Business Leadership exam Su
1/293
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
294 Terms
The Abbreviation for The Big 5 Personality Traits
OCEAN
What are the components of OCEAN?
Openness, Conscientiousness, Extroversion, Agreeableness, Neuroticism
OCEAN: Extroversion determines
ones comfort level with relationships
Extroverts Tend to..
be friendlier and outgoing, spend much of time maintaining and enjoying a large number of relationships
Introverts
tend to be reserved and have fewer relationships, comfortable with solitude
OCEAN: Agreeableness is
the degree to which someone is good-natured, cooperative, and trusting
An Agreeable person ___
gets along with others, agrees to everything, is helpful
Disagreeable people are…
are source of conflict and discomfort to others
OCEAN: Conscientiousness is..
the degree to which someone is responsible, dependable, and carefulorganized, goal-oriented, and disciplined.
A conscientious person focuses..
on what can be accomplished and meets commitments (organized, order, starts crucial tasks rights away)
A person who lacks conscientiousness is..
careless, often tryin to do too much and failing or doing too little
OCEAN: Neuroticism is..
degree to which someone is relaxed, secure, and unworried
A person who is neurotic..
is emotionally unstable, anxious, nervous, tense
A non-neurotic person is…
emotionally stable, confident
OCEAN: Openness is
degree to which someone is curious, open to new ideas, and imaginative
An open person is..
broad-minded, receptive to new things, open to change
A Person who lacks openness (is closed off)..
is narrow-minded, has few interests, resistant to change
Big Five traits, It’s relevance, and influence
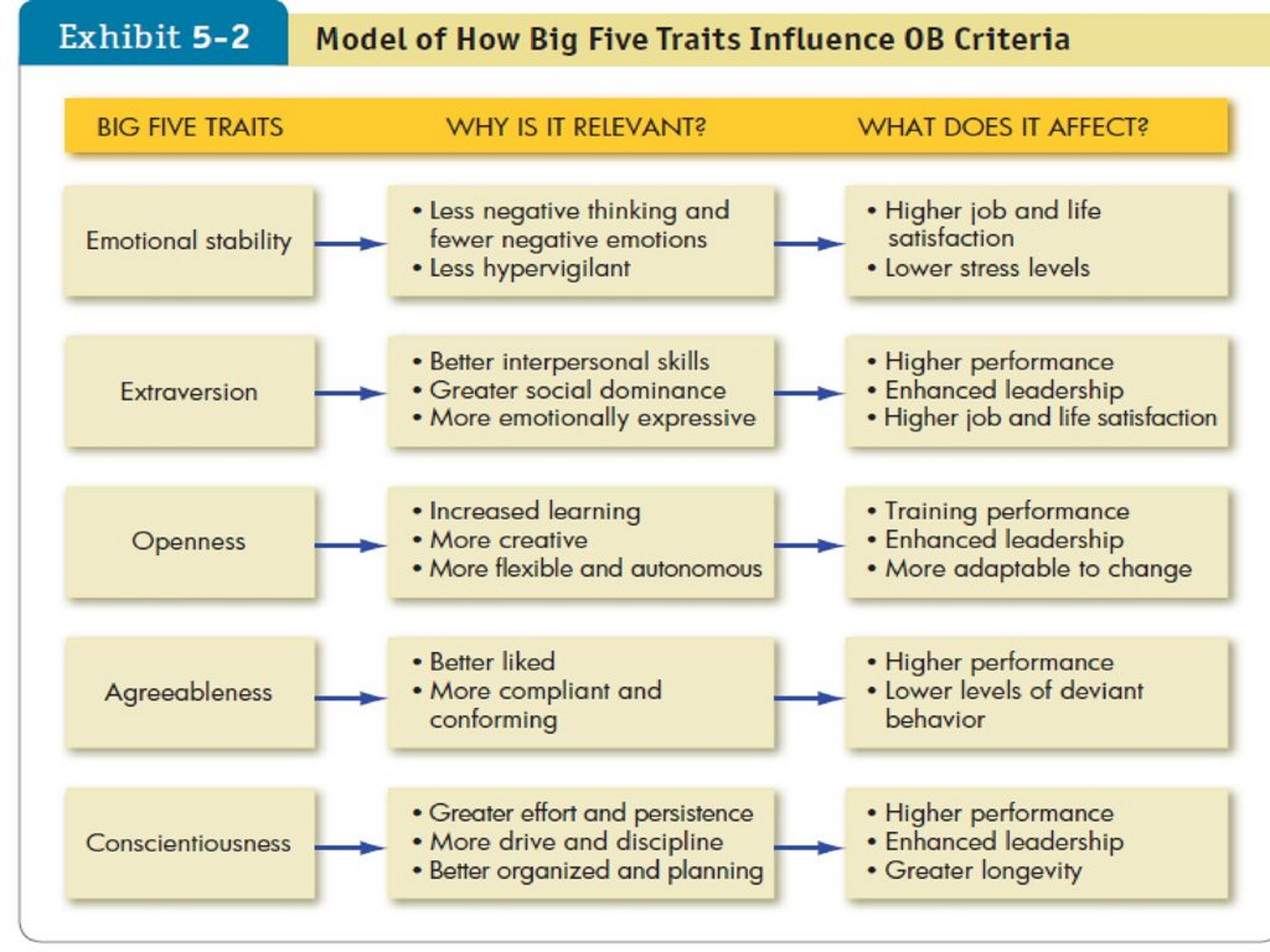
Emotional Intelligence Definition
ability to read one’s own and other’s emotions, and be able to understand, label, express, and regulate them. It involves self-awareness, self-regulation, motivation, empathy, and social skills.
Characteristics of Emotionally Intelligent People
empathetic, can look at things with alternate perspective, open-minded, persevere, bounce-back from challenges
Four functions of management
planning, organizing, controlling, leading
3 Eras of Management Are
1. Classical Management
2. Behavioral/Human Relations Management
3. Modern Management
Time Frame of Classical Management
1900-1920
Classical Approach to Management entails workers to be..
-expected to be rational
- consider opportunities, take whatever needed to get monetary and personal gain
Classical Approach has a system...
a rigid system of hierarchy, specialization of tasks and financial incentives
Theories Under Classical Management and Who's responsible
1. Scientific Management (Fredrick Taylor)
2. Administrative Principles (Henri Fayol)
3. Bureaucratic (Max Weber)
Fredrick Taylor
1856-1915
Father of Scientific Management
Scientific Management Theory Believes
There is one best way to do a job
Scientific Management Emphasizes (3)
Emphasizes the use of time and motion methods to improve productivity and efficiency in the workplace
- efficiency, time studies, and job specialization
Scientific Management Objectives
science, harmony, cooperation, maximum output, development
- maximum output and efficiency/productivity is extremely important
Time and Motion Studies Steps (S.M)
breaking the task into motions, analyzing for efficiency, eliminate motions, combine with time study to develop workflow, improve speed and ergonomics
Pig Iron Experiment (S.M, T&M)
studied how much iron workers would carry
- broke tasks down, and timed ea.
- found optimal way to increase productivity
later recognized shovel decreases efficiency, changed that to improve
Scientific Management Application
- applied in factories and assembly lines
- managers planned, workers executed
Criticisms of S.M (5)
- ignored human emotion, creativity
- workers = mechanics, reducing humanity
- motivation based on solely $$
- work environments were too inflexible
- lead to burnout
Relevance of S.M today
- influences manufacturing and operations
- time-motion studies are still used
- now must be balanced with humanity and collaboration
Where is S.M still applied
Food Service (assembly line)
Retail (Inventory)
Customer Service (Call Centers)
Why is S.M related to Science?
- applied systematic, date-driven methods to improve efficiency
- work can be studied, measured, and optimized like scientific experiments
Henri Fayol
(1841-1925)
Father of Modern Management + Classical Management
- French
- mining engineer + management theorist
- one of fist to analyze managerial behaviour scientifically
Administrative Principles Believes
- specific tasks enhance employee efficiency + skill development
- multi-tasking = overwhelms
Administrative Principles Began As..
solution to difficulties managing big companies during the industrial revolution
How Many Principles of Management in Adminstr. Principles theory
14
Key 4 Admin. Principles
Unity of Command. Remuneration, Scaler Chain, Espirit de Corps
All 14 Principles
1. Division of Work
2. Authority
3. Discipline
4. Unity of Command
5. Unity of Direction
6. Subordination of Individual Interest
7. Remuneration
8. Centralization
9. Scalar chain
10. Order
11. Equity
12. Stability of Tenure
13. Initiative
14. Espirt de Corps
Scalar Chain Concept
shows how organizations are structured
- stresses clear communication between management levels
Scalar Chain Concept Emphasizes
flow of authority and information up and down the chain
Scalar Chain Concept: Gang Plank
in case of emergencies a subordinate of one line of authority can communicate with another subordinate of another line of authority
Unity of Command
employees should receive order from only one superior
Unity of Command Aims to...
prevent confusion and conflicting instructions
- ensures clarity and efficiency in decision making + execution
Espirt de Corps
- team spirit or group morale
- Fayol: idea that managers should work to build harmony, unity, and strong sense of belonging
Remuneration
- payment or compensation employees receive for their work, includes wages, salaries, bonuses, benefits, and other rewards
Fayol's 5 Primary Functions of Management
1. Planning
2. Organizing
3. Commanding
4. Coordinating
5. Controlling
(++ Forecasting)
Influence of Fayol's Theory, Adminstr. Princps.
- Influenced early 20th century business practices
- basis for administrative theory
- taught in business schools (1900s_
Implementation in the Workplace (A.P - Fayol)
- used in large organizations
- applied in military, government, corporate settings
- promote clearer chains of command
Criticisms of Administrative Principles - Fayol (4)
- too rigid and hierarchical for modern organizations
- ignores human motivation and group dynamics
- emphasizes on efficiency + profits
- not ideal for innovative or agile companies
Relevance of Administrative Theory Today
- useful for core function for management
- still used in structured environments
needs adapting for modern workplaces
Max Weber
1864-1920
Father of Sociology
Bureaucratic Theory Emphasizes
formal system of organization and administration designed to ensure efficiency and effectiveness
Bureaucracy =
is rational efficient form of organization founded on logic, order and legitimate authority
Weber Believed Bureaucracy was..
ideal type of organization to maintain order in complex societies
Motivators for Bureaucracy
industrial revolution transformed workspaces
- there was problems with favoritism, disorganization and lack of clear roles
- weber was interested in industrial capitalism
6 Principles of Weber's Theory
1. Task Specialization
2. Hierarchical Authority
3. Formal Selection
4. Rules and Requirements
5. Impersonality
6. Career Orientation
6 Principles of Weber's Theory: Task Specialization
Each Person is matched with what they do best
- specialized roles/tasks improve efficiency
- overstepping = NG
6 Principles of Weber's Theory: Hierarchical Authority
Clear levels of command
- supervises those below them, subject to control of level above
6 Principles of Weber's Theory: Formal Selection
Employees chosen based on technical skills and competencies
- education, experience, training
- position determines salaries
6 Principles of Weber's Theory: Impersonality
Relationships are professional, objective
- NO FAVOURTISM
6 Principles of Weber's Theory: Career Orientation
- achievement, experience --> promotions
- merit based achievements
- personality not a factor
Pros of Bureaucracy
Provides Systematic Framework for organizing, managing government institutions
- helps professionalize management and shape the managerial environment for many years
How is Bureaucracy Relevant or Seen in Today's Society
- still used in governments, schools, hospitals, large corporations
- promotes fairness and equity
Hierarchical authority still exists heavily in many organizations
- some things need rigid structure (govs, systems)
Criticisms of Bureaucracy
- too rigid and slow to adapt
- can reduce creativity
"Red Tape" and excessive paperwork
Behavioural Management/Human Relations Movement era
1920-1950s
Stimulants for B. Management/Human Relations Movement
Bigger Organizations + Human Metter More
Focus of Behavioural M. + Human Relations
Focuses on Human side of workplace
- people seek social relationships and personal fulfillment
- people start to matter
Elton Mayo - Hawthorne Studies
1880-1949
- Australian Psychologist
- One of the first to realize human qualities and emotions
Historical Context of Hawthorne Studies
- early 20th Century
- rise of factory and scientific management (Taylorism)
- but harsh conditions, repetitive, worker dissatisfaction
- managers treated workers like machines
4 Main Hawthorne Studies
1. Illumination Studies
2. Relay Assembly Test Room Experiments
3. Experiments in Interviewing Workers
4. Bank Wire Room Experiment
4 Main Hawthorne Studies: Illumination Studies
Tested how lighting affects productivity
4 Main Hawthorne Studies: Illumination Studies Results
Productivity Increased Regardless of lightning changes, (bc they were being watched)
4 Main Hawthorne Studies: Relay Assembly Test Room Experiments
Study performed on 5 women
- given better working conditions, rest breaks
4 Main Hawthorne Studies: Relay Assembly Test Room Experiments Results
productivity rose
- researchers puzzled: assumed it would be distraction
4 Main Hawthorne Studies: Experiments in Interviewing Workers
Study involved interviewing workers to understand attitudes, opinions, and experiences of the workplace
4 Main Hawthorne Studies: Experiments in Interviewing Workers Results
Significant impact of employees attitudes and relationships to performance
- positive work environment
4 Main Hawthorne Studies: Bank Wire Room Experiment
explored how social dynamics and group norms influence worker productivity
4 Main Hawthorne Studies: Bank Wire Room Experiment Results
Study highlighted the importance of social interaction as workers were more responsive to their peer's expectations than to management incentives
Key Finding of the Hawthorne Studies + definition
The Hawthorne Effect
- people change behaviour when they know their being observed
Mayo's Hawthorne Studies Believes Worker Productivity is Strongly Influenced (3)
1. Social Interactions (Employee Well-being)
2. Sense of Belonging
3. Supervisor Attention (Hawthorne Effect)
Hawthorne Studies Believed Workers Are Motivated..
By more than just money
Where Should Hawthorne Studies be Implemented
- tech companies, remote workplaces
- physical and mental well-being, collaboration and managing
Hawthorne Studies: the shift from Scientific to H.R Approach
Shifted Management Style:
Control --> Collaboration
Output --> Morale
Criticisms of Hawthorne Studies - E. Mayo
- experiments lacked control groups
- focused on social factors ignoring pay and physical working conditions
- manipulated: improve morale just to boost output
- ignore individualism --> looks @ groups as a whole
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
1. Physiological Needs
2. Safety Needs
3. Love and Belonging
4. Esteem Needs
5. Self-Actualization
Douglas McGregor - Theory X & Y
(1906)
contributor to development of management and motivational theory
Development of McGregor's Theory X + Y
- ideas came from working in MIT (1950s)
- influenced by Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
Theory X and Y- McGregor
two sets of assumptions about Human Nature and Behaviour that are related to the practice of management
Theory X
negative view of human nature
- people generally, naturally irresponsible for work, require close supervision
Theory X is applicable for what type of manager
Autocratic Style Managers
Theory X Workers Must.
be controlled and directed
Pros of Theory X
- help keep new or inexperienced on task + learn basics of job
- guarantees that staff will be minimally productive and not waste time
Cons of Theory X
- can lower creativity of staff, making them feel unmotivated to finish tasks with best ability
- does not build trust between employers and their employee
Characteristics of Applying Theory X
preplanned, detailed schedules, and steps to be executed
Theory X Role is..
for simplistic, less creative workplaces
- with low motivation = more supervision + control