week 1 2 Universe and earth strucutre
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Earths orbital configuration controls what?
climate and habitability
earths orbit around the sun
ecliptic
tilt
23.45 degrees perpendicular to the ecliptic (why we have seasons)
North tilti towards sun
summer solstice (june 21)
south tilt towards sun
winter solstice
precession
slow movement of the axis of a spinning body around another axis due to a torque
polestar changes : 26k yrs
gravity-induced, slow, and continuous change in the orientation of an astronomical body's rotational axis
Eccentricity
currently 0.016
causes 6.4% annual variation in solar radiation
varies over 100,000-400,000 yr cycles
a dimensionless number measuring how much an orbit deviates from a perfect circle, ranging from 0 (perfect circle) to just under 1
Perihelion
earth closest to sun
Aphelion
earth furthest away from sun
Milankovitch cycles
long-term, natural variations in Earth's orbit and axial tilt
change the amount and distribution of solar radiation received, influencing climate patterns like ice ages over thousands of years
Contoled the formation of glaciers
Northern hemisphere ice growth
low obliquity (low seasonal contrast)
northern hemisphere summers during aphelion (cold summers in the north)
high eccentricity
Northern hemisphere ice melt
High obliquity (high seasonal contrast)
northern hemisphere summers during perihelion (hot summers in the north)
high eccentricity
key roles of the moon
stabilise angle of axial tilit: 22.1-24.5 (mars chaotically tilits 0-60)
generates the lunar tides slows earths rate of rotation
obliquity
tilt
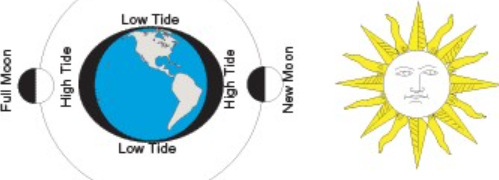
Neap tides
when moon and sun at 90 degrees
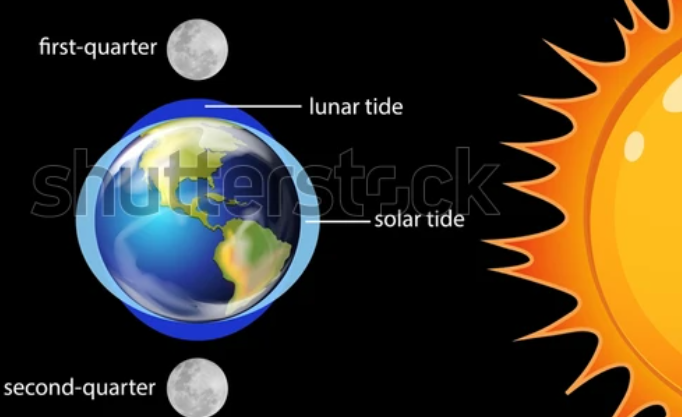
spring tides
when moon and sun aligned
intertidal zone
dynamic area of the seashore between the high tide and low tide marks, constantly exposed to air and submerged by water
key evolution for land-walking animals
perigee
moon closest to earth
apogee
moon furthest away from eath
moons orbital plane
inclined about 5.2° from the ecliptic
lunar eclipse
earth shadows moon
needs to be a new moon
solar eclipse
moon passes infront of sun
only a small spot on earth will see it
has to be full moon
stars formation:
when outward pressure from nuclear fusion of H to He balances gravitational collapse
Stellar nucleosynthesis
H to He stop at Fe-56
Rare earth factor
the crucial role rare earth elements have
galactic habitable zone
high metality - likely to have habitable life
small stars < 0.33 M(sun)
becomes a white dwarf
large stars 10x size of sun bigger
red giant phase
Nebular theory
Shockwave: trigger instability of nebula
collapse under own gravity
gravitational potential energy→ kinetic energy → heat
as size decrease rotate faster (conservation of angular momentum )
trigger star formation
sun forms centre of disk
dust→ pebbles→ rocky planets form and planetestimals
moon formed by another planet hitting earth
What changes with depth
pressure (P) - weight of overlaying rock increases
temp - heat generated in earths anteriror - radiocativity
temperature increase
Geothermal gradient
rate at which Earth's temperature increases with depth
determined by tetonic setting
P waves
compressed (solid and liquid)
S waves
shear - travel through solid but not liquid
2 types of earthquakes - solid earth (P and S waves)
seismological evidence for liquid outer core
drives earths magnetic field
outer core:
liquid iron-nickle sulfur
2,225 km thick
10-12 g/cm cubed
Inner core
solid iron- nickle alloy
13 g/cm cubed
solar wind
continuous stream of charged particles (plasma) — mainly protons and electrons
constantly flowing outward from the Sun's outer atmosphere (corona) at high speeds
carries the Sun's magnetic field throughout the solar system
solar wind distorts what
the magentosphere : teardrop shape
Magnetosphere
deflects most of the solar wind, protect from ionising radiation
Earths layers
Crust
Mantle
outer core
inner core
Lithosphere
crust and upper mantle
uppermost 100-150 km of Earth
rigid
Astenosphere
upper mantle below the lithosphere
shallow under oceanic lithosphere
deeper under continental crust
flows as a soft solid
Crust
Oceanic
continental
Oceanic
thinner
high density (floats lower)
Mafic (ballistic and gabroic) in composition,- less silica
Continental
thicker (thickest under mountains)
low density (floats higher )
felsic (granitic) to intermediate in composition, more silica