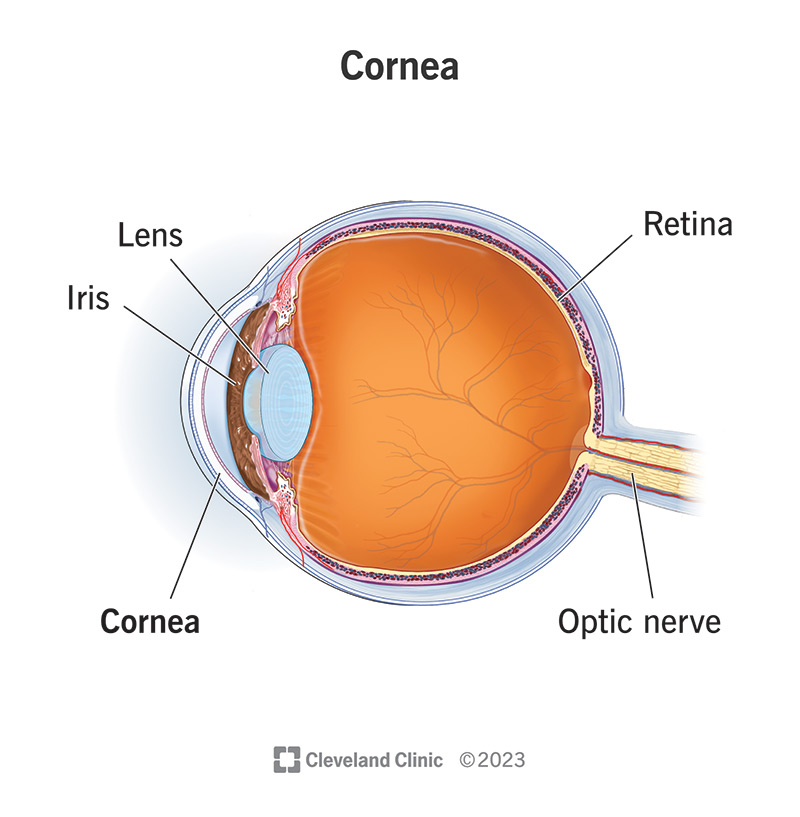
iris
the colored, muscular part of the eye that controls the side of the pupil, regulating the amount of light entering the eye to allow for clear vision in various light conditions; between the cornea and the lens
aqueous humor
a clear, watery fluid that fills the front part of the eye; provides nutrients to avascular structures like the lens and cornea, maintains the eye’s shape and regulates intraocular pressure.
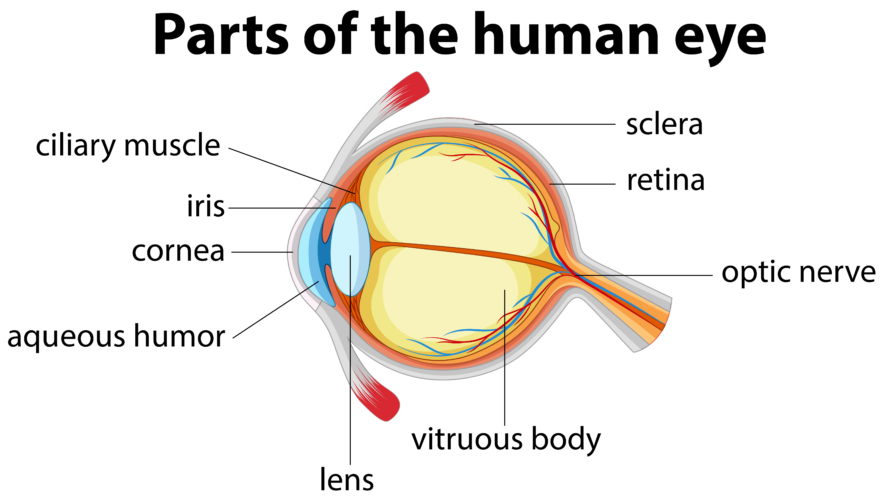
vitreous humor
a clear, gel-like substance that fills the center of the eyeball; fills the space between the lens and the retina.
pupil
the black, circular opening in the center of the iris; regulates the amount of light entering the eye.
neural tunic
the innermost layer of the eye; known as the retina; contains several layers.
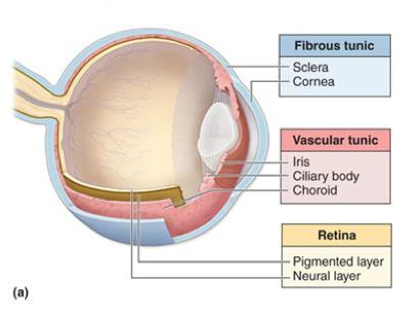
pigmented layer
a layer in the retina; between the choroid and the photoreceptor layer that contains rods and cones.
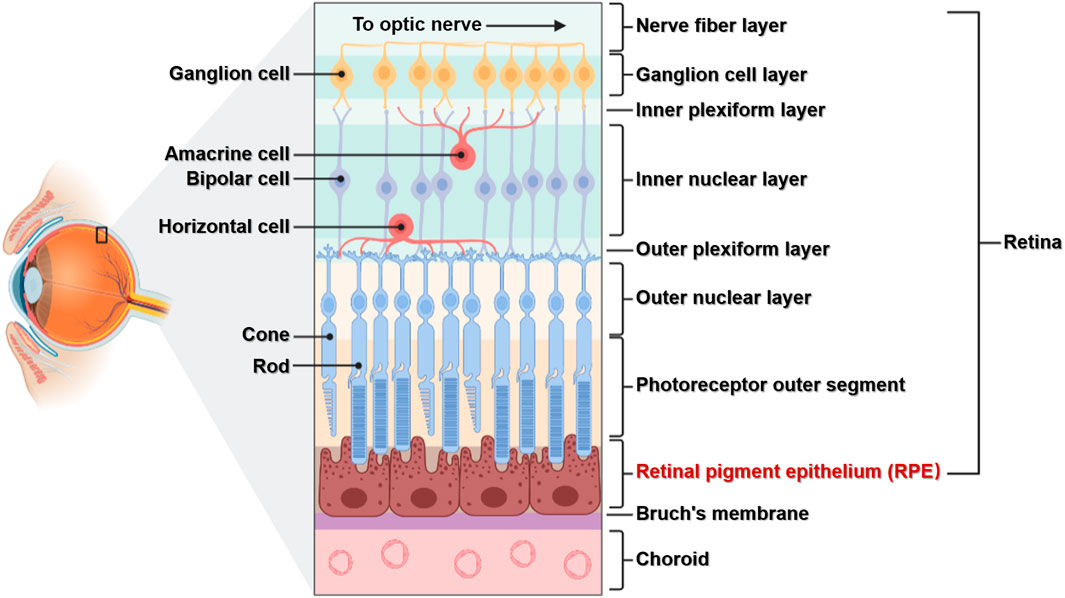
photoreceptor layer
a layer in the retina; contains rods and cones which are responsible for processing light; between the pigmented layer and the bipolar/cell layer
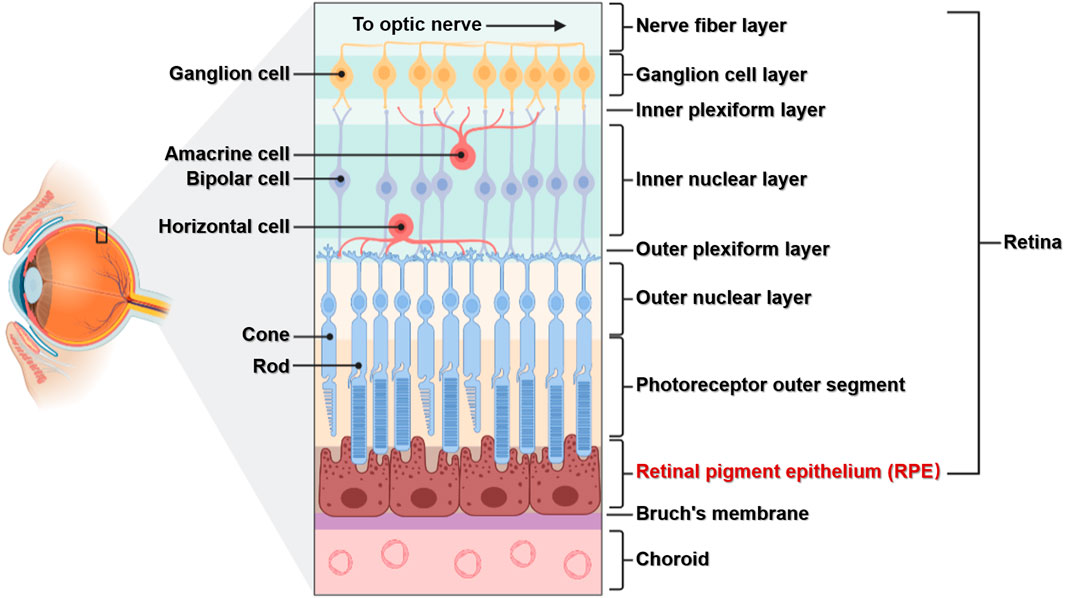
rods
part of the photoreceptor layer in the retina; processes black/white in vision; looks like tunnels
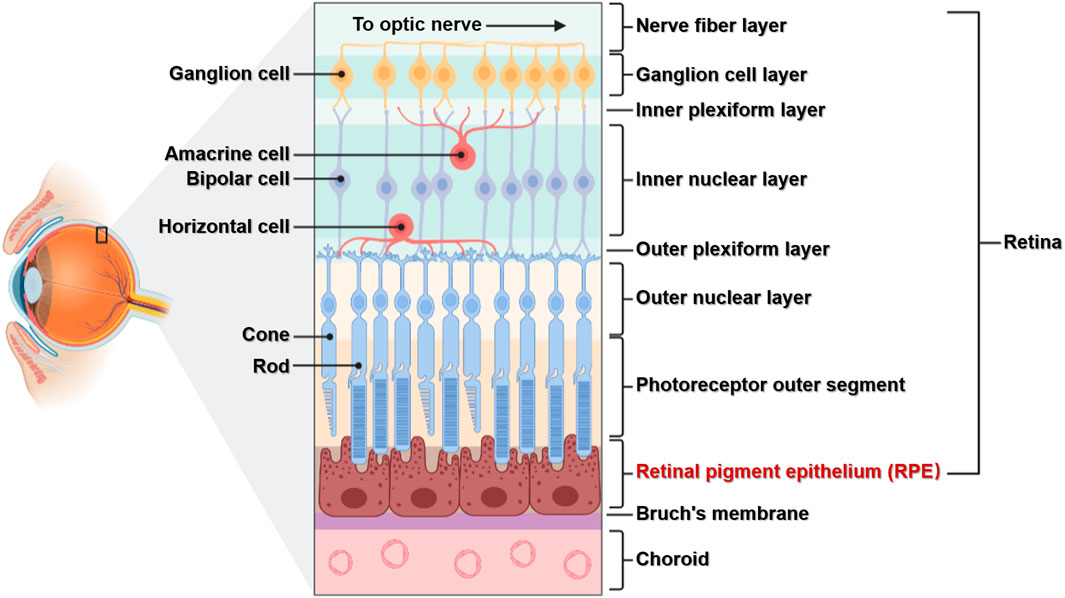
cones
part of the photoreceptor layer in the retina; processes color in vision; looks like serrations in a butter knife.
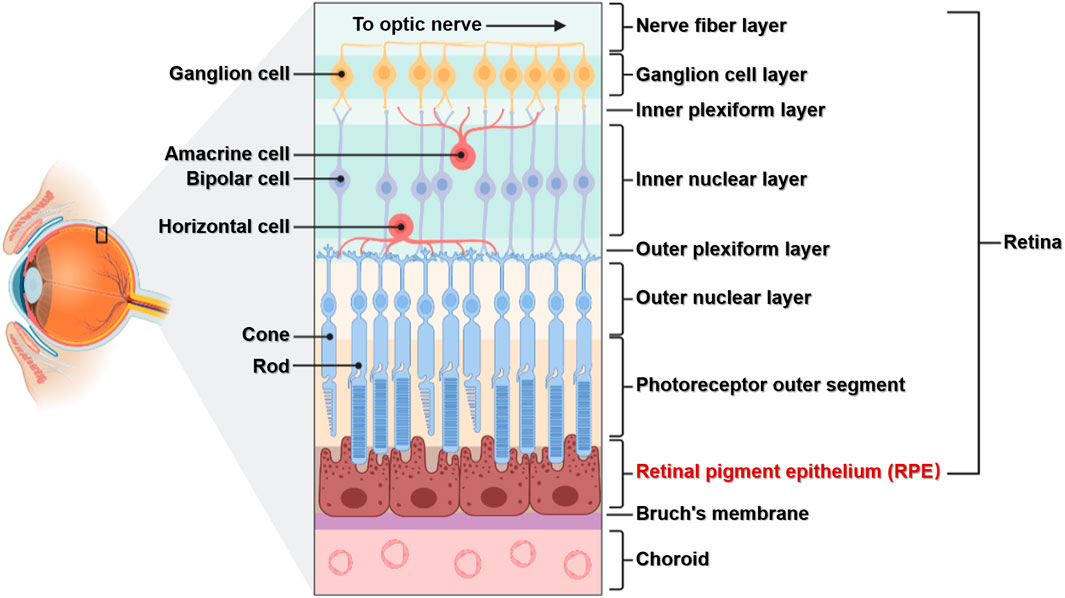
bipolar layer
part of the retina; between the ganglionic layer and the photoreceptor layer; home to bipolar cells which act as the primary conduit for transmitting visual signals from the photoreceptor cells to retinal ganglionic cells.
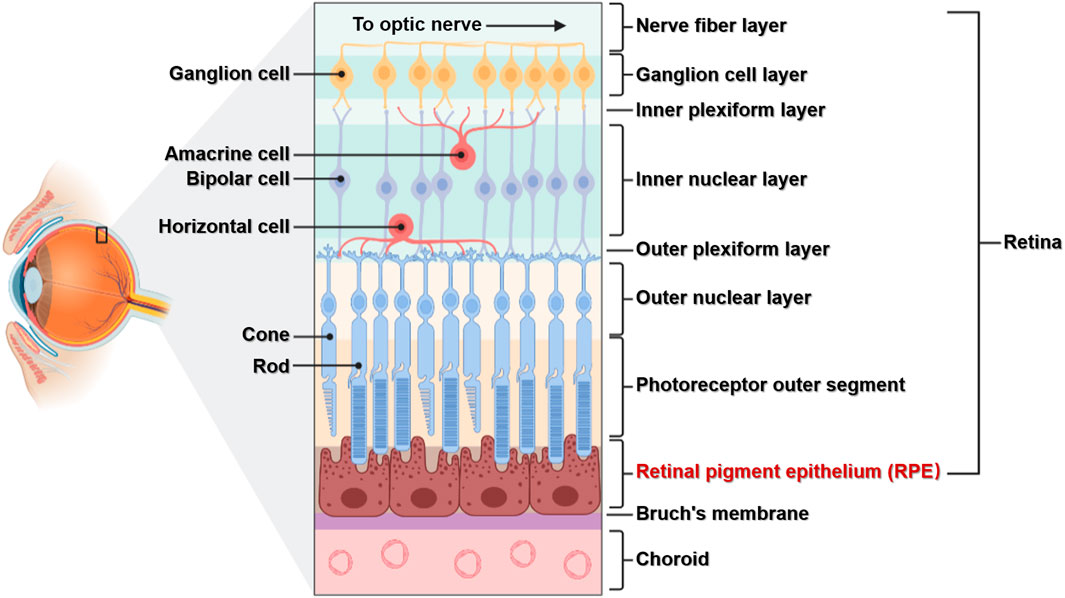
ganglion layer
part of the retina; above the bipolar layer of the retina; a thin layer of neurons located near the inner surface of the retina; receives and processes signals from photoreceptor cells.
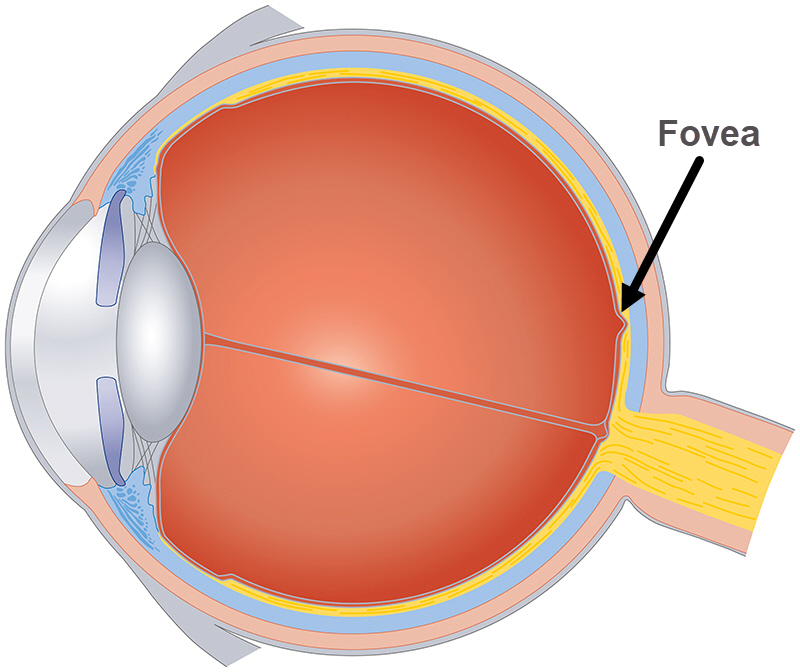
fovea
a small, highly specialized area of the retina located in the center of the macula, a small pin dot on models relatively near the optic nerve/disc.
optic disc
the beginning of the optic nerve and its point where the axons of the retinal ganglion cells come together.
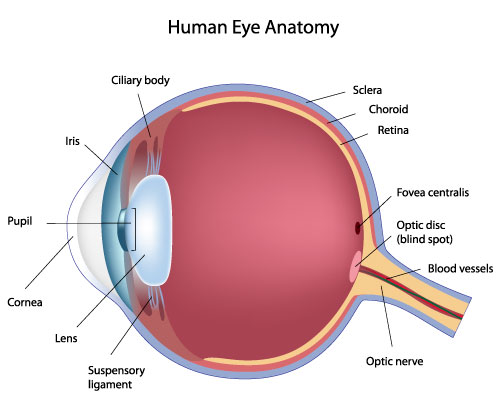
optic nerve
CN II, carries visual information from the retina in the eye to the brain
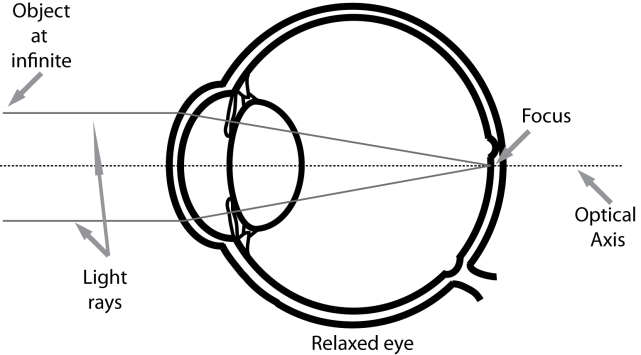
Emmetropic eye
normal, clear vision that occurs when the eye’s optical components are properly aligned and focused
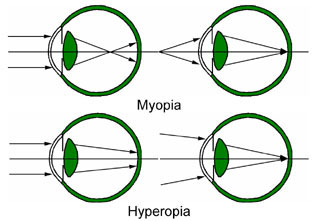
hyperopia
farsightedness, a refractive error where the eye’s focal point is located behind the retina instead of on it.
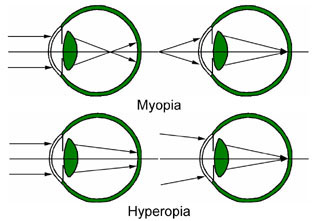
myopia
nearsightedness, a common condition where distant objects appear blurry while close objects remain clear.
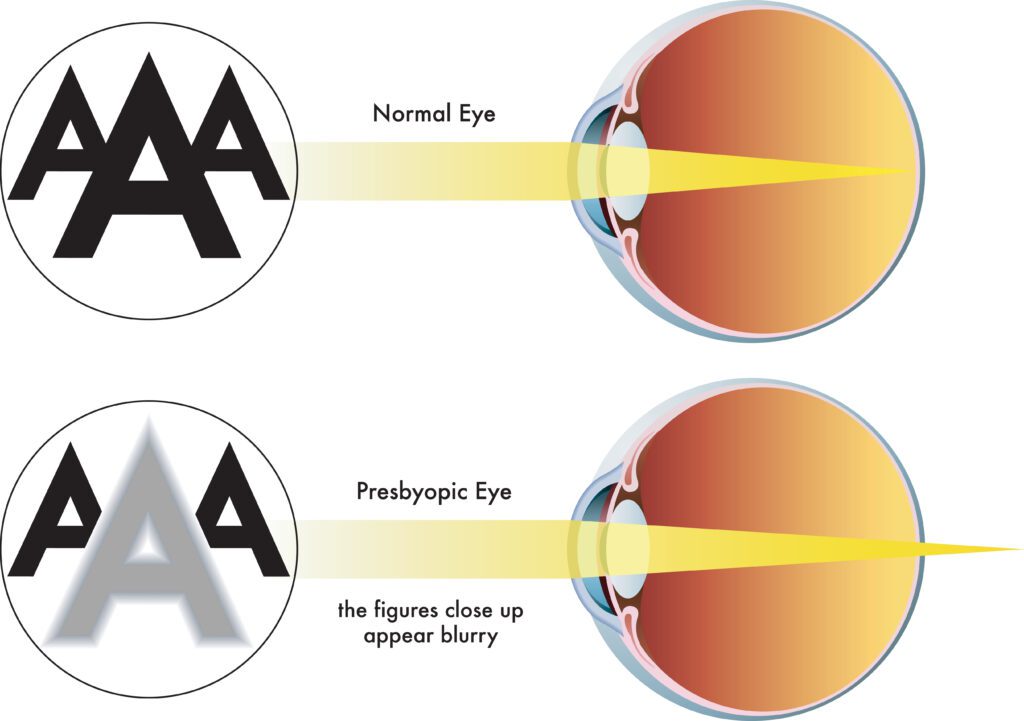
presbyopia
a common age related condition that affects the eye’s ability to focus on near objects; why older people hold phones far away from themselves
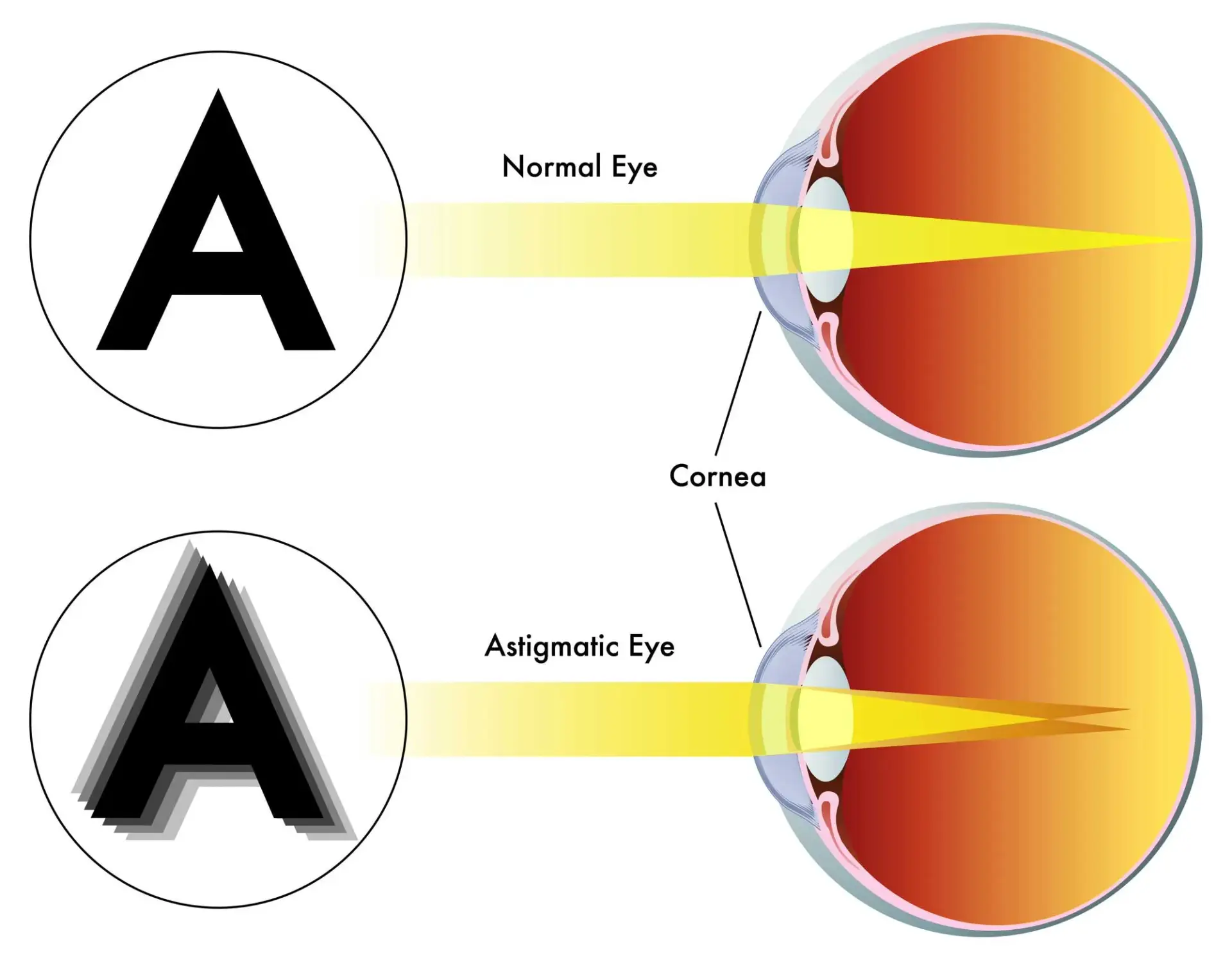
astigmatism
a common eye condition where the cornea, the clear front part of the eye is not perfectly curved; results in uneven light focus on the retina, resulting in blurred or distorted vision.