Homologous recombination
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
1
New cards
Genetic recombination
Strand exchange between helices
2
New cards
What are the three types of recombination?
1. Homologous recombination
2. Site specific recombination
3. Illegitimate recombination
3
New cards
What is the range of bp for homologous recombination?
23 - the whole chromosome
4
New cards
What are the three requirements for homologous recombination?
1. 2 DNA sequences with similar/identical bp sequences
2. Ability to form stable H bonds between DNA
1. Proteins needed to perform recombination
5
New cards
What are the simplified steps of homologous recombination?
1. Two similar DNA sequences come together
2. The sequences form stable H bonds between each other
1. DNA is resolved and re-ligated into two different strands
6
New cards
What would happen to HR if there was a break in the DNA strand?
The replication fork would collapse and have to start over again
7
New cards
How can DNA be damaged?
reactive oxygen species (ROS) ds breaks, irradiation
8
New cards
What is RecA?
RecA is the main protein that drives HR
* 38 kDa protein
* RecA is highly conserved and is often used to conduct phylogenetic comparisons
* 38 kDa protein
* RecA is highly conserved and is often used to conduct phylogenetic comparisons
9
New cards
What are the functions of RecA?
* binds ssDNA every 3 nucleotides
* Oligomerizes and coats ssDNA
* A DNA-dependent ATPase
* Binds the ssDNA and dsDNA (strand invasion)
* Oligomerizes and coats ssDNA
* A DNA-dependent ATPase
* Binds the ssDNA and dsDNA (strand invasion)
10
New cards
What are recB, recC, and recD together called?
Exonuclease V or RecBCD
11
New cards
What is RecBCD?
* ATP-dependent exonuclease for dsDNA
* Exo and endo nuclease for ssDNA
* Exo and endo nuclease for ssDNA
12
New cards
What are the functions of RecBCD?
* nucleases that digest the dsDNA and ssDNA
* A helicase that unwinds the DNA
* A helicase that unwinds the DNA
13
New cards
What are the basic steps that RecBCD follows?
1. Bind to the strand break
2. Unwind DNA on one strand
3. Digest the DNA in 3’ to 5’
4. Identify the chi site, stop 3’ to 5’ exo and start 5’ to 3’ exo
5. ssDNA formed
1. RecA recruited to bind ssDNA
14
New cards
What is a chi site?
A crossover hotspot
* ensures that the replication fork is regenerated in the right direction
* ensures that the replication fork is regenerated in the right direction
15
New cards
What are the steps of HR including chi?
1. RecBCD is loaded at the ds break
2. RecBCD uses ATP to move down DNA and unwind at the 5’ end and degrade the 3’ end
3. When RecBCD hits the chi site, the exonuclease direction switches
1. RecA bound ssDNA can then find the homologous sequence
16
New cards
What is a synapse?
The joining of the two DNAs
17
New cards
What is strand invasion?
Strand invasion is where an invading strand can replace one of two strands in a ds DNA
18
New cards
What is a Holliday junction?
The extension of a filament into the dsDNA that is synthesized by RecA
19
New cards
What happens when the Holliday junctions are formed?
* RecA dissociates
* DNA pol and ligase can fill in the gaps on the DNA
* RuvABC (RecG) is formed
* DNA pol and ligase can fill in the gaps on the DNA
* RuvABC (RecG) is formed
20
New cards
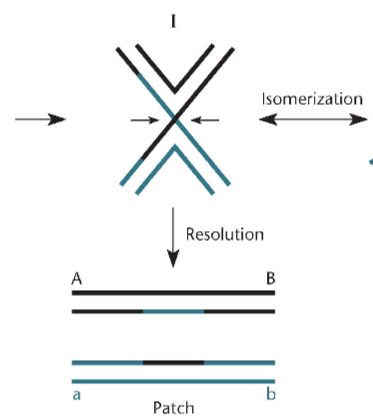
What happens when form I (Holliday junction) is cut?
The result is two chromosomes with only small patches exchanged
21
New cards
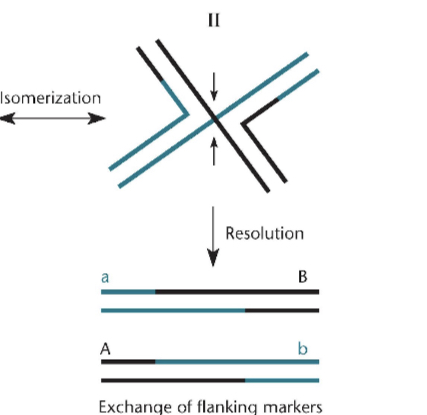
What happens when form II (Holliday junction) is cut?
The result will be two new chromosomes but there are crossovers
22
New cards
What is RuvA?
DNA binding protein that recognizes the gross structure of the Holliday junction
* creates a short middle section of the junction where the strands are not base paired
* creates a short middle section of the junction where the strands are not base paired
23
New cards
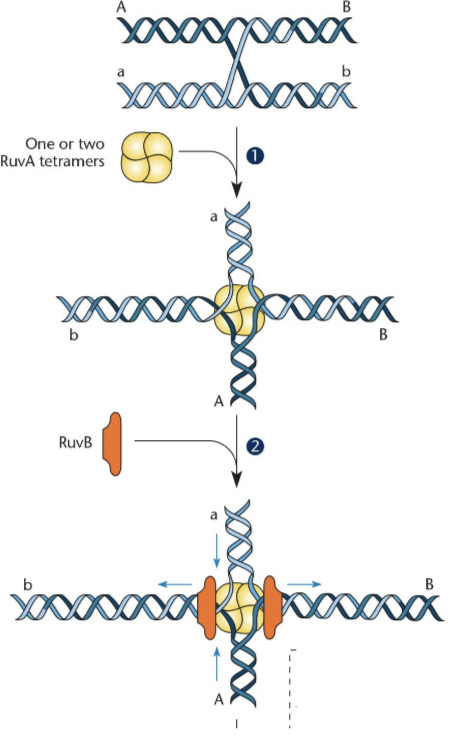
What are the steps to begin strand migration?
1. RuvA recognizes the Holliday junction
2. RuvA recruits RuvB (an ATPase)
3. RuvB provides ATP to exchange base pairs
4. DNA is pumped through the RuvB ring to drive migration
24
New cards
What are the steps to finish strand migration?
1. RuvC is an endonuclease (resolvase)
2. RuvC binds to the complex and cuts two of the junction strands where RuvAB pauses
3. Where the RuvC breaks the DNA will result in different configurations of helices