Electrostatics
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
Presence and flow of electron charges
Electricity
Electrical nature of matter
Electric charge
Symbol for Electric charge?…
q
What are the 2 general types of Electric Charge?…
Positive
Negative
True or False:
The Law of Magnetism states that like poles attract and opposite poles repel…
False
What is the SI unit of Electric charge?…
Coulomb
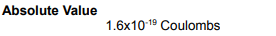
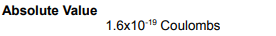
What are the 3 ways to transfer charge?…
Friction
Induction
Contact
When two different insulating materials are rubbed, electrons get transferred from one body to another…
Friction
A changing magnetic field induces an electric current in a conductor, converting mechanical energy into electrical energy, as seen in generators.
Induction
Energy transfers when two objects physically interact…
Contact
Material that allows electric current to pass through…
Conductor
Material that does not allow electric current to pass through
Insulator
Result of interaction between 2 charged particles…
Electric Force
True or False
If two electrically charged objects are moved farther away from one another, the force between them gets smaller…
True
True or False:
Gravity can be repulsive…
False
True or False:
Gravitational force acts by pulling objects together
True
True or False:
Electric force can attract objects together or pull them apart
True
True or False:
Electric force is vastly more powerful than gravitational force
True
Field that exists at a point where a test charge experience an electrostatic force…
Electric Field
Symbol for Electric Field?..
E
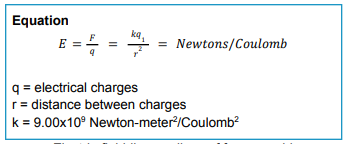
Equation for Electric Field (E)
_______ or lines of force provide a map of the electric field in the space surrounding electric charges
Electric field lines
Electric field lines are directed (to/away) from positive charges and toward negative charges.
away
True or False:
Number of lines leaving a positive charge or entering a negative charge is proportional to the magnitude of the charge
True
Energy needed to move a charge against an electric field?…
Electric Potential Energy
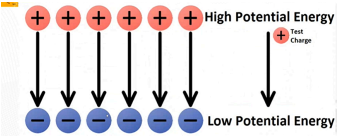
Electric potential energy is _______ energy present in electric charges…
stored
The capability of the charged particle to do work?…
Electric Potential
Unit for electric potential?…
Volt
Work done per unit of charge while moving the charge between two points in an electric field to move a test charge between two points…
Electric Potential Difference
_______ is required to push/pull a charged particle against an electric field of a charged body….
Work
Component that stores electric charge and energy?…
Capacitors
Electric potential produced by either electrochemical cell or by changing the magnetic field…
Electromotive Force
A Electromotive Force forces a unit 1._____charge to move from the 2.______to the 3._____terminal of the source. It 4._____ the two charges from each other
Positive
Positive
Negative
separates
_______ is used for the conversion of energy from one form to another…
Generator
Flow/Movement of charged particles…
Current
Unit for current?…
Ampere
True or False:
A current can be present even w/o an electric potential between 2 points?…
False
What are the 2 types of Electric Current?…
1.________
2.________
Direct Current
Alternating Current
What type of current is this?…
Charges move around the circuit in the same direction
Uni-directional
E.g. Batteries
Direct Current
What type of current is this?…
Charges move first one way and then the opposite way
Changes direction each half-cycle
E.g. household current
Alternating Current
Electron Flow is _____ to ______…
Negative to Positive
Conventional Current (Direction to the Current) is _____ to ______…
Positive to Negative
Conducting path that allows a charge to flow from one terminal to the other
Electric Circuit
Produces a potential difference which can then make charges move…
Battery
What are the 3 components of a circuit?..
Source
Wires
Loads
Measure of the opposition….
Resistance
What is the SI Unit of Resistance?…
Ohm
A wire or an electrical device that offers resistance to electrical flow…
Resistor
Property of the conductor due to which it offers resistance to the flow of current through it..
Resistivity
Rate at which electric energy is converted into another form such as mechanical energy, heat, or light…
Electric Power