a&p lab practical 2 (bones)
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
the axial skeleton consists of:
skull
hyoid bone
vertebral column
ribs
sternum
auditory ossicles
the appendicular skeleton consists of:
pectoral girdle
clavicle
scapula
upper limb
humerus
radius
ulna
carpals
metacarpals
phalanges
lower limb
femur
patella
tibia
fibula
tarsals
metatarsals
phalanges
process
general term for projection from the surface of the bone
tubercle
a relatively small bump on a bone
tuberosity
relatively large, rough area on a bone
spine
short, sharp projection
condyle
a smooth surface that articulates with another bone
epichondyle
projection above a chondyle
head
a terminal projection that articulates with another
neck
constriction below the head
crest
an elevated ridge of bone
line
smaller elevation than a crest
facet
smooth, flat face
trochanter
a large bump (on femur)
greater or lesser
foramen
a shallow hole
sinus
cavity
meatus or canal
deeper hole
fossa
a depression in a bone
notch
a deep cut out
groove or sulcus
elongated depression
fissure
long, deep cleft
epiphysis
proximal and distal ends of long bone
epiphyseal plate
line of hyaline cartilage that increases in thickness with the division of chondrocytes
diaphysis
shaft of the long bone
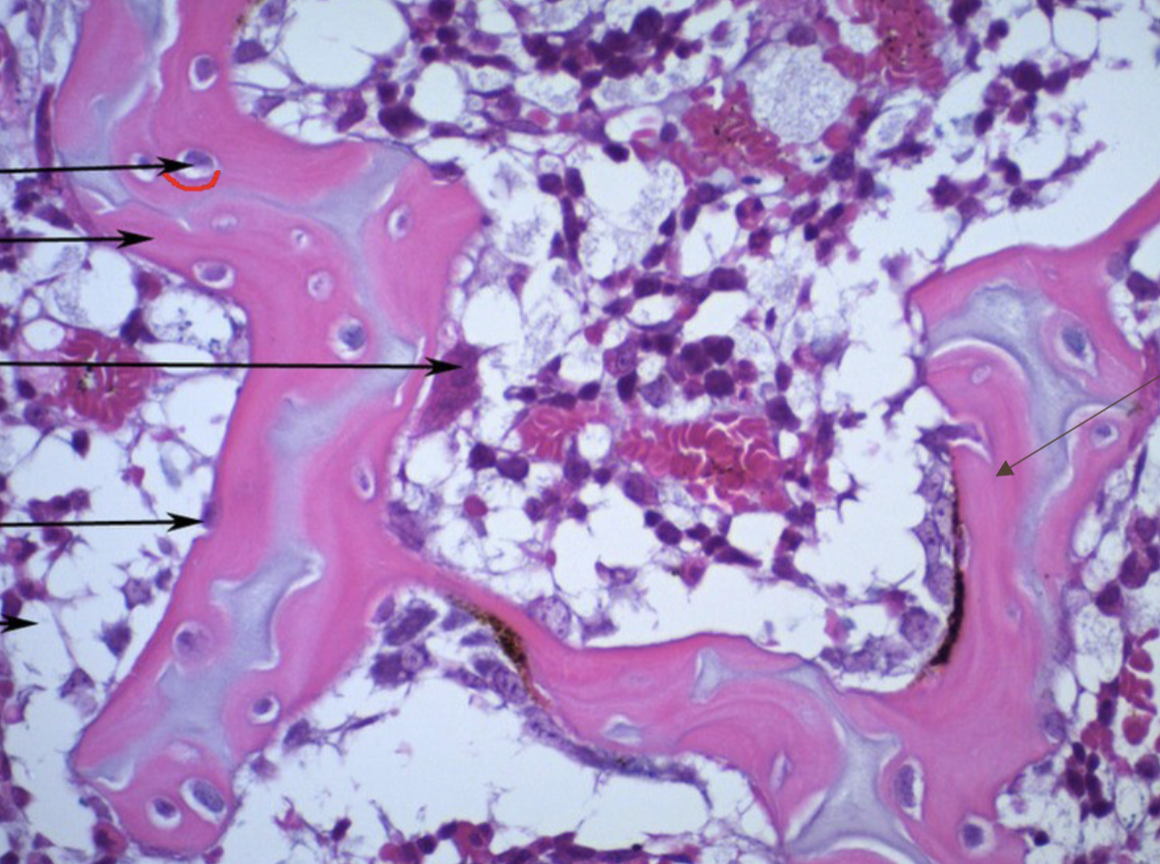
spongey bone
cancellous
porous, lattice like structure
provides strength and reduces weight
inner most bone type
made of trabeculae: thin rods of bone that run parallel with stressor
compact bone
cortical
dense, hard outer layer
provides strength and skeletal protection
yellow bone marrow
adipose containing
soft, spongey
found in hollow center of long bones
red bone marrow
hematopoietic (blood forming)
spongey, soft tissue
as person ages, red marrow changes to yellow
found in long bones, ribs, skull, spine, and pelvis
articular cartilage
found in epiphysis at ends of long bones
composed of hyaline cartilage and helps reduce friction at ends of joints
periosteum
dense connective tissue that covers the outer portion of bone
where nerves and blood vessels are located
anchoring point for tendons and ligaments
osteon
modular unit of bone
central canal of osteon
hole in the middle of osteon
houses blood vessels and nerves in dense bone tissue
typically runs vertically
osteocytes of osteon
mature bone cells
respond to stress on bone and remodel bone in response
lacunae of osteon
small cavities that contain mature bone cells
houses osteocytes
canaliculi of osteon
thin tubes that connect lacunae
provides passageway through dense bone material
3 types of lamellae:
concentric
interstitial
circumferential
concentric lamellae
cylindrical layers of bone matrix that surround central haversian canal
interstitial lamellae
irregularly shaped bone tissue remains that fill spaces between osteons
circumferential lamellae
thin, flat layers of bone matrix that wrap completely around the circumference of bone shaft
long bones
longer than they are wide with prominent shaft and two ends
femur
tibia
fibula
humerus
radius
ulna
phalanges
short bones
cube-like shape
carpals
tarsals
flat bones
thin, broad, sometimes curved
skull bones
ribs
sternum
scapulae
pelvic bones
irregular bones
complex in shape
vertebrae
pelivs
skull bones
hyoid
mandible
maxilla