Neuro ch 7 vision
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
steve became depressed as his neurological condition
impairs his ability to perceive faces
t or f steve was able to get through elementary school by memorizing voices and mannerisms of the small amount of people he knew
t
steve’s disorder is called
prosopagnosia
prosopagnosia translates to
face ignorance
t or f patients with prosopagnosia use things like voice, gait, or hair to recognize others
t
t or f syratefies to recognizeothers when u have prosopagnosia develop later on
t
t or f its uncertain how many people struggle from prosopagnosia
t
1 in ____ people may suffer from prosopagnosia
50
prosopagnosia helps us understand
that visual processing involves many subcomponents
retina
neural structure at the back of the eye where visual perception happens
t or f most of the outer eye has the goal of focusing light onto the retina
t
pupil
opening in eye that allows light to get in based on its contraction or relaxation
size of pupil is controlled by the contraction or relaxation of
iris
iris
structure that contracts/relaxes and surrounds pupil
t or f the iris is pigmented so it determines eye color
t
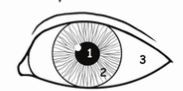
1
pupil
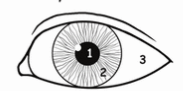
2
iris
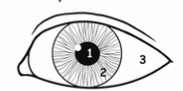
3
sclera
t or f pupil and iris are 2 most distinct feature of human eye
t
sclera
white part that surrounds iris
pupil and iris are a human obsession because
larger than other animals, sclera shows, we see where others are looking
main function of iris is to
control pupil size allowing control over amount of light entering
t or f the light from pupil/iris is sent to back of eye by lens to the retina
t
retina sends about _____ bits of information per second to the brain
10,000,000
to see your eye needs to transfer _____ into _______
(like action potential or neurotransmitters)
photons, signals brain can understandp
photons
particles of light
after photons are turned into signals, signals _______ areas in brainn to create a _______ scene
activate, visual
conversion of photons to signals happen int
retina
photoreceptor cells
contain (light absorbing molecule) Retinal that changes shape when photon collides with it
t or f shape change in retinal lead signals to travel from photoreceptor cells to other cells in retina and eventually the brain
t
2 types of photoreceptor cells
rods and cones
cones see ________
color vision
rods see _________
black and white visiont
t or f rods are only useful in dim light
t
t or f cones can adapt to greater illumination and continue sending info about photons theyre absorbing
t
t or f we only use cones during night
F
opsins
prompt absorption of different wavelengths of light
retinal iin cones are connected to _____ (retinal in rods is too but only _)
opsins, 1
we have three different cone types, each sensitive to specific wavelenght:
short (blue), medium (green), long (Red)
_% of men have some formof color blindness
8
___% of women have some form of color blindness
0.5
t or f the most common colorblindness is to green and red light and genes that encode colors are found in X chromosome
t
guys have 1 X chromosome while women have 2, so color issue is likely to _____ out in women but _____ in men
cancel, persist
red-green color blindness occurs in cones sensitive to green light creating problems in
discriminating green hues causing yellow and green to appear red
t or f some species have only one cone and thus have minimal colorvision
t
dogs only have
2 cones
dogs vision can be compared to a human with
redgreen color blindness
carrots are rich in ________which is used to make _________ which is important to healthy vision
beta-carotene, vitamin A
cones are responsible for _______ color and for gpod visual __________
distinguishing, clarity
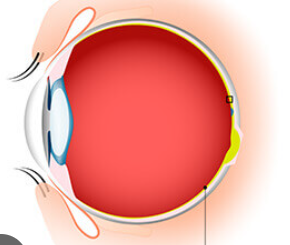
retina
t or f we instinctually turn towards light so it hits our fovea
t
fovea
area of highest cone density, found in retina, center of it contains no rods
photoreceptor cells pass sginal to
retinal ganglion cells
retinal ganglion cells
carry signal out of eye to brain
optic disc
where bundle of axons leave through
optic disc has no
rods or cones
t or f optic disc’s presence creates a blind spot in our visual field
t
the small blind spot from optic disc is hardly noticeable as your other eye…
fills in the missing information
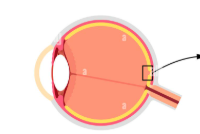
fovea
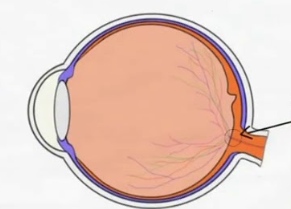
optic disc
optic nerve
carries visual information back to brain
optic chiasm
optic nerve from one eye meets the other (junction), mix and travel into brain
t or f the visual fields are also processed by opposite sides of the brian
t
visual signal goesfrom optic nerves to _______
thalamus
there are _ thalami
2
thalami is made up of as many as -___ smaller nuclei
50
thalamus is called gatekeeper or relay because it acts as a
stopping point for neurons that travel to cortex
t or f senses stop at thalamus except for smells
t
thalamus is also involvedin
analyzing and modifying info
Boerhaave observed a beggar with no skullcap, people would touch his cortex and B noticed
seeing stars/flashes of light, if more pressure blindness would follow, more pressure than that would result in loss of consciousness
Munk intentionally damaged parts of dogs occipital lobes, damage on small area resulted in ______, damage on large area resulted in ____
lack of recognition (no recall memories), blindness
psychic blindness
blind to importance of certain things
primary visual cortex
does intial processing for vision, goes herefollowing thalamus
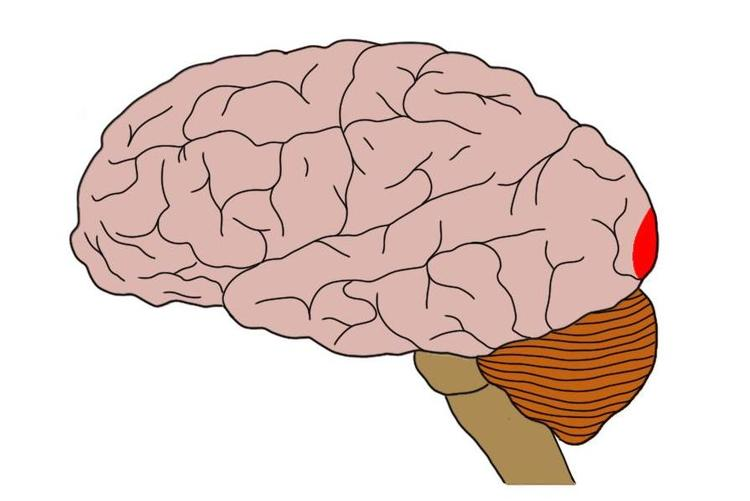
primary visual cortex
primary visual cortex can dealwith
orientation, depth, color, motion
LM has blood clot in brain and said she couldn’t see _______
movement
akinetopsia
without seeing movement
middle temporal visual area
devoted to processing movement related visual info
fusiform face area
important for recognition of faces
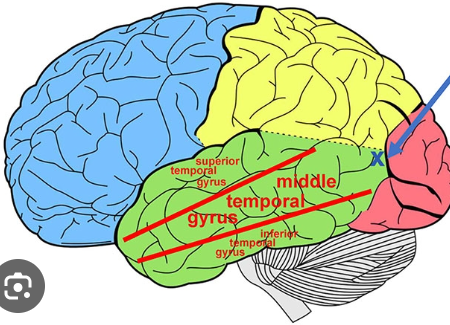
middle temporal visual area
little light green circle
fusiform face area
t or f what we see isn’t a perfect replica
t
saccades
short back and forth darting movements helping to gather information rapidly
t or f sometimes brain tries to speed up analysis environment by drawing on past experience or inferences
t
t or f many animals (rats, kitchen,koalas) would be considered blind by human standards
t
t or f watching TV up close can make you blind
F
most common causes of blindness
untreated cataracts
cataracts
accumulation of protein in lens that impedes passage of light to retina
In US, blindness is most caused by
diabetes
t or f diabetes can cause blindness by impairing blood vessel supply to retina
t
t or f blind people often rely more on other senses (sens of touch)
t
those who can see can hear up to ____ syllables a second while the blind can hear up to ___ a second
10, 22
Underwood had retinal cancer resulting in both eyes being removed, he could understand his surroundings by making
clicking noises that bounce back to tell him sizes and where the objects are (echolocation)
echolocation
sonar system used by animals to perceive environment by emitting sounds and interpreting the echoes
t or f bats are blind
F
Tim had difficulty making eye contact, showed little recognition, and saw things without anything being there and nothing when there were things
visual anosognosia (Anton-Babinski syndrome)
anosognosia
without knowledge of disease
visual anosognosia - around only __ cases have been identified since the 1960s
30