NRSG 111 midterm
1/151
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
152 Terms
Illness
A subjective experience of loss of health. Only the person experiencing it can say they are ill.
Disease
A objective state of health. Can be diagnosed and measured.
Health
Physical, mental, social, and spiritual. Objective, characterized by functional stability, balanced, integrity
Wellness
Subjective, determined by the person experiencing health
WHO definition of health
Physical, social, and mental well-being
Medical approach to health
Only looked at the medical aspect. “ You are obese and at risk for a stroke”
Behavioral approach to health
Focused on changing peoples lifestyles. “You eat poorly so lets focus on making smarter choices”
Socioenvironmental approach to health
Focused on what leads people to make the choices they do. “You eat poorly because you are trying to provide for your family”
Health Inequity
Health differences: social, economic, environmental, disadvantage, genetics, choices
Health equity
Access, health care for all
Impact of health and wellness on the individual
behavior and emotional changes
loss of autonomy
self-concept and body image changes
life style changes, financial adjustments
denial, anger, guilt, hopelessness
Impact of health and wellness of the family
depends which member is ill (mom, dad, baby)
depends on seriousness and length of illness
financial demands
cultural and social customs the family follows
Individual
1 human being
Family
2 or more individuals who all depend on each other for emotional, physical, or finical support
Group
Groups within a population (youth with diabetes)
Community
People and relationships that emerge among them as they develop and commonly shared agencies, insituations, or physical space
Population
a large group of people who have at least 1 characteristic in commom and reside in a community
Society
The system that incorporates the social, political, economic, and cultural infrastructure to address issues of concern
What influences your lens
previous experiences
upbringing
culture
gender
socioeconomic background
Why is public heath important?
The average lifespan of Canadians has increased by 30 years since 1900s, and 25 of those are attributable to advances in public health
12 achievements- Control of infectious diseases
Controlling the spread has been a fundamental goal of public health
12 achievements- safer workplaces
Rate of work related injury has been steadily declining
12 achievements- Motor vehicle safety
Invention of seatbelts and drinking and driving laws
12 achievements- Safer and healthier food
Canada has safe and high-quality food
12 achievements- Decline in death from cardiovascular disease
Canada is a world leader in treatment and control
12 achievements- recognition of tobacco use as a health hazard
Dramatic decline in tobacco consumption
12 achievements- healthier mother and babies
Health of mothers and children in Canada is among the best in the world
12 achievements- universal policies
The term “universal” applies benefits that are awarded based on age, citizenship, without recipients income. Universal programs, social welfare and healthcare help Canada maintain high standards of living.
12 achievements- family planning
invention of birth control and abortion becoming legal
12 achievements- healthier environments
Policies have increased community health and reduced toxic admissions
12 achievements- vaccination
Because of vaccinations, diseases now cause less than 5% of all deaths
12 achievements- Acting on SDOH
Recognition that health is influenced by many factors outside the healthcare system
Social determinants of health
Conditions in which people are born, grow, work, live, and age, the wider set of forces and systems shaping the conditions of daily life
SDOH- income
money impacts resources, housing, general health, and food security
lack of money increases stress and increases risk of life threatening coping behaviors
SDOH- education and literacy
Literacy is often closely tied to income and enables increased understanding and ability to obtain and use info
Functional literacy
Reading and math ability
Interactive literacy
Apply new info to changing circumstances
Critical literacy
Advanced ability to analyze info for understanding
SDOH- employment
unemployment, job security, working conditions
nursing has the highest rate of calling in “sick” because of workload
SDOH- development
Ages 0-6 are most impactful, caring, environments, and supportive parenting will set your kids of for success
SDOH- health services
physical environment: geography, housing, food security
what do you have access to: safe drinking water, fresh air, location of healthcare
SDOH- gender
how does our understanding and feelings about gender influence our health, and everyone’s health
SDOH- culture, race, racism
BIPOC, minority groups, immigrants, refugees
Racism
individual
Systematic racism
Policy, laws, regulations- colonization
Racialazation
Seen as belonging to a particular race
Colonialism
European policy and intuition of domination
SDOH- social environment
social safety net, social exclusion, disability
family, friends, people you connect with
Primary Healthcare
high level of health and wellbeing
equitable distribution
patients centered
early access
on a continuum
accessible
intersectoral cooperation- everyone working together
Prerequisites for health
Peace, education, shelter, food, income, ecosystem, resources
with a focus on social justice and equity
Health Equity
The absence of systemic disparities in health (everyone gets what they need)
health inequity puts those disadvantaged at a further disadvantaged
reflects social justice and is critical and necessary to achieve health for all, with the concept health is a human right
Social Justice
rooted in responsibility and fairness
focus in on relative social advantage of individuals or groups over others
examine roots causes of inequities and how to eliminate them
SDOH strategies: health promotion
is directed towards increasing the level of well-being and self actualization
SDOH strategies: disease promotion
is action to avoid or forestall illness/disease
Strategies outlines in Ottawa Charter
build public health policy
create supportive environments
strengthen community action
develop personal skills
reorient health services
Primary disease prevention
Prevent disease/injury before it occurs
Secondary disease prevention
Reduce impact of disease/injury which has already occurred (early detection)
Tertiary disease prevention
Management of illness/injury with long term effects
Growth and Development
understanding human development informs nursing plans and promotes optimal health
impacted by gender, culture, and sexuality
not always orderly and predicable
sociocultural, biological and psychological forces are interacting
Genomics
the study of genes and how they can be altered during growth and development
Epigenetics
factors outside of genes that change cellular function
intergenerational
poverty
stress
Physical growth
Quantitative and measurable - genetic
Delevoplemnt
progressive, continuous
increasing capacity and skills to function
qualitative, difficult to measure
move from simple to complex
Cephalocaudal
Head to toe (neck and head develops before extremities)
Proximodistal
Midline to periphery (central NS develops before peripheral NS)
Differentiation
Simple to complex (babies make noises before talking)
Screening
Helpful to determine growth and development areas of issues for early intervention
Erikson’s theory of psychosocial development
8 stages throughout life
each stage = resolution of conflict
recognizes environments but focuses on individual mastering the conflict
conflicts are predominant at stages but exist at all times and may emerge over again
consider nursing implications for the person that is struggling with successful resolution of a stage
Infancy- trust vs mistrust
teach with anticipatory guidance - prevention with understanding the G&D stage
focus is on the parents
Early childhood - autonomy vs shame and doubt
learn about independence and self confidence (what they can do wrong)
teach with empathetic guidance
Preschool - initiative vs guilt
teach about cooperation and control, helping them learn independence
stick with something from start to finish
School age - industry vs inferiority
allow for opportunities, helping them learn about interests and challenges
learn risk taking - pushed out of comfort zone
Adolesence - idenity vs role confusion
who am I?
what do you believe?
Young adulthood - intimacy vs isolation
learn to be part of society and learn their ow identity, and develop close relationships
Middle adulthood - generativity vs stagnation
expanding within society and supporting the future
nurses can support social interactions
Maturity - integrity vs despair
nurses can practice without ageism, showing respect, value, involvement
reflective- what is happening?-changing/aging
Piaget’s theory of cognitive development
4 periods of time, experience by all cultures
children making means of the physical world
through to adults learning to cope with health challenges
maturation, dependent on opportunity, simulation and challenge
spontaneous process where individuals play active role in development
Sensorimotor (0-2)
infant explores the world through direct sensory and motor contact
object permeance and separation anxiety develop
Preoperational (2-6)
child uses symbols to represent objects (cant logically reason)
ability to pretend
child is ego centric
Concrete operational (7-12)
think logically about concrete ideas (addition or subtraction)
understands conversation
Formal operational (12-adult)
adolescent can reason abstractly
think in hypothetical terms
Theory 2: Premoral
Will not follow rules
Theory 2: Conventional
Will follow rules
Theory 2: Autonomous
Mutual respect for rules impacted by morals and consequences
Kohlberg’s moral development theory: Level 1
Pre-conventional
obedience and punishment orientation
self-interest orientation
Kohlberg’s moral development theory: Level 2
Conventional
interpersonal accord and conformity
authority and social-order maintaining orientation
Kohlberg’s moral development theory: Level 3
Post conventional
social contract orientation
universal ethical principals
Why is understanding G&D important for nurses?
understanding risks
implementing appropriate strategies
knowing when to involve the patient vs parent
Who makes health care decsions?
under 19 is a minor
or if deemed as incompetent
Infants act
Under 19 can make health care decisions if its in their best interest and they are making an informed decision
Health risks or risk factors
Increase susceptibility to disease
What guides our choices?
beliefs
values
attitudes
knowledge
demographics
access/resources
TTMOC- Pre contemplation
No plans to take action
TTMOC- contemplation
Acknowledges need to change
TTMOC- preparation
intends to take action immediately
TTMOC- action
Actively implements the behavior
TTMOC- maintenance
strives to prevent relapse
TTMOC- termination
Problem is no longer a threat
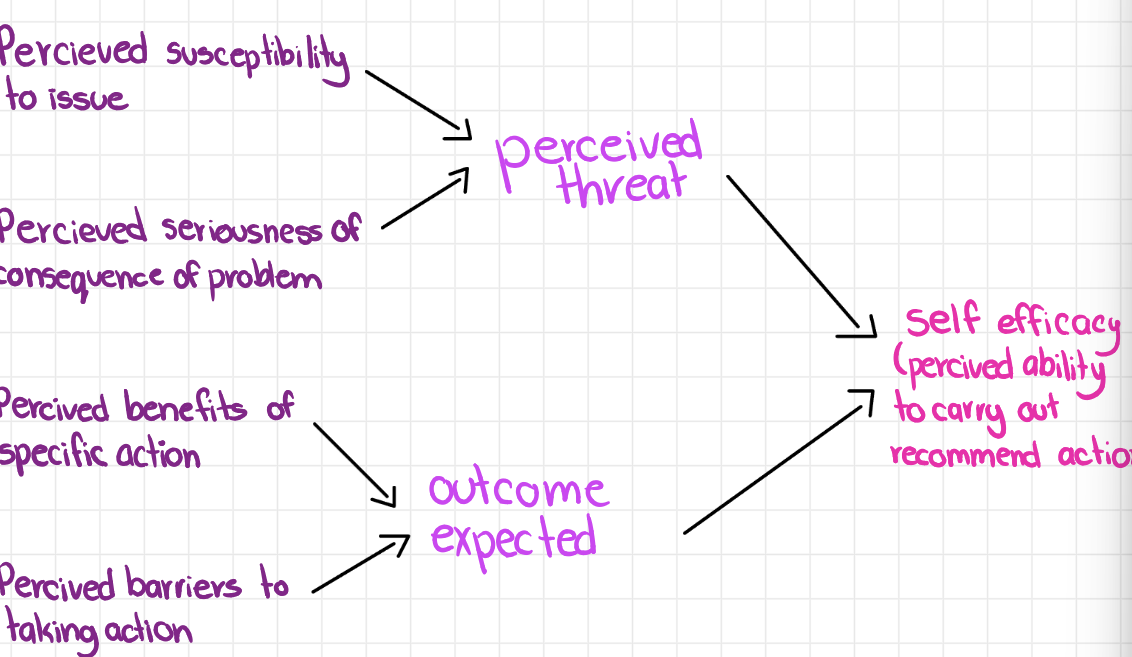
Health belief model
is it serious?
am i susceptible?
is it worth it to change?
what barriers are there?
Cyclic
People move through the stages in order, however relapse to earlier stage is possible