Physics Unit 3 Forces
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
What is Newton’s first law?
an object at rest will stay at rest and an object in motion will status in motion with the same velocity unless acted upon by an external force (Inertia)
Inertia
the resistance of an object to change its motion
What factor impacts inertia?
mass (NOT speed)
a car is harder to stop than a bicycle even if the bicycle is going faster
What is an example of the law of inertia?
when you get in a car accident without a seat belt and you fly through the windshield
an external force acted on the car but you and the car were moving at the same rate
no external force was acting on you so you stayed in motion
What is Newton’s Second law?
F net = ma (net force= mass x acceleration
force
a push or pull on an object (applied force)
What is the unit for forces?
newtons
Which object will have a larger acceleration, a smaller mass or larger mass?
smaller mass will have a larger acceleration (less stuff slowing you down)
net force
the vector sum of all forces acting on an object
How do you get the net force when two forces are going in opposite directions?
you subtract (cancels eachother out)
ex. 15 N force going to the right, 10 N force to the left
net force = 5 N
What do forces cause objects to do?
accelerate
If 15N force is going in the right direction and the net force is 5, what is the force of friction?
10 N (15-5)
because friction opposes motion (slowing it down)
What happens when the acceleration of an object is zero?
the net force is zero (force makes things accelerate, no acceleration = no forces winning out over the other)
forces are in equillibrium or balanced
What two things does no acceleration mean in terms of the object?
either not moving
or moving at a constant velocity
weight
measure of gravity (normal force)
in newtons
mass
amount of stuff your made of
in kg (usually)
what does Fg mean?
force due to gravity
also known as weight
How do you calculate weight?
Fg= mg
m= mass
g= acceleration due to gravity (always 9.81)
friction (Ff)
a force that always opposes motion (goes in opposite direction)
air resistance (Fair)
type of friction (also goes opposite)
How does surface area impact air resistance?
the more surface area the more air molecules there are to push the object up
as an object moves faster, there are also more air molecules pushing up (more air resistance)
tension (FT)
force that is transmitted through a string, rope, ect.
always points along the length of
How does an elevator move up?
the force of tension is greater than the gravity (weight) pulling it down
free body diagrams
shows relative magnitude and direction of ALL forces acting on an object
make sure the length of arrows are correct (force of friction would need to be obviously less than applied force if the object is accelerating)
Textbook pushed across a desk at constant velocity (ex.)
constant velocity = no acceleration
this means force of friction and applied force are = (net force would be zero)
Fg and Fn would also be equal
normal force
support force exerted upon an object that is in contact with another object
ex. book on a table (the table is pushing upwards on the book)
How do you draw normal force?
always perpendicular to the object
What is Newton’s third law?
for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction
ex. you slap the table but YOUR hand stings, why?
the table slapped you back
another ex. you have to push DOWN on the ground in order to jump UP (the floor pushes you up when you push down on it with the same force)
forces come in pairs
What are the values of the force due to gravity (Fg) and Fn when something is on an horizontal surface?
the forces would be equal
if they weren’t then the object would either be floating or going through the table
ex. 60 N sled, pulling it with a force of 20 N, what magnitude of force does the sled exert on the student?
20 N
you are pulling with a force of 20N so the sled is pushing you back with a force of 20 N
What are the two different types of friction?
static and kinetic
Static friction
stronger of the two (always)
the force that must be overcome in order to start moving something (objects must be at rest)
kinetic friction
weaker of the two
when 2 surfaces are sliding over one another
requires an object to be in motion
Why is static stronger?
it is harder to start moving something than to keep it moving
What type of friction is present when a wheel is turning?
static even though the tire is moving
the tire is not sliding against the road
certain spots on the tire are hitting the ground ONCE then moving on
What does friction depend on?
roughness of the surfaces
mass (lighter = less friction (not pressing down as much))
normal force
NOT affected by surface area
What is the equation to find the force of friction?
Ff= μFn
μ = the coefficient of friction (determined by the types of surfaces) (on reference table)
Fn can USUALLY be found by finding Fg
Problems with angles
30 kg wooden crate is pulled across an unpolished hard wood floor by attaching a rope to the crate and pulling with a force of 115 N at an angle of 35 degrees. Acceleration?
find components of the applied force (its being pulled at an angle)
then write the net force statements ( in separate x and y directions because now you have x and y components)
Fnetx= fappx— Ff
Fnety = Fapp y+ Fn - Fg (add forces going in same direction, subtract force going in opp)
What do you do after you find the net force statements?
trying to find acceleration (it is only accelerating in the x direction because its not being lifted off the ground)
use force net statement
solve for Ff by finding Fn (not = to Fg because of angle)
find Fn using y net force statement
plug into x net force statement
then you plug net force into f=ma
Inclined plane problems
the components are of Fg and they are perpendicular and parallel
no applied force because a component of gravity is moving it
How do you find parallel and perpendicular components?
using soh CAH toa
Fg is the hypotonuese
Fg sin= Fg parallel
Fg cos = Fg perpendicular
calc in degree mode
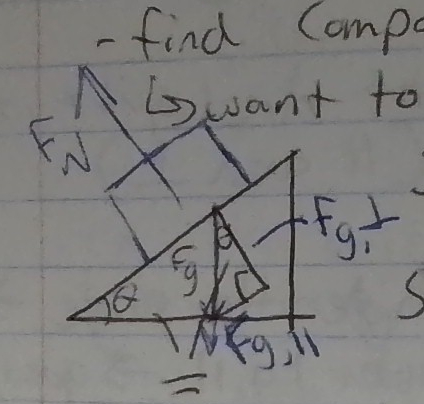
Net force statements for Fnet parallel
Fg parallel - Ff
Net force statement for Fg perpendicular
Fn - Fg perpendicular ( in same type of direction (both parallel to object but going different ways= subtraction))
Is the normal force equal to Fg when there are angles involved?
no (are not opposite of each other)
How does the angle impact the speed of the object?
higher the angle the faster the object moves (greater parallel)
uniform circular motion
object moving in a circle in a constant speed
Where is the velocity pointed when something is moving counterclockwise?
velocity is always tangent to the circle

Does the object accelerate though?
not in terms of magnitude but in terms of direction
the vector is changing
called centripetal acceleration
What does centripetal mean?
center seeking
always pointed towards the center of a circle (centripetal force and acceleration)
How do you calculate centripetal acceleration?
a=v²/r
r= radius (half of diameter)
What is the net force called? (acceleration means there is a net force)
centripetal force (center seeking)
How do you calculate the centripetal force?
Fc= mv²/r
m = mass of the thing MOVING (not what’s holding it)
What does the centripetal force do?
keeps the object moving in a circle (force necessary to keep it moving)
larger mass = larger Fc
How do you get the velocity? (in circular motion)
v= 2πr/T
capital T = the period
What is the period?
how long it takes to go around the circle ONCE
how to find it = Total time/ number of revolutions
Law of Universal Gravitation Equation
FG= G m1 x m2/r²
G= universal gravitational constant (never changes, in reference table)
m1 and m2- masses of two objects
r = distance between two objects (not radius in this context)
How do you figure out the plotted relationships between two variables?
find the equation and cover up all other variable besides the two you need
then look at the relationship (y=m is linear)
ex. relationship between r and force F= G m1 x m2 /r²
F= 1/r² - inverse squared relationship
Proportional math
if the variable is doubled, tripled, ect, what happens to the second variable?
What are the steps to solving these problems?
write equation and solve for the variable you want to know about
replace all variable that do NOT change with 1
replace variable that are changing with how much they change by (doubled—> 2)
solve and write times as much after your answer
Example problem
If m1 is doubled, what happens to FG?
FG = G m1xm2/r² (Fg is already solved for)
FG = (1)(2)(1)/(1)² - keep squared
FG = 2 times as much