Chem basics and Biomolecules
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Covalent bonds
two atoms share one (or many) electrons
Oxygen electronegativity
3.5
Nitrogen electronegativity
3.0
Sulfur and Carbon electronegativity
2.5
Phosphorus and Hydrogen electronegativity
2.1
Non-polar covalent bonds
atoms with similar electronegativity, electrons are equidistant
polar covalent bond
dissimilar electronegativity between atoms, electrons are closer to the atom with higher electronegativity
Potential energy in covalent bonds
PE is greater in bonds with w/ equal electronegativity (polar) than bonds w/ unequal electronegativity (non-polar)
Build up of the cell system
electrons—> atoms —> molecules —> macromolecules —> organelles —> cell!
Structural isomer
same chemical formula, differs in structure (ex: branch point)
Cis-trans isomers
same formula, different geometric (3-D) structure due to double bonds restricting rotation
enantiomers
same formula, inverted/right and left hand images of each other
Hydroxyl group
—OH, hydrophilic (hydrogen bonds w/ water) alcohols
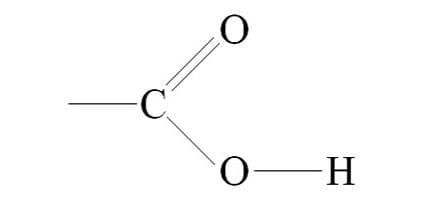
Carboxyl group
hydrophilic acids, can donate H+ bc O—H is polar
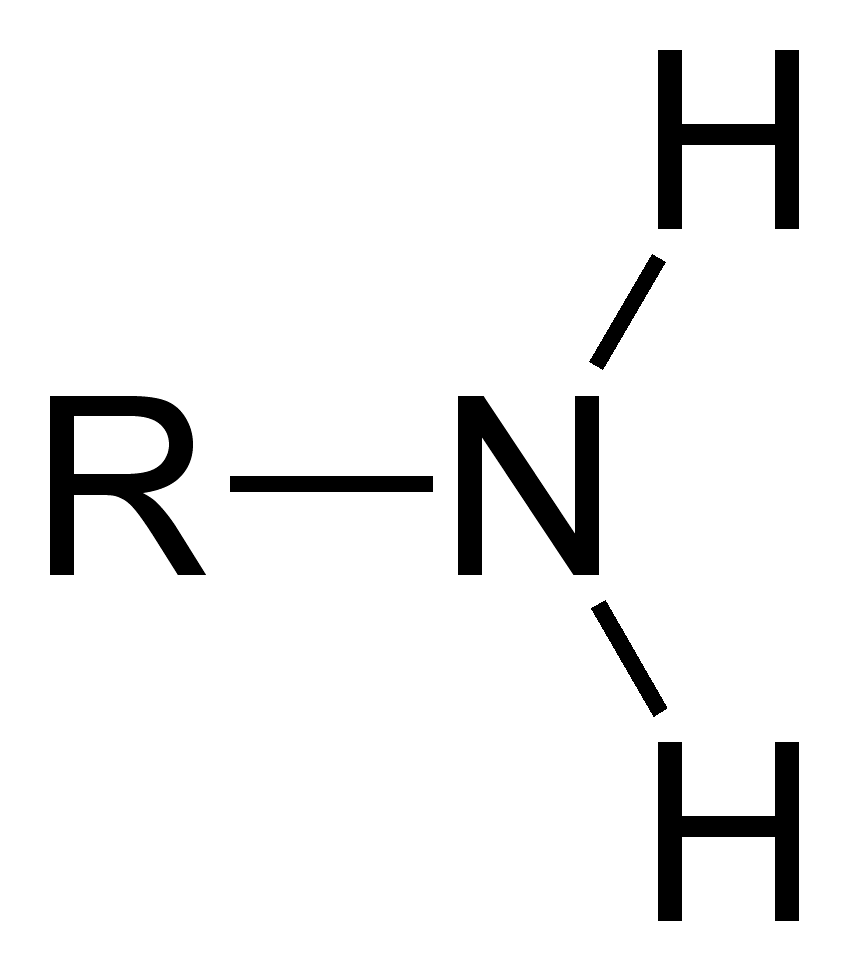
Amino group
—NH2, hydrophilic amines, act as base and can pick up H+,
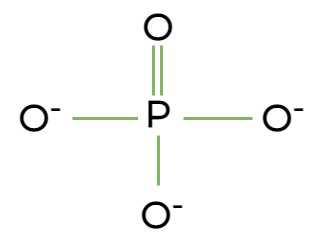
Phosphate group
phosphate, polar and hydrophilic
Polysaccharides
Sugars
Lipids
Glycerol and fatty acids
Amino acids
proteins
Nucleic acids
sugars and nucleotides
Carbohydrates functions
fuels (source of energy, breaking down sugar, glucose hydrolysis), storing energy (ex: glycogen, starch), structure (maintain integrity of cells, ex: cellulose)
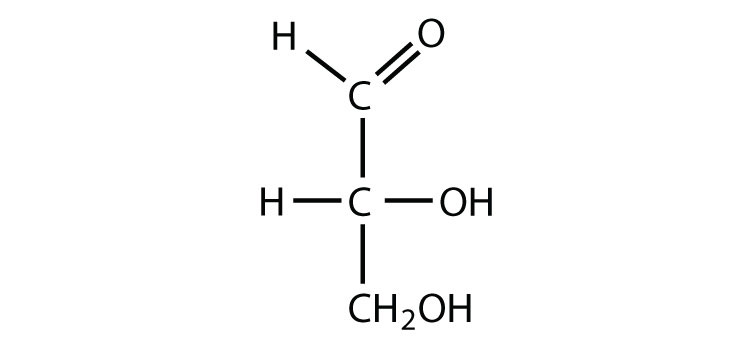
Triose sugar
Pentose sugar
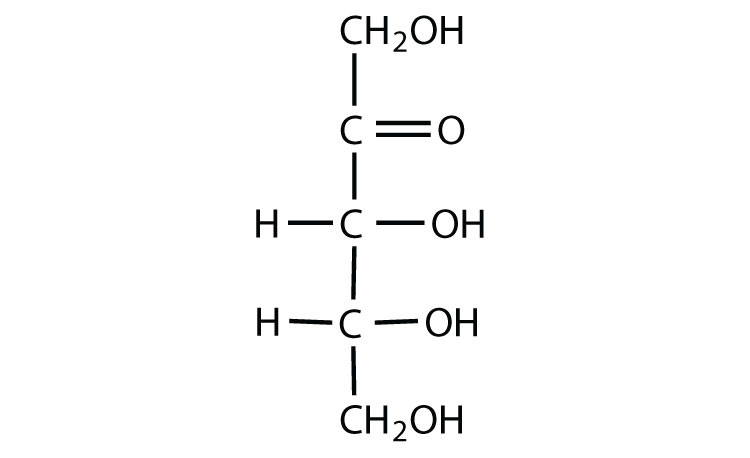
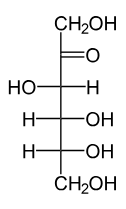
Hexose sugar
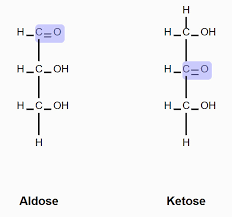
Aldose vs. ketose sugar
C-O group (carbonyl) location
Glycosidic linkage
Bond connecting monosaccharides, caused by dehydration reaction connecting C 1-4 (maltose) or C 1-2 (sucrose)
1-4 linkage orientations
alpha consistent orientation, beta alternating orientation
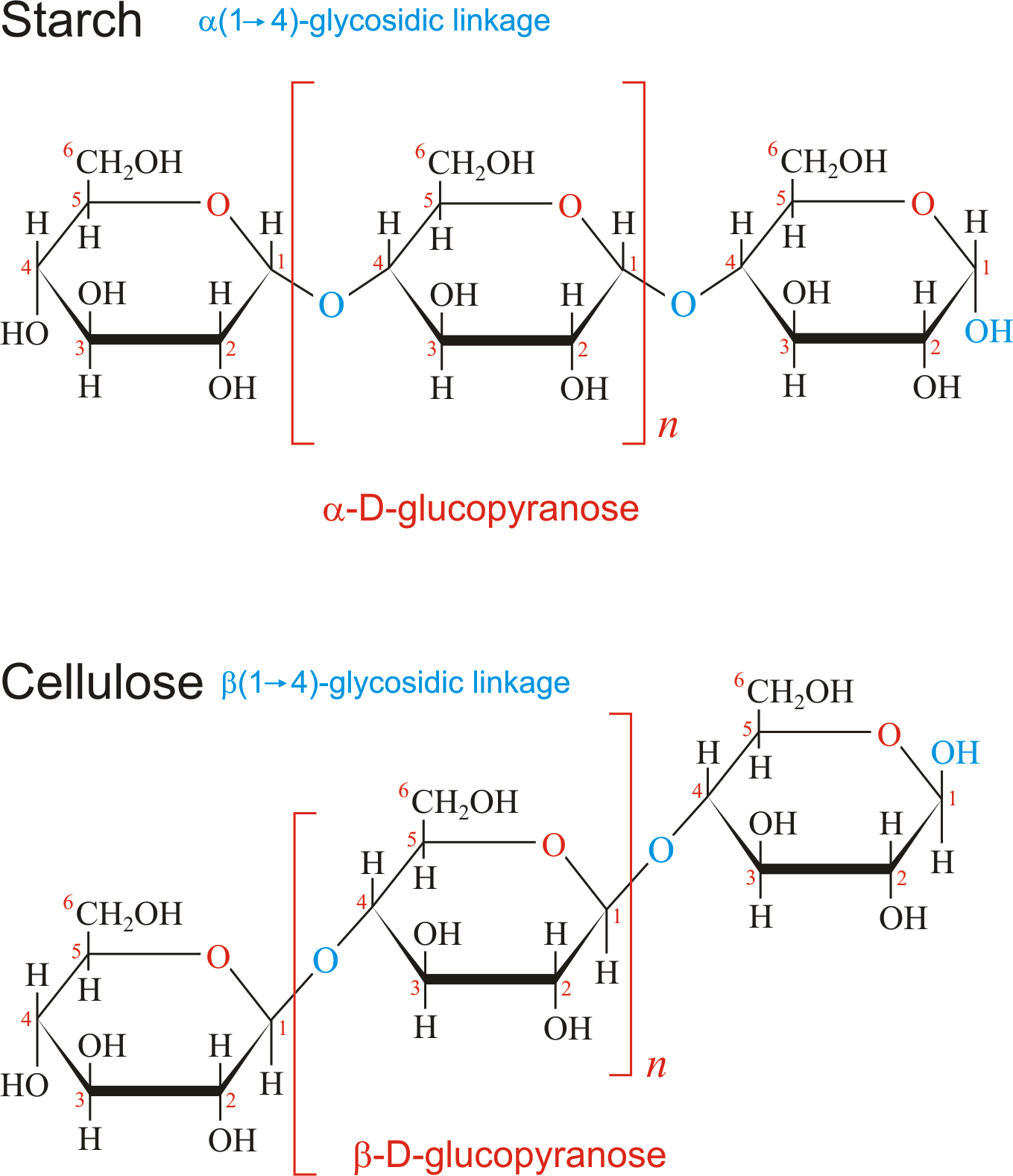
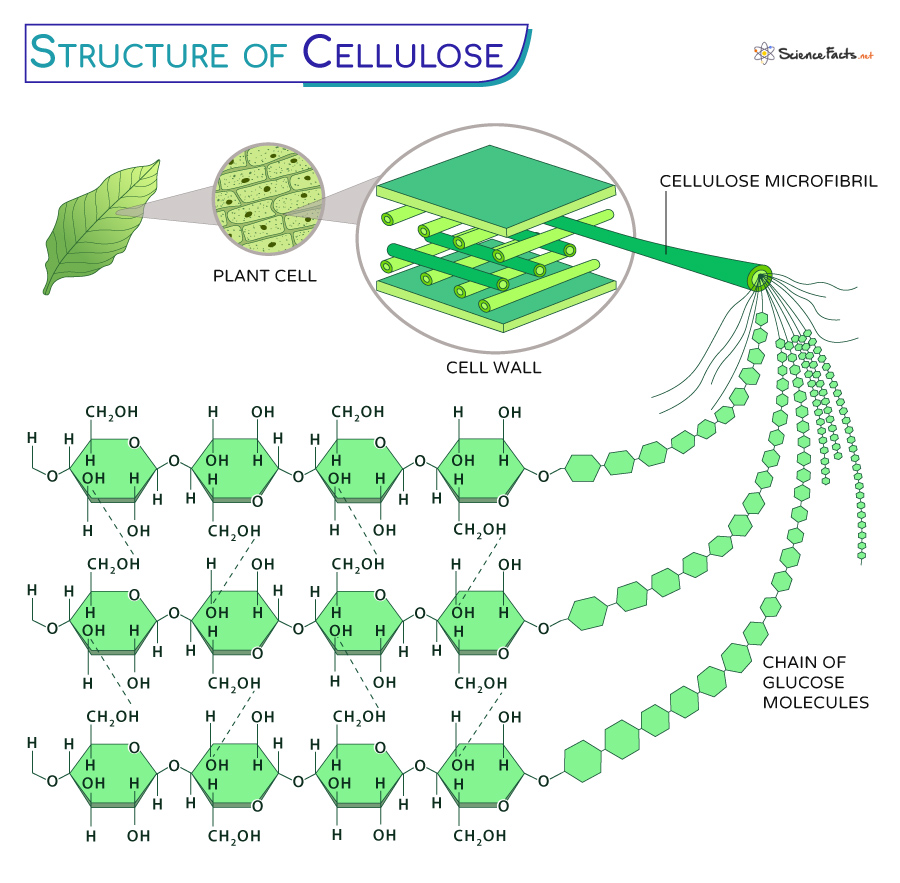
Cellulose traits
beta glucose, 1-4, No branching
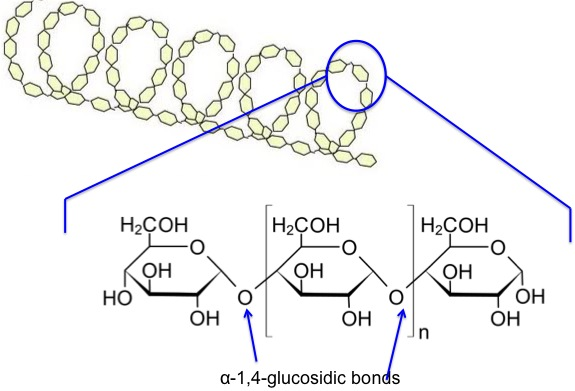
Starch- amylose
alpha glucose, 1-4, no branching
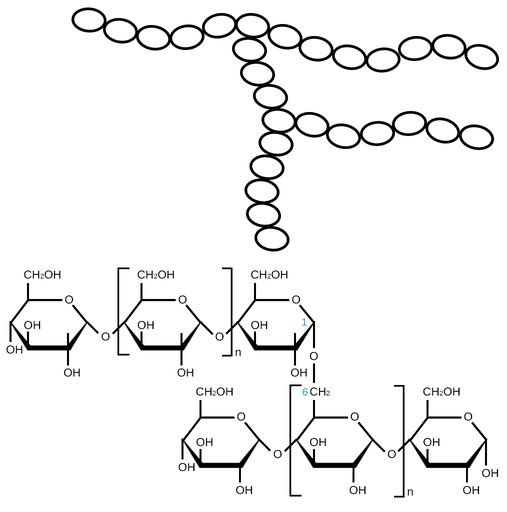
Starch- amylopectin
alpha glucose, 1-4 and 1-6, branching ~ 20 units
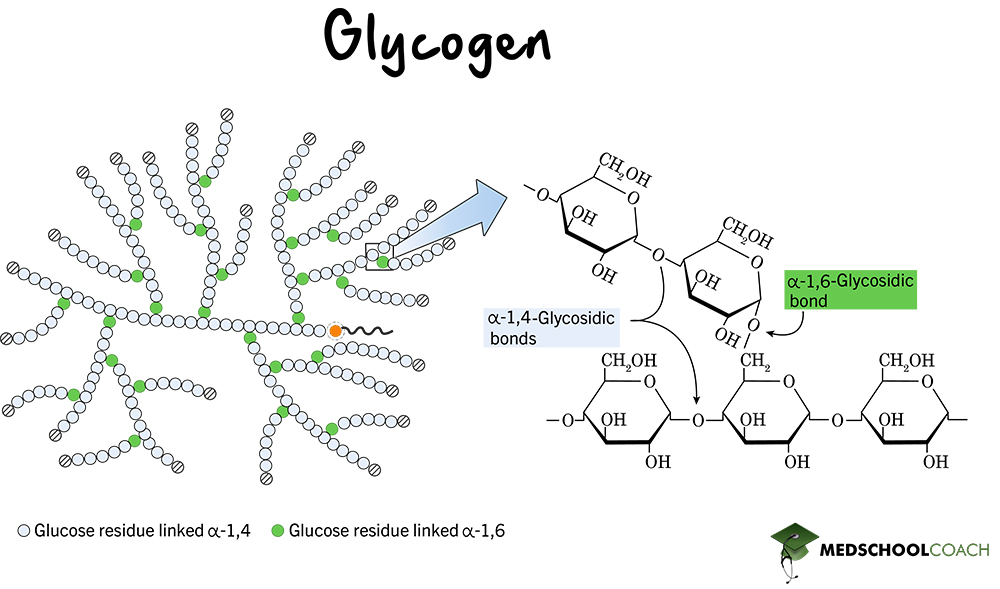
Glycogen
animals, alpha glucose, 1-4 and 1-6, branching ~ 10 units
Lipid functions
strongly hydrophobic bc of lots of non-polar C-H bonds, fuel (break down lipids slowly), storage (store in adipocytes/fat), some support structure of cell membranes
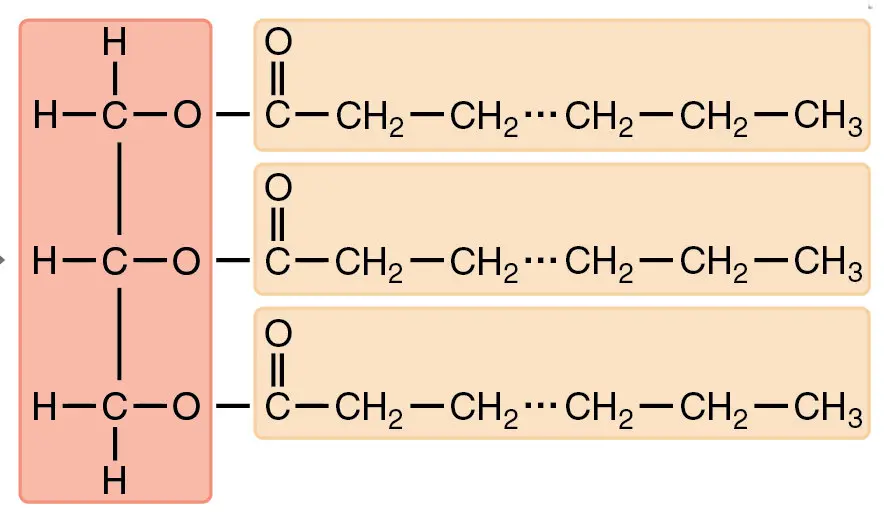
Triglyceride structure
glycerol and fatty acids, ester linkages bond fatty acids to glycerol (3 carbon alcohol)
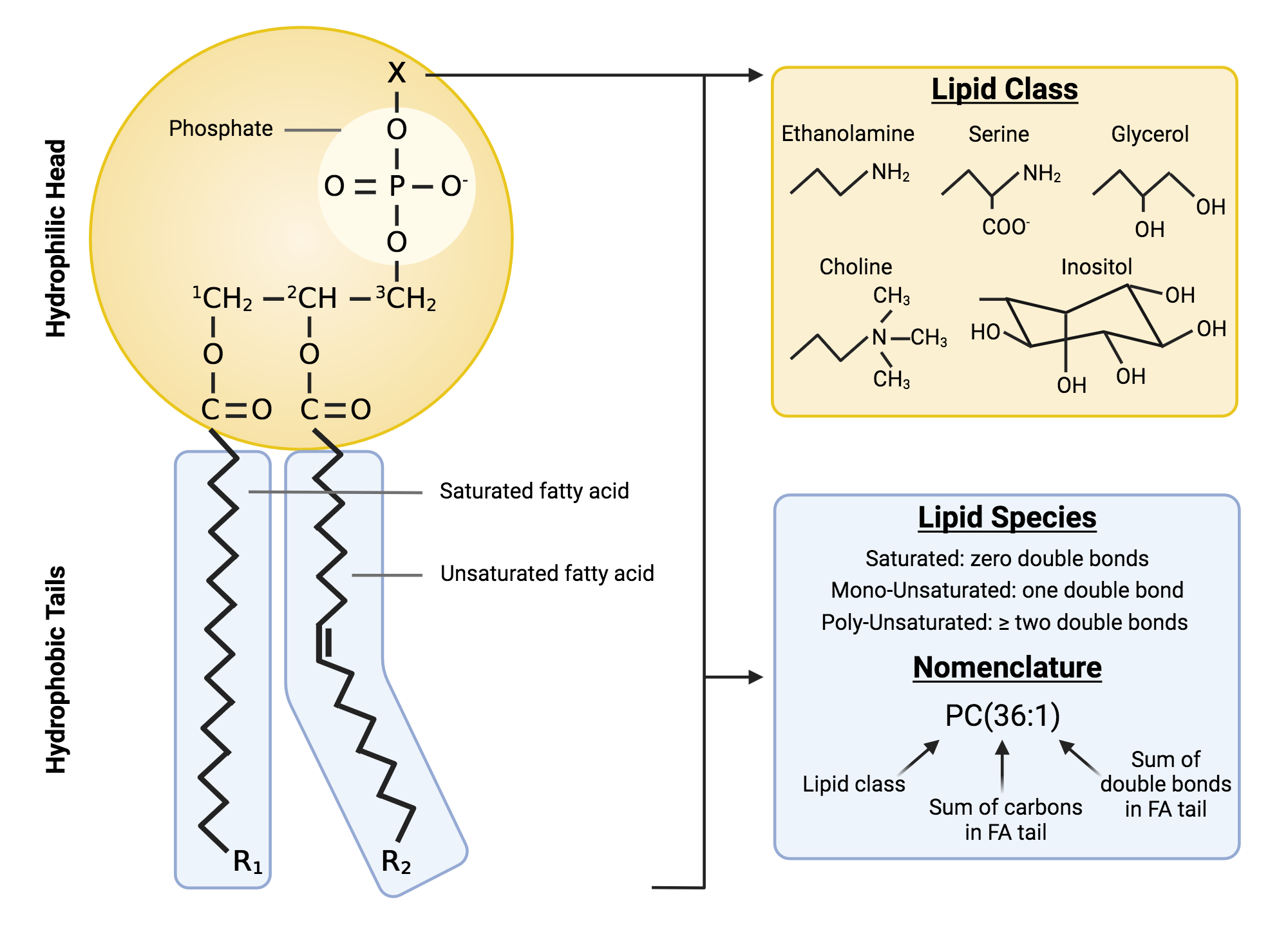
Phospholipid structure
2 fatty acids bonded to a glycerol bonded to a phosphate and functional group (hydrophillic head, hydrophobic tail)
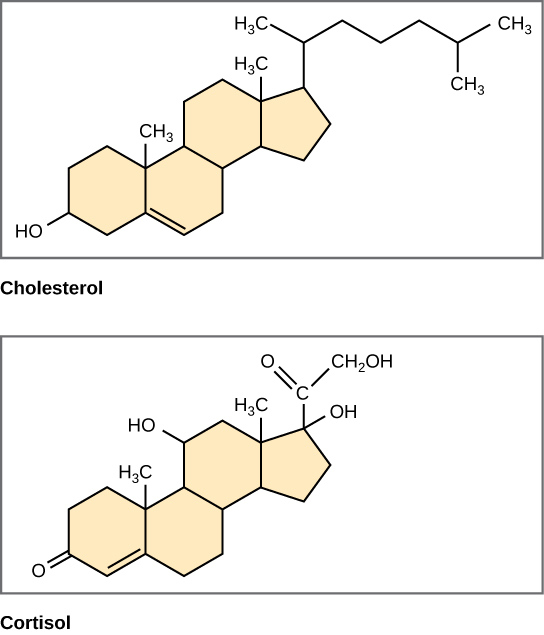
Steroid structure
Generally a 4 ring hydrophobic structure, hydrophilic hydroxyl left side, functional group right side
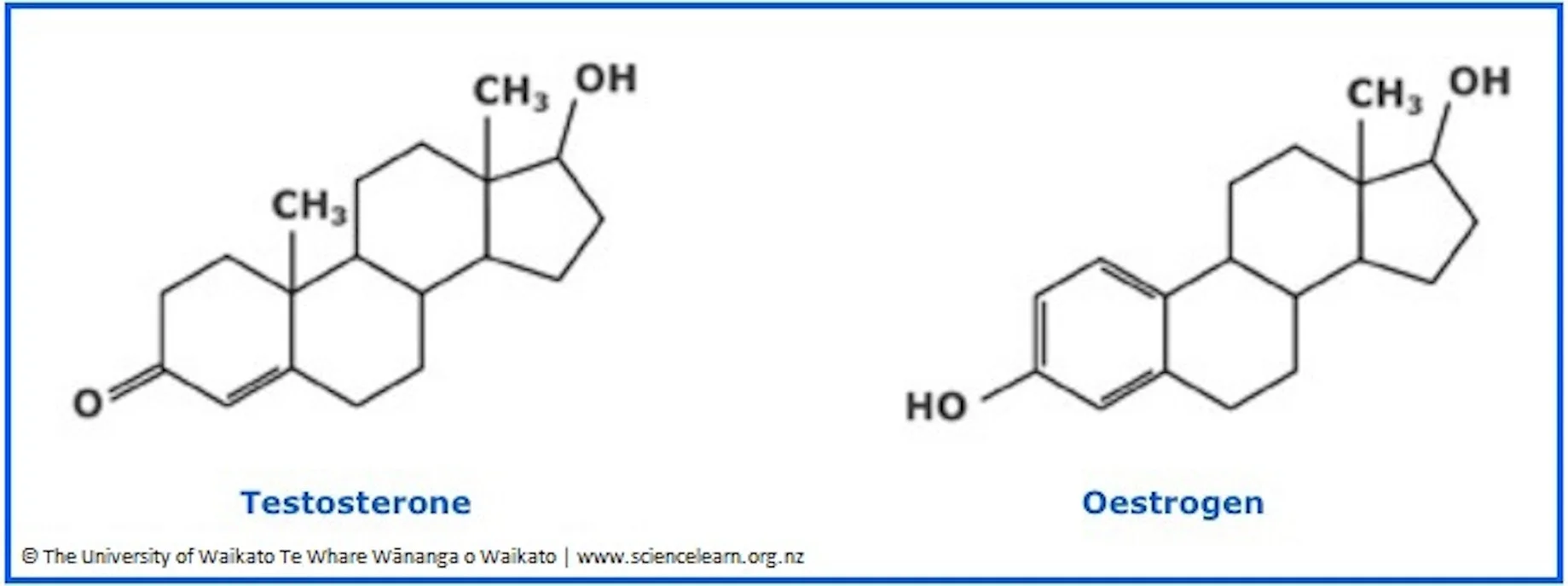
Sex hormones
derived from cholesterol
Peptide bond
connects amino acids into a polypeptide chain with a dehydration reaction
polypeptide and proteins
made of amino acid/peptide chains
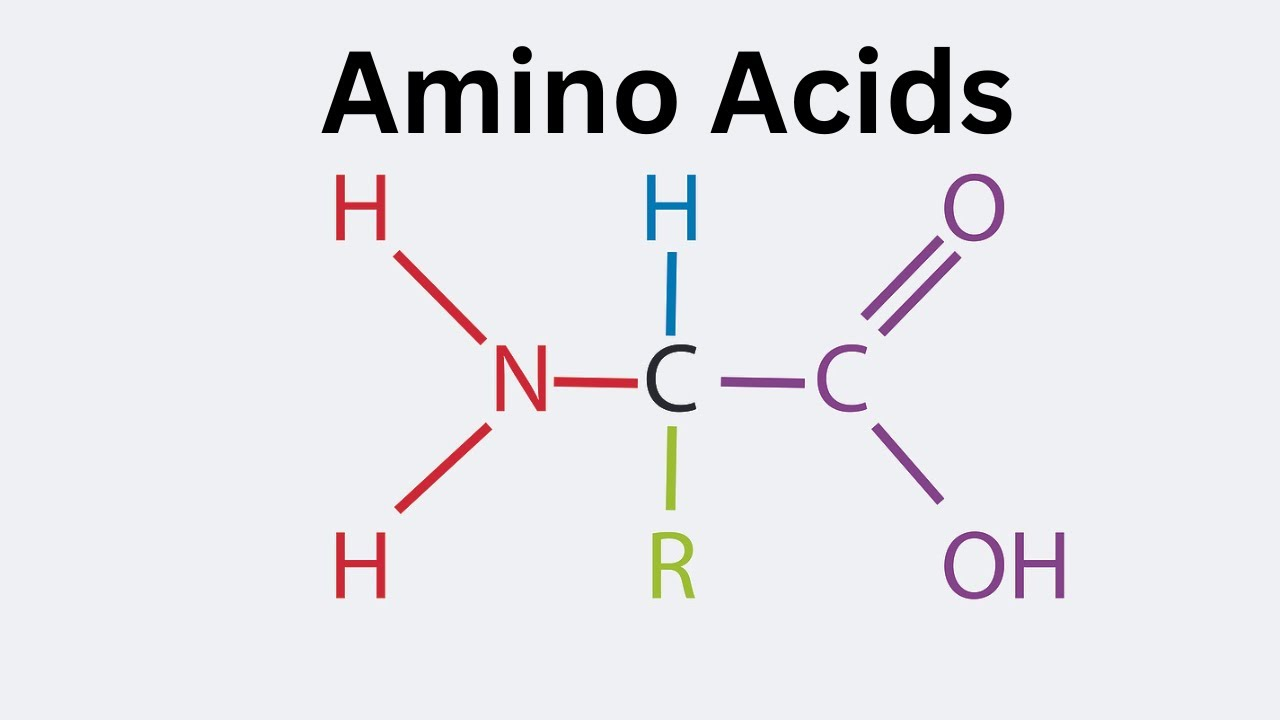
amino acid
composed of an amino group (NH2), carboxyl group (COOH), variable side chain (“R”), a hydrogen, all connected to a central carbon
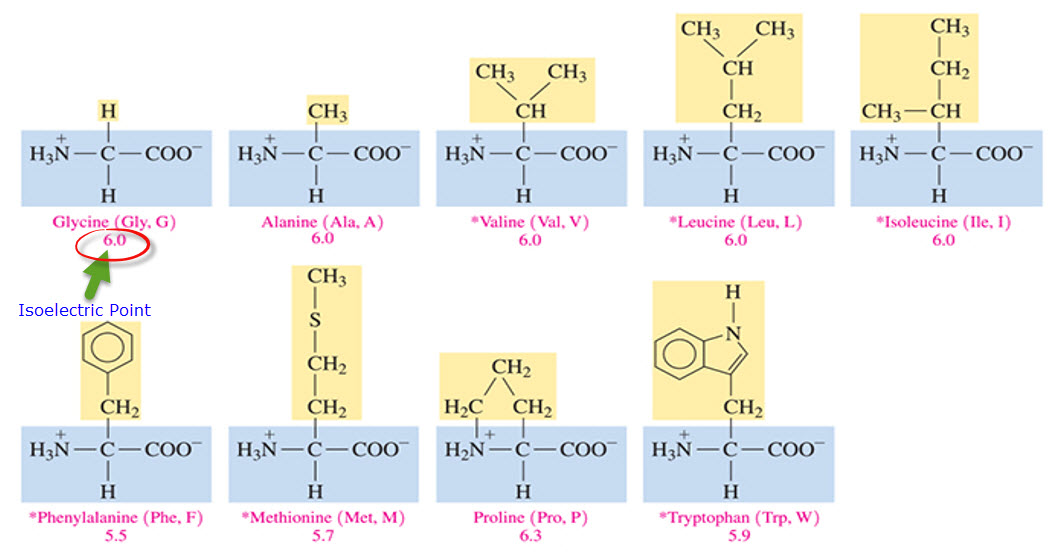
Nonpolar hydrophobic side chains
-CH bonds
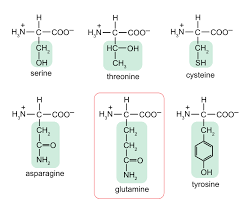
Polar hydrophillic side chains
C-O, C-S, C-N
Electrically charged side chains
negative= acidic, positive=basic
polysaccharides vs proteins
glycotic linkages vs. peptide bonds (w/ dehydration reactions)
Primary structure
amino acid sequence (peptide bonds), hydrophobic interactions
secondary structure
hydrogen bonds, alpha helices and pleated sheets
tertiary structure
all bonds (ionic, hydrogen, covalent disulfide), overall 3-D shape
quaternary structure
all bonds (ionic, hydrogen, covalent disulfide), connection of multiple subunits/multiple peptide chain
glycoprotein
macromolecule linking a protein and a small polysaccharide
nucleic acid functions
forms basis of inheritance/instructions to make proteins
nucleic acid composition
nucleotides—> polynucleotides/nucleic acids linked by phosphate group and pentose sugar (ribose or deoxyribose)
nucleotides
include phosphate group, pentose sugar, and nitrogenous base
pyrimidines
nitrogenous bases with 1 ring, cytosine, thymine, and uracil
purines
nitrogenous bases with 2 rings, adenine and guanine
ribose sugar structure
pentose with -OH at carbon 2
deoxyribose sugar structure
pentose with -H at carbon 2 (more stable)
central dogma 😛
DNA→RNA→Protein, DNA→mRNA (leaves nucleus)→ribsome translates into protein in cytoplasm