Biology Final (Test #4)
1/115
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
116 Terms
Variations of homologous genes that result in differences in structure and function are
alleles
An example of a genotype is Topic: Sec. 19.1
A) attached earlobes.
B) homozygous dominant.
C) brown hair color.
D) long fingers.
E) blood type AB.
B) homozygous dominant
Place the following in order from smallest, simplest, least complex, to largest and most inclusive. Topic: Sec. 19.1
A) chromosome, gene, genome, nucleotide
B) nucleotide, gene, chromosome, genome
C) genome, chromosome, gene, nucleotide
D) gene, nucleotide, genome, chromosome
E) nucleotide, gene, genome, chromosome
B) nucleotide, gene, chromosome, genome
The law of segregation states that
when gametes are formed in the parents, the alleles separate from each other so that each gamete gets only one allele of each gene.
The Punnett square is a useful tool for Topic: Sec. 19.2
A) determining the rate of segregation of alleles.
B) calculating how many mutations occur during DNA replication.
C) determining which genes or traits assort independently during gamete formation.
D) predicting the ratios of possible genotypes of a particular combination of alleles.
E) predicting the level of crossing over that will occur during meiosis.
D) predicting the ratios of possible genotypes of a particular combination of alleles.
The offspring resulting from a cross between a nearly white horse (cc) and a chestnut-colored horse (CC) is of an intermediate color (between white and chestnut). Which one of the following patterns of inheritance best explains this? Topic: Sec. 19.2
A) complete dominance
B) codominance
C) sex-linked
D) polygenic inheritance
E) incomplete dominance
E) incomplete dominance
The flower color in this plant is inherited by incomplete dominance. If a red flower that is homozygous dominant is crossed with a white flower that is homozygous recessive, the color of the offspring flowers will be expected to be Topic: Sec. 19.2
A) all red.
B) all pink.
C) all white.
D) 50% white and 50% pink.
E) 50% white and 50% red.
B) all pink.
Name / give example(s) of codominance in human traits
AB Blood type, sickle-cell anemia
A father is blood type B and a mother is blood type A. They have a child with blood type O. What are the genotypes of the father and mother? Topic: Sec. 19.3
A) The father must be BB and the mother must be AO.
B) The father must be BO and the mother must be AA.
C) The father must be BO and the mother must be AO.
D) The father must be BB and the mother must be AA.
E) This isn't possible.
C) The father must be BO and the mother must be AO.
In polygenic inheritance, Topic: Sec. 19.4
A) all individuals in the population are initially heterozygous for a particular trait.
B) the environment has no influence in phenotype expression.
C) the genotype makeup of individuals in a population is the only factor influencing phenotypes.
D) multiple alleles and genes contribute to a phenotype.
E) all traits are expressed as incomplete dominance.
D) multiple alleles and genes contribute to a phenotype.
The trend toward increased height and weight due to improved nutrition in certain human populations is an example of the effect of ________ on phenotypes. Topic: Sec. 19.4
A) gene linkage
B) the environment
C) codominance
D) polygenic inheritance
E) genetic disorders
B) the environment
12. What is the significance of crossing-over, independent assortment, and random fertilization?
an increase in the genetic diversity of gametes and zygotes
When is a phenotypic trait considered sex-linked?
the genes for the phenotype occur on X or Y chromosomes
If a piece of chromosome breaks off during mitosis or meiosis and does not reattach, the event is called Topic: Sec. 19.6
A) nondisjunction.
B) translocation.
C) dysplasia.
D) nondysplasia.
E) a deletion.
E) a deletion.
A person born with Edwards syndrome has a genotypic condition identified as Topic: Sec. 19.6
A) trisomy 21.
B) trisomy 18.
C) nondisjunction.
D) XO.
E) XXY.
B) trisomy 18.
16. When a piece of chromosome breaks off and reattaches at another site on the same or another chromosome, this is called Topic: Sec. 19.6
A) a deletion.
B) nondisjunction.
C) translocation.
D) nontranslation.
E) recombination.
C) translocation.
A(n) ______ refers to the complete set of DNA within the chromosomes of an individual.
genome
Failure of homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids to separate properly is called
nondisjunction
A(n) _____in a chromosome is often lethal and occurs when a part of chromosome breaks off or is lost.
deletion
During DNA replication, a(n) ________ added to a DNA template serves as the beginning site of nucleotide addition. Topic: Sec. 20.1
A) initiation codon
B) 5' OH end of sugar group
C) 3' OH end of sugar group
D) primer
E) poly A tail
D) primer
After a strand of DNA has been cut with restriction enzymes, the pieces are attached again by the action of Topic: Sec. 20.2
A) DNA ligases.
B) stop codons or sequences.
C) DNA polymerase.
D) plasmids.
E) primers.
A) DNA ligases.
During polymerase chain reaction, DNA amplification can come to an end Topic: Sec. 20.2
A) when there are no more free nucleotides.
B) once the DNA template is used up.
C) once the RNA template is used up.
D) as DNA polymerase is produced.
E) when the stop codon is added to the template.
A) when there are no more free nucleotides.
Bacterial _____DNA can be easily removed from the bacterium, modified by adding a gene of interest, and then reinserted into the bacterium to be replicated.
plasmid
A scientist is working in a lab sequencing DNA. After reading the results from a column of gel scanned in a fluoroscope, she determines that the sequence of bases in the newly synthesized DNA is AATTCCCGG. What would be the sequence of bases on the complementary strand?
TTAAGGGCC
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is useful for amplifying a small piece of DNA but is not a good technique for cloning genes because Topic: Sec. 20.2
A) DNA ligase cannot be used in PCRs.
B) PCRs do not generate palindromic sequences.
C) copies of DNA produced by PCRs lack the regulatory genes and proteins required to activate genes.
D) PCRs only generate primary transcripts that require excision of introns.
E) ribosomes are required to produce active genes.
C) copies of DNA produced by PCRs lack the regulatory genes and proteins required to activate genes.
26. What determines the specific segment of DNA that is amplified by PCR? Topic: Sec. 20.2
A) the plasmid used
B) the type of DNA polymerase
C) the use of DNA ligase
D) the source of nucleotides
E) the primers used
E) the primers used
27. Which one of the following enzymes catalyzes the attachment of nucleotides to a growing complementary strand? Topic: Sec. 20.2
A) restriction enzyme
B) DNA polymerase
C) plasmid
D) DNA ligases
E) transgenic
B) DNA polymerase
28. The following are steps involved in producing recombinant DNA using human DNA and a plasmid. What is the proper order of these steps? Topic: Sec. 20.2
1. select bacteria that contain human DNA
2. isolate and purify DNA to be recombined
3. add DNA ligase to join human DNA with plasmid
4. cut human DNA and plasmid with restriction enzyme
5. introduce new plasmid to bacteria
4, 1, 5, 2, 3
29. When DNA fragments from different sources are mixed together, they begin combining with each other due to Topic: Sec. 20.2
A) complementary base pairing.
B) the action of restriction enzymes.
C) a change in pH.
D) electrical currents present in the mixture.
E) a change in temperature.
A) complementary base pairing.
30. Which one of the following human proteins, produced by transgenic bacteria, is used to prevent or break down blood clots? Topic: Sec. 20.3
A. insulin
B. tissue plasminogen activator
C. erythropoietin
D. growth hormone
E. factor VIII
B. tissue plasminogen activator
31. To synthesize DNA in a laboratory, the enzyme called DNA _____ must be used to facilitate the addition of nucleotides on the new strand. Topic: Sec. 20.1
polymerase
In recombinant DNA technology, DNA is cut at specific nucleotide sequences by _____ enzymes. Topic: Sec. 20.2
restriction
Small, circular DNA molecules that are located outside the main chromosome of bacteria and are capable of self replication are _____.
plasmids
Short single-stranded pieces of DNA called _____attach to a DNA template to serve as the beginning site of DNA replication. Topic: Sec. 20.1
primers
______ is a useful technique in criminal investigations because humans contain many copies of repeating or junk sequences, the length of which can be unique to an individual. Topic: Sec. 20.2
DNA fingerprinting
The zona pellucida and corona radiata are associated with which one of the following? Topic: Sec. 21.1
A. human egg
B. uterine lining
C. midpiece of the human sperm
D. cilia of the oviducts
E. vaginal wall
A. human egg
The figure below shows a human sperm. Which part of the sperm contains the most mitochondria for generating ATP?
B
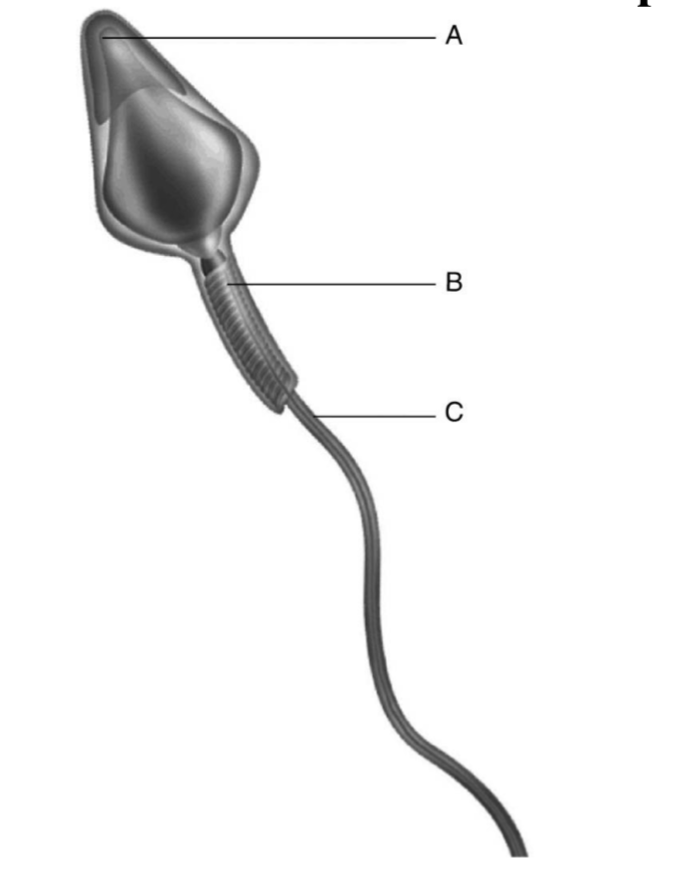
Fertilization is generally considered complete when the Topic: Sec. 21.1
A. zygote enters the uterus.
B. sperm reaches the zona pellucida.
C. ovulation is inhibited.
D. placenta begins to form.
E. haploid sperm unites with the mature ovum.
E. haploid sperm unites with the mature ovum.
When a sperm cell enters a secondary oocyte, what event in the oocyte is immediately triggered? Topic: Sec. 21.1
meiosis II
To penetrate the zona pellucida of the ovum, the sperm Topic: Sec. 21.1
A) uses the swimming action of the flagellum to move inside the egg.
B) releases digestive enzymes from the acrosomal cap.
C) releases a hormone that signals the egg to dissolve the thick coating.
D) passes down a channel in the protective layer to reach the egg membrane.
E) stimulates opening of ion channels along the egg membrane by releasing sodium ions from the acrosomal cap.
B) releases digestive enzymes from the acrosomal cap.
While normally one secondary oocyte ruptures from an ovarian follicle at ovulation, what will be the result if two are released and both are fertilized? Topic: Sec. 21.2
A) identical twins
B) single birth because only one secondary oocyte can be fertilized
C) single birth because even though both may be fertilized, only one will be able to complete development
D) fraternal twins
D) fraternal twins
The first four days of human embryonic development occur in the Topic: Sec. 21.2
A) uterus.
B) vagina.
C) cervix.
D) oviduct.
E) ovary.
D) oviduct.
Name the process by which an embryo undergoes rapid changes in form and shape.
Morphogenesis
There are a series of cell divisions that produce no cell growth during the first four days following fertilization. Name this process.
Cleavage
All of the following processes are associated with embryonic development EXCEPT which one? Topic: Sec. 21.2
A) cleavage
B) meiosis
C) morphogenesis
D) differentiation
E) growth
B) meiosis
During the development following fertilization, the morula becomes a hollow ball of cells called ________
blastocyst
The blastocyst begins to form a second hollow cavity that will eventually become the Topic: Sec. 21.3
A) placenta.
B) fundus.
C) amniotic cavity.
D) embryonic disk.
E) embryo.
C) amniotic cavity.
What event marks the end of the pre-embryonic period and the beginning of the embryonic period?
the formation of the ectoderm and endoderm in the embryonic disk
The blood vessels of the umbilical cord are derived from which one of the following structures? Topic: Sec. 21.4
A) allantois
B) chorion
C) embryonic disk
D) amnion
E) yolk sac
A) allantois
Mesoderm gives rise to
muscle and connective tissues
The placenta forms from embryonic tissue and Topic: Sec. 21.4
A) bone marrow.
B) amniotic fluid.
C) the embryonic disk.
D) endometrium.
E) the yolk sac.
D) endometrium.
Which one of the following embryonic features is the forerunner of the brain and spinal cord? Topic: Sec. 21.4
A) pharyngeal arches
B) somites
C) yolk sac
D) neural groove
E) chorionic villi
D) neural groove
The muscles and nervous system of the fetus become mature enough for movement to occur by the _____ month of development.
fifth
Which organ system is not functional until birth and must become fully functional immediately?
Respiratory system
Which cardiovascular structures in the fetus shunt blood away from the fetal lungs?
foramen ovale and ductus arteriosus
Oxytocin from the mother's pituitary gland targets what organ to begin contractions?
Uterus
Name the hormone that triggers the sequence of events referred to as "labor."
ACTH
Describe the action/function of Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone (GnRH) during puberty.
LH and FSH stimulate the production of sex hormones
59. The development of an embryo involves four processes. Match each process to its description.
A) cleavage
B) growth
C) differentiation
D) morphogenesis
1) cells increase in number and size
2) cells divide rapidly, resulting in a ball of unspecialized cells
3) cells take on a certain structure and function
4) embryo undergoes rapid change in shape and form
A2, B1, C3, D4
For sperm to be able to penetrate the zona pellucida of the egg, enzymes are released from the_____
acrosome.
The formation of the _____ cavity and the differentiation of the embryonic disk into ectoderm and endoderm occurs at the end of the pre-embryonic period of development.
amniotic
Which extra-embryonic membrane is the source of germ cells that eventually develop into gametes?
yolk sac
One hypothesis for why we age, or at least why our cells age, is that every time that mitosis occurs, _____ at the ends of chromosomes shorten, and eventually the cell runs out of these units at the ends of chromosomes.
telomeres
A) umbilical vein
B) ductus arteriosus
C) umbilical artery
D) ductus venosus
E) foramen
11) opening located between the right atrium and the left atrium
12) structure that transports oxygenated blood from the placenta to the fetus ovale
13) shunt between the pulmonary artery and the aorta that causes most of the blood to bypass the lungs
14) structure that transports deoxygenated blood from the fetus to the placenta
15) shunt that bypasses the liver
A14, B13, D12, E11
There are several sources of scientific evidence to support the theory of evolution. Match each of the following to its description.
A) comparative biochemistry
B) fossil record
C) comparative embryology
D) taxonomy
E) comparative anatomy
1) study of the structure of molecules to infer evolutionary relatedness of organisms
2) study of homologous and analogous structures
3) branch of science that focuses on classifying and naming life-forms
4) preserved remains of organisms
5) study of the early development of organisms
A1, B4, C5, D3, E2
List the characteristics of fossils / fossil records
Fossils are made from once-living organisms.
Fossils are made of rock that replaced the body of the organism or filled in an impression left by the organism.
Fossils are typically made from sedimentary rock rather than igneous or metamorphic rock.
Fossils are formed from plant matter or bones of an organism because soft tissue decays before a fossil is formed.
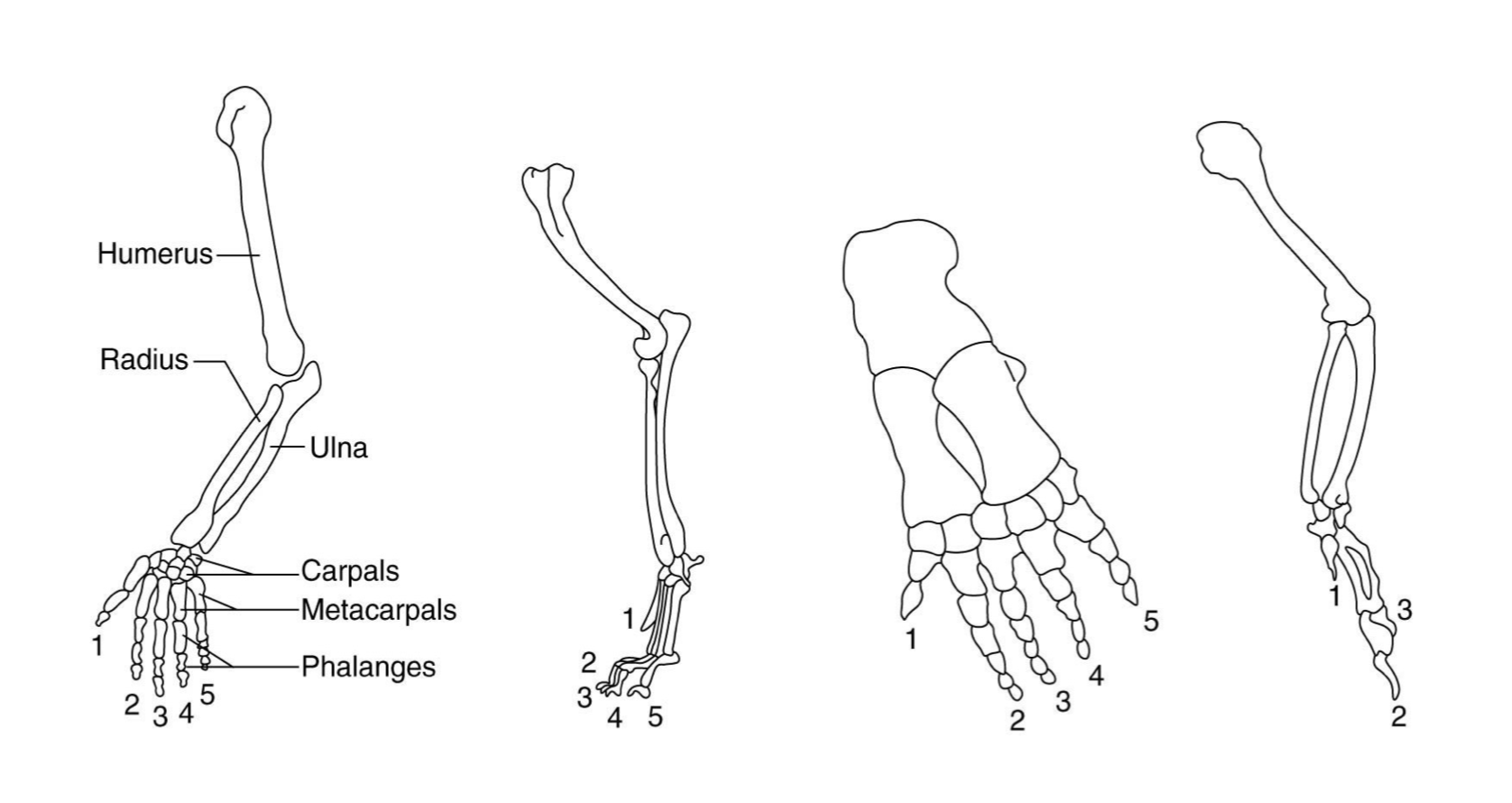
The figure below shows the skeletal structure of the forelimbs of several vertebrates. Because these skeletal elements are similar in form and are believed to have evolved from a common ancestral structure, they are said to be_____
homologous.
When two species contain identical or nearly identical molecules such as proteins, this suggests Topic: Sec. 22.1
A) genetic modification has occurred to the populations.
B) the two species share a common ancestry.
C) the two species are in fact only one species displaying divergent evolution.
D) the two species are in fact only one species displaying convergent evolution.
E) the two species overlap in niches and likely share a common diet.
B) the two species share a common ancestry.
The wings of birds and insects share similar functions but evolved from different structures. These wings are said to be_____
analogous
The process of ________ has had a major impact on species distributions worldwide. Topic: Sec. 22.1
A) continental drift
B) comparative biochemistry
C) genetic engineering
D) divergent speciation
E) adaptive mobility
A) continental drift
Cytochrome c is a small protein that is found in present-day organisms. Comparison of the structure of cytochrome c from different organisms to infer evolutionary relationships would be part of the science involving
A) fossil evidence.
B) developmental biology.
C) comparative biochemistry.
D) migration patterns.
E) comparative anatomy.
C) comparative biochemistry.
Differences in populations may arise over time when physical structures in the environment, such as mountains or large bodies of water, change. These structures are referred to as
A) Pangaea.
B) continental drift.
C) macroevolution.
D) geographical barriers.
E) micro-isolation bottleneck effect.
D) geographical barriers.
Anatomical parts of the body that serve little or no function are referred to as _____
vestigial structures
The theory that individuals with certain traits are more fit for their local environment and therefore are more likely to survive and reproduce is known as ______
natural selection
In each local environment, populations of living organisms have evolved to possess the traits necessary to survive and reproduce. This concept is called _____
natural selection
The figure below shows an evolutionary tree. At which of the following locations (Label A, B, C, or E) does this map indicate extinction?
A and D
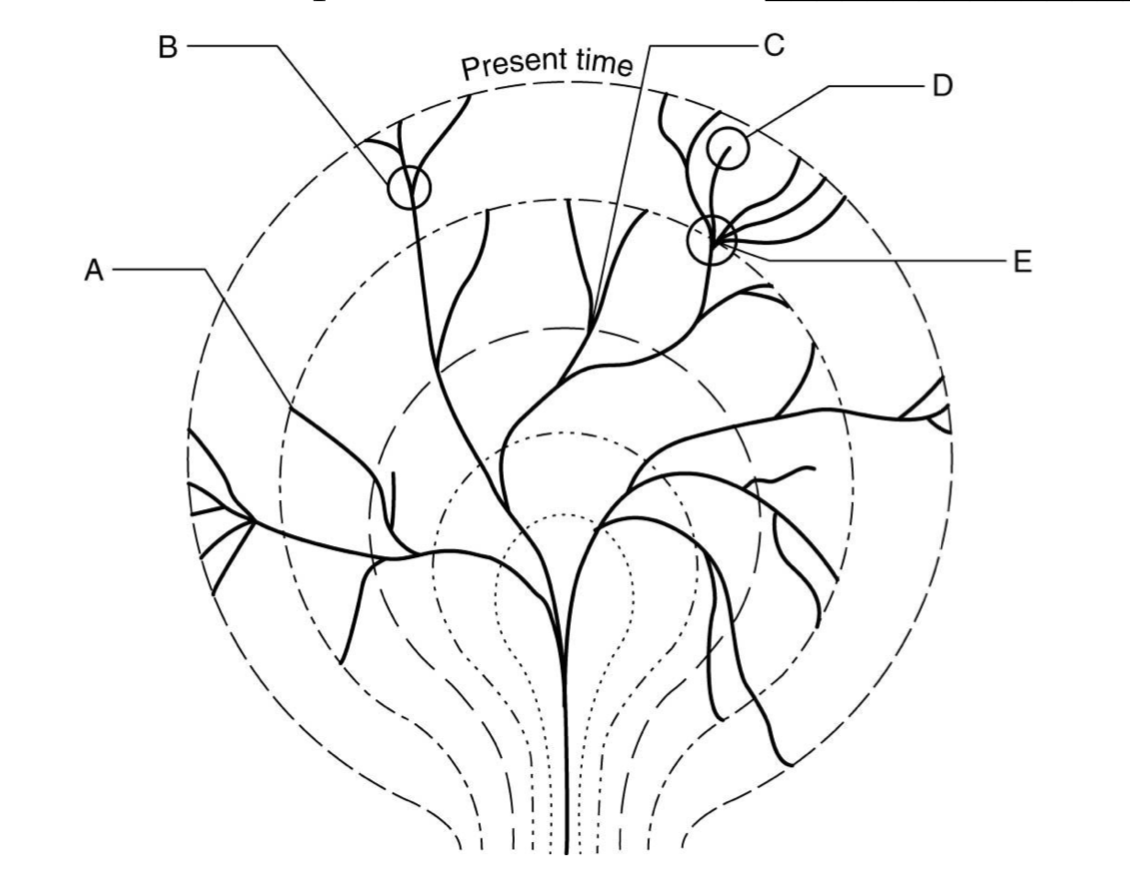
Movement of individuals into or out of the population, called gene flow, impacts evolution of populations because Topic: Sec. 22.2
A) it can lead to extinction of one or more populations.
B) it may cause genetic drift.
C) it leads to a redistribution of alleles.
D) adaptive radiation results.
E) a founder effect will occur.
C) it leads to a redistribution of alleles.
When conditions are right, many new species may develop in a relatively short period of time from a single ancestor. Such short bursts of evolutionary activity are called Topic: Sec. 22.2
A) gene flow.
B) adaptive radiation.
C) the founder effect.
D) population explosion.
E) genetic drift.
B) adaptive radiation.
Which one of the following processes tends to mix gene pools? Topic: Sec. 22.2
A) gene flow
B) the bottleneck effect
C) founder effect
D) continental drift
E) adaptive radiation
A) gene flow
The first step in the development of living organisms was the formation of Topic: Sec. 22.4
A) DNA.
B) organic molecules from gases in the atmosphere.
C) enzymes.
D) inorganic molecules from elements in the ocean waters.
E) simple sugars.
B) organic molecules from gases in the atmosphere.
The following is a list of events that were involved in the formation of self-replicating living cells. What is the sequence / order of the events that best represents the order in which these events are believed to have occurred?
1. formation of RNA
2. enclosure of small organic molecules within a membrane
3. formation of simple organic molecules from atmospheric gases
4. formation of a lipid-protein membrane
3,1,4,2
Name the process that describes the ability to extract oxygen from the environment and use it to make energy.
Cellular respiration
Why are humans classified as hominoid?
Humans have bodies that are genetically and structurally very similar to those of the Great Apes and so we are classified in the Great Apes sub-group which is also known as the hominids (Family Hominidae).
In the history of Earth and in the evolution of living cells, two self-replicating molecules have formed: DNA and RNA. Determine whether each of the following characteristics can be attributed to DNA or RNA. Answers may be used more than once.
A) both DNA and RNA
B) DNA
C) RNA
10) molecule that directs production of proteins in modern cells
11) molecule first formed on templates of clay in mudflats,13) first molecule to evolve
12) the self-replicating molecule of present-day cells
13) first molecule to evolve
14) more stable of the two molecules
A10, B12, B14, C11, C13
The process of evolution ultimately depends on changes that occur in the _____ of organisms.
DNA
When considering evolution, structures of present-day organisms that have the same function but did not develop from the same ancestral structure are said to be ______.
analogous
The early embryos of vertebrates follow the same pathway of development; one structure that all vertebrate embryos have in common is the _______, which serves as a primitive support structure.
notochord
Movement of individuals into or out of population that results in a redistribution of alleles is called ______.
gene flow
Darwin's proposal that organisms that are better suited to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce is termed _______
natural selection
_______refers to random changes in allele frequency as a result of chance events.
genetic drift
The early atmosphere of Earth did not contain the gas________; it is believed that life as we know it would not have evolved if this gas had been present.
O2
The process of producing energy from organic substrates in the absence of oxygen is called _______ metabolism.
anaerobic
As geographically isolated human subpopulations became adapted to different environments over time, different phenotypes resulted, causing the evolution of various human _____
races.
List / describe effects of rising atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gasses
produces a positive climate forcing, or warming effect
95. Name the two countries that are the largest emitters of greenhouse gasses
United States and Russia.
The major concerns regarding the effects of air pollution fall into the areas of smog, acid rain, destruction of the ozone layer, and Topic: Sec. 24.1
A) pesticides.
B) sustainable development.
C) global warming.
D) chlorofluorocarbons.
E) denitrification.
C) global warming.
Why are gases such as nitrous oxide and carbon dioxide are called greenhouse gases
permit sunlight to enter but trap the heat energy in the atmosphere
Example(s) of pollutants that can destroy the ozone layer
CFCs, halon, CCI4
Name / list the main human activities that have raised atmospheric CO2 levels
Burning fossil fuels, releasing chemicals into the atmosphere, reducing the amount of forest cover, and the rapid expansion of farming, development, and industrial activities
Describe / define “greenhouse effect”.
The process in which heat is trapped near Earth’s surface by substances known as greenhouse gasses.