TRANSPORT IN ANIMALS OVERALL
1/127
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
128 Terms
What are some features of a transport system?
Medium to carry substances, Pump, Valves,
What is the importance of medium to carry substances
liquid is able to dissolve substances
what is the importance of a pump in a transport system?
move the fluid
what is the importance of valves in a transport system?
maintain one way flow
What are some features that a transport system may have>
Respiratory pigments
System of vessels
Why might a transport system have respiratory pigments
increases volume of oxygen that can be transported
Why might a transport system have a system of vessels
System of vessels with a branching network allows distribution of the transport medium to all parts of the body
What are the two types of circulatory systems?
Open circulatory systems
Closed circulatory systems
Open circulatory system
the blood does not move around the body in blood vessels but bathes the tissue directly while held in a cavity called the haemocoel
Describe the vascular system of insects
Open circulatory system
Dorsal tube shaped heart
Respiratory gases not carried in blood
Why do insects not have respiratory pigments?
As oxygen diffuses directly into the tissues from the tracheoles so blood does not have respiratory pigments and does not transport blood
Closed circulatory system
Blood moves in blood vessels
Two types of closed circulatory systems
Single
Double
Single circulatory system
Blood moves through heart once in its passage around the body.
Fish:
Ventricles of the heart pump ____________ blood into the _____.
where capillary network reduces its __________,
oxygenated blood is carried into _________.
deoxygenated blood returns to _______ of the heart and blood moves to the ___________ and ______________ starts again
deoxygenated
gills
pressure
tissues
atrium
ventricle
circulation
Describe the vascular system of earthworms
Vascularisation
Closed circulatory systems
Respiratory gases carried in blood
Double Circulatory System
Blood passes through the heart twice in its circuit around the body
What circulatory systems do mammals have?
Double
What are the advantages of a double circulatory system
Maintains blood pressure around the whole body
Uptake of oxygen is more efficient
Delivery of oxygen and nutrients is more efficient
Blood pressure can differ in pulmonary and systemic circuits
Describe double circulatory system in humans
Pulmonary Circuit - heart and lungs
Systemic Circuit - heart to organs
Name the blood vessels
Arteries
Arterioles
Veins
Venules
Capillaries
Describe the pathway of blood through blood vessels
Heart
Arteries
Arterioles
Capillaries
Venules
Veins
Heart
What direction do arteries carry blood in?
away from the heart under high blood pressure
Adaptations of arteries
Thick, muscular walls
Elastic tissue
Narrow Lumen
How do thick muscular walls help with their function?
Handle high pressure without tearing
How does elastic recoil help arteries with their functions
allows recoil to prevent pressure surges
How does narrow lumen help arteries with their function
Narrow lumen to maintain pressure
What is the function of veins
Carry blood towards the heart under low pressure
What adaptations do veins have
Thin walls
Valves
Less muscular and elastic tissue
How does thin walls help veins with their function
Thin walls due to lower pressure
How do valves help arteries carry out their function?
Require valves to ensure backflow of blood doesn’t occur
How does less muscular and elastic tissue help veins in carrying out their functions
as they don’t have to control blood flow
What is the function of capillaries
Form a large network through the tissues of the body and connect the arterioles to the venules
Adaptations of capillaries
One cell thick
Very narrow
Numerous and highly branches
How do one cell thick walls help capillaries carry their function out?
short diffusion pathway
How does capillaries being very narrow help capillaries carry their function out?
So can permeate tissues
Red blood cells can lie flat against the wall, reducing the diffusion distance
How does capillaries being numerous and highly branched help capillaries carry their function out?
provides a large surface area
What is the function of arterioles
connect the arteries and the capillaries
Function of venules
Connect the capillaries and the veins
Relate the structure of arterioles and venules to their function:
Branch off arteries and veins in order to feed blood into capillaries
Smaller than arteries and veins so that the change in pressure is more gradual as blood flows to the capillaries
What are the four chambers of the mammalian heaty
Left atrium
Right atrium
Left ventricle
Right ventricle
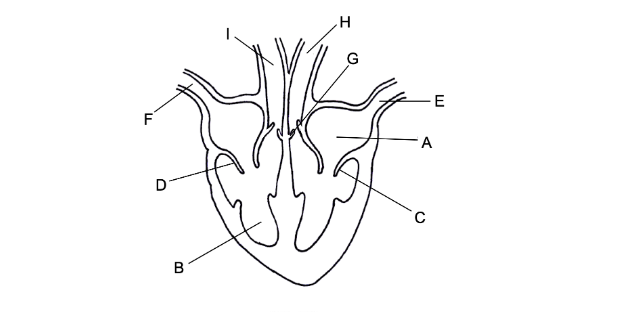
Identidy the structures below:
A - left atrium
B - right ventricle
c - bicuspid valve
d - tricuspid valve
e - pulmonary vein
f - vena cava
g - semi-lunar valve
h - aorta
i - pulmonary artery
Describe the pathway of blood around the body
PLLAVRRP
Pulmonary Vein
Left atrium
Left ventricle
Aorta
Vena Cava
Right atrium
Right ventricle
Pulmonary Artery
Where are the atrioventricular valves found and what is their function?
Found between atria and ventricles
Prevent the backflow of blood from the ventricles into the atria
What are the two types of atrioventricular valves?
Bicuspid (left side)
Tricuspid (right side)
Where are the semi-lunar valves found
Between the ventricles and arteries
Semi - lunar valves function
Prevent the backflow of blood from the arteries into the ventricles
What is the cardiac cycle?
describes the sequences of events of one heartbeat (contraction and relaxation)
Define the term systole
Where the heart muscle contracts
Define the term Diastole:
The stage of the cardiac cycle in which the heart muscle relaxes.
What stages does the cardiac cycle consist of?
Atrial Systole
Ventricular Systole
Diastole
Atrial Systole:
The atrium walls __________. Blood pressure in atria ________. This pushes the blood through ___________ and __________ down into relaxed ventricles
contract
increases
tricuspid
bicuspid
Ventricular Systole:
Ventricle walls _________ and increase blood pressure in the ___________.
Forces blood up through _______________ valves out of heart and into _____________ artery and aorta.
Blood cannot flow back as the valves are _________ due to high _____________ pressure.
Pulmonary Artery carries ____________ blood to lungs and aorta carries _____________ blood to the rest of the body.
contract
increases
semi - lunar valves
pulmonary
closed
ventricular
deoxygenated
oxygenated
Diastole:
The ventricles ________ therefore the volume of the ___________ increases. Pressure in the ventricles ________.
This risks blood in _____________ artery and aorta falling ________ into the ventricles.
relax
ventricles
falls
pulmonary
back
The atria also ________ during diastole so blood from _______ ______ and pulmonary veins enters _________ and cycle starts again
relaxes
vena cava
atria
Myogenic contraction
the heartbeat is initiated within the muscle cells themselves and is not dependent on the nervous or hormonal stimulation
The two sides of the heart work ____________. The atria contract at the _______ time, followed ____________ later by ventricles contracting together. A complete contraction and ___________ of whole heart which results in a _____________.
together
same
milliseconds
relaxation
heartbeat
When is the chamber emptied of blood
when it contracts W
When is the chamber filled with blood
when it relaxes
Atria walls have ________ muscle as blood only goes to _______________. Ventricle walls contain more muscle, generate more __________ as they have to send blood ___________ _______.
little
ventricles
pressure
further away
Why does the left ventricle have a thicker muscular wall?
Left ventricle has a thicker muscular wall than the right ventricle as it has to pump blood a short distance to lungs
What does the heartbeat being myogenic mean?
initiation comes from heart itself
What role does the sino atrial node play in initiating the heartbeat
acts as a pacemaker
sends wave of excitation across atria
causing them to contract simultaneously
What role does the layer of connective tissue play in initiating the heartbeat.
prevents waves of excitation passing down to ventricles
So the wave can pass to the atrioventricular node
where there is a delay to complete the contraction
What role does the atrio ventricular node play in initiating the heartbeat
sends impulses down the bundle of His to the apex of the heart
Where does the impulse then travel up?
branched Purkinje fibres
What role do the purkinje fibres play in initiating the heartbeat
simulate ventricles to contract from the bottom up which ensures all blood is pumped out
A: Pressure in atrium __________ as it contracts, ________ blood through ____-__________ valves into the ventricles. As atria empties the valves ______ _____
increases
forcing
atrio ventricular
snap shut
B: _________ of thick muscular walls increases pressure in the ____________ when pressure in the ventricle ________ pressure in aorta, the _____ _________ valve leading to the aorta is forced open and blood enters the _______ increasing __________.
Contraction
ventricle
exceeds
semi lunar
aorta
pressure
C: As __________ wall relaxes, pressure drops in ______ ventricle and aorta. The semi lunar valves ________ preventing blood flowing back into ventricle
_________ ________ of aorta walls increases pressure momentarily
ventricle
both
close
elastic recoil
D: As ventricles fully relax, ___________ in aorta walls causes atrio-ventricular valves to ______ and the ventricle to fill with ______.
contraction
open
blood
What does ECG stand for?
Electrocardiogram
The __________ activity that spreads through the heart during the ________ cycle can be detected using ___________ placed on the skin and shown on a _________ ray oscilloscope
electrical
cardiac
electrodes
cathode
What does the P wave show?
Depolarisation of atria - Atrial Systole W
What does the QRS wave show?
Spread of depolarisation through ventricles - Ventricular Systole W
What does the T wave show?
Repolarisation of ventricles - Diastole
Arrythmia
The heart beating at a wrong speed and wrong rhythm
Fibrillation
Irregular and often rapid rate
When does fibrillation occur?
when two upper chambers of your heart experience chaotic electrical signals
Myocardial Infarction
Heart attack or cardiac arrest
When does myocardial infarction occur?
when blood flow decreases or stops to the peart of a heart causing damage to heart muscle
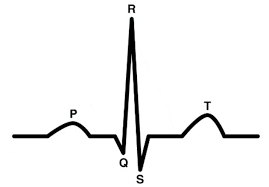
Normal ECG
Blood
tissue made of cells and plasma
Main function of red blood cells
transport oxygen from lungs to respiring tissue
Adaptations of red blood cells
Biconcave disks
Thin centre
No nucleus
Advantage of: Biconcave discs
Large surface area Advantage of:
Advantage of: thin centre
short diffusion pathway Advantage of:
Advantage of: no nucleus
more room for haemoglobin
Red Blood
Oxygenated B
Blue Blood
Deoxygenated
Oxygen Dissociation Curve:
Red blood cells _______ oxygen in the lungs where oxygen’s ________ pressure is high and haemoglobin is ___________ with oxygen. The cells carry oxygen to __________ tissue, there partial pressure of oxygen is _____.
load
partial
saturated
respiring
low
Foetal Dissociation Curve:
The haemoglobin in the blood of a foetus must ________ oxygen from __________ haemoglobin at placenta.
The foetus has haemoglobin that _______ which gives foetal haemoglobin a ________ affinity for oxygen than mother’s haemoglobin at the ________ partial pressure of oxygen.
Their blood flows very _____ in placenta so oxygen transfers to ________ blood and at any partial pressure of oxygen _____________ of the foetus blood is ___________ than the mother’s moving the whole dissociation curve to the ______.
absorb maternal
differs higher same
close foetus’ saturation higher left
Dissociation curve:
With an increase in _________, oxygen partial pressure in atmosphere ___________.
Llamas’ haemoglobin has a dissociation curve that is to the _______ of human hB. Its haemoglobin has a higher _______ for oxygen at _____ oxygen partial pressure so loads more oxygen more ________ in the lungs and releases oxygen when partial pressure is _____ in its respiring tissues.
altitude decreases
left affinity all readily low
What happens when CO2 concentration increases?
Haemoglobin releases oxygen more readily.
Why are points all lower on the curve
Haemoglobin is less saturated with oxygen at any oxygen partial pressure.
What does the shift account for?
unloading of oxygen from oxyhaemoglobin in respiring tissues where partial pressure of CO2 is high
Bohr Effect
The movement of the oxygen dissociation curve to the right at a higher partial pressure of CO2 because at a given partial pressure has a lower affinity for oxygen.
Chloride Shift
Diffusion of chloride ions from the plasma into the red blood cells, preserving electrical neutrality
How can carbon dioxide be transported?
Hydrogencarbonate ions - 85%
Combines directly to haemoglobin to make carbaminohaemoglobin - 10%
Dissolved in plasma - 5%
Where does the chloride shift occur
tissue capillaries