Chapter 1: The Development of Neuropsychology
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/71
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
1
New cards
brain theory
states that they brain is the source of behavior
2
New cards
neuron theory
the unit of brain structure adn function is the neuron (nerve cell)
3
New cards
brain
the tissue found within the skull (cranium)
4
New cards
hemispheres
the two symmetrical halves of the brain
5
New cards
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
the fluid that cushions the brain and helps remove toxic waste
6
New cards
cerebral cortex
the outer layer of the brain
7
New cards
gyri
the folds/bumps in the cortex
8
New cards
sulci
the breases between the gyri
9
New cards
longitudinal fissure
the large sunci that divides the two hemispheres
10
New cards
lateral fissure
the larg sulci that divides each hemisphere in half
11
New cards
forebrain
the front part of the neural tube that makes up an embryo’s primitive brain, and mediates cognitive functions
12
New cards
brainstem
the “tube” underlying the cortex that mediates regulatory functions (e.g., eating, drinking, moving)
13
New cards
corpus callosum
the pathway (commissure) that connects the brain’s hemispheres
14
New cards
temporal lobe
the area below the lateral fissure under the temporal bone
15
New cards
frontal lobe
the area above the temporal lobe under the frontal bone
16
New cards
parietal lobe
the area behind the frontal lobe under the parietal bone
17
New cards
occipital lobe
the area at the back of each hemisphere between the parietal and temporal lobes, under the occipital bone
18
New cards
spinal cord
a string nerves connected to the brainstem that conveys sensory information into the brain and sends commands from the brain to the muscles to move
19
New cards
central nervous system (CNS)
the brain (inside the skull), and spinal cord (inside the vertebrae)
20
New cards
peripheral nervous system (PNS)
the nerve fibers carrying information into or away from the CNS
21
New cards
somatic nervous system (SNS)
consists of sensory receptors on the bodys surface and muscles that enable the brain to sense the world and react
22
New cards
sensory pathways
collections of fibers that carry messages for specific senses on one side of the body mainly to the opposite hemisphere
23
New cards
motor pathways
groups of nerve fibers that connect the brain and spinal cord to the body’s muscles through the SNS
24
New cards
autonomic nervous system (ANS)
consists of pathways that control internal organs (e.g. heart beat, stomach contractions, etc.)
25
New cards
mentalism
a theory on how the brain and behavior are related proposed by Aristotle that states a person’s mind is responsible for behavior
26
New cards
dualism
a theory on how the brain and behavior are related proposed by René Descartes that states mind and body are separate but can interact
27
New cards
the mind-body problem
states that a person is capable of consciousness and rationality only because they have mind, but how can a nonmateria mind produce movements in a materia body?
28
New cards
materialism
rational behavior can be fully explained by the workings of the nervous system (Alfred Russel Wallace and Charles Darwin)
29
New cards
natural selection
explains how new species evolve and change over time
30
New cards
species
a group of organisms that can breed among themselves and usually not with mebers of other species
31
New cards
phenotype
traits that we can see or measure
32
New cards
epigenetics
the science that studies difference in gene expression related to environment and experience
33
New cards
neurplasticity
the nervous system’s potential for physical or chemical change that enhances its adaptability to environmental change and its ability to compensate for injury
34
New cards
localization of function
states that a different, specific brain area controls each kind of behavior. (Franz Josef Gall)
35
New cards
phrenology
the study of the relation between the skull’s surface features and a person’s mental faculties (Johann Casper Spurzheim)
36
New cards
cranioscopy
a device was placed around the skull to measure its bumps and depressions.
37
New cards
lateralization of function
certain functions are localized in specific areas of brain hemispheres (Jean Baptiste Bouillaud)
38
New cards
Broca’s area
the anterior speech region of the brain
39
New cards
Broca’s phrases
the syndome that results from damage to Broca’s area
40
New cards
Wernicke’s area
the region of the brain thats responsible for understanding and hearing speech
41
New cards
Wernicke’s (fluent) aphasia
the syndrome that results from damage to Wernicke’s area
42
New cards
conduction aphasia
speech sounds and movements are retained, but speech is impaired because it cannot be conducted from one region to the other; the person cant reapeat what is heard
43
New cards
Alexia
a disconnection between the brain’s visual area and Wernciek’s area, which causes the inability to read
44
New cards
apraxia
a disconnection between motor and sensory areas, which causes an inability to make sequences of movements
45
New cards
persistent vegetative state (PVS)
when the person is alive but is unable to communicate or function independently even at the most basic level
46
New cards
minimally conscious state (MCS)
when the person can ocassionally utter single words and make few movements, but cant feed themselves
47
New cards
clinical trial
a consensual experiment directed towards developing a treatment
48
New cards
hierarchial organization
information is processed serially and organized as a functional hierarchy; higher levels control more-complex aspects of behavior, and does so via the lower levels (John Hughlings-Jackson)
49
New cards
epilepsy
a condition characterized by recurrent seizures associated with disturbance of consciousness
50
New cards
amnesia
partial or total loss of memory
51
New cards
binding problem
although the brain analyzes sensory events through multiple paralle channels, we perceive a unified experience, a memory
52
New cards
visual form agnosia
when a person cant see the shapes of objects nor recognize objects visually by their shape
53
New cards
ventral steam
a pathway from the visual cortex to the temporal lobe for object indentification (where brain legions occur in people with agnosia)
54
New cards
ataxia
the ability to make errors in reaching for objects while still being able to describe the objects accurately
55
New cards
dorsal stream
a pathway from the visual cortex to the parietal cortex that guides action relative to objects (where brain legions occur in people with ataxia)
56
New cards
glia
cells that help the neurons by holding them together and providing other support functions (e.g. delivering nutruents, removing waste)
57
New cards
cell body (soma)
the core region
58
New cards
dendrites
a neuron’s branching extensions
59
New cards
axon
the main root of a neuron
60
New cards
topographic organization
the study of how the cortex forms topograohic neural-spatial representations of the body’s different parts
61
New cards
transcranial magnetic stimulation
used to induce electrical activation in the brain by passing a magnetized coil across the skull to study how the typical brain produces behavior, andd which parts participate in partiular actions
62
New cards
synapse
the junction between neurons
63
New cards
Hebb or plastic synapses
strengthened connections between synapses that occur when individual neurons are activated at the same time
64
New cards
cell assemblies
occurs when Hebb’s or plastic synapses form together
65
New cards
trephining
cutting a circular hole in the skull to relieve pressure from a swelling brain
66
New cards
psychometrics
the science of measuring human mental abilities
67
New cards
intelligence quotient (IQ)
(mental age / chronological age) \* 100
68
New cards
multiple sclerosis (MS)
the hardening of nerve fiber-pathways in the spinal cord, which resulted in a loss of sensory and motor function
69
New cards
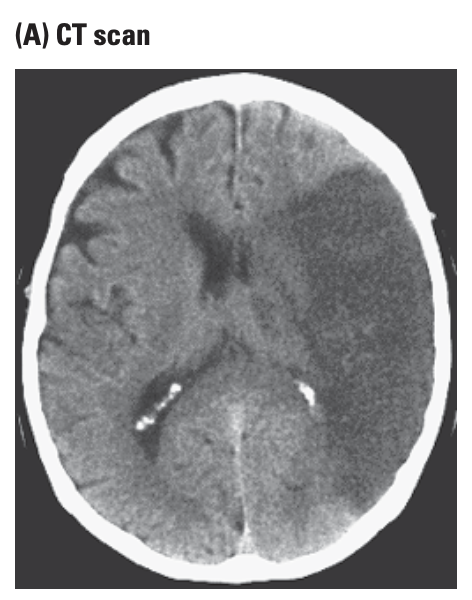
computer tomography (CT)
passes X-rays through the head which are aborbed mess by fluid than by brain cells and less by brain cells than by bone.
70
New cards
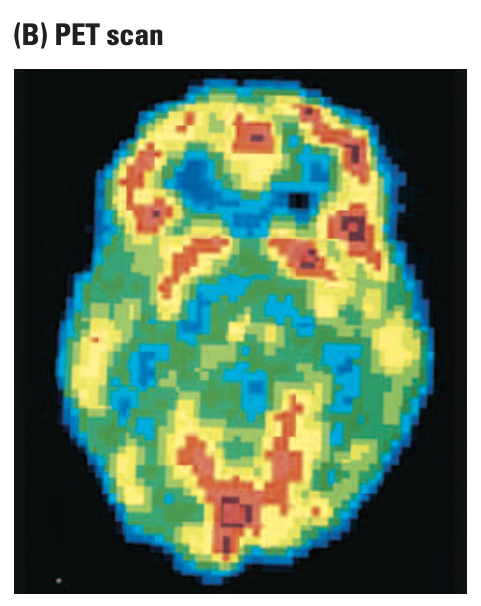
positron emission tomography (PET)
injecting radioactive substances that decay in minutes into the blooodstream to reach the brain, which gives off photons and allows the computer to draw their location on a two- or three-dimensional reconstruction of the brain. red areas represent strong blood flow, and blue areas represent weak blood flow
71
New cards
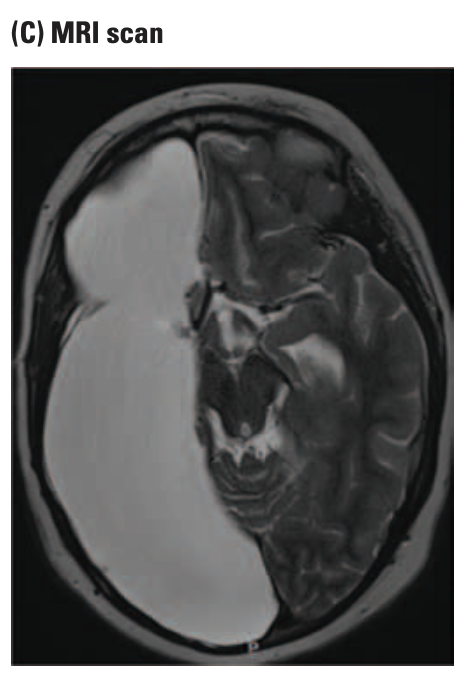
magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
calculates the location of moving molecules by detecting the electrical charge their movement generates.
72
New cards
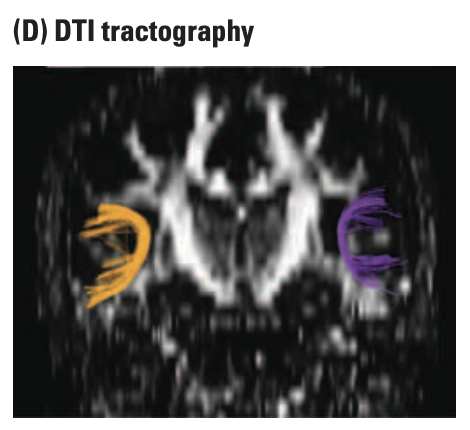
diffusion tensor imaging (DTI)
an MRI method that detects the directional movements of water molecules to create virtual images of the brain’s nerve fibre pathways