Special Senses - Ears and Eyes
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
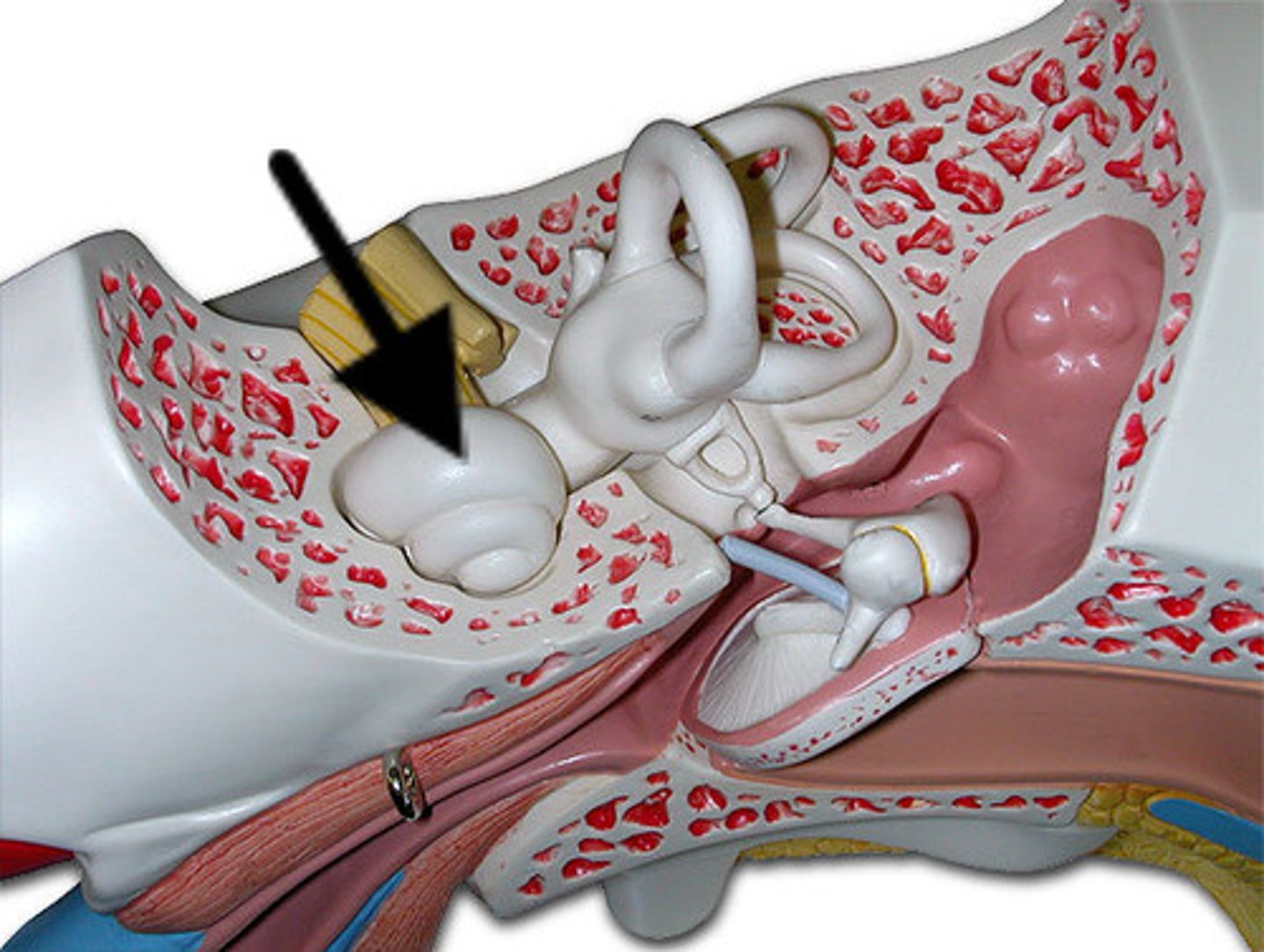
auricle
external ear
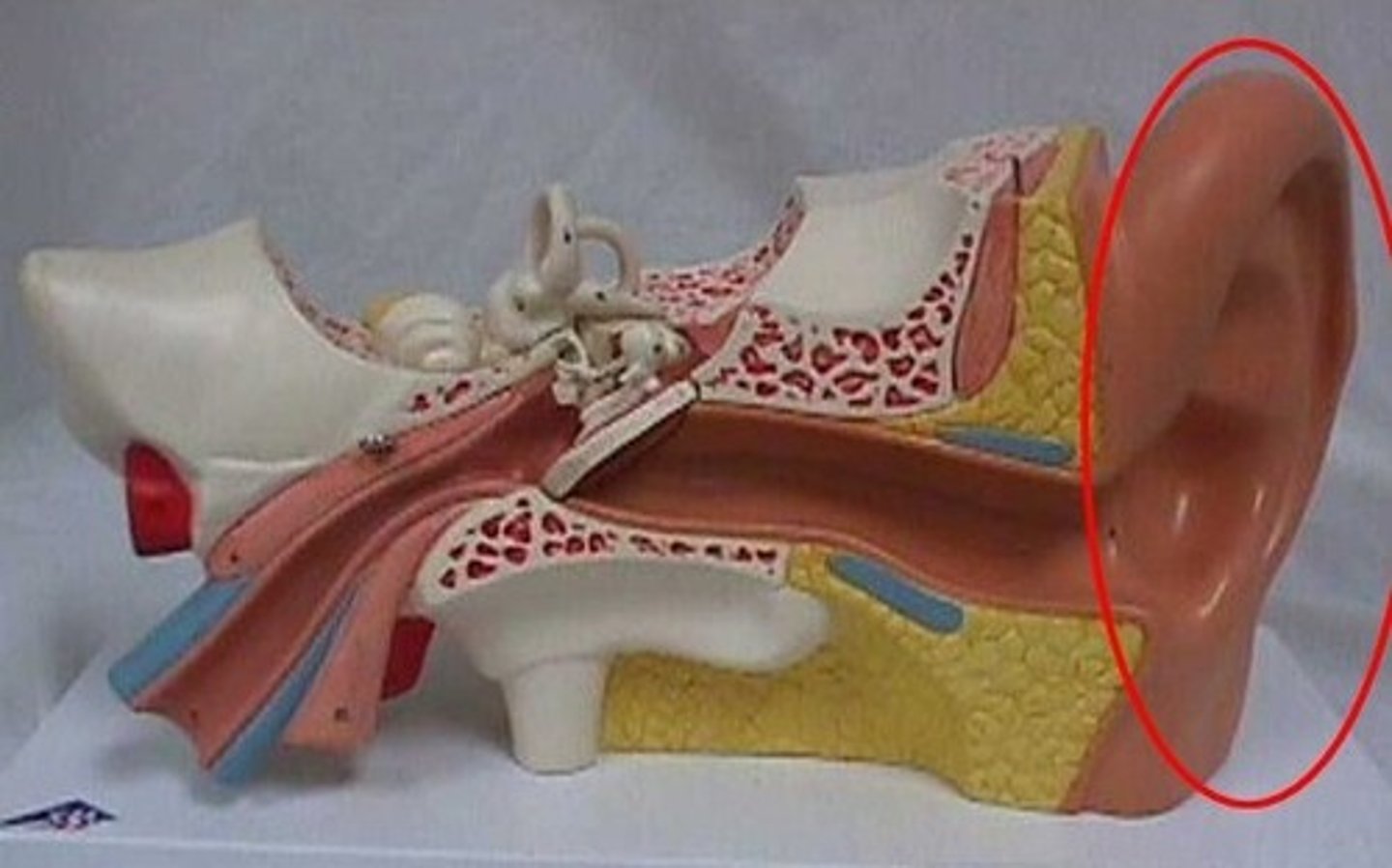
external auditory meatus
ear canal
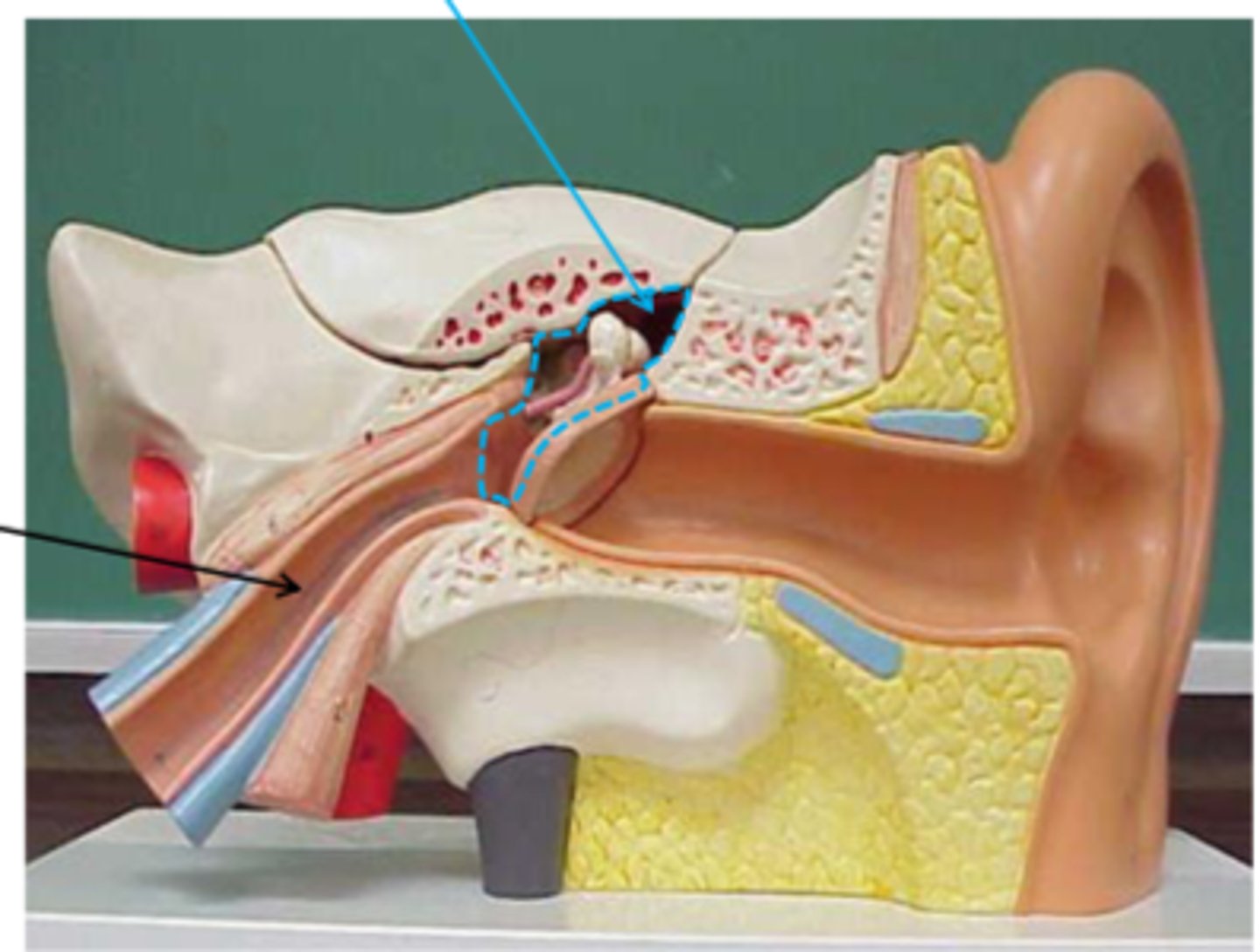
tympanic membrane
The eardrum. A structure that separates the outer ear from the middle ear and vibrates in response to sound waves.
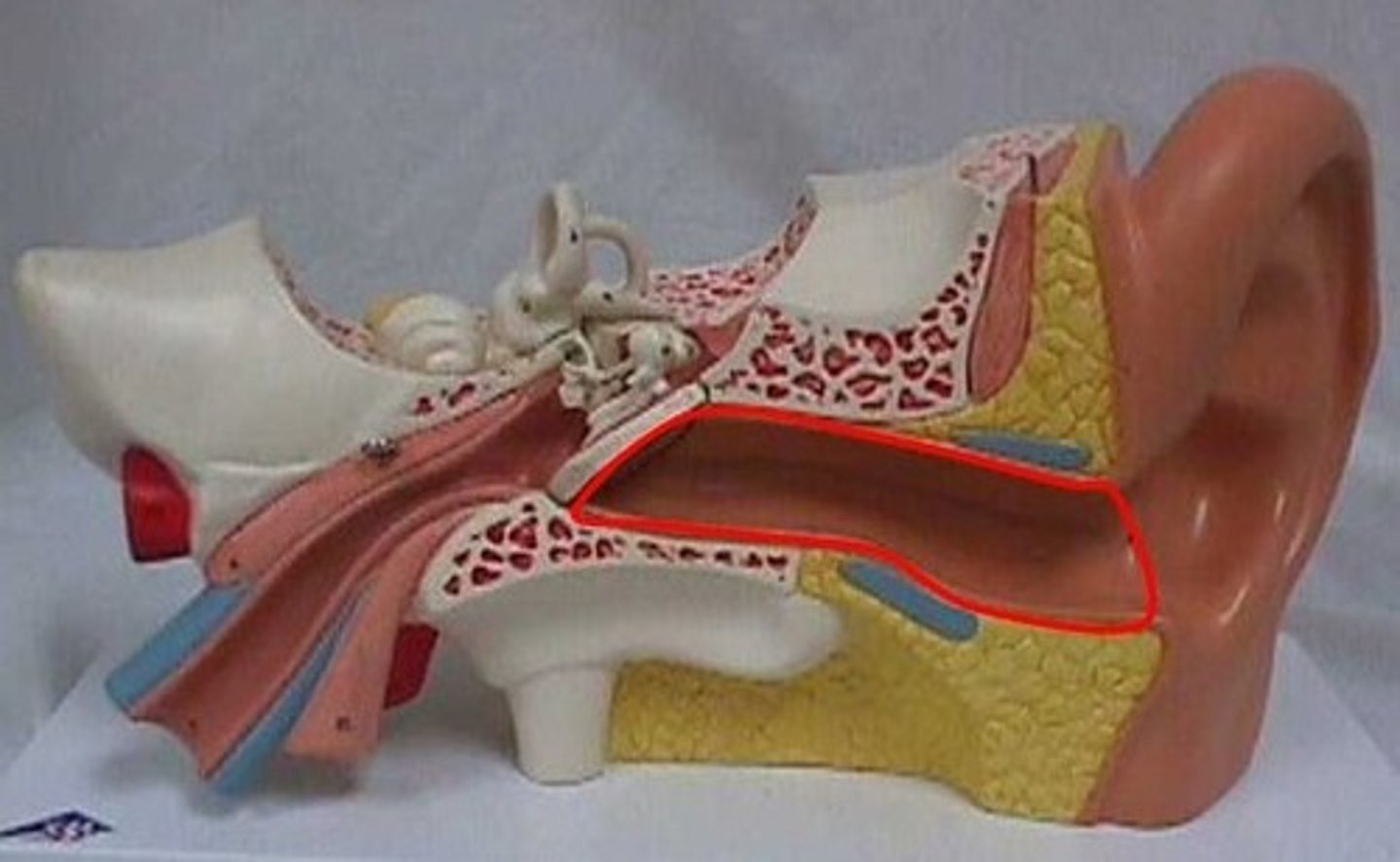
tympanic cavity
air filled space in temporal bone
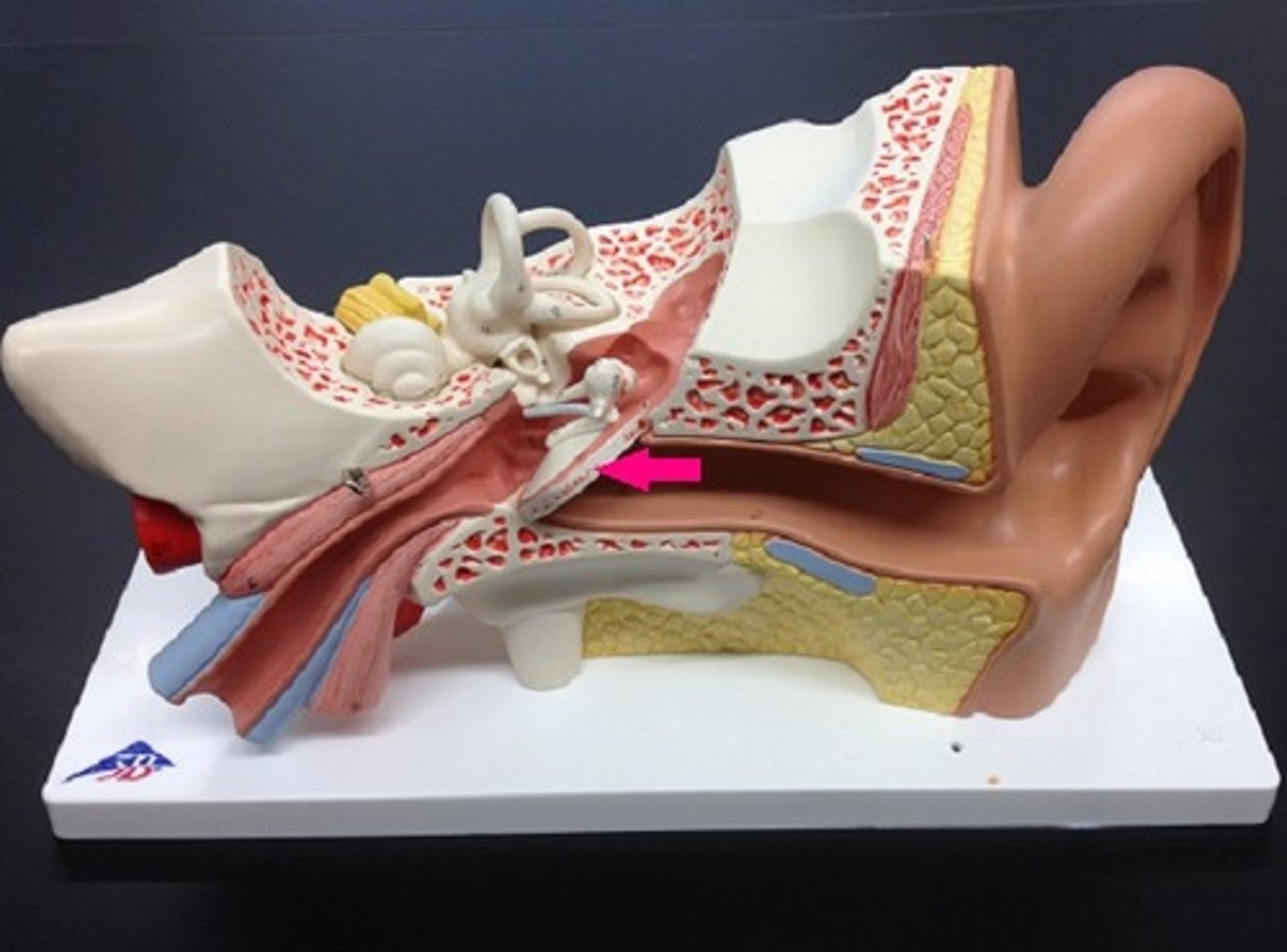
auditory ossicles
-three small bones linked together that connect the eardrum to the inner ear
-malleus, incus, stapes
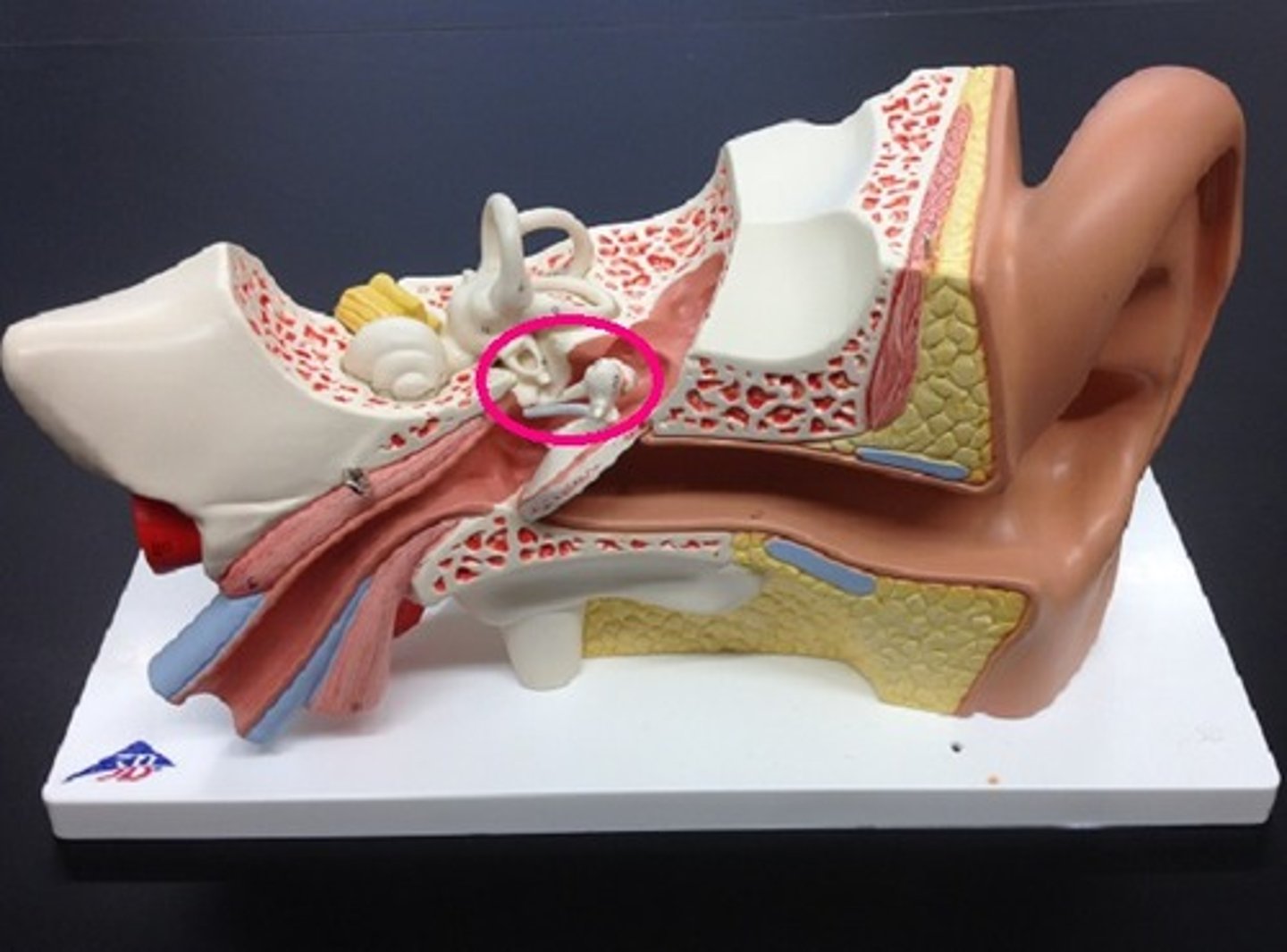
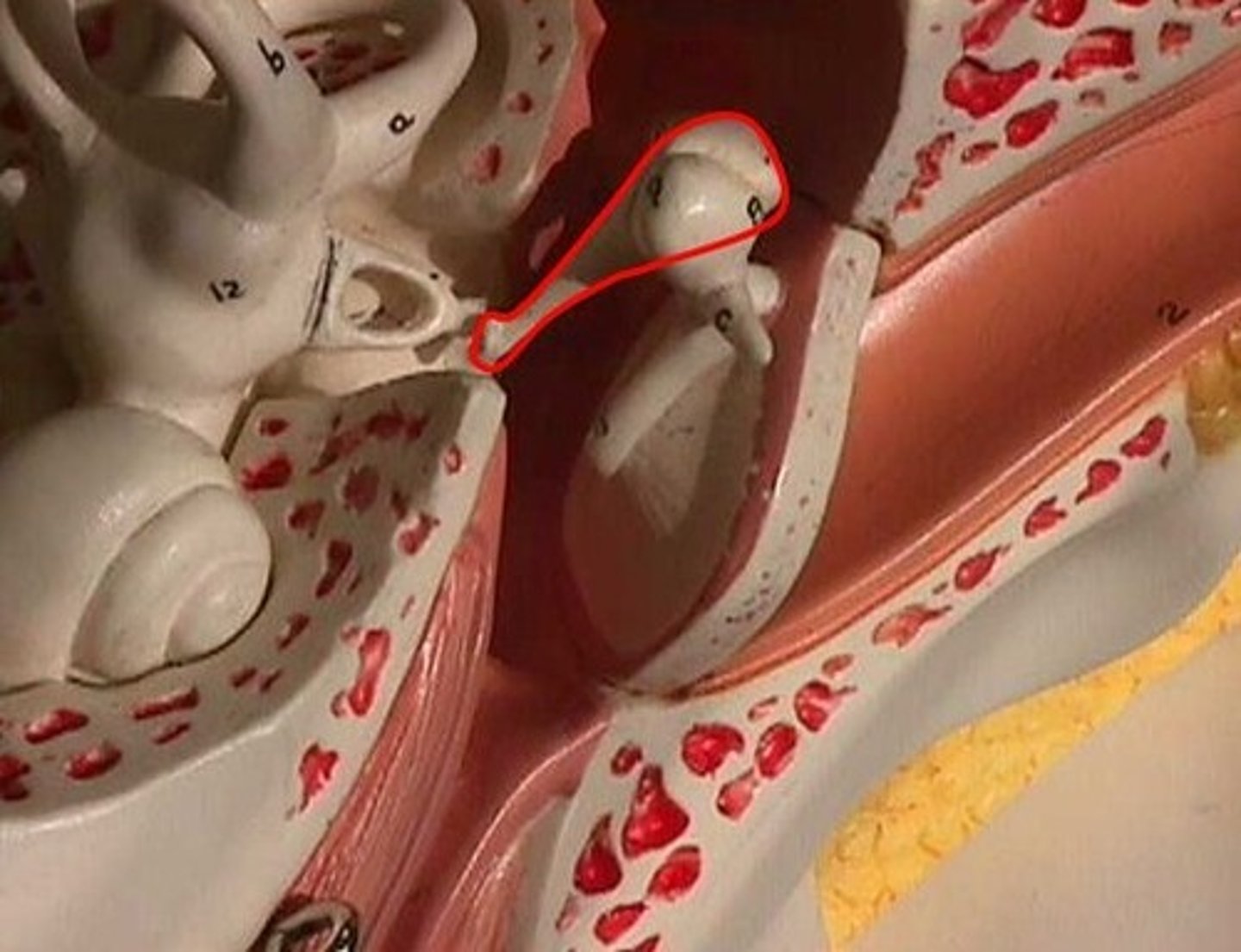
malleus
hammer; first of the three auditory ossicles of the middle ear
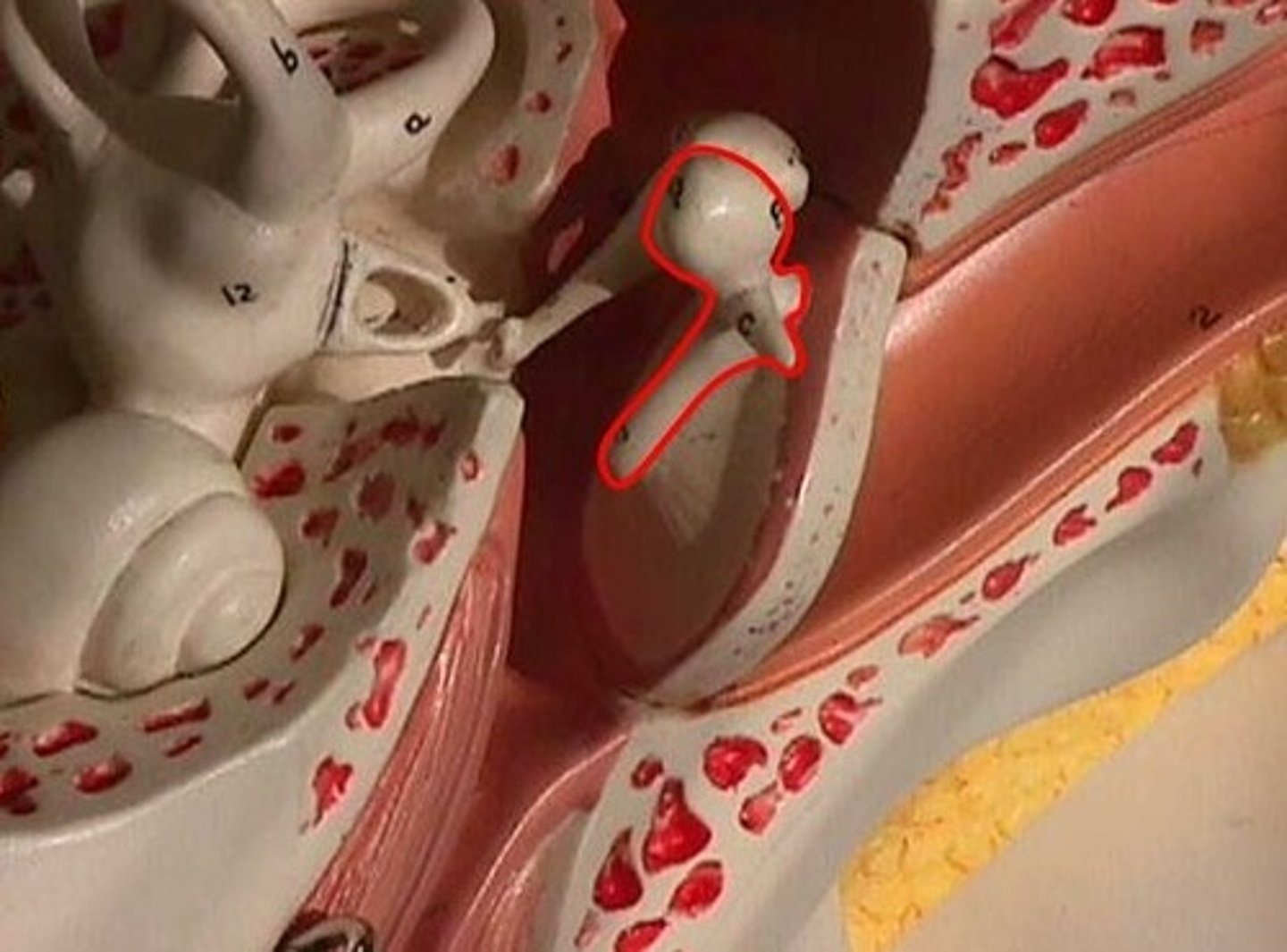
incus
anvil; middle of the three auditory ossicles of the middle ear
stapes
stirrup; last of the three auditory ossicles of the middle ear
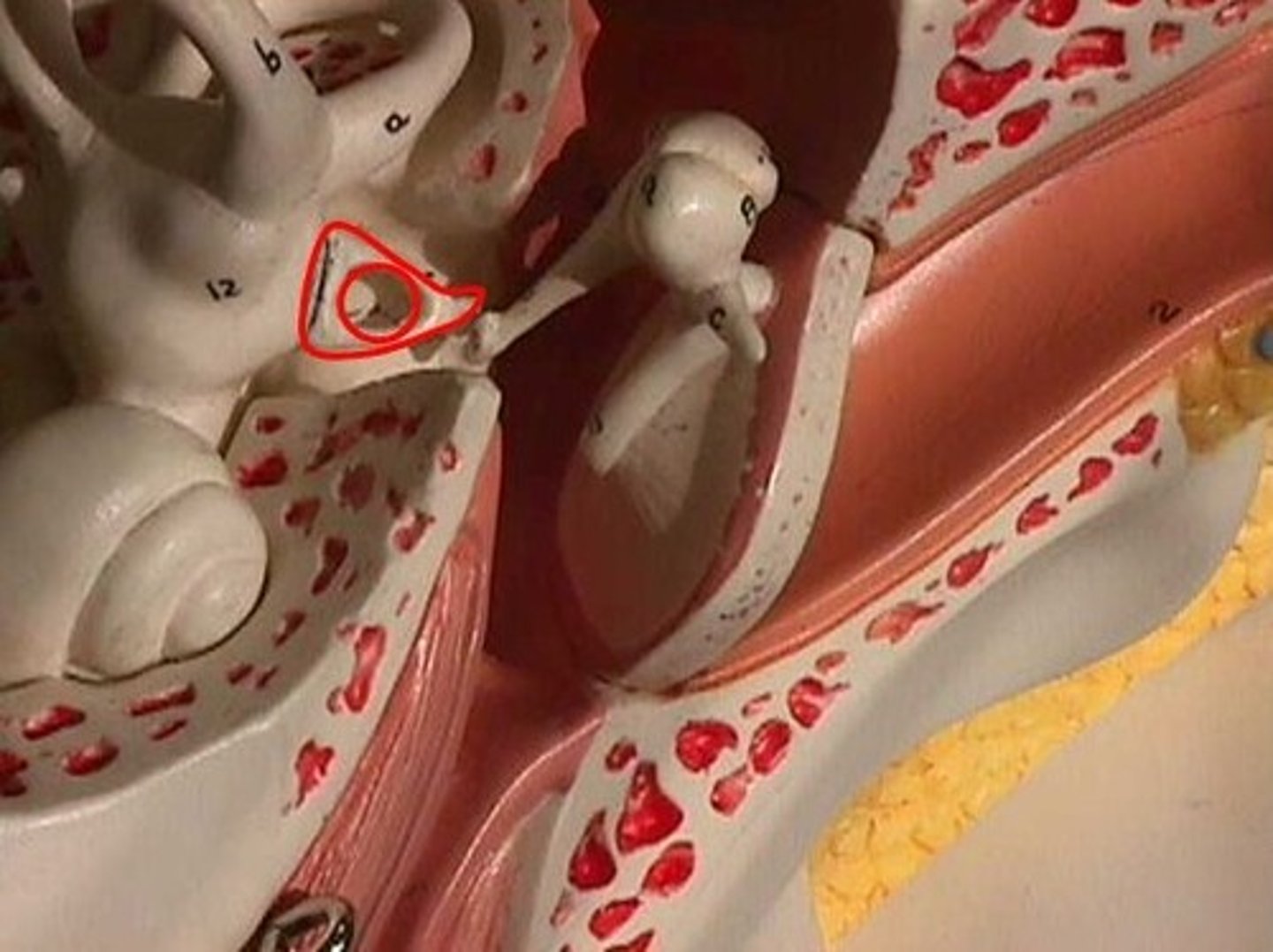
oval window
membrane at the enterance to the cochlea through which the ossicles transmit vibrations
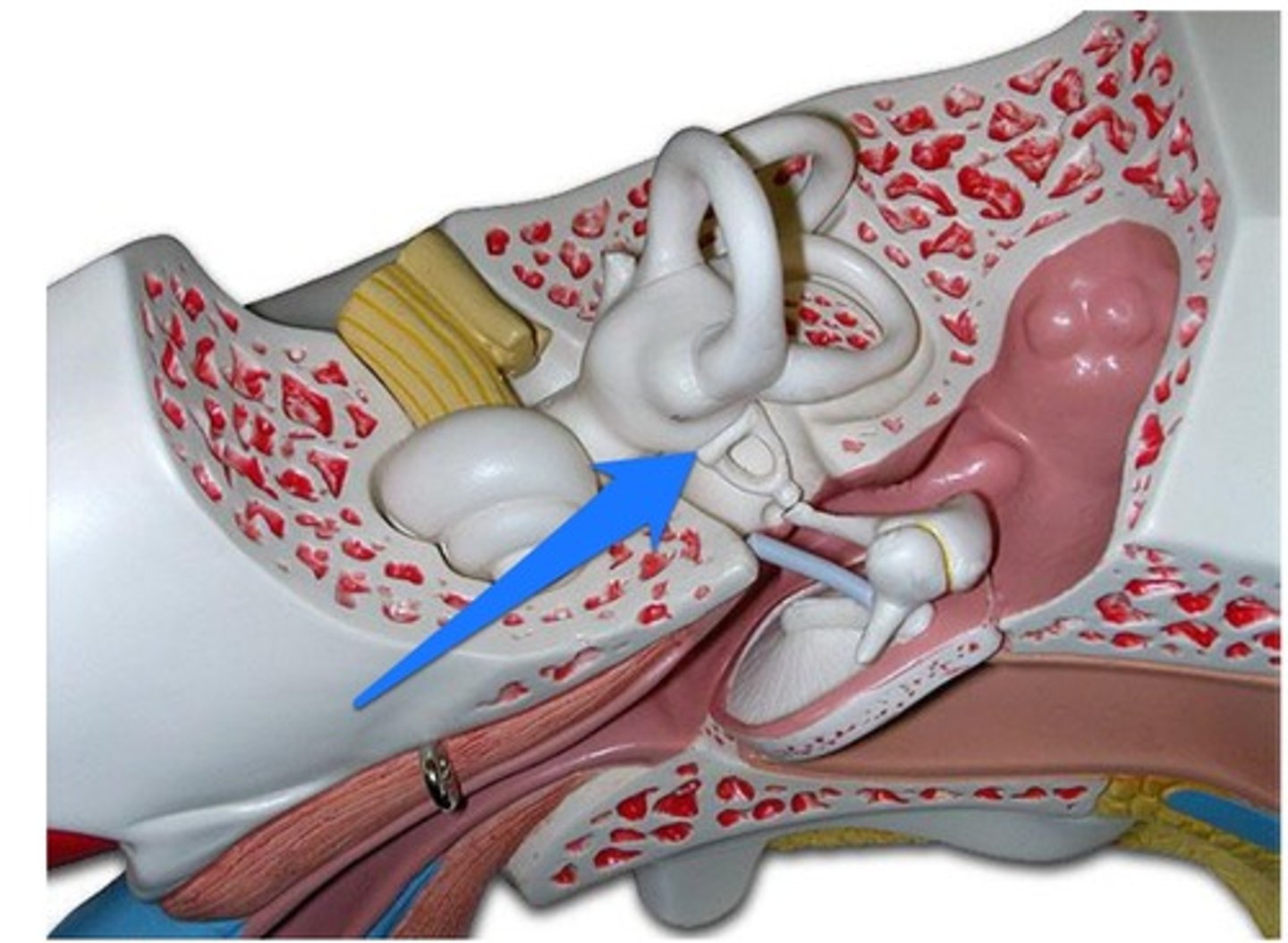
auditory (eustachian) tube
connects the middle ear with the nasopharynx, equalizes air pressure
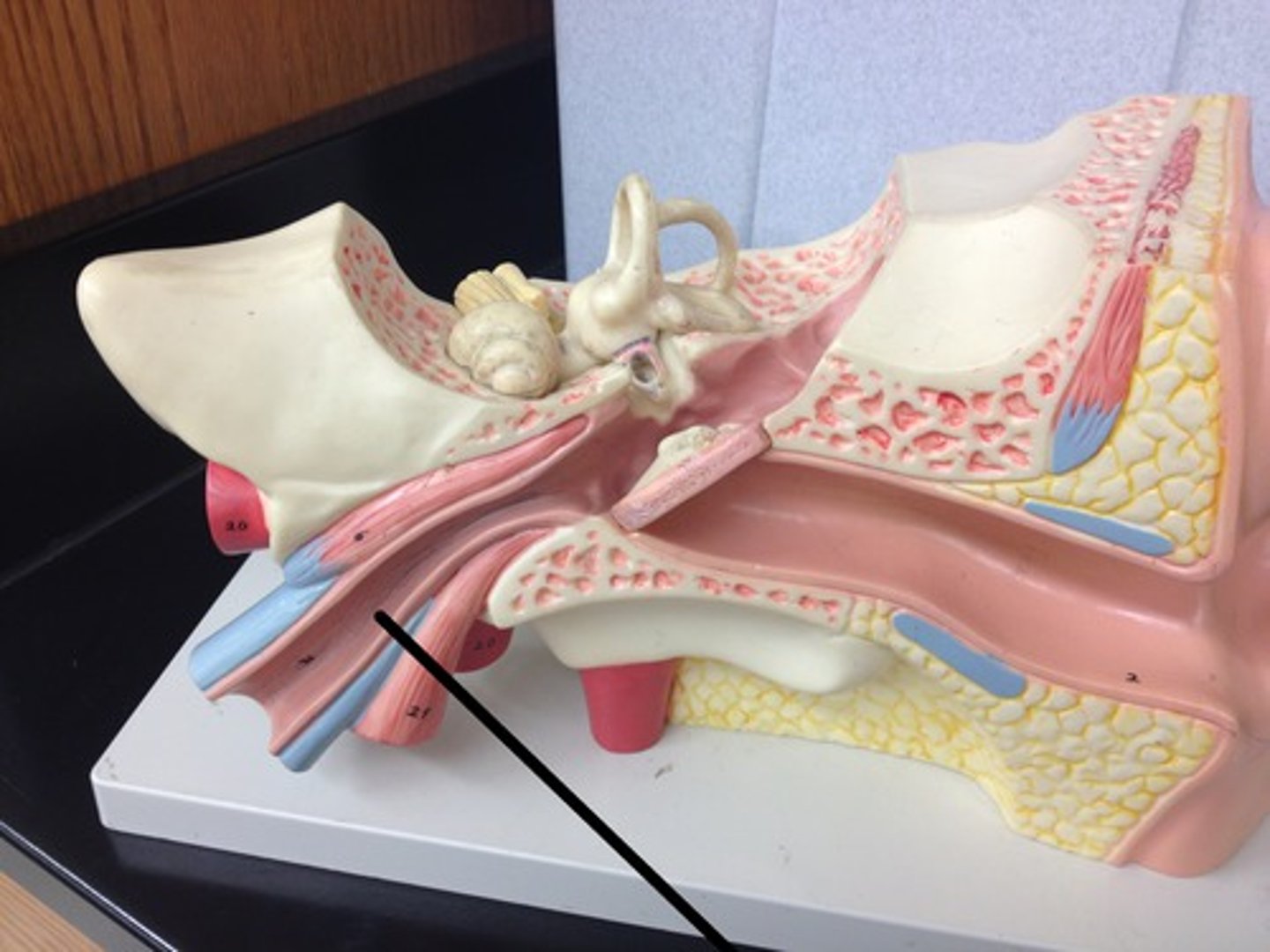
bony labyrinth
passageways in temporal bone
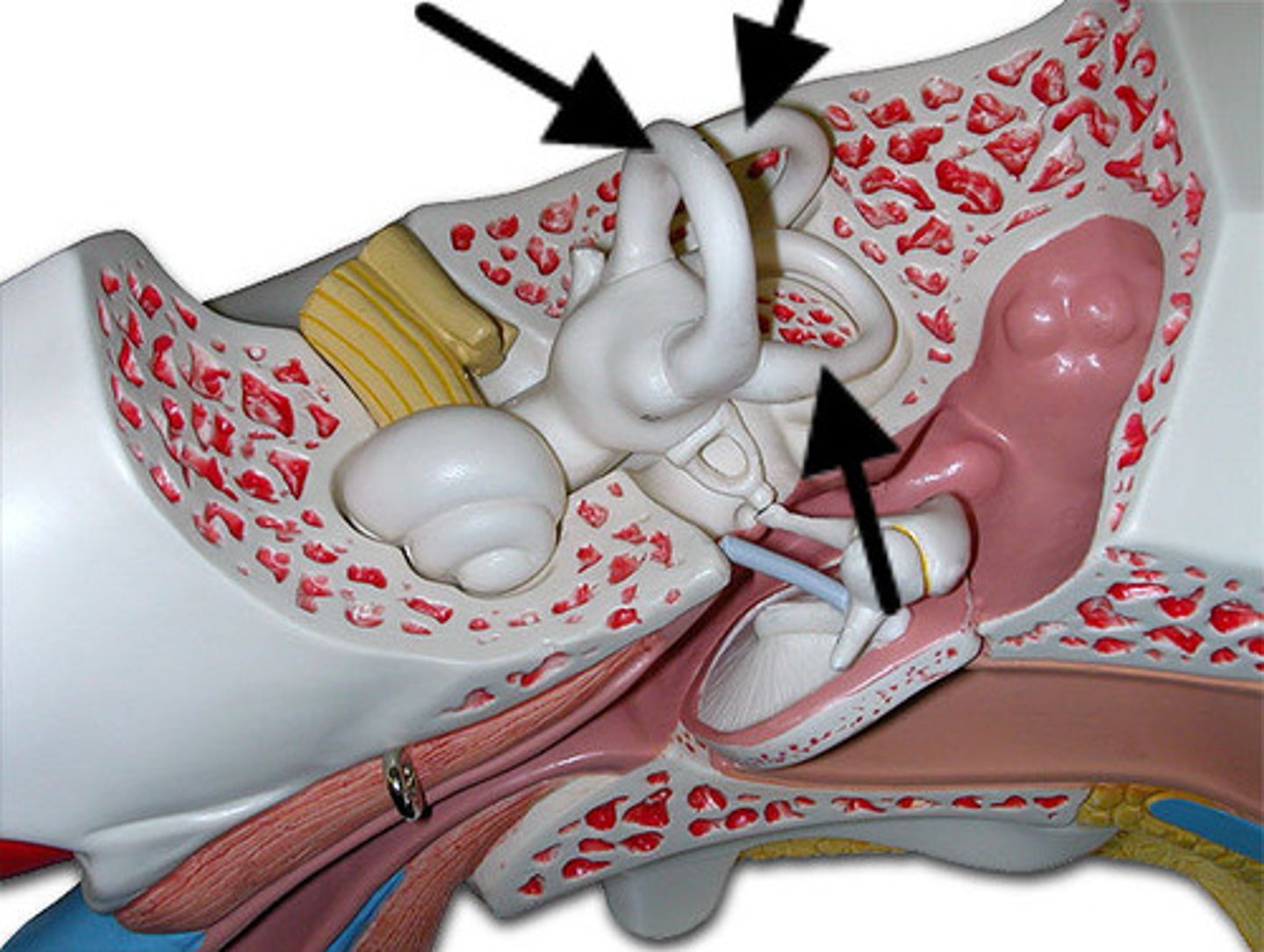
semicircular canals
three canals within the inner ear that contain specialized receptor cells that generate nerve impulses with body movement
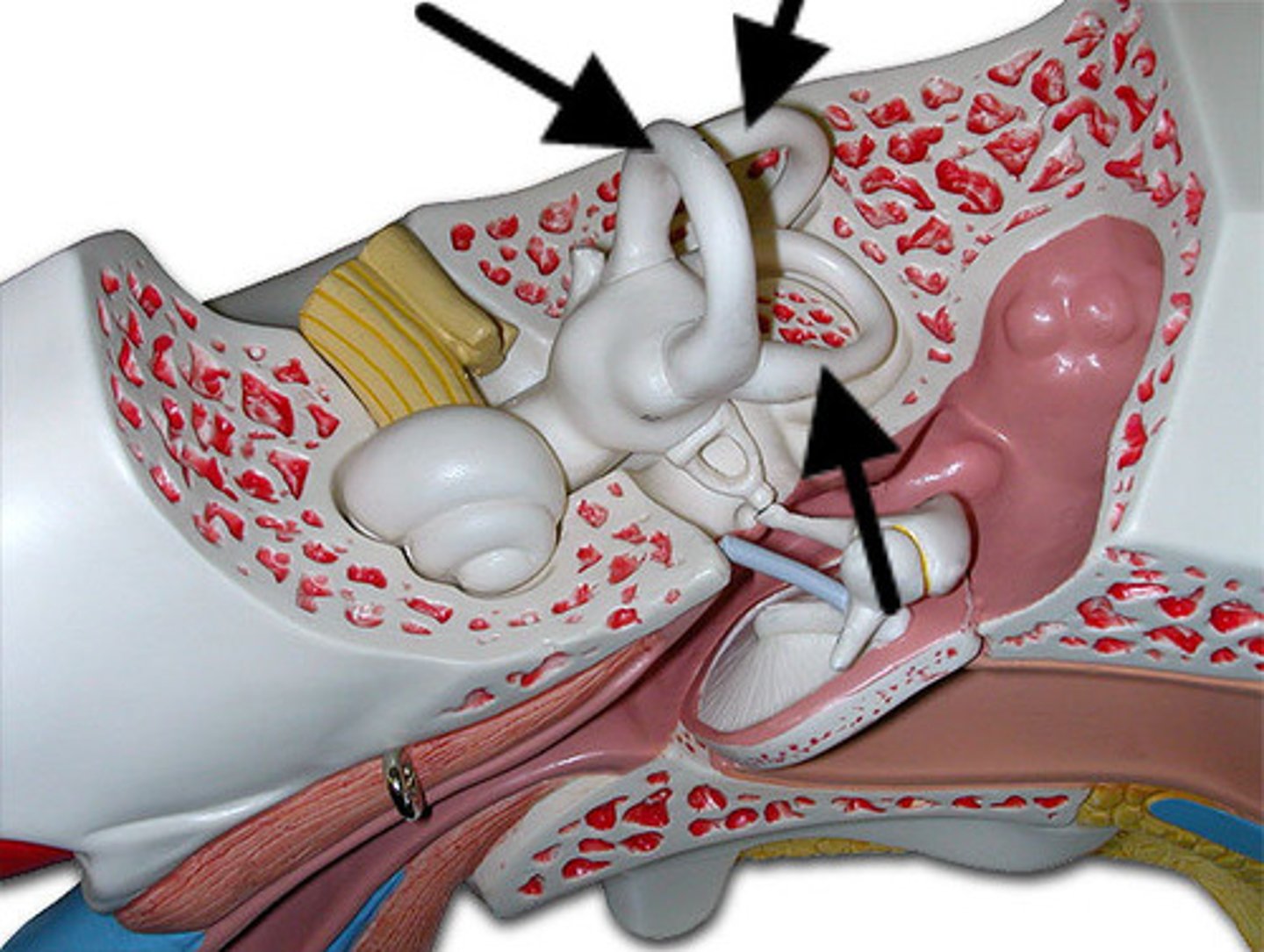
superior semicircular canal
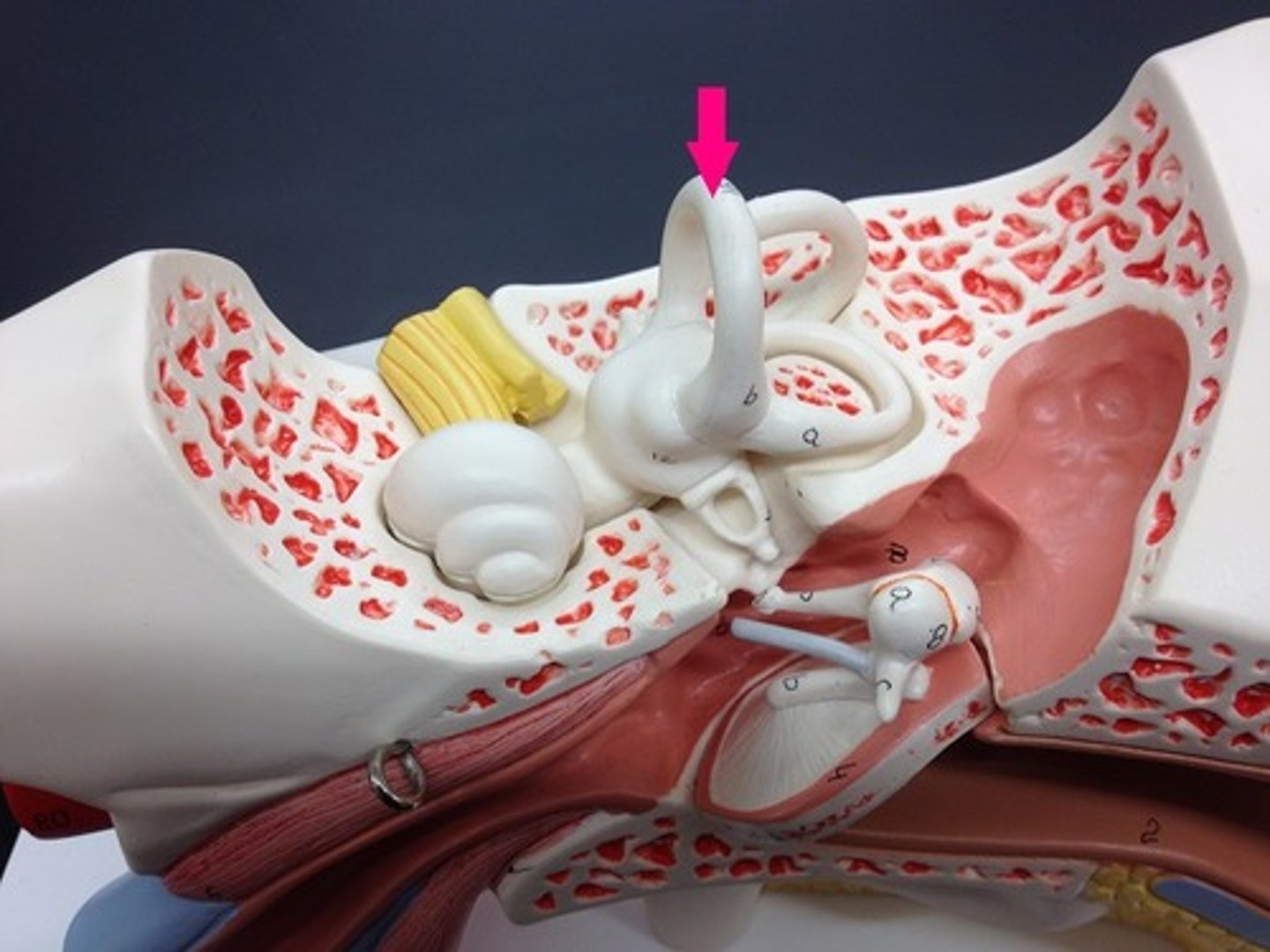
posterior semicircular canal
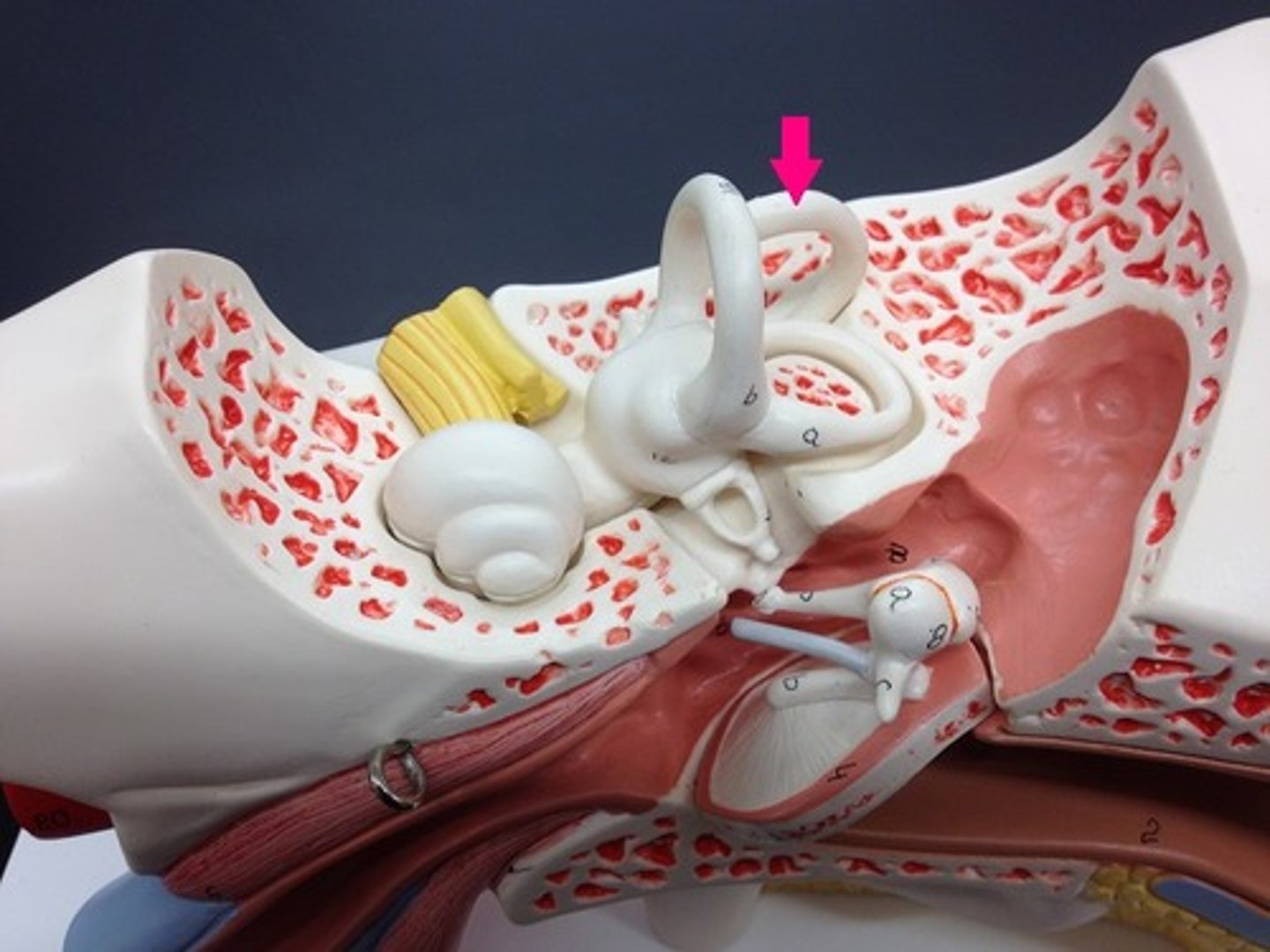
lateral semicircular canal
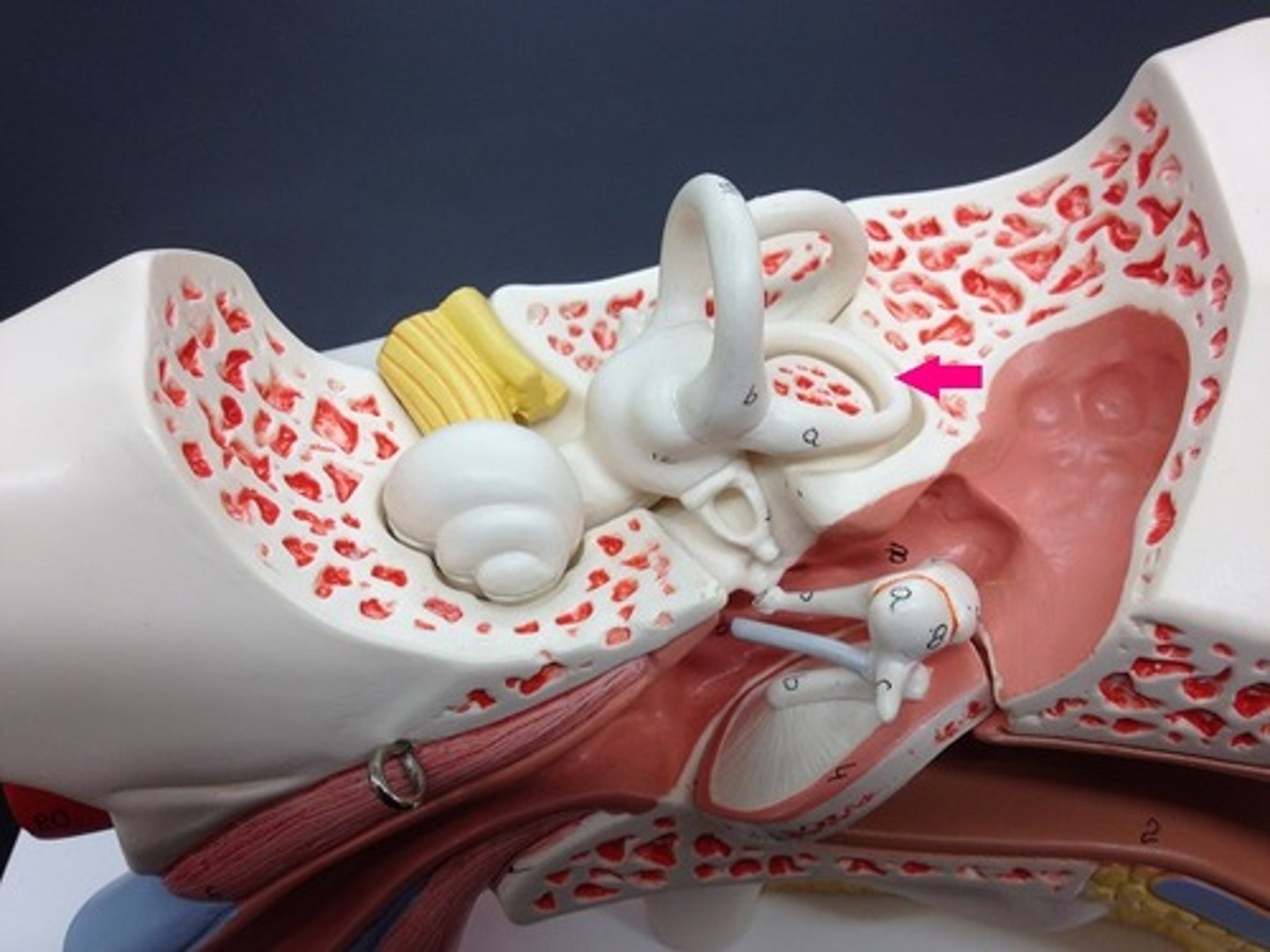
vestibule
The portion of the inner ear that senses the position of the head. Its sensory epithelium is contained in two saclike spaces: the utricle and the saccule.
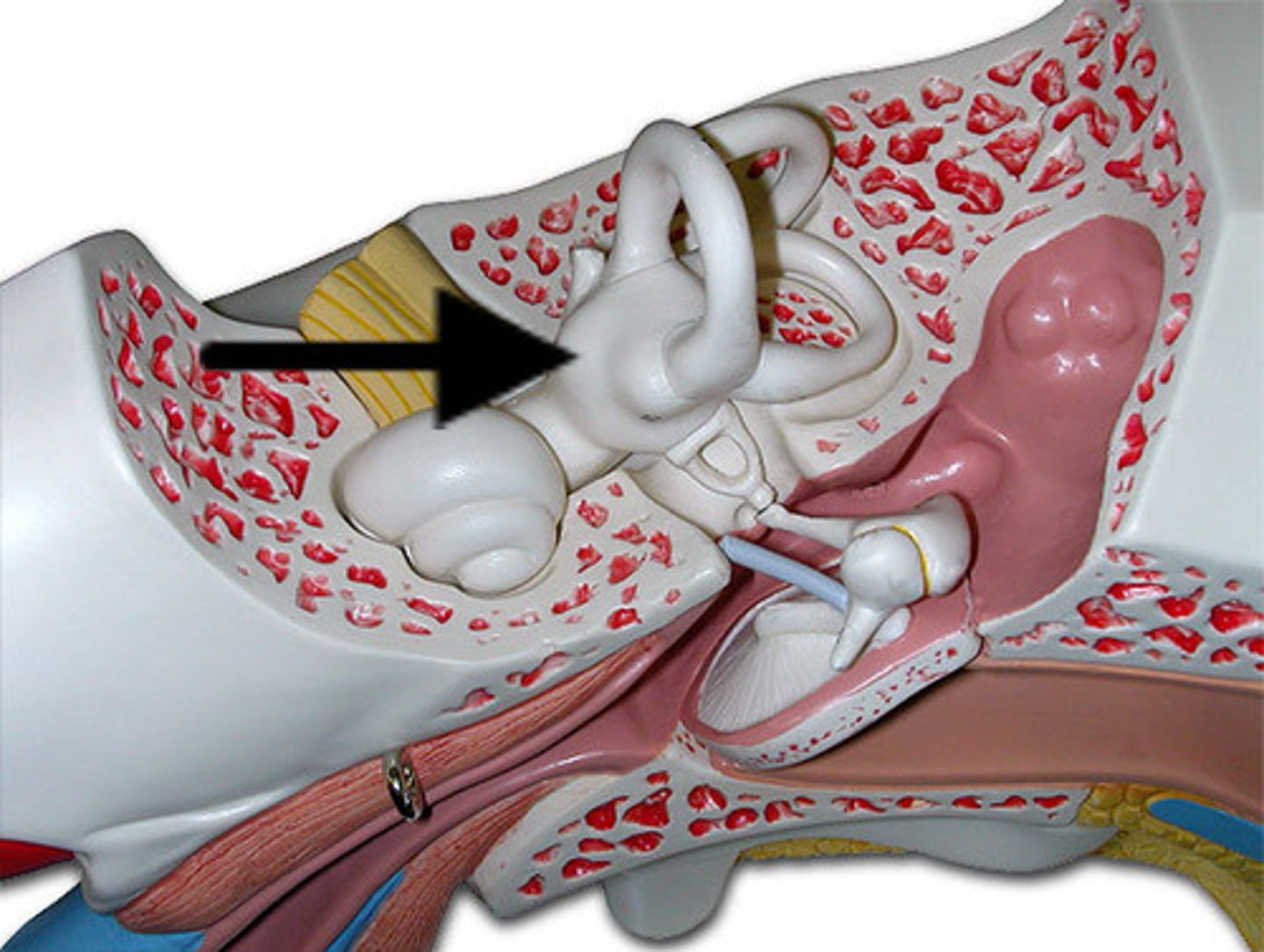
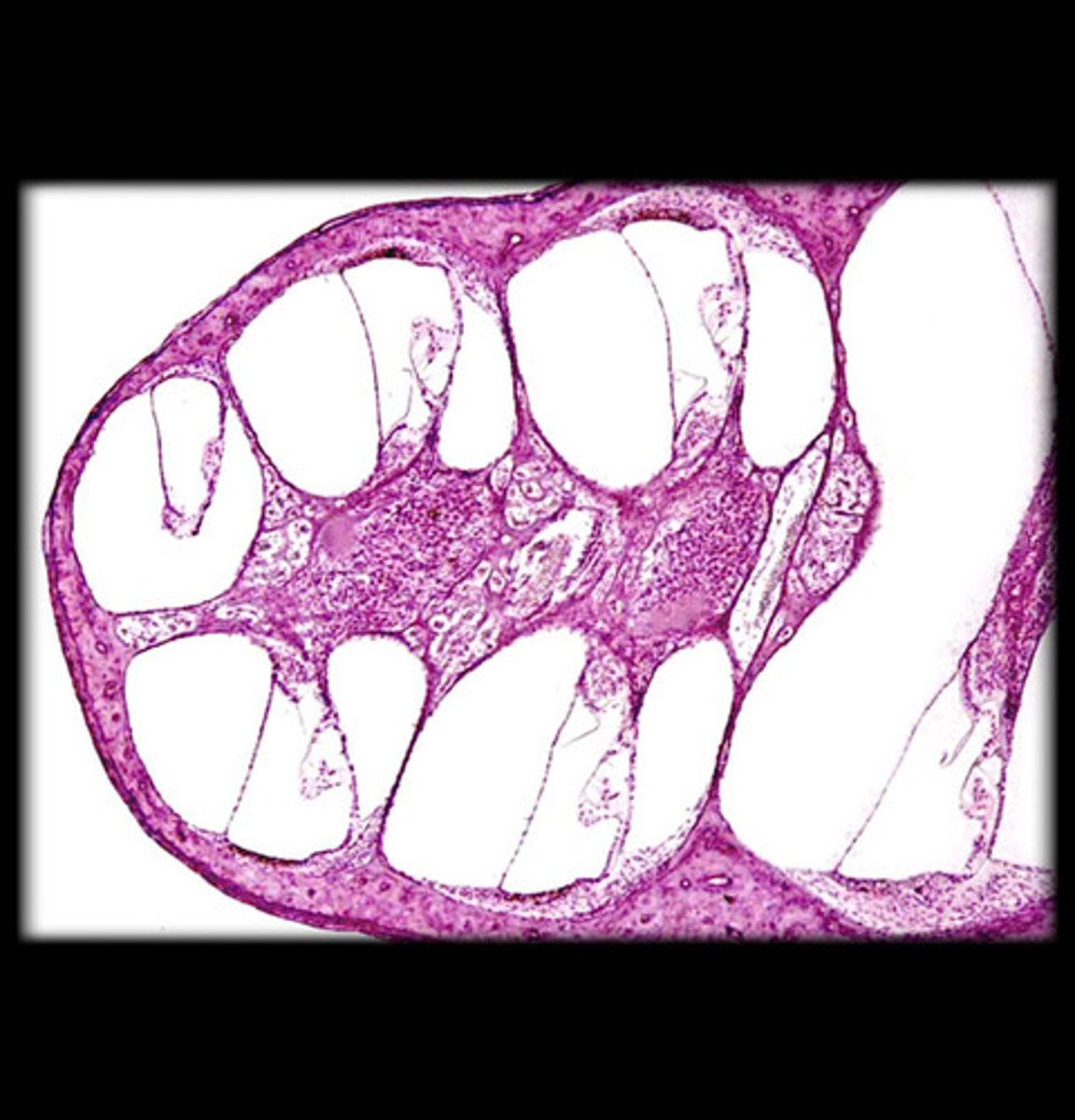
cochlea
a coiled, bony, fluid-filled tube in the inner ear through which sound waves trigger nerve impulses
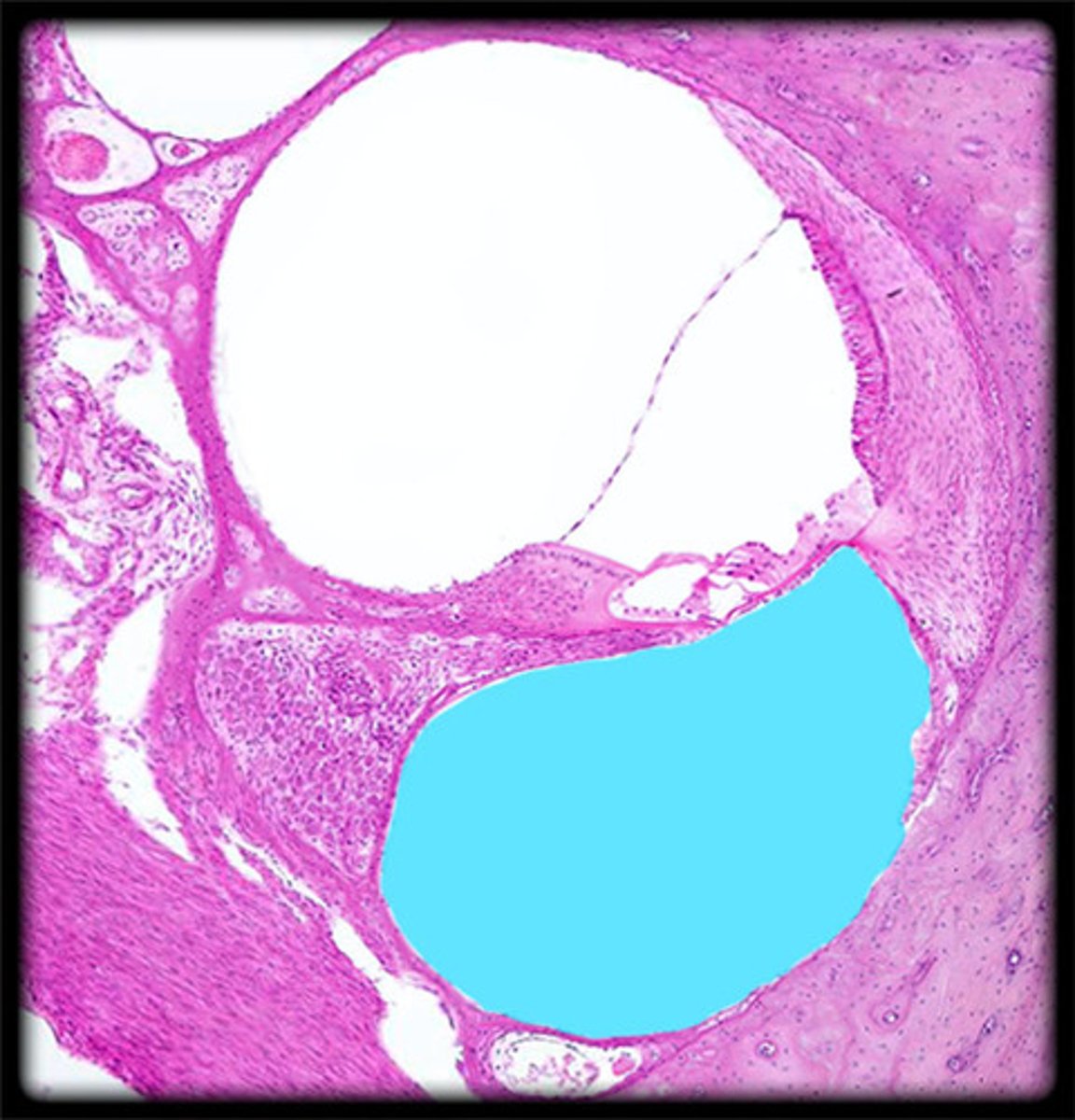
cochlea histology
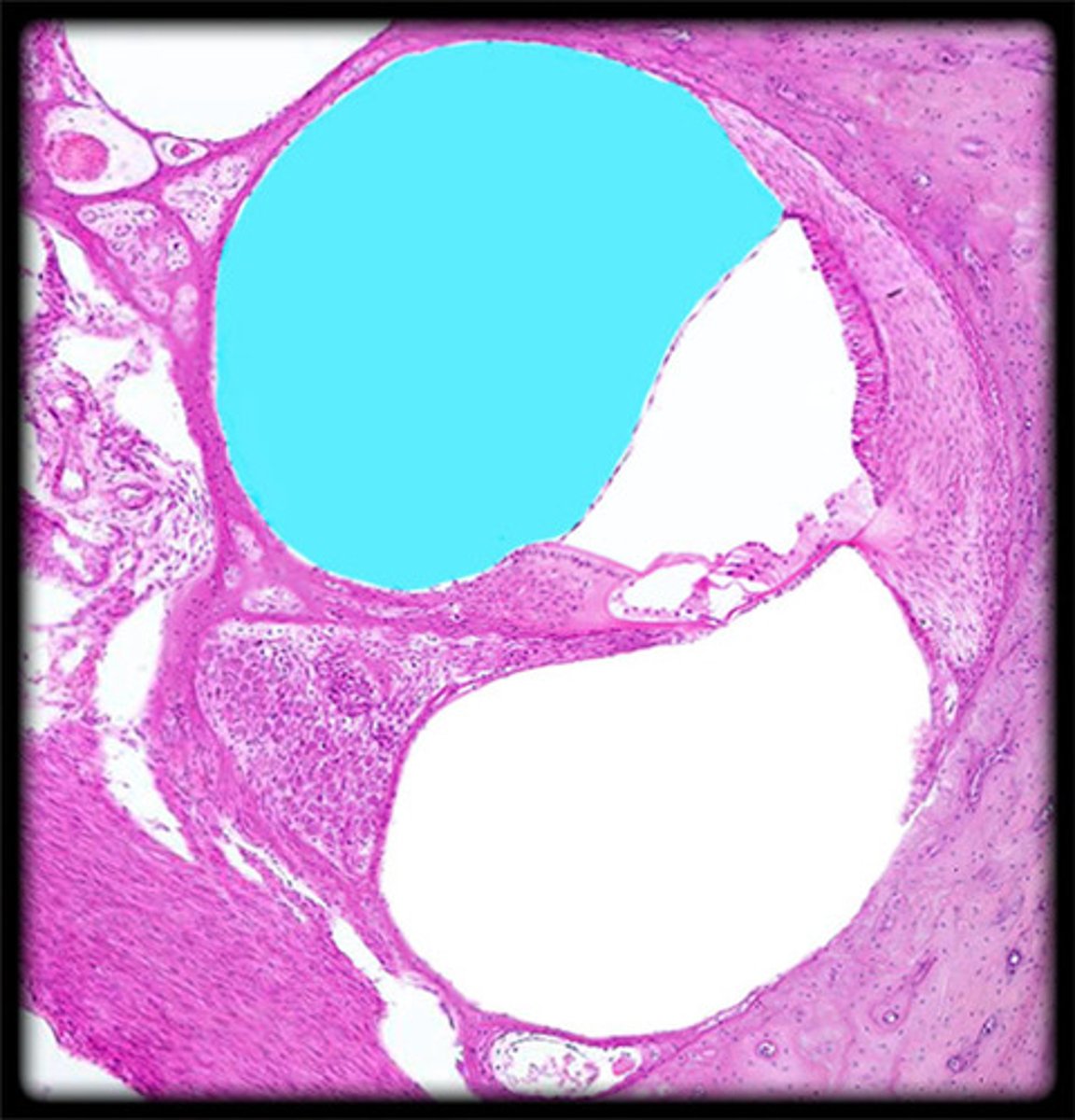
scala vestibuli
contains perilymph
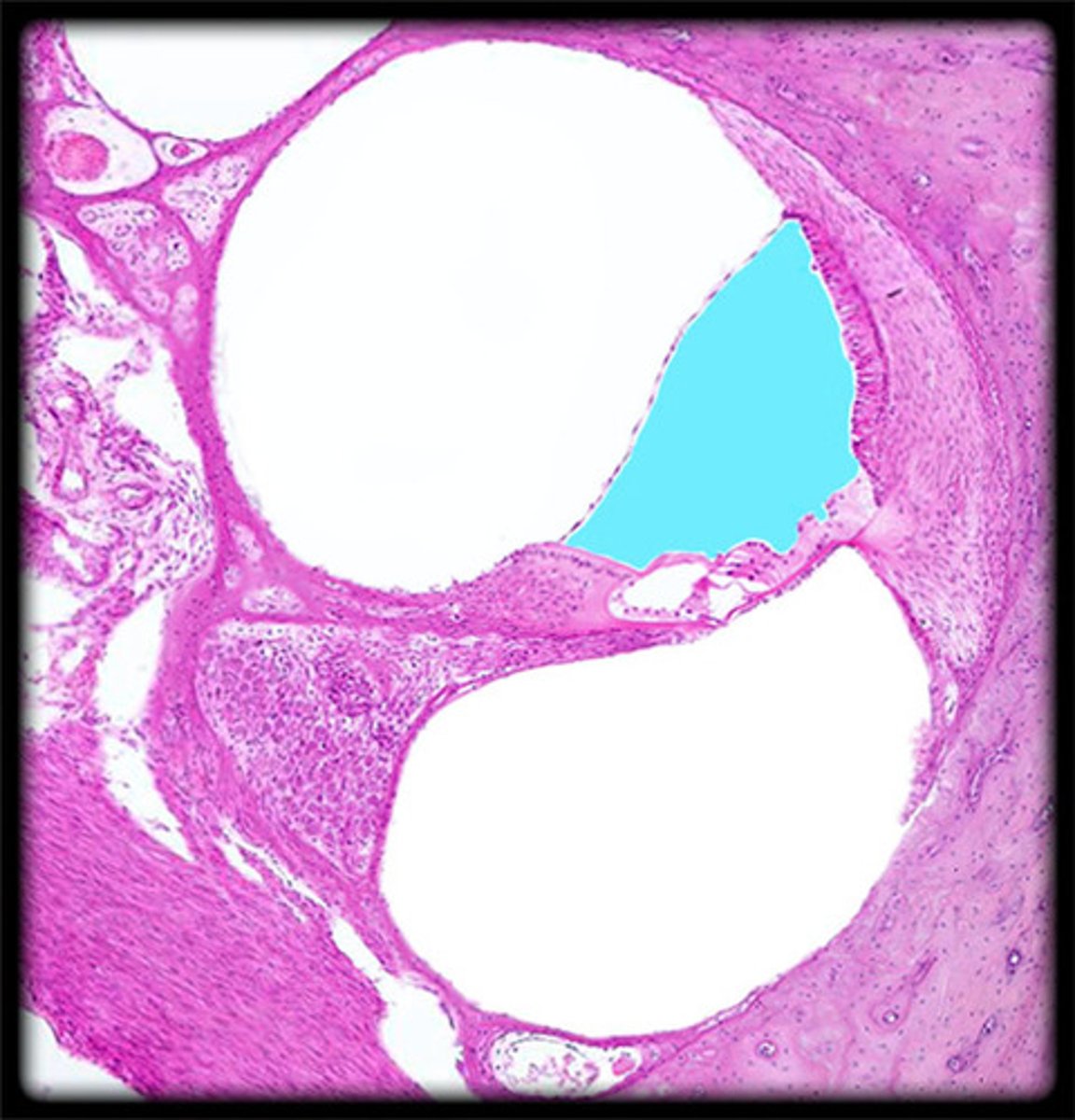
scala media
contains endolymph
scala tympani
contains perilymph
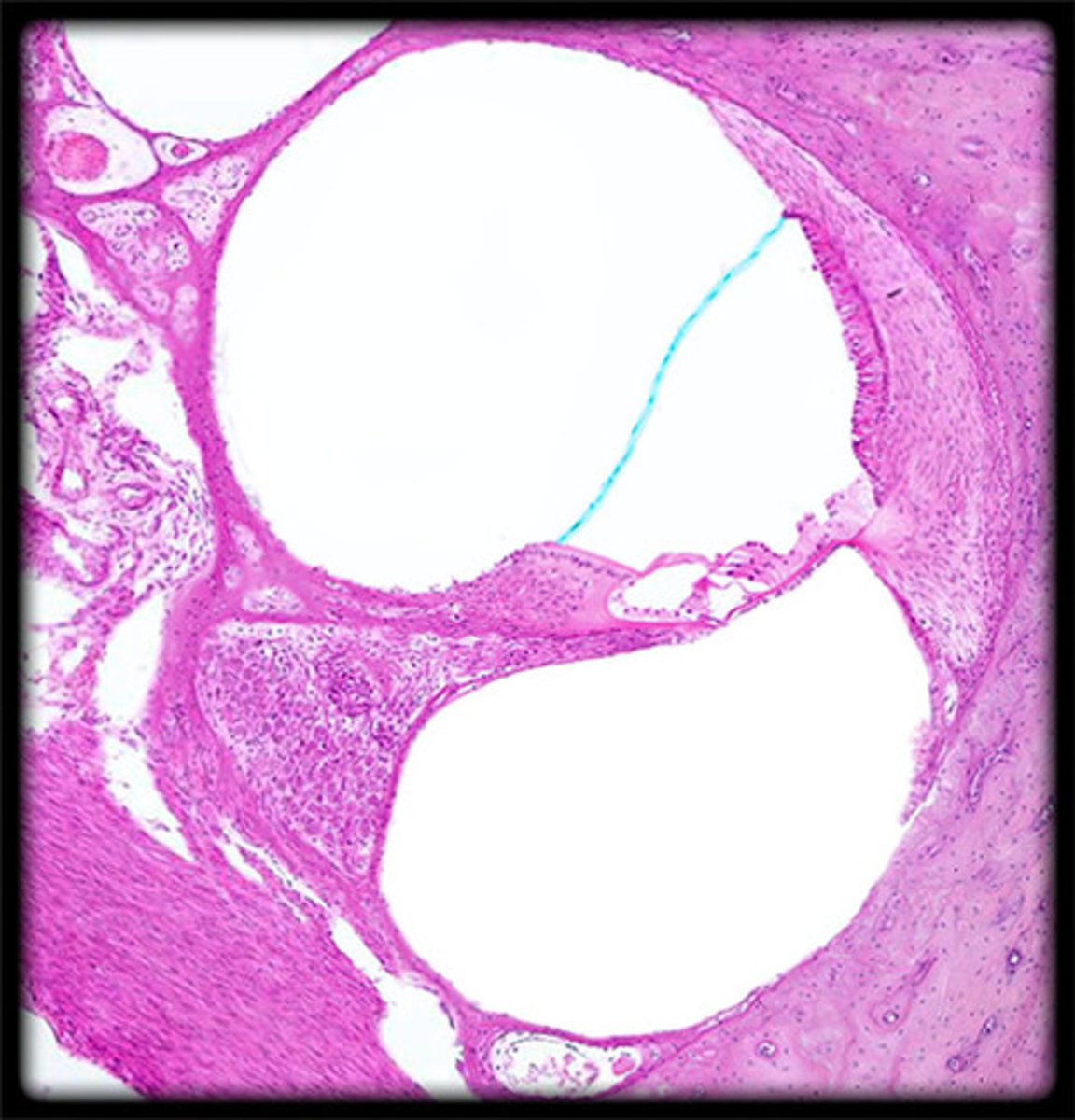
vestibular membrane
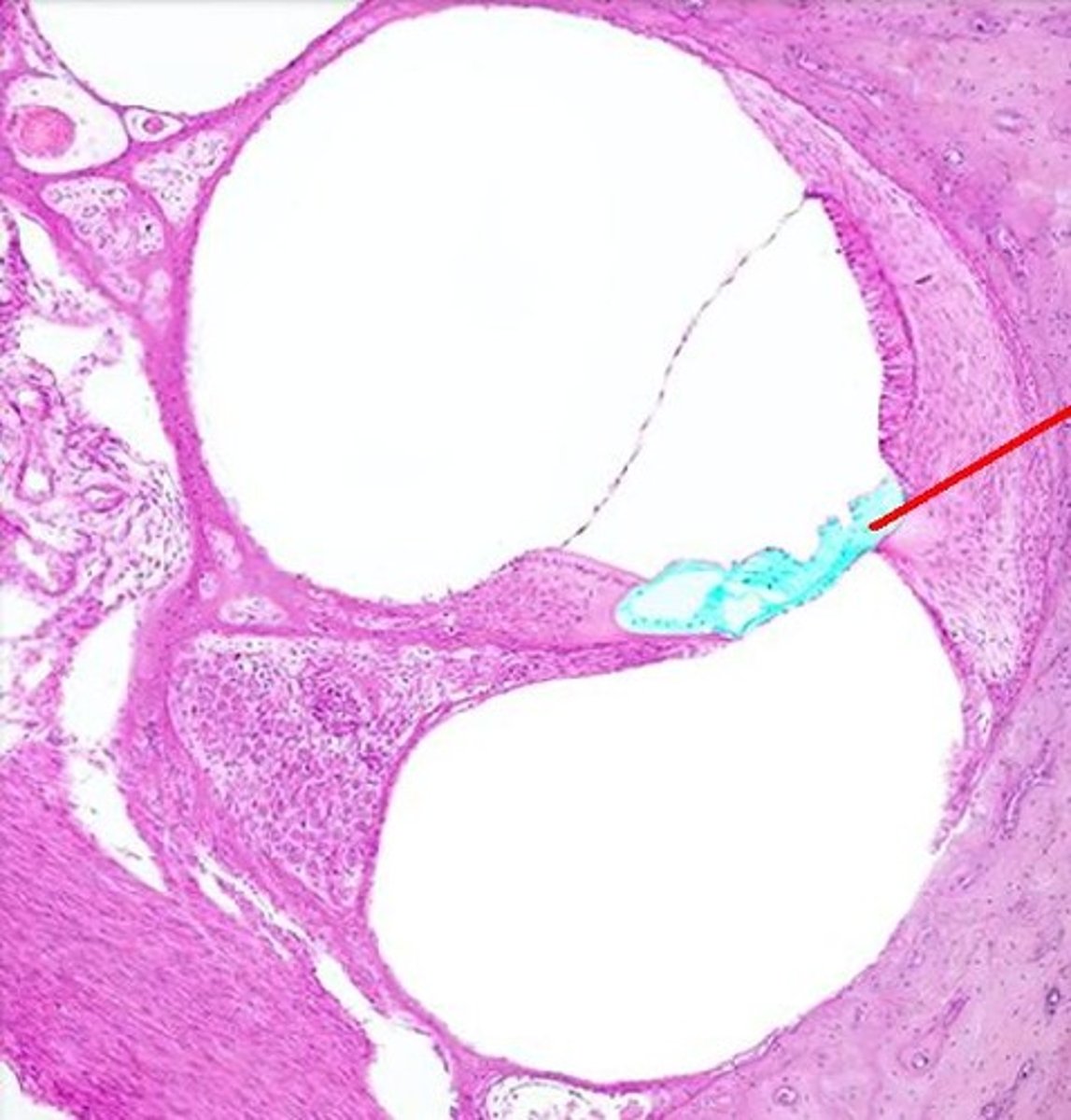
organ of Corti
tissue containing the hair cells necessary for hearing
basilar membrane
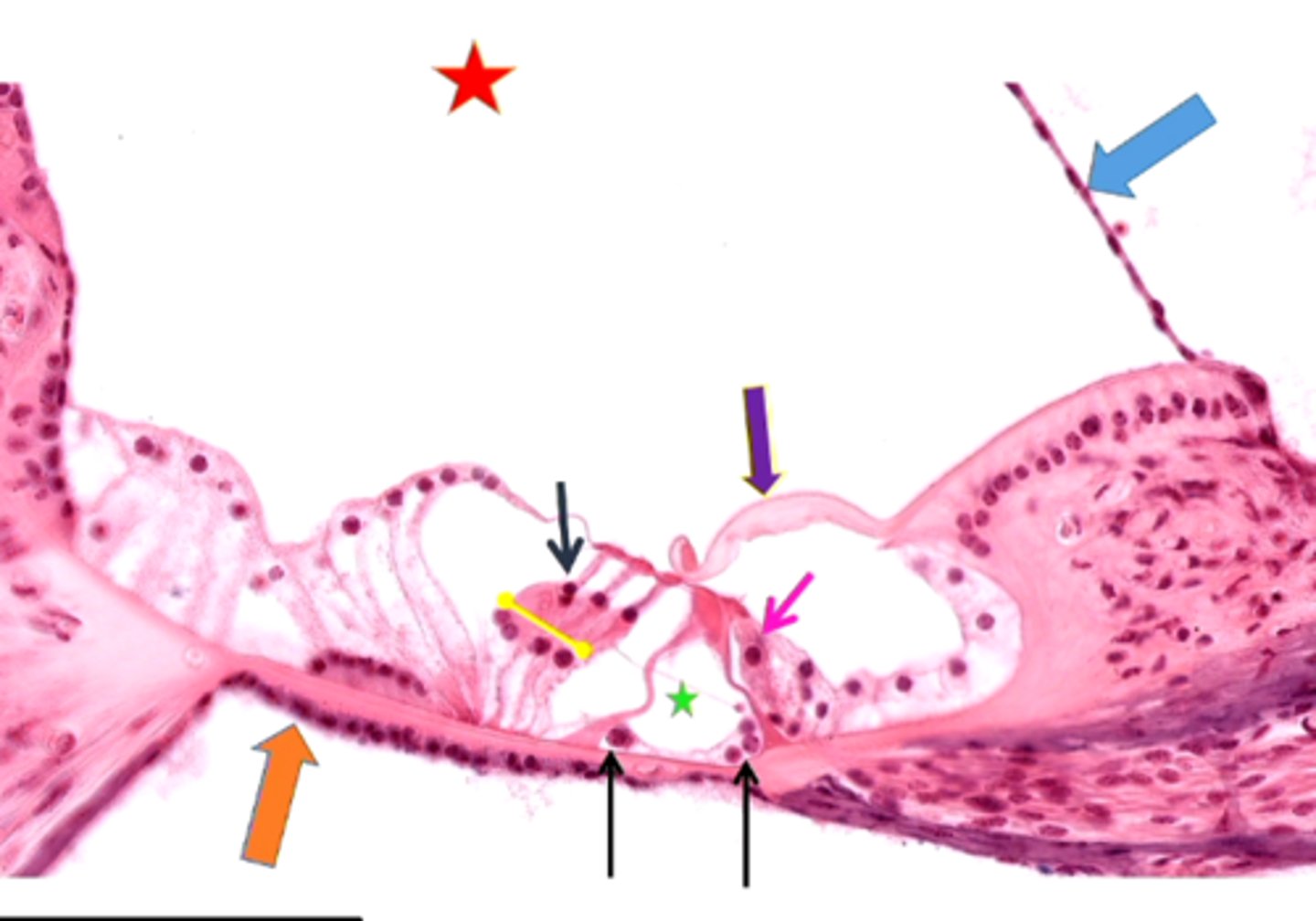
hair cells
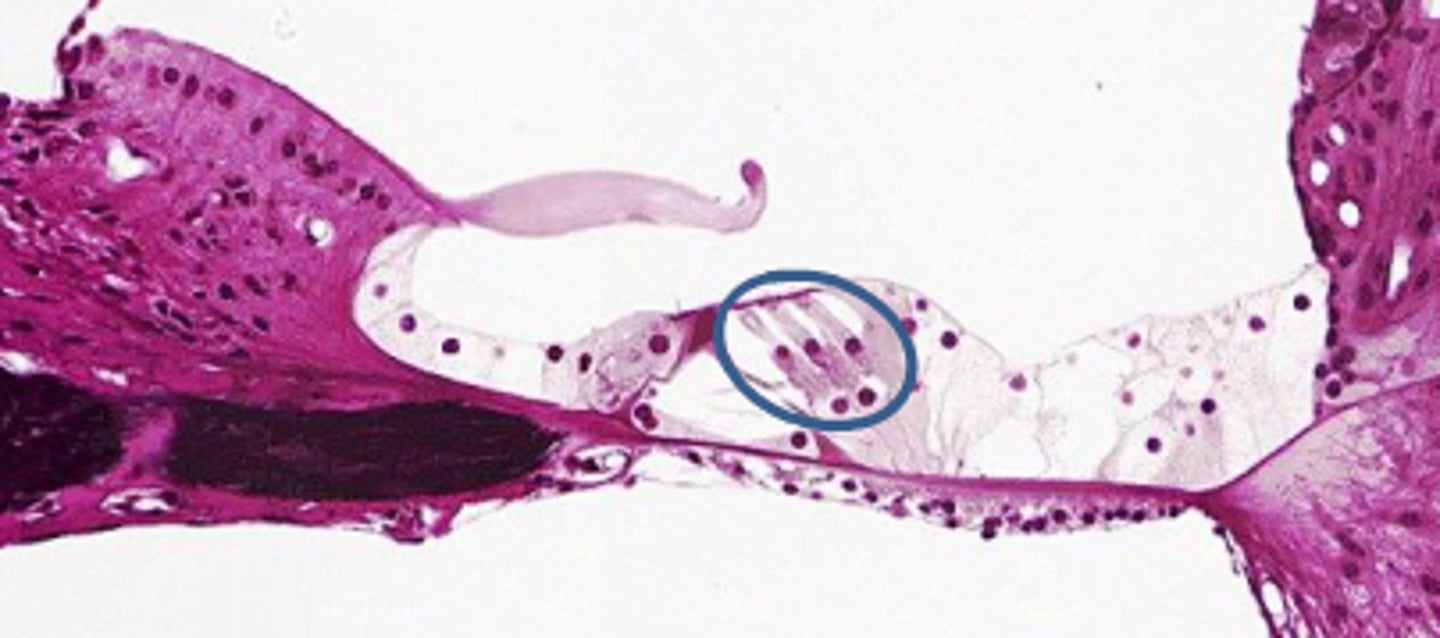
tectorial membrane
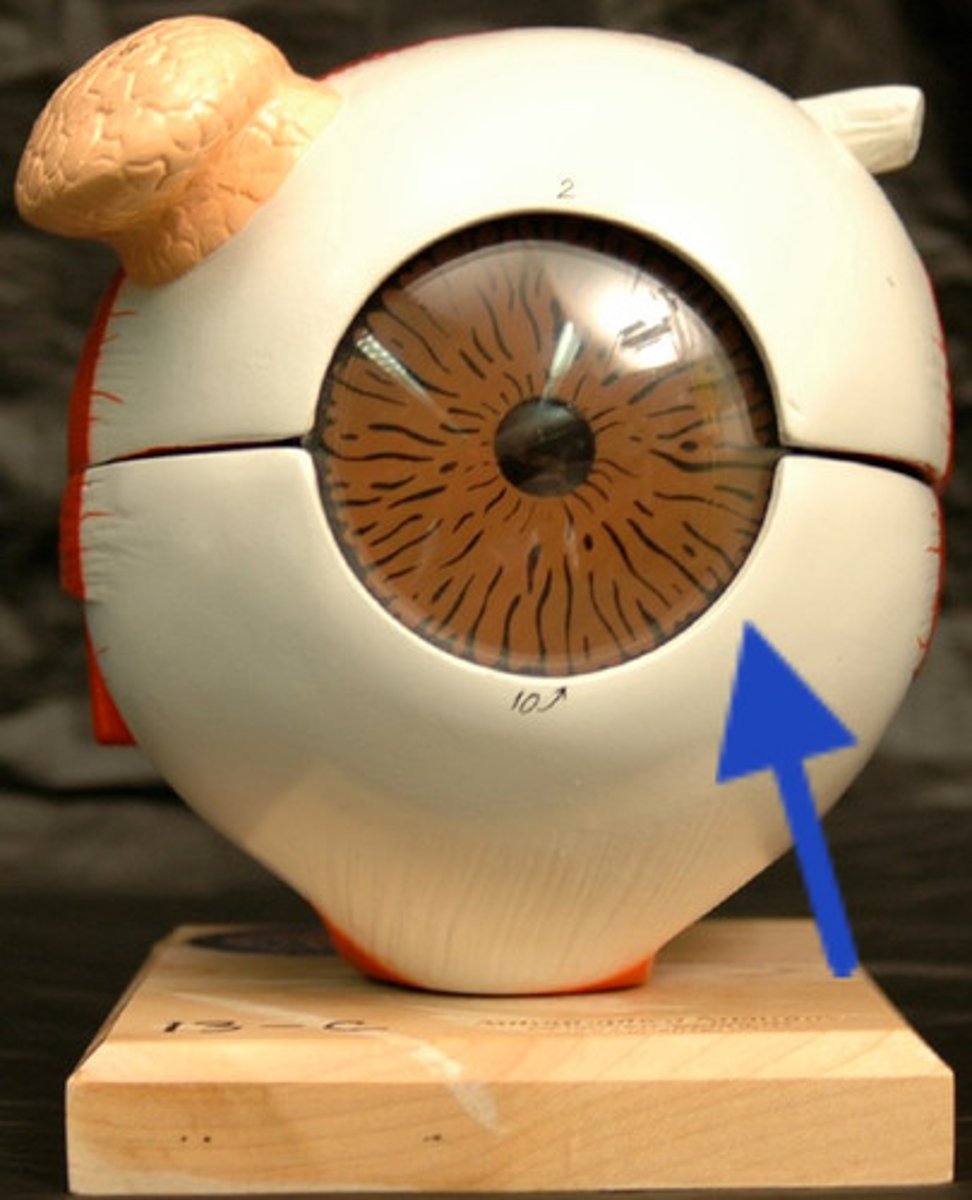
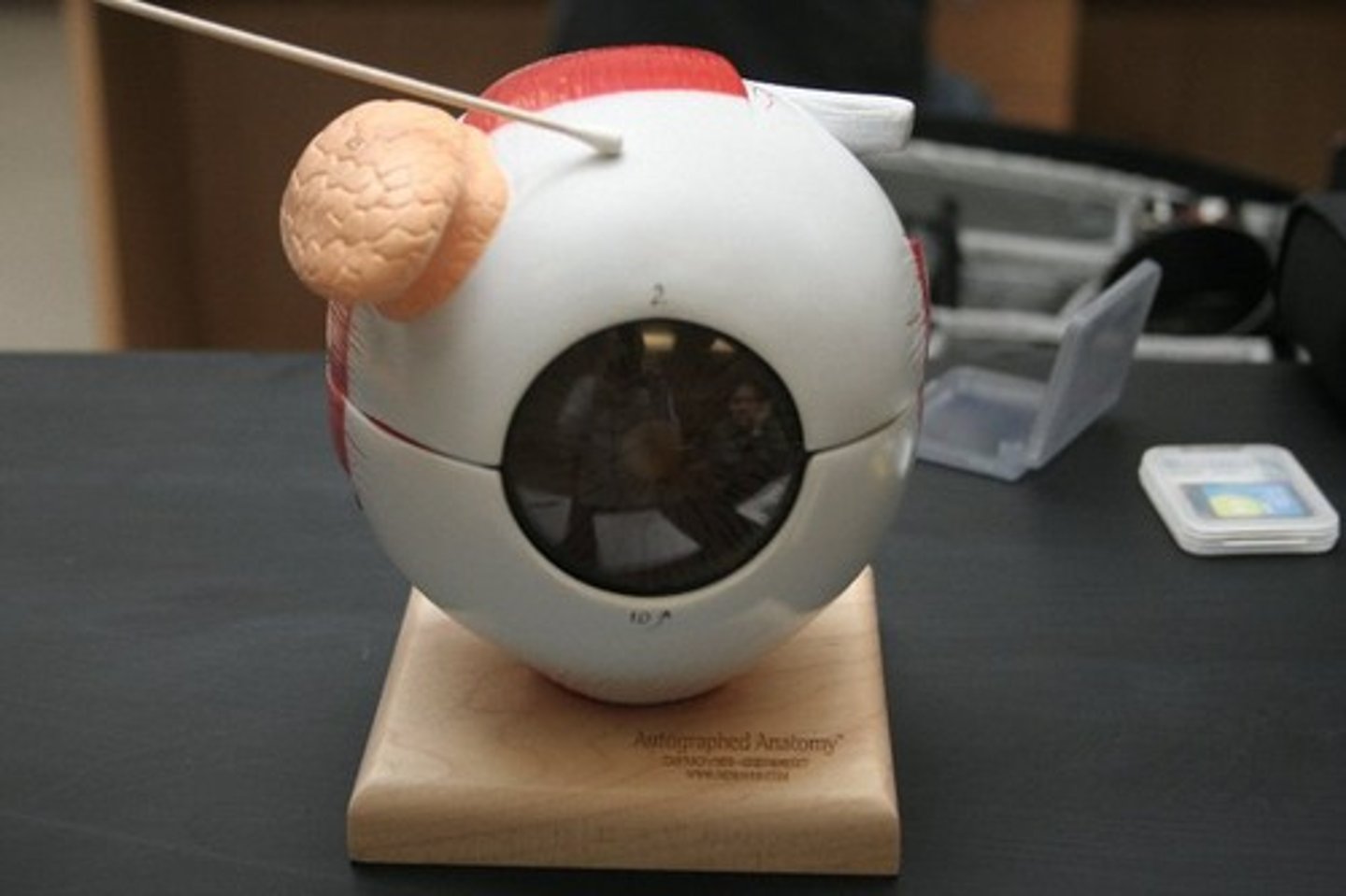
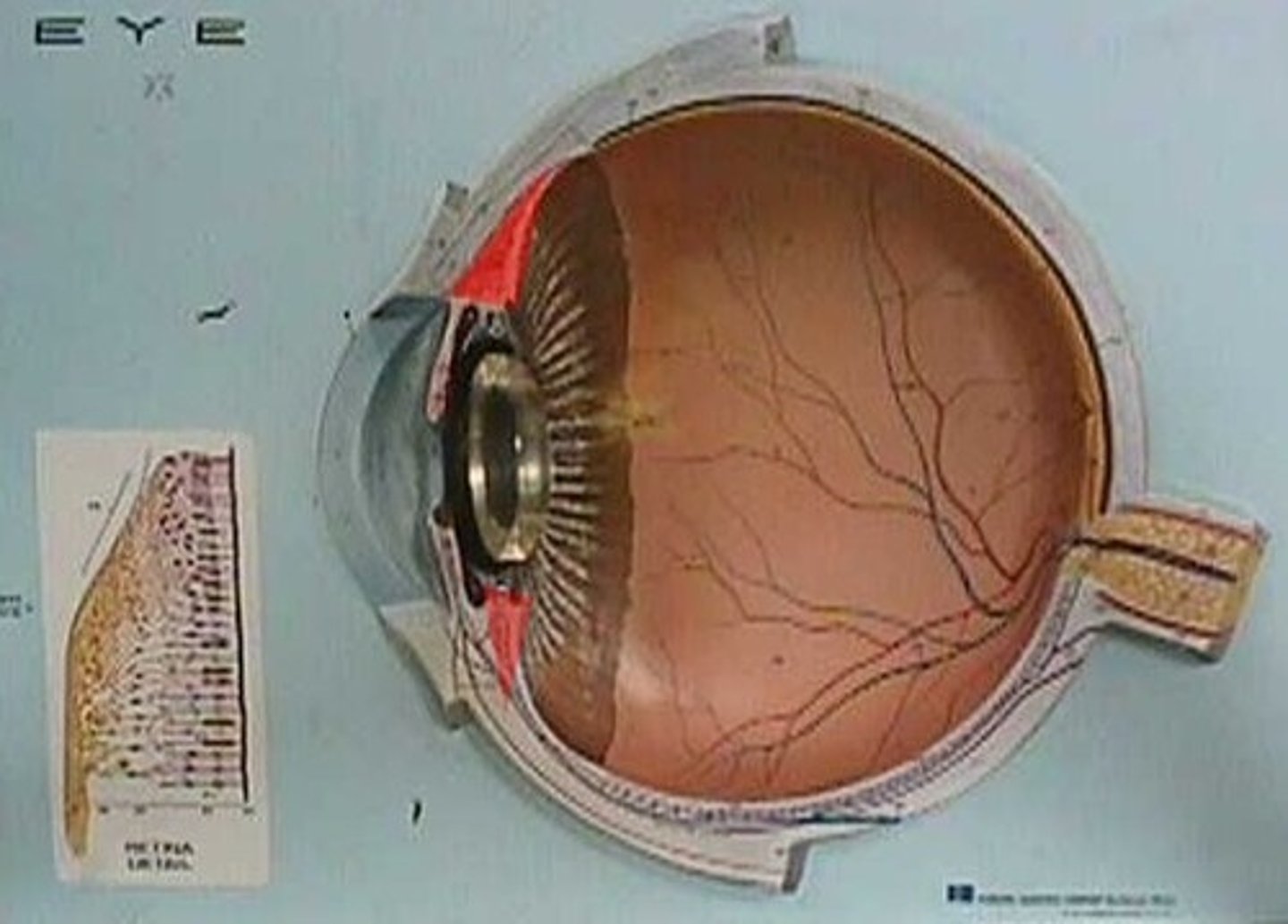
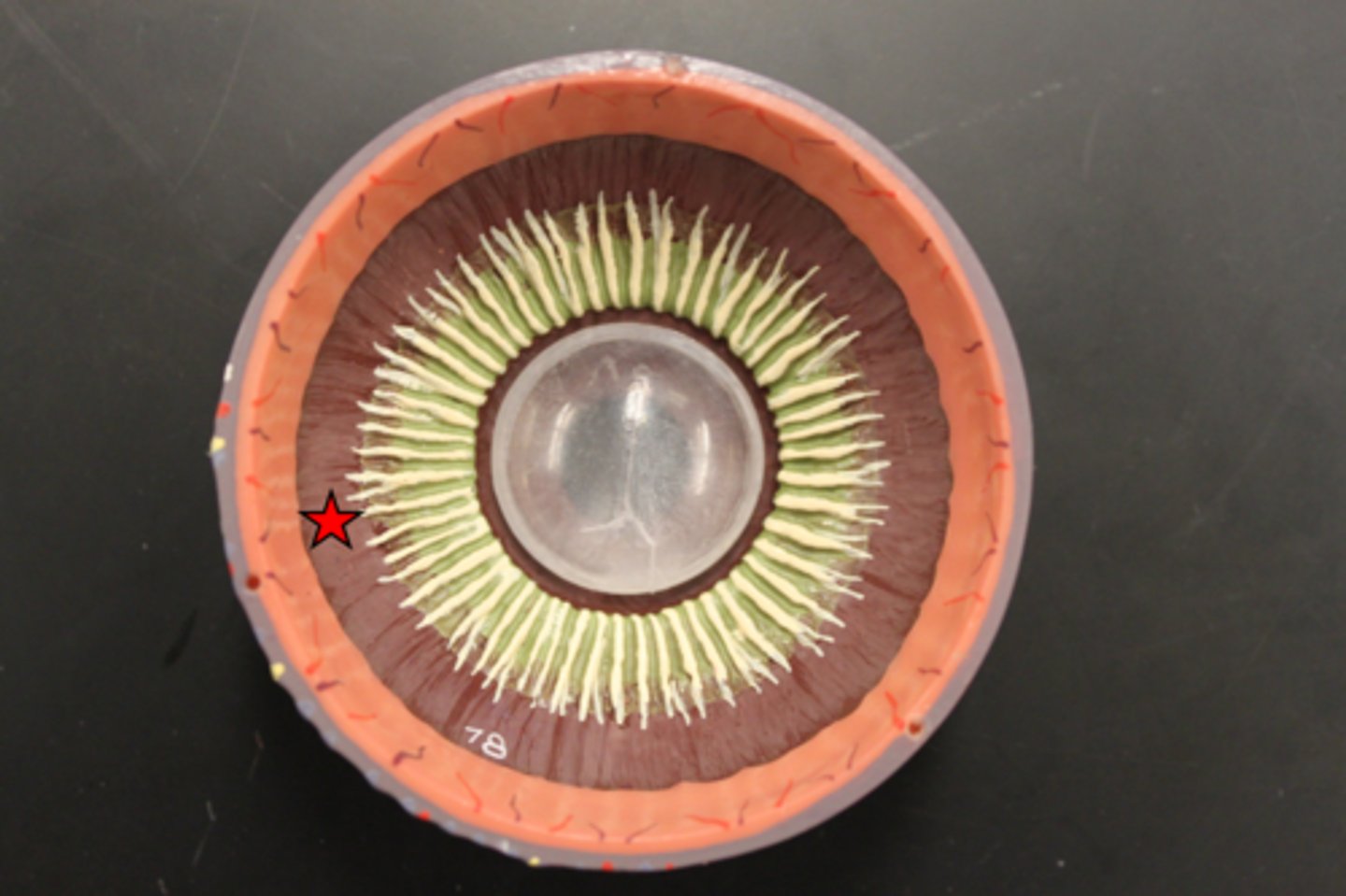
outer (fibrous) tunic (model)
cornea and sclera
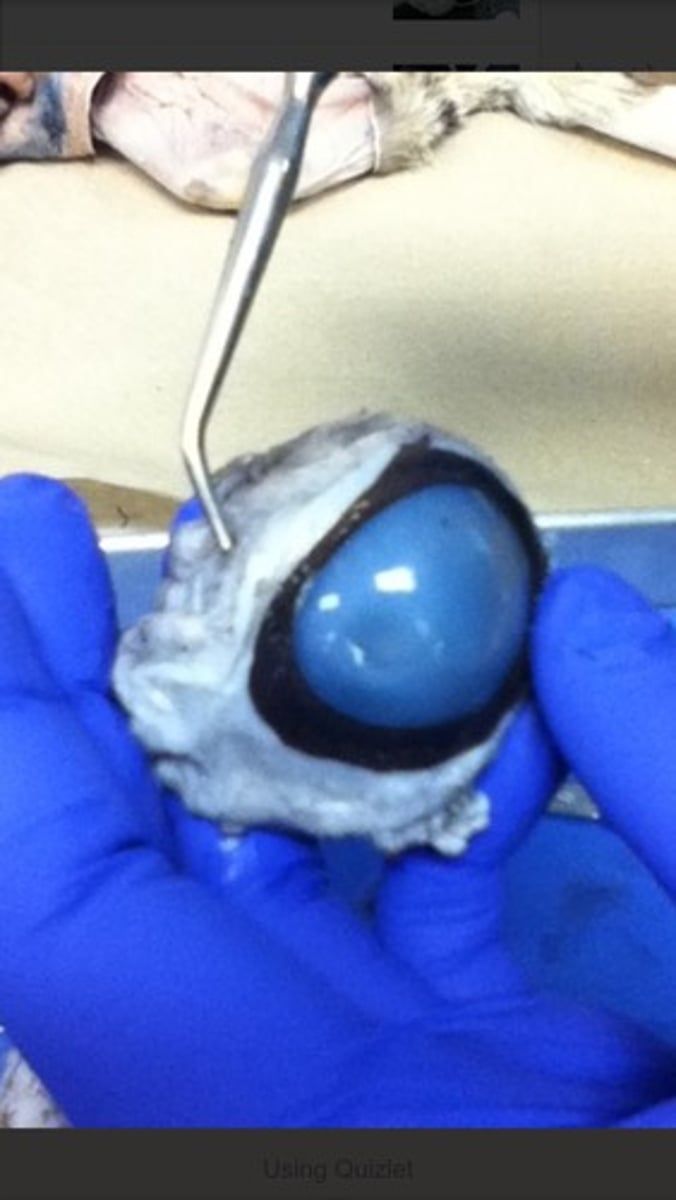
outer (fibrous) tunic (dissection)
sclera (model)
outermost white layer

sclera (dissection)
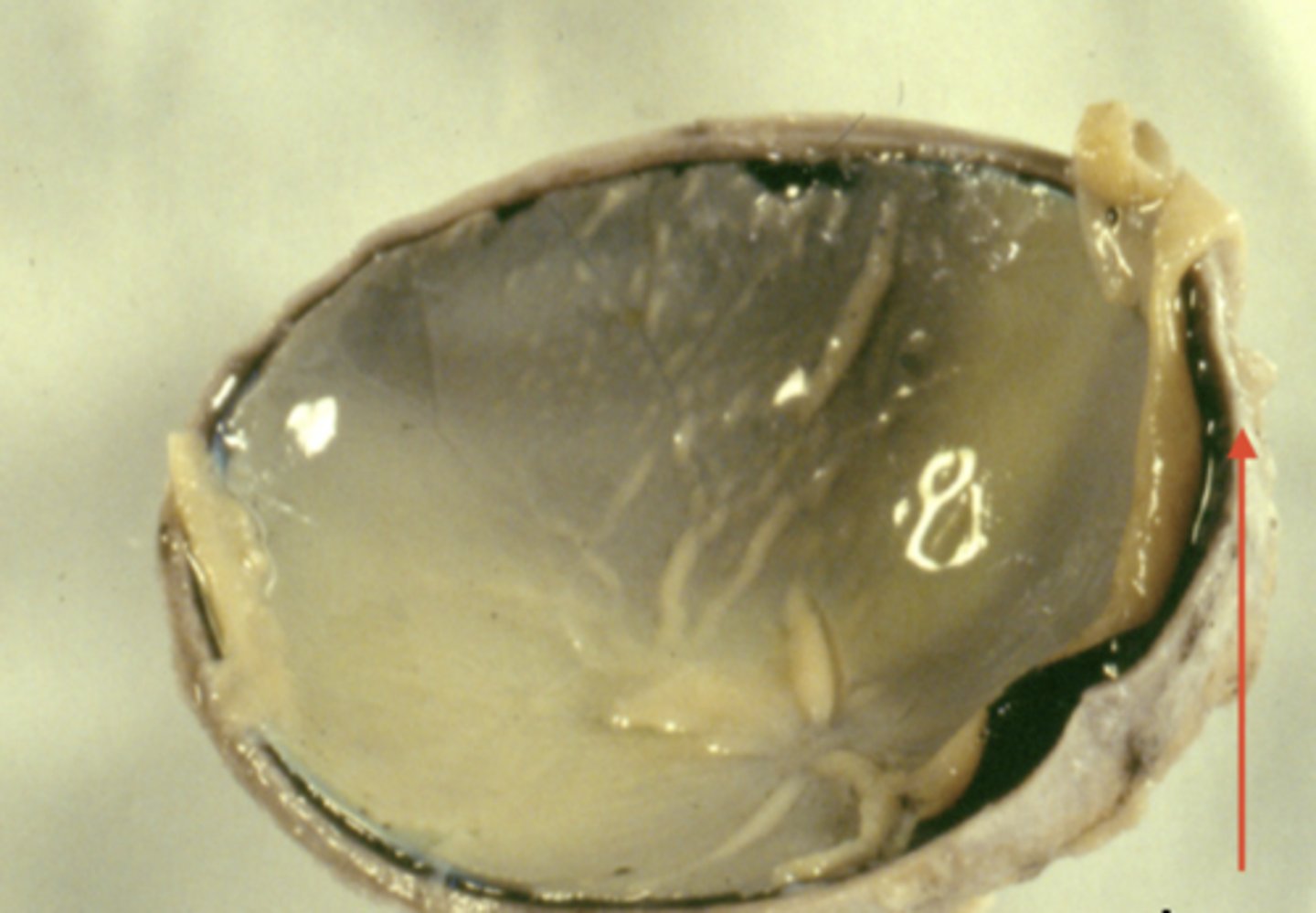
cornea (model)
Clear front piece

cornea (dissection)
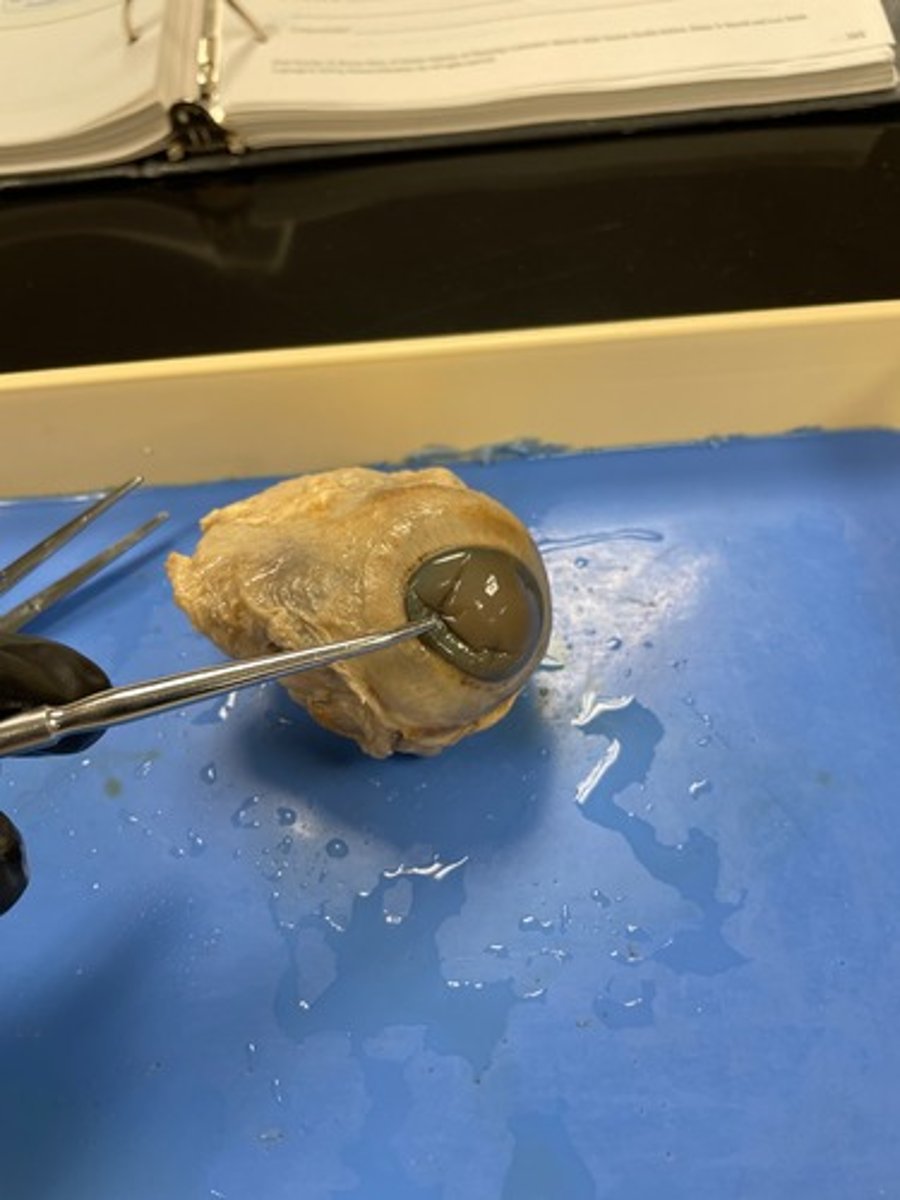
middle (vascular) tunic (model)
iris, ciliary body, choroid
middle (vascular) tunic (dissection)

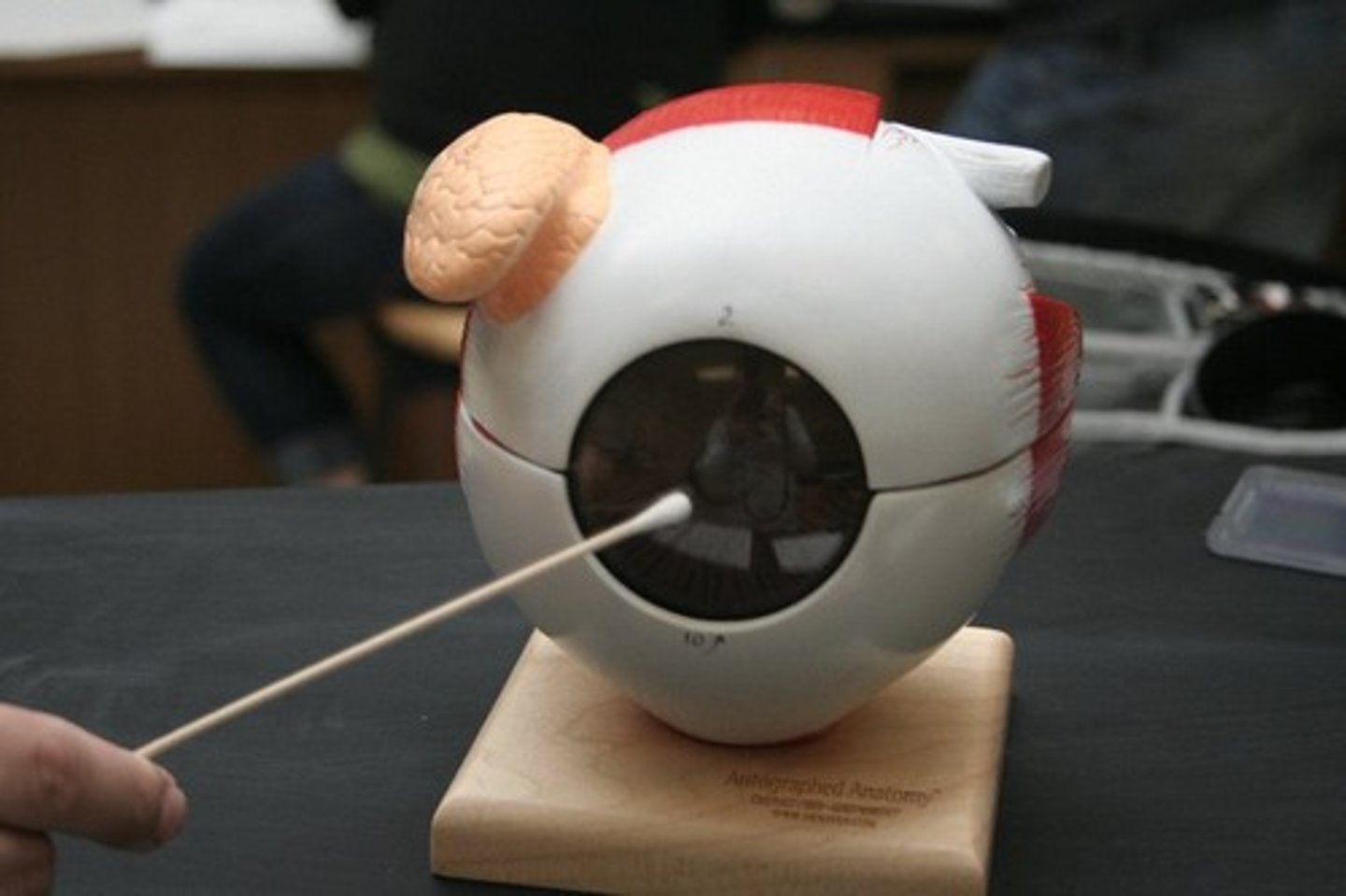
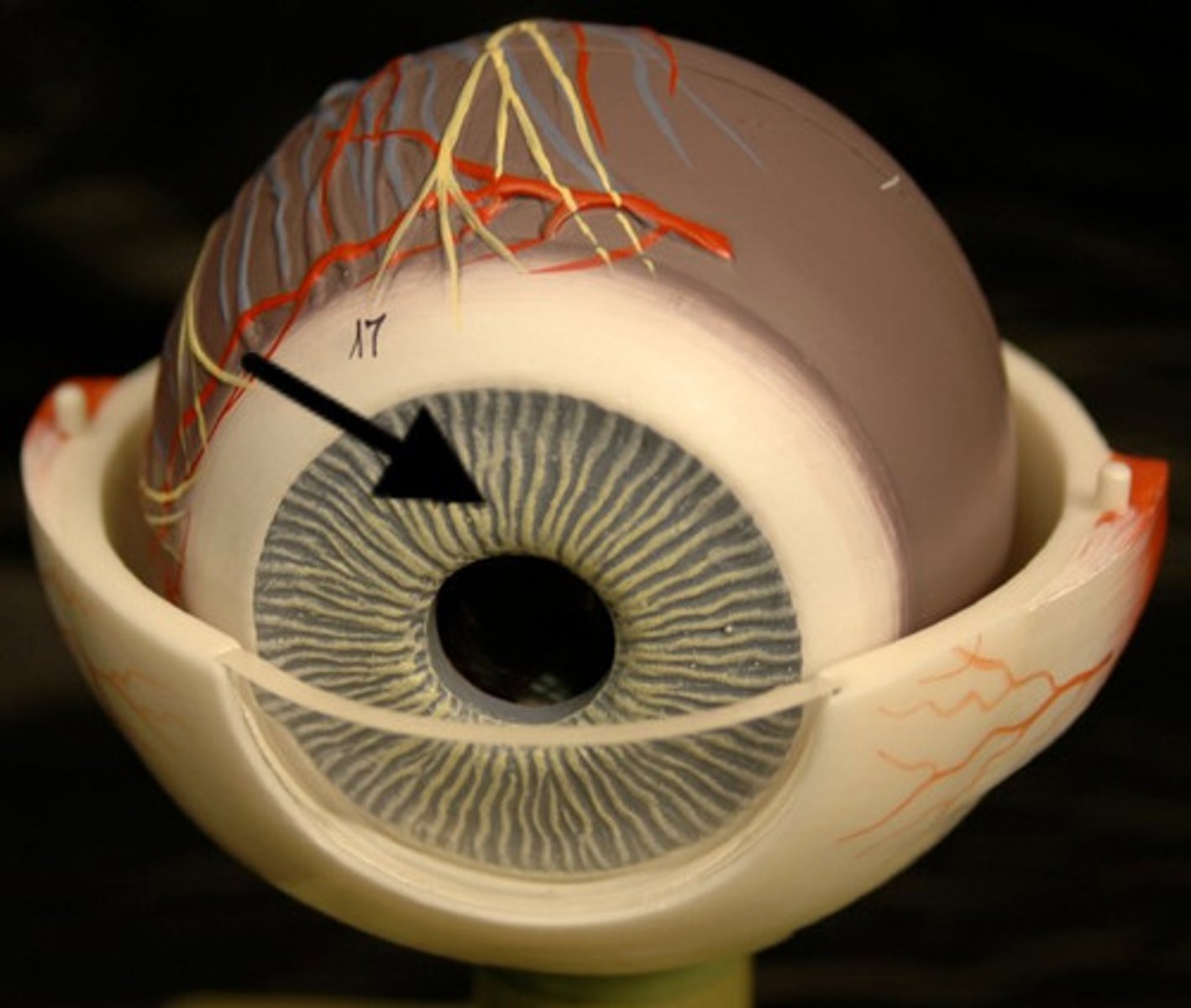
iris (model)
iris (dissection)

pupil (model)
Black central hole
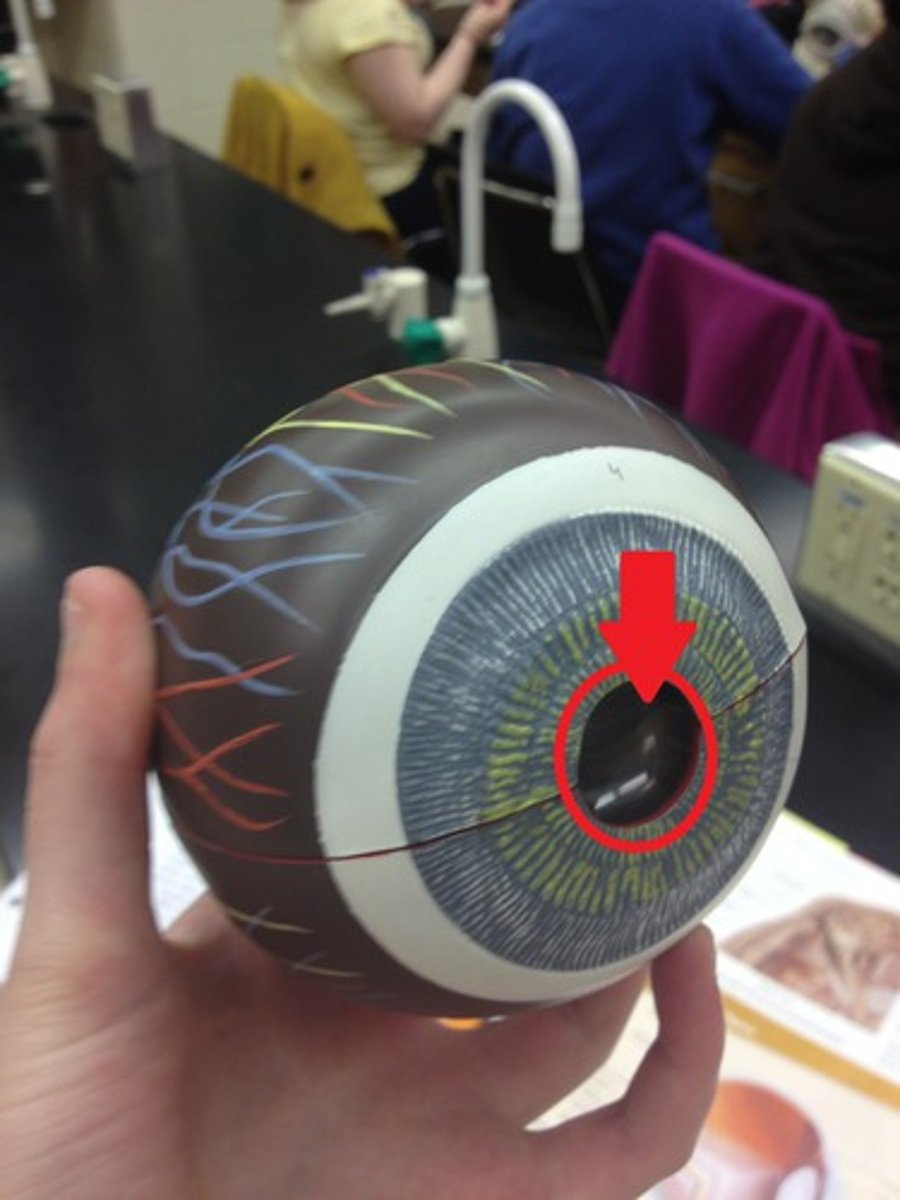

pupil (dissection)
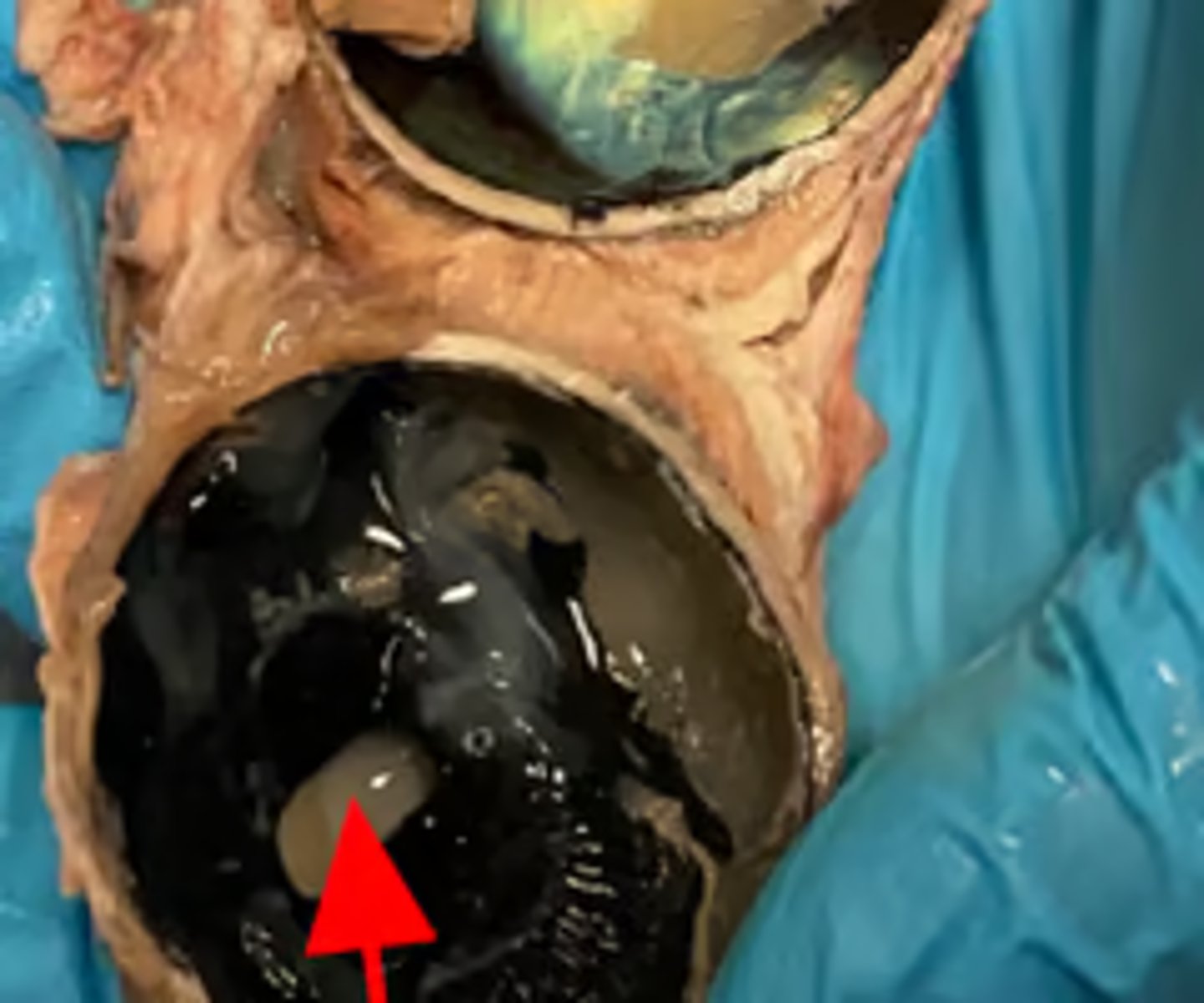
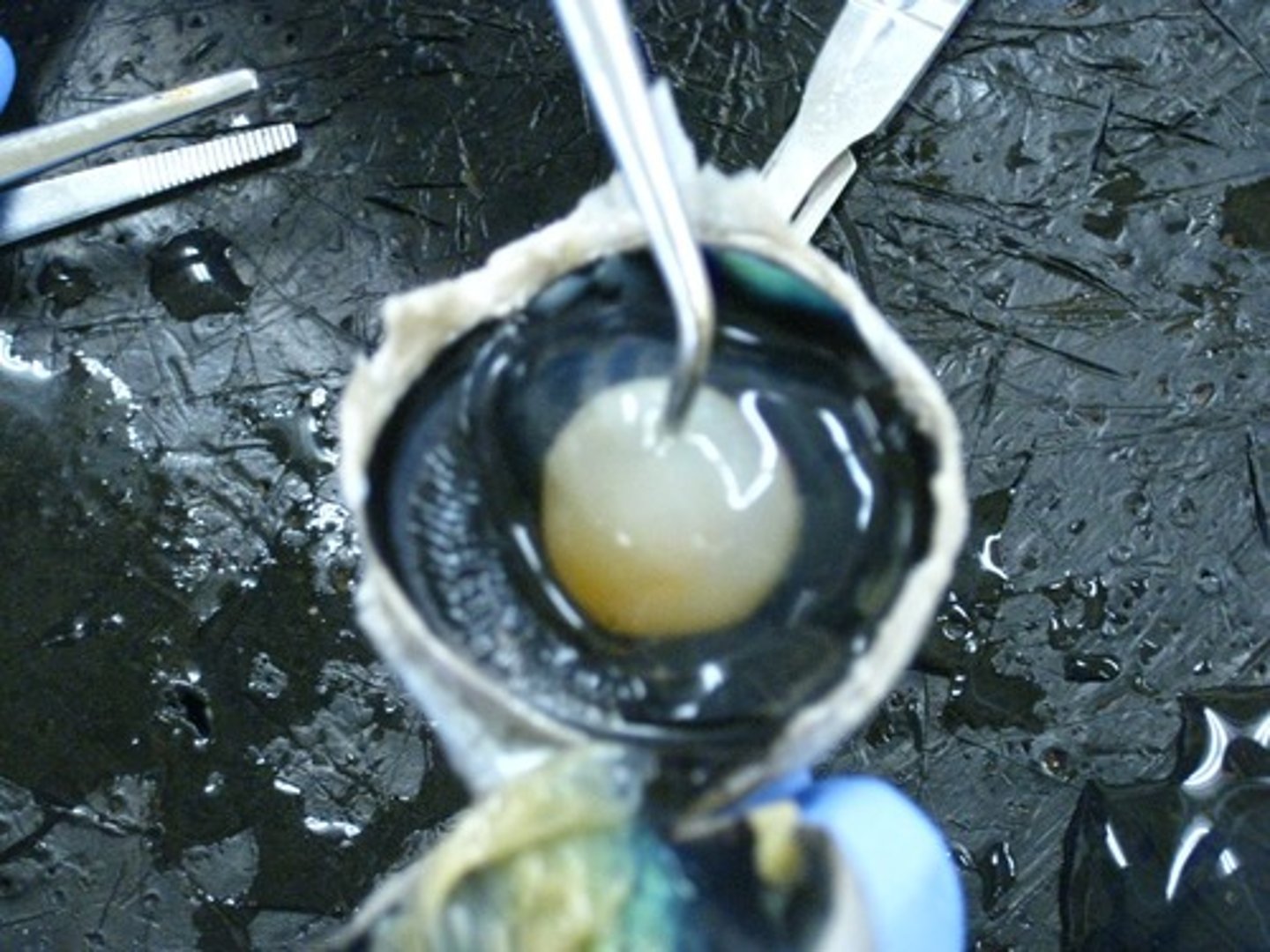
lens (model)
lens (dissection)
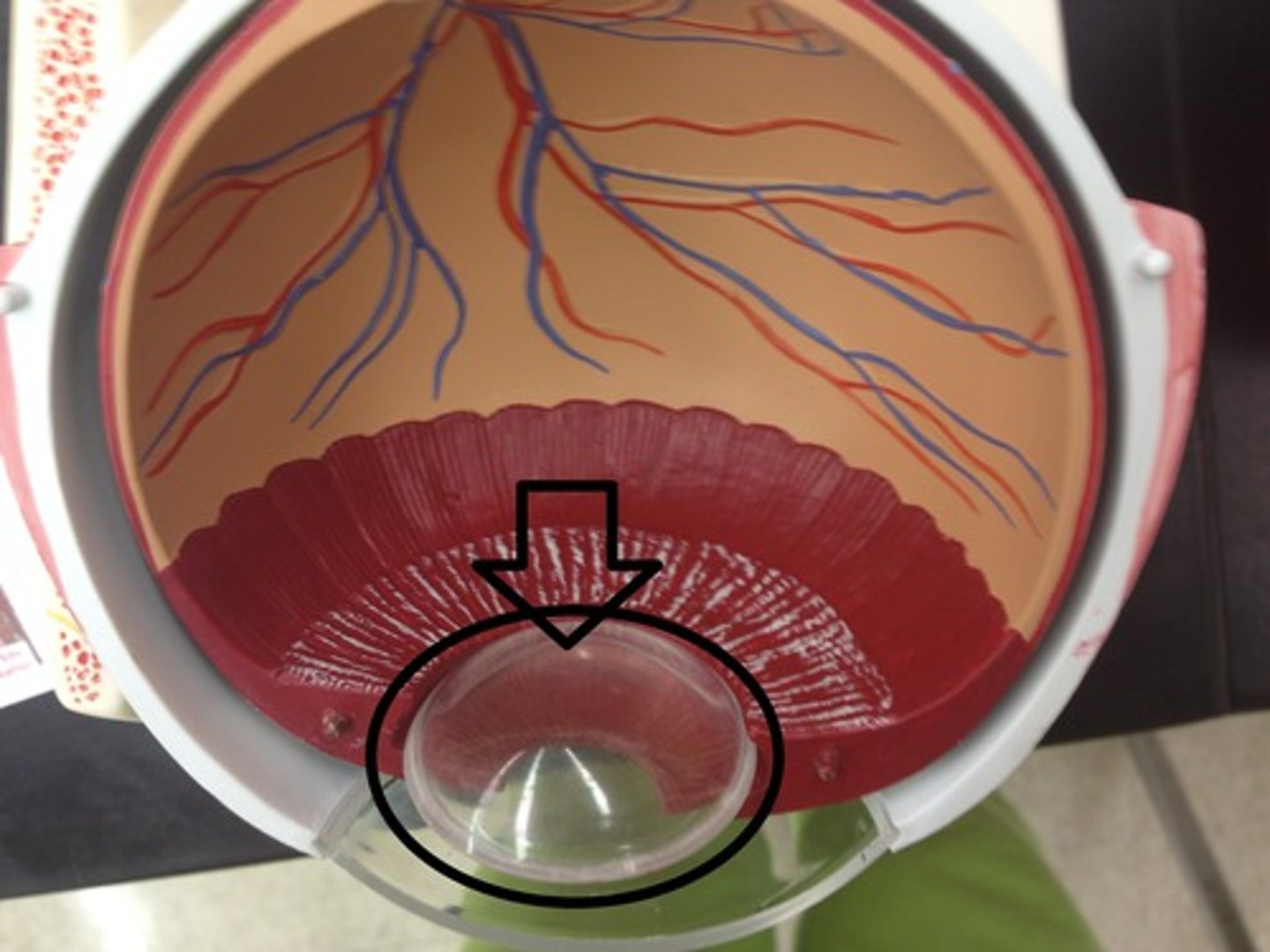
suspensory ligament (model)
attaches the lens to the ciliary body
ciliary body (model)
ring of tissue behind the peripheral iris that is composed of ciliary muscle and ciliary processes
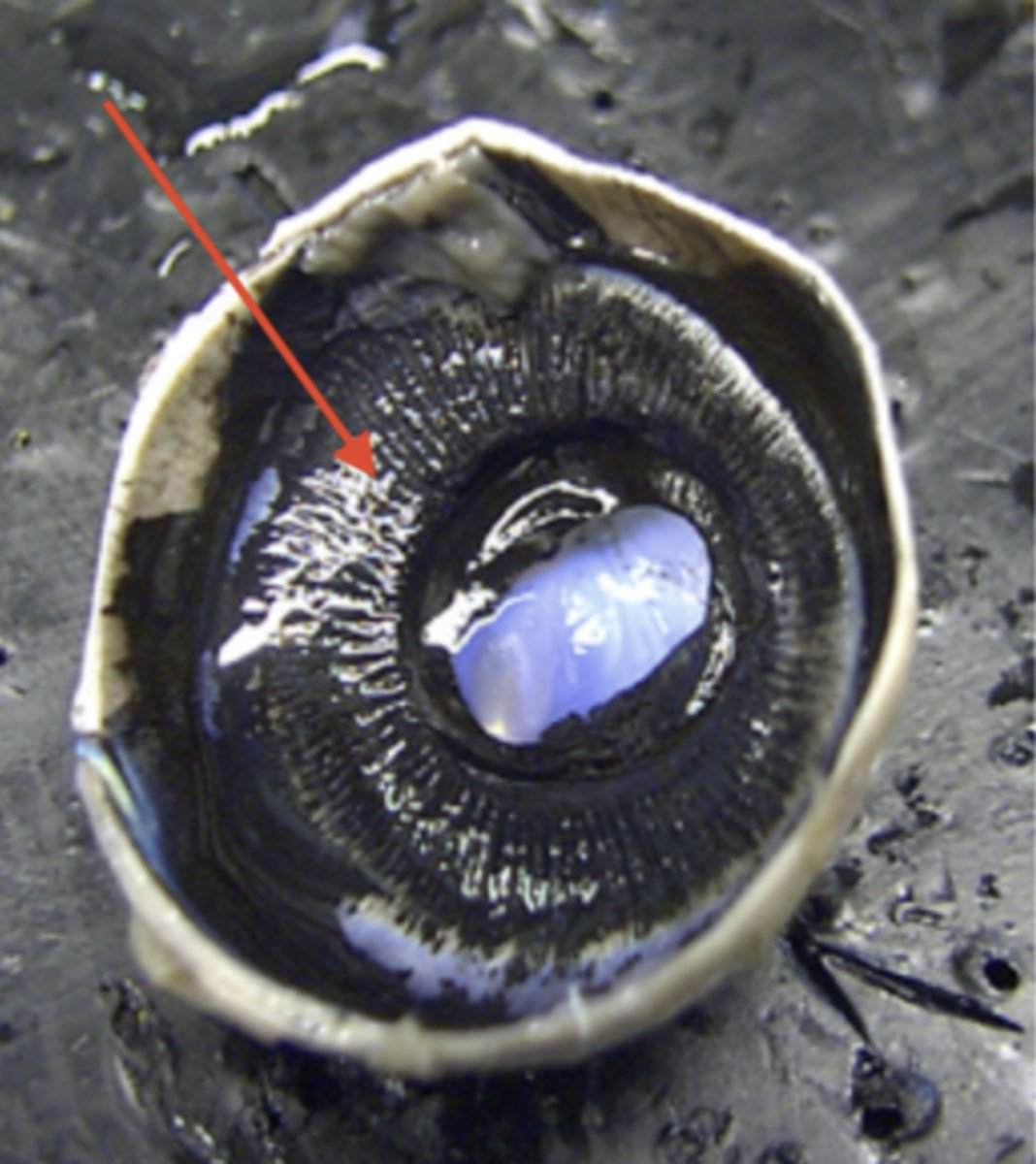
ciliary body (dissection)
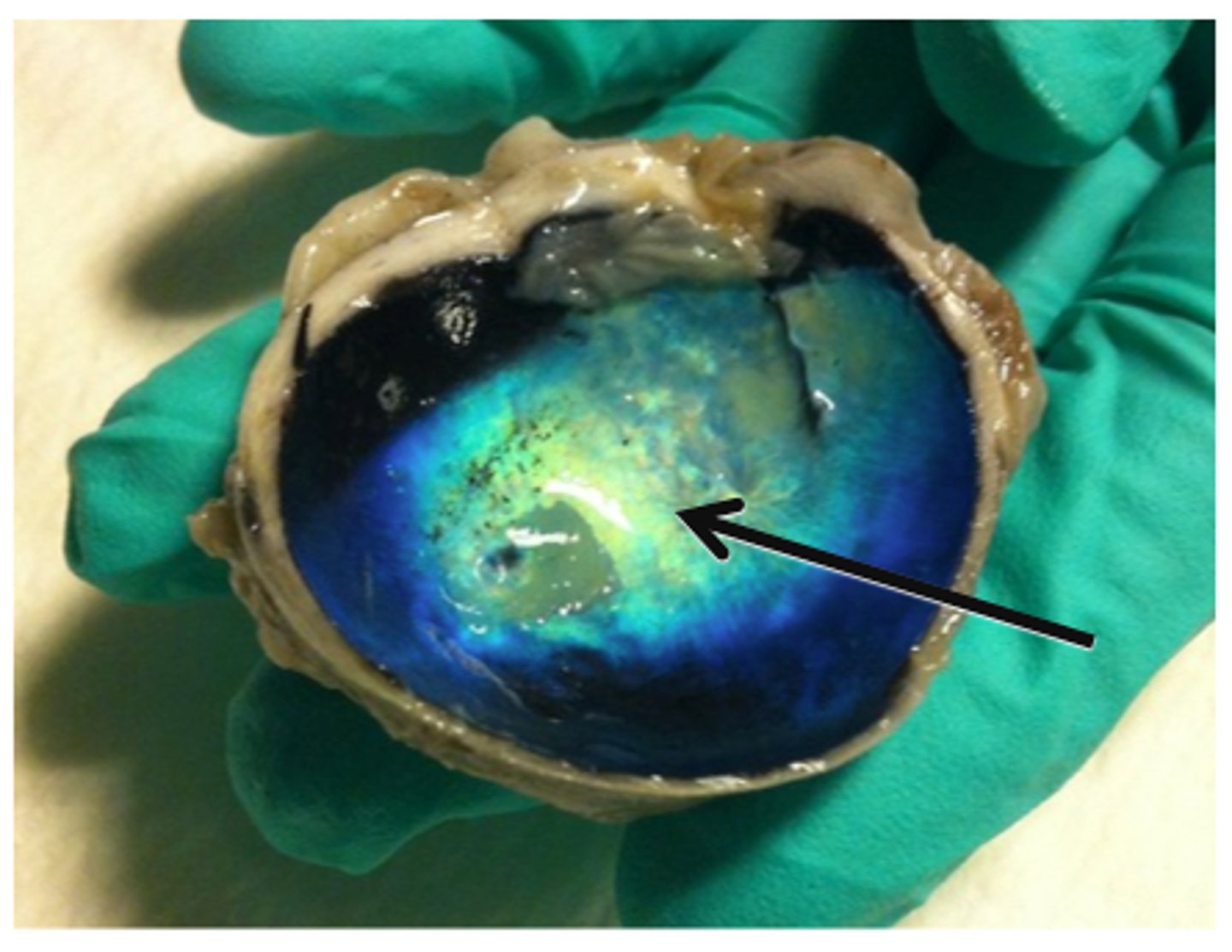
choroid (model)
middle, vascular layer of the eye, between the retina and the sclera
choroid (dissection)
inner tunic/retina (model)
visual receptor cells
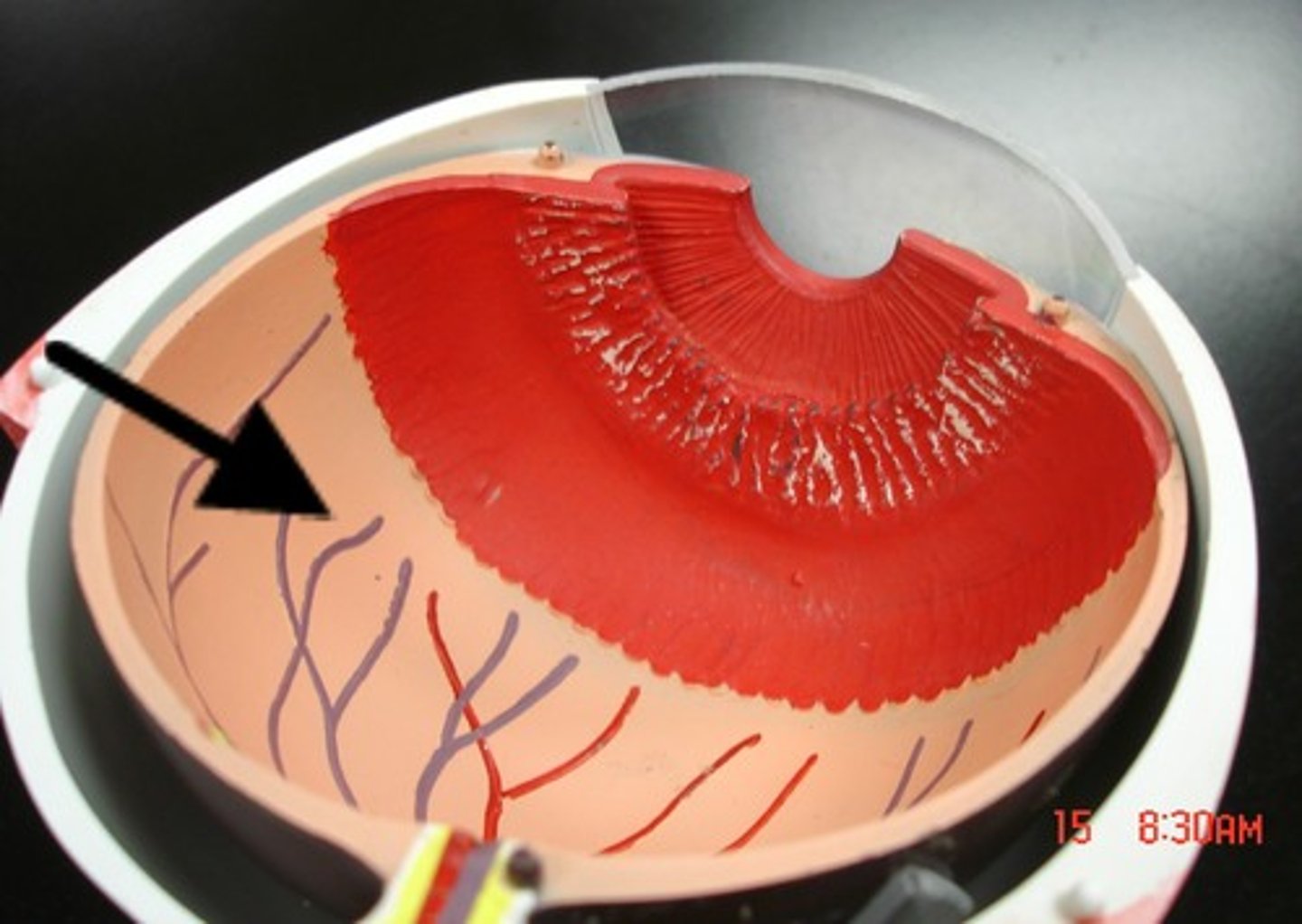
retina (dissection)
a layer at the back of the eyeball containing cells that are sensitive to light and that trigger nerve impulses that pass via the optic nerve to the brain, where a visual image is formed.
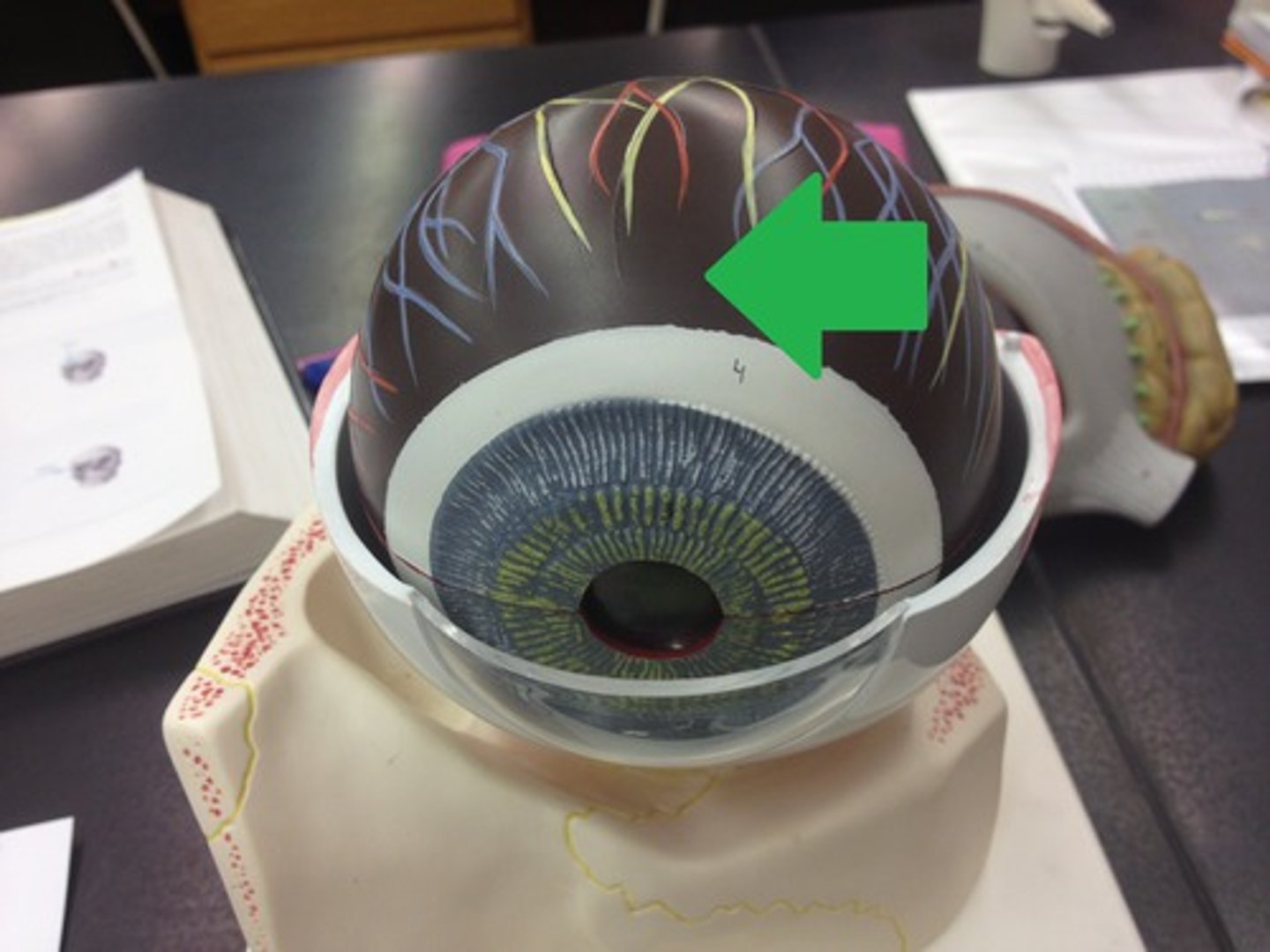
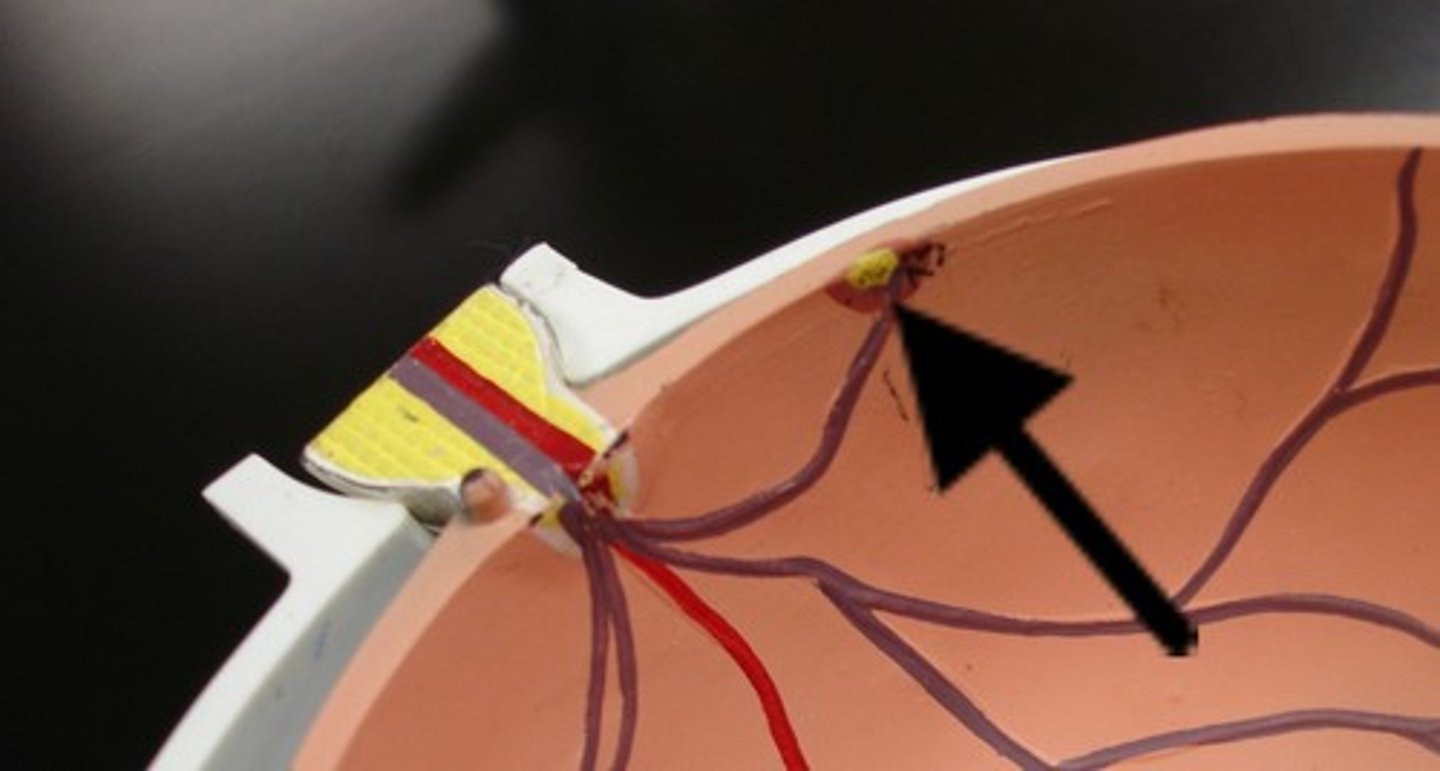
optic disc (model)
blind spot
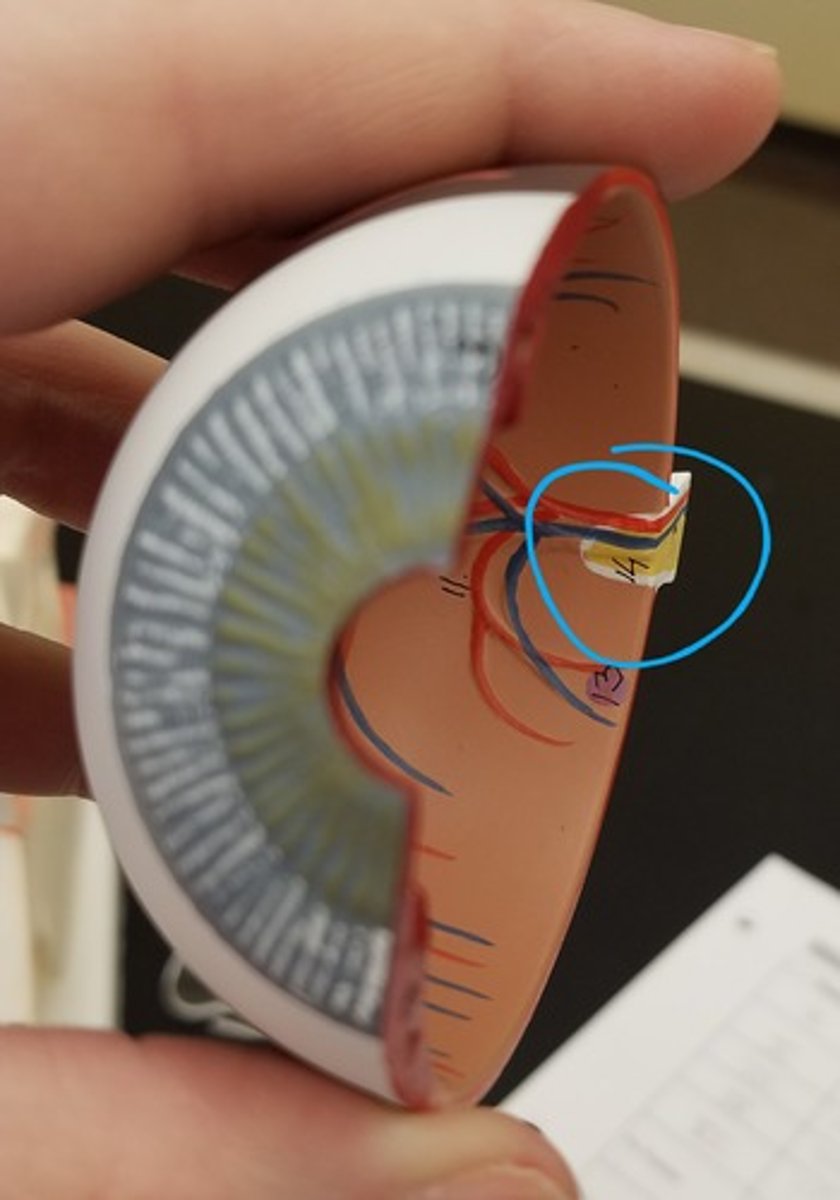

optic nerve (model)
the nerve that carries neural impulses from the eye to the brain
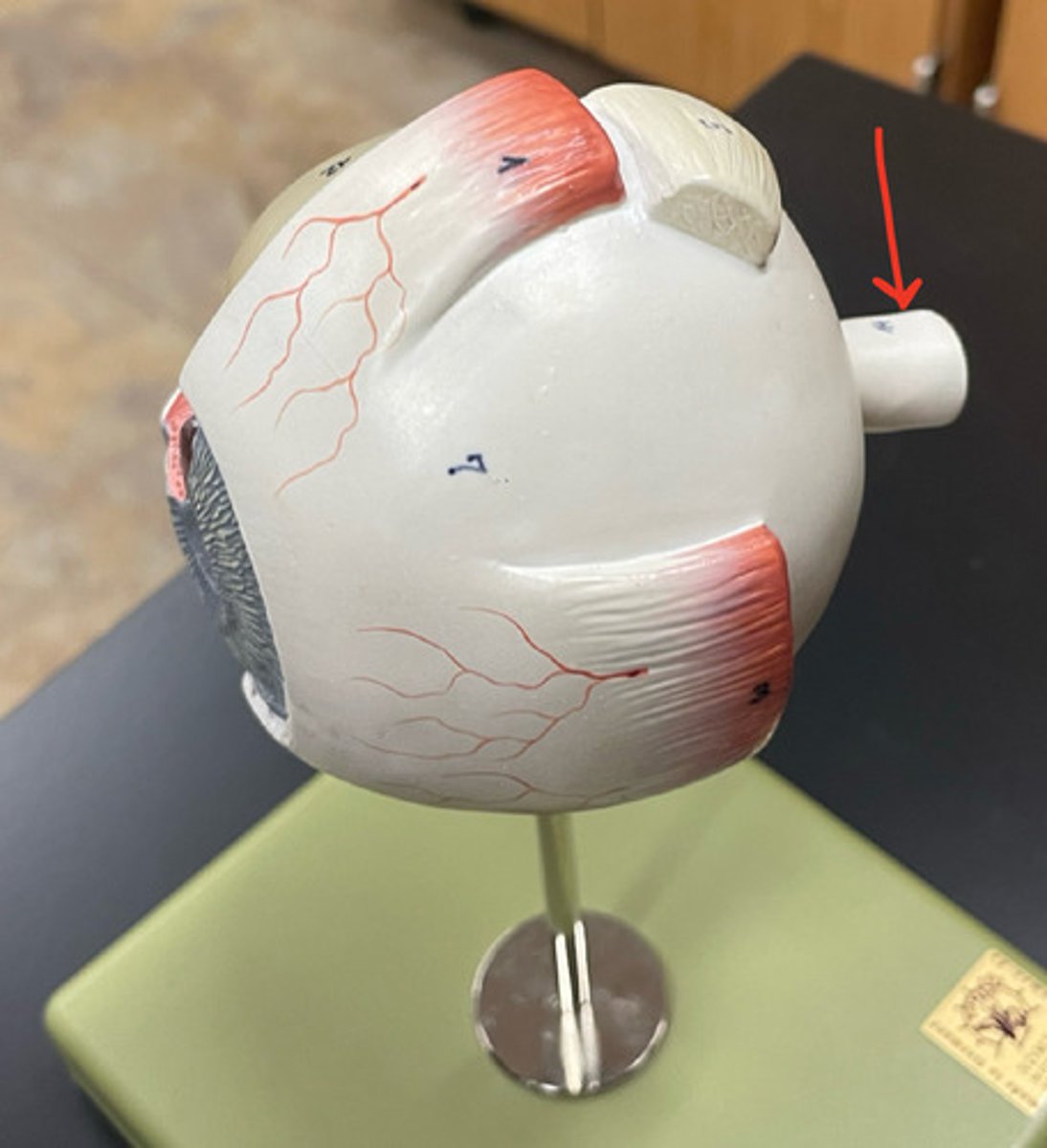

optic nerve (dissection)

macula lutea (model)
a yellowish central area of the retina that is rich in cones and that mediates clear detailed vision
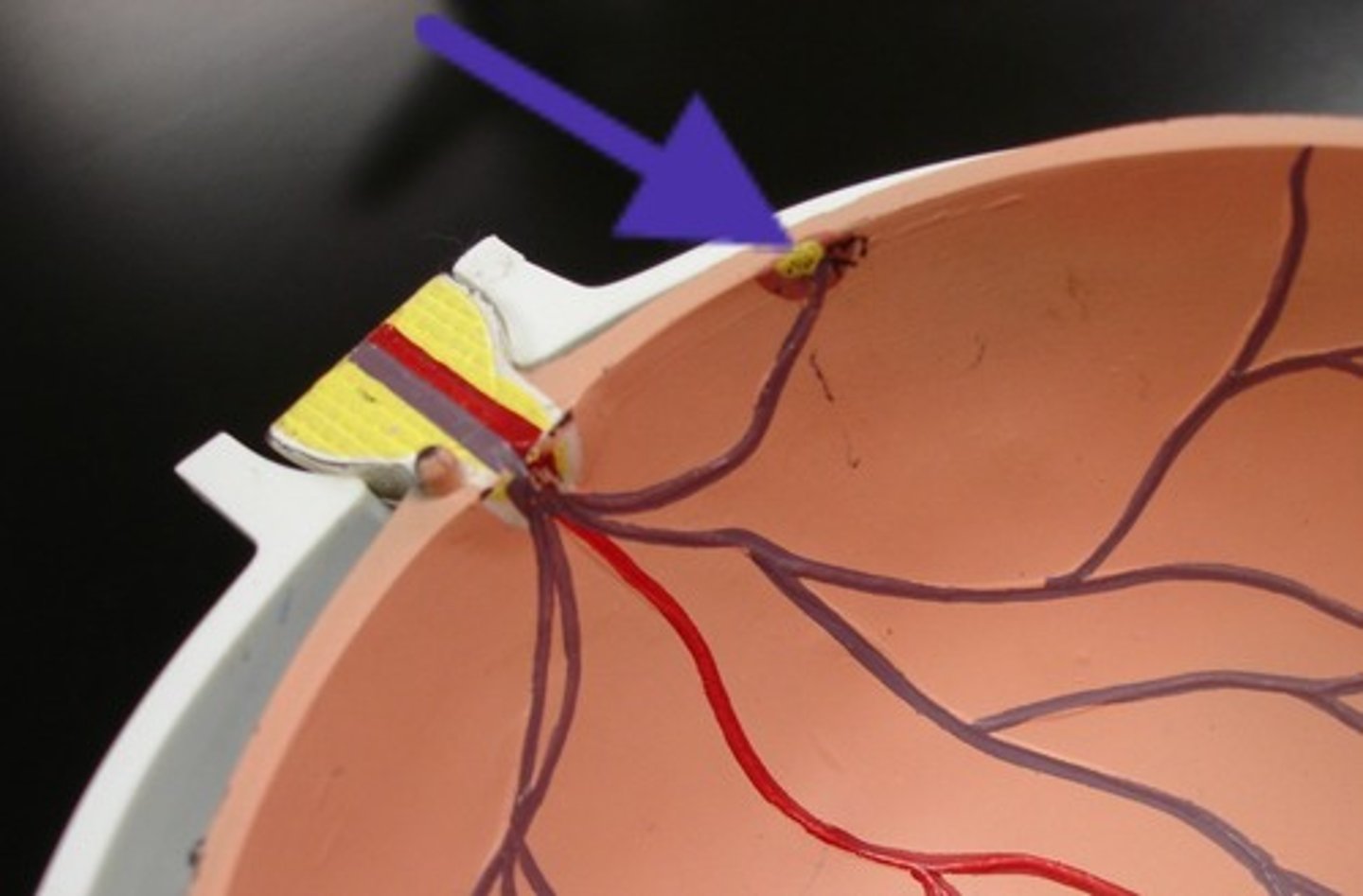
fovea centralis (model)
tiny pit or depression in the retina that is the region of clearest vision
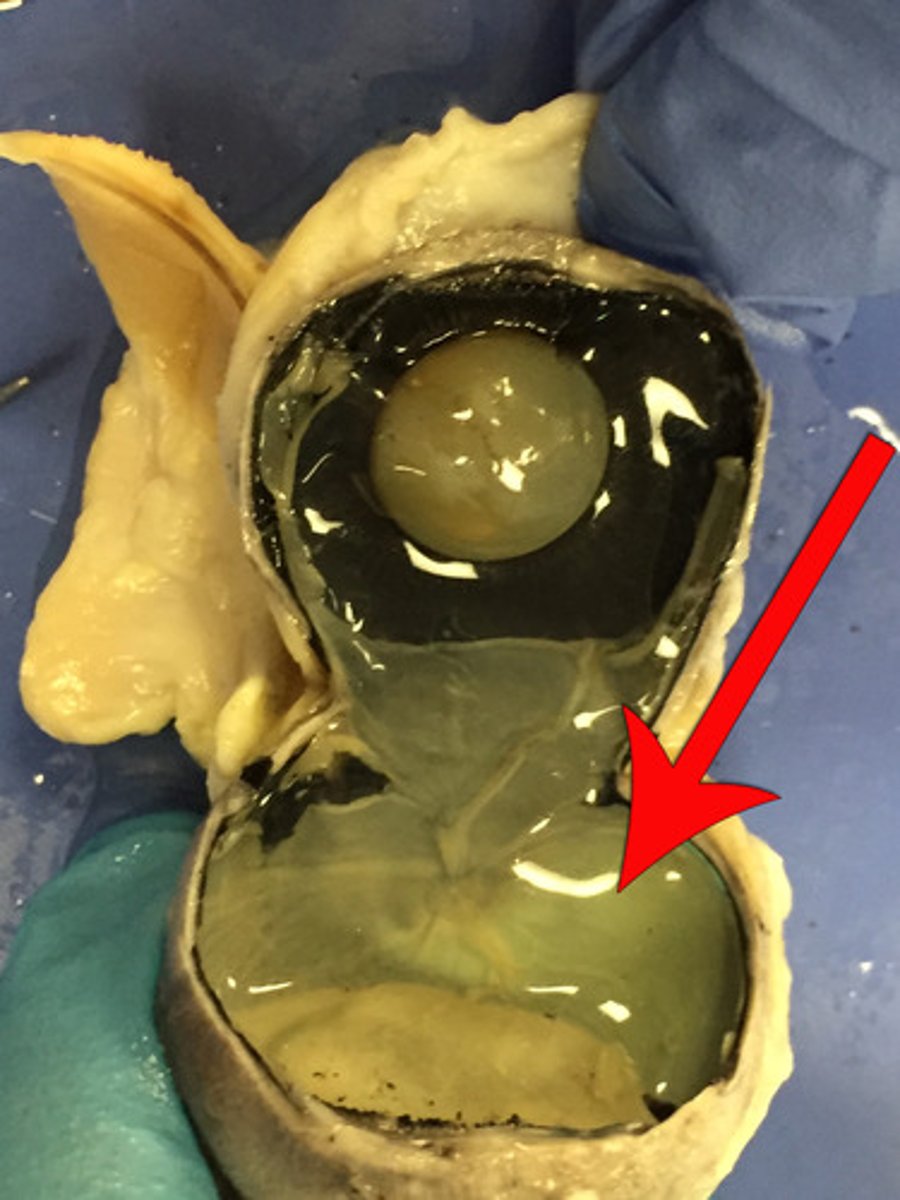
anterior compartment
anterior to lens; filled with aqueous humor
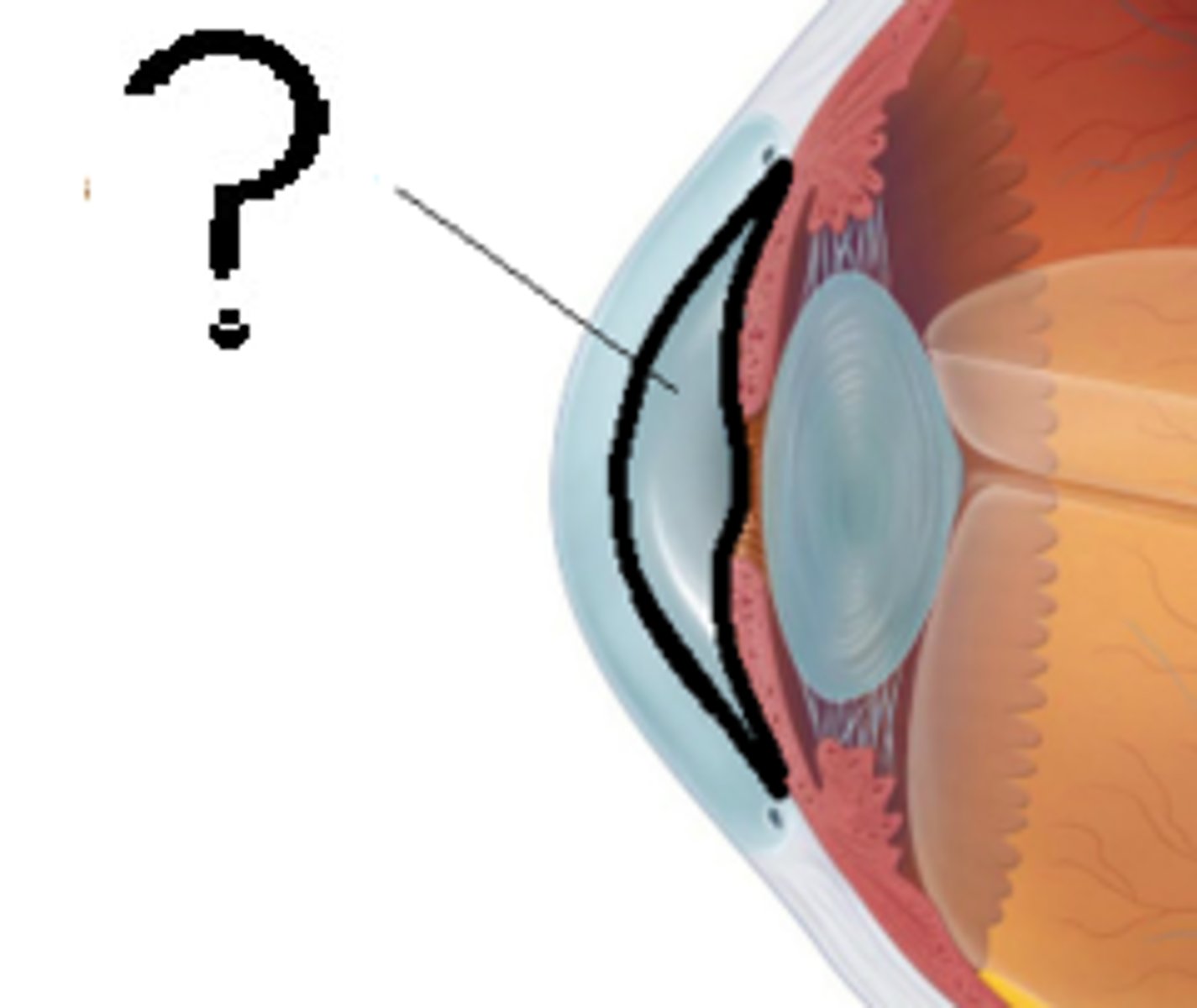
posterior chamber
between iris and lens
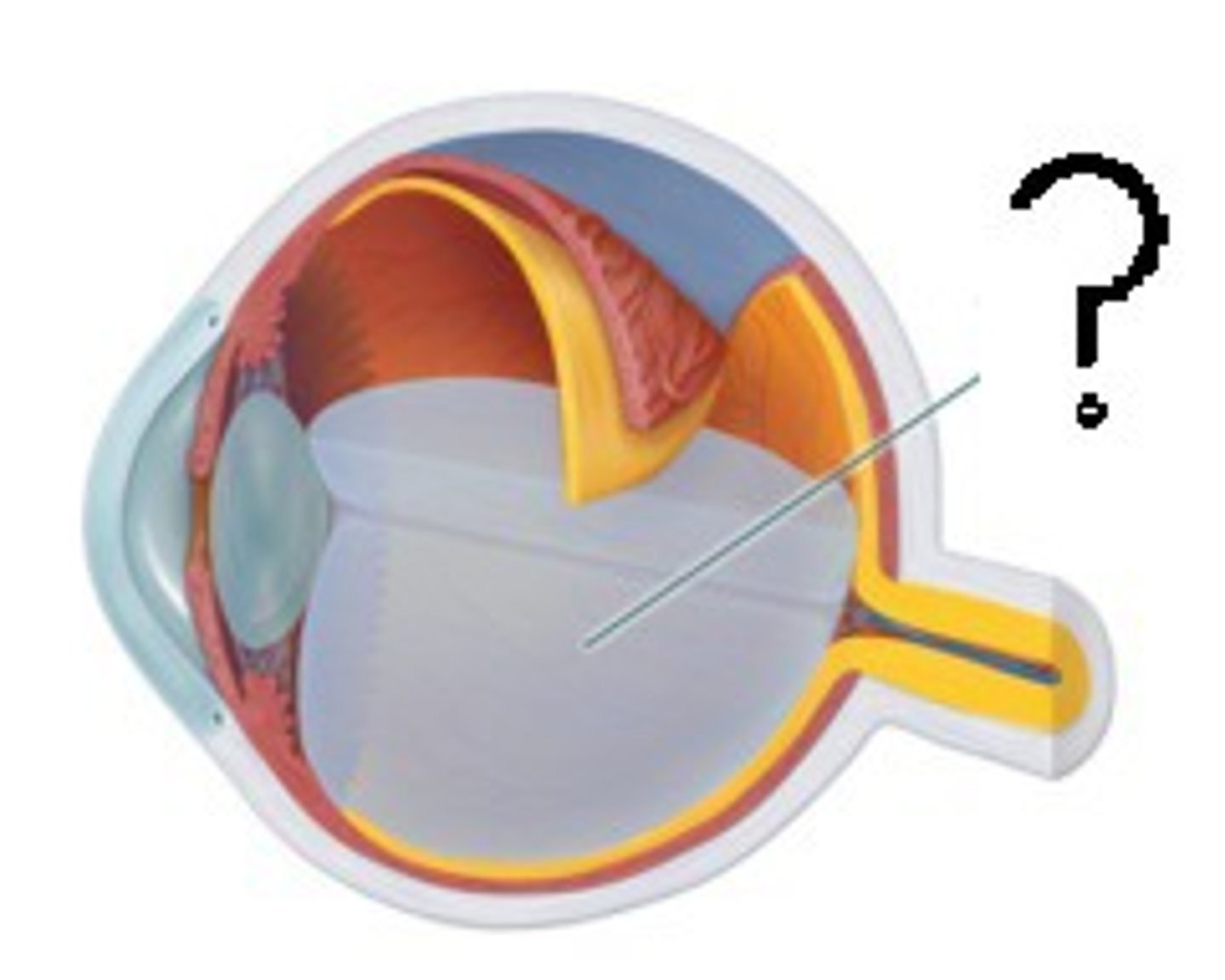
posterior compartment
behind the lens, contains vitreous humor
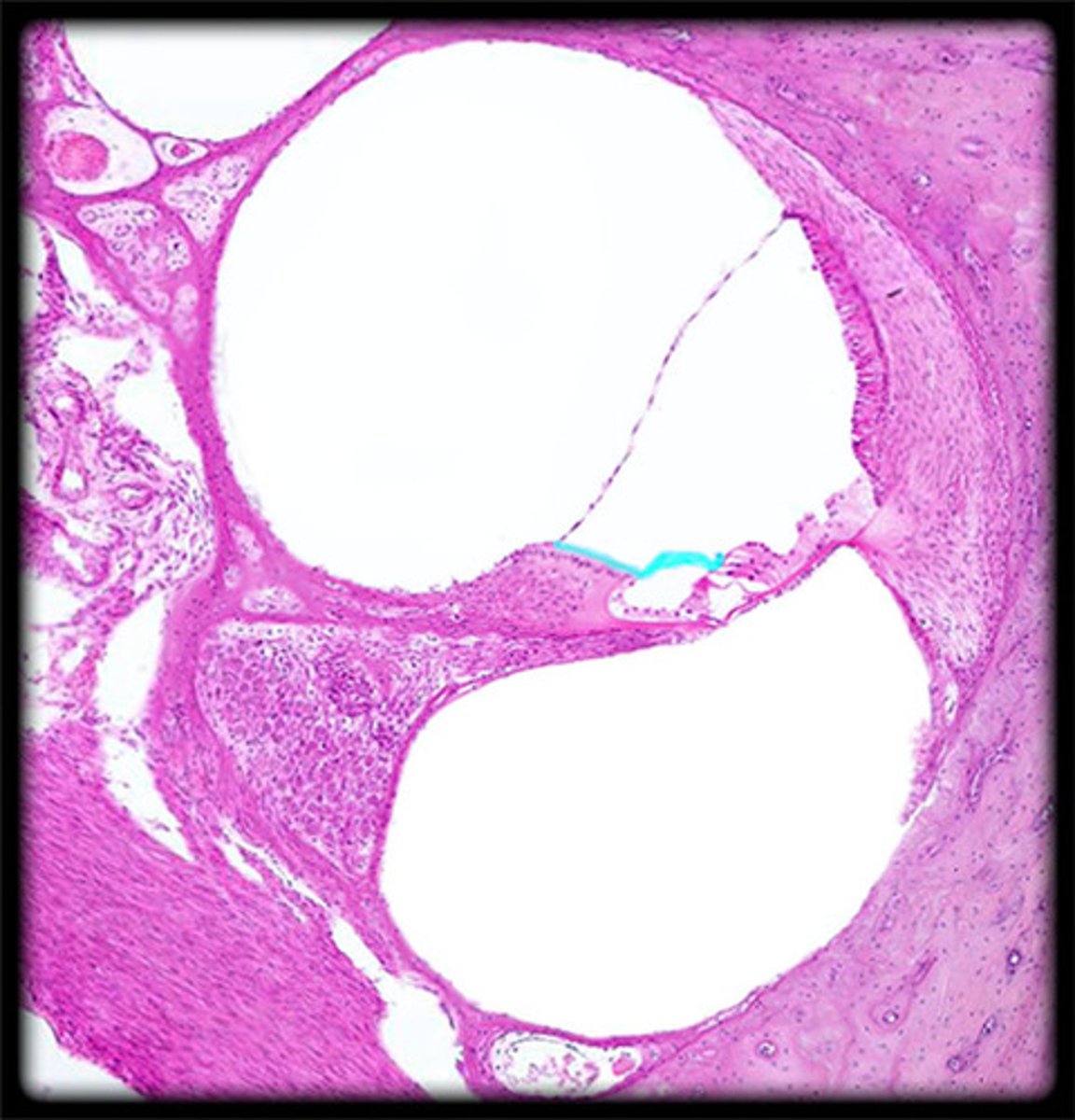
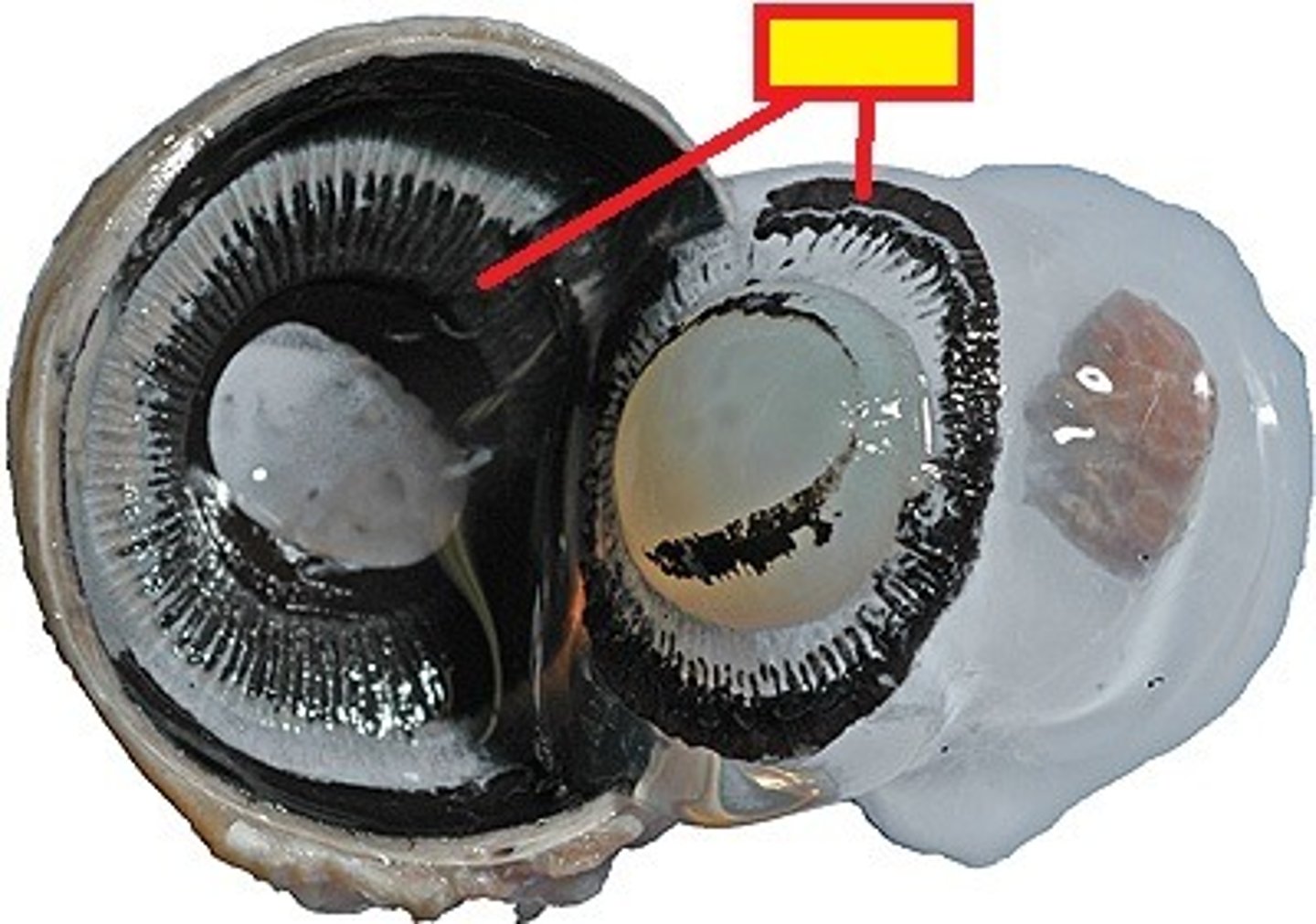
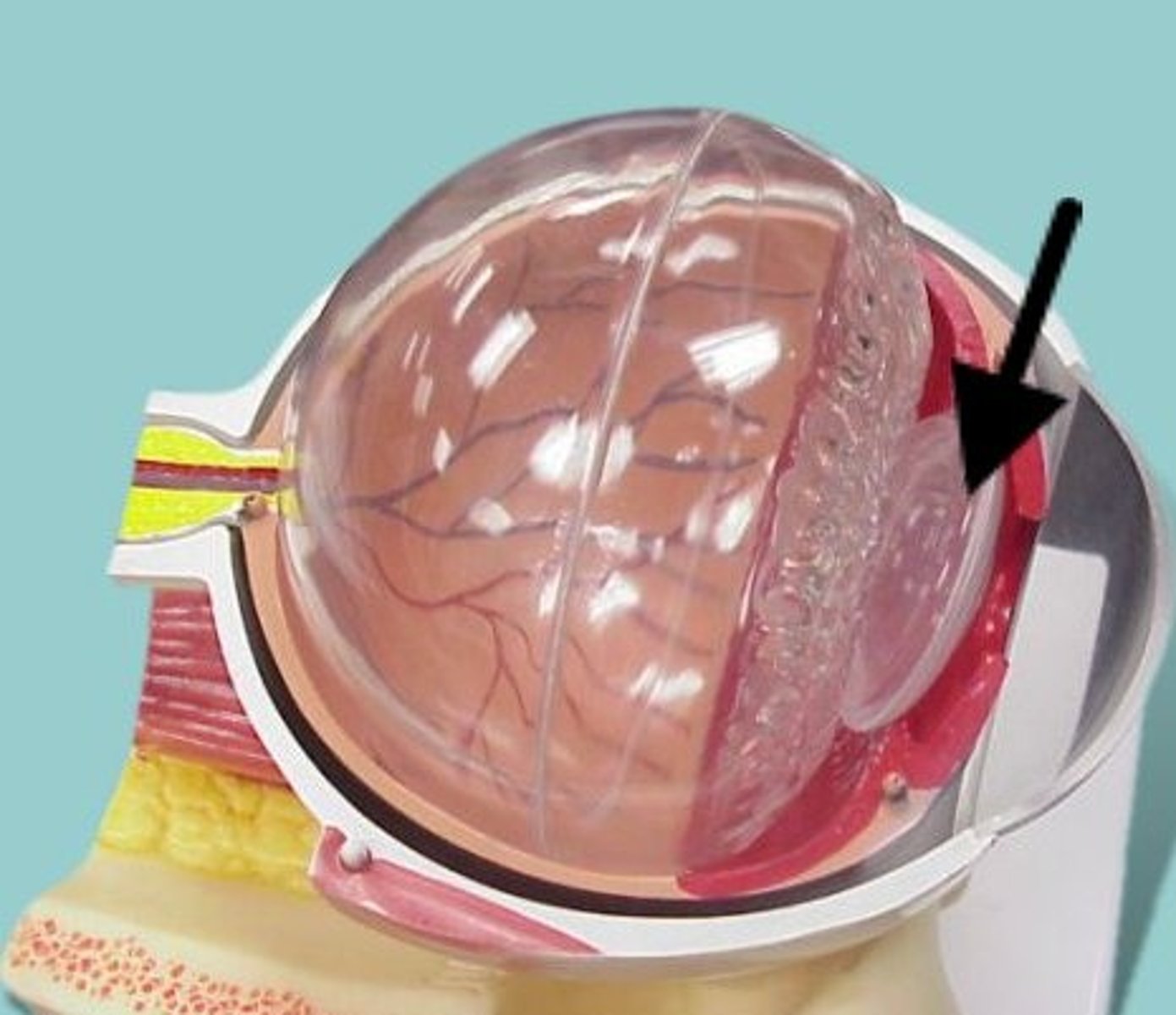
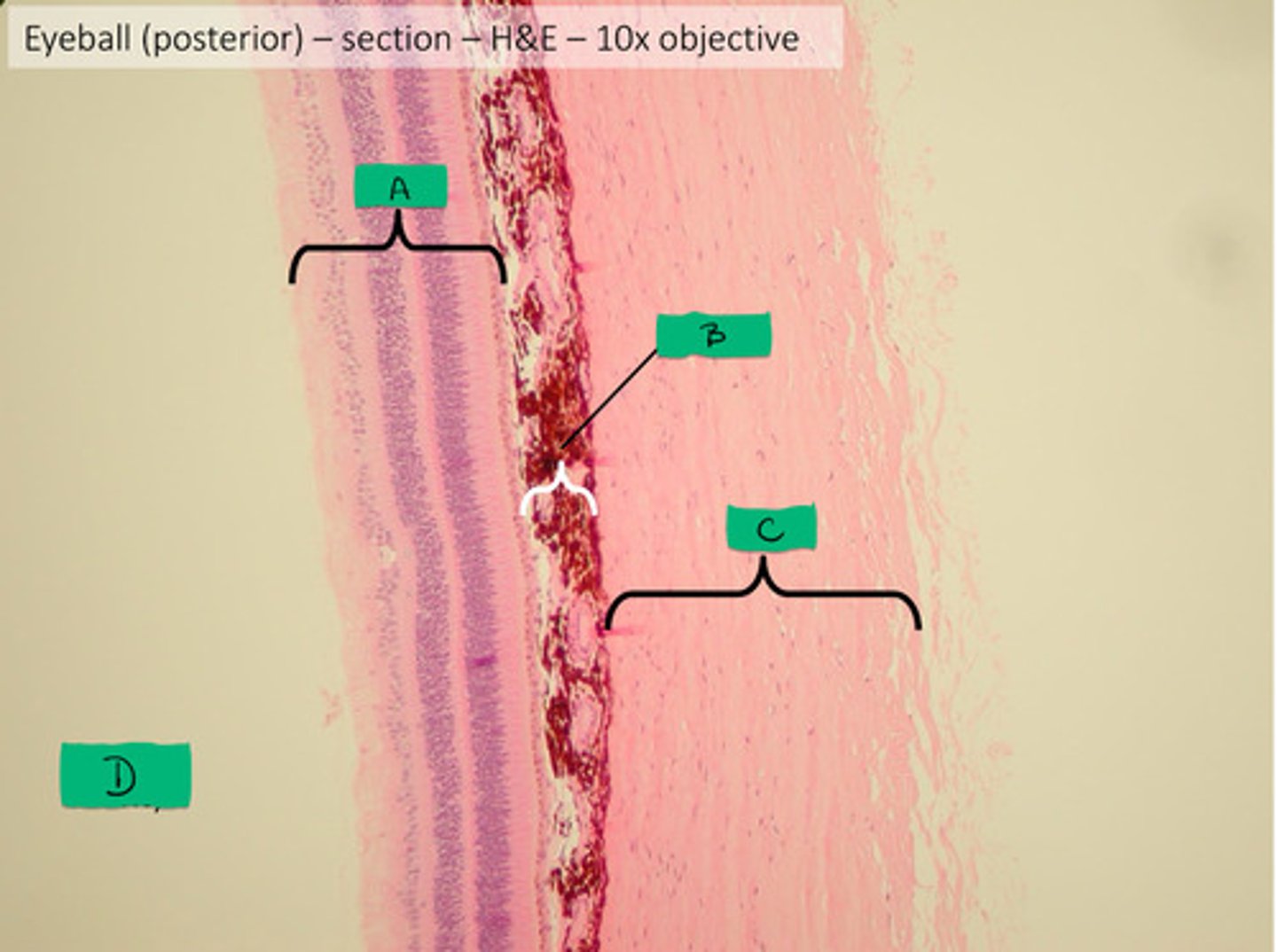
sclera histology
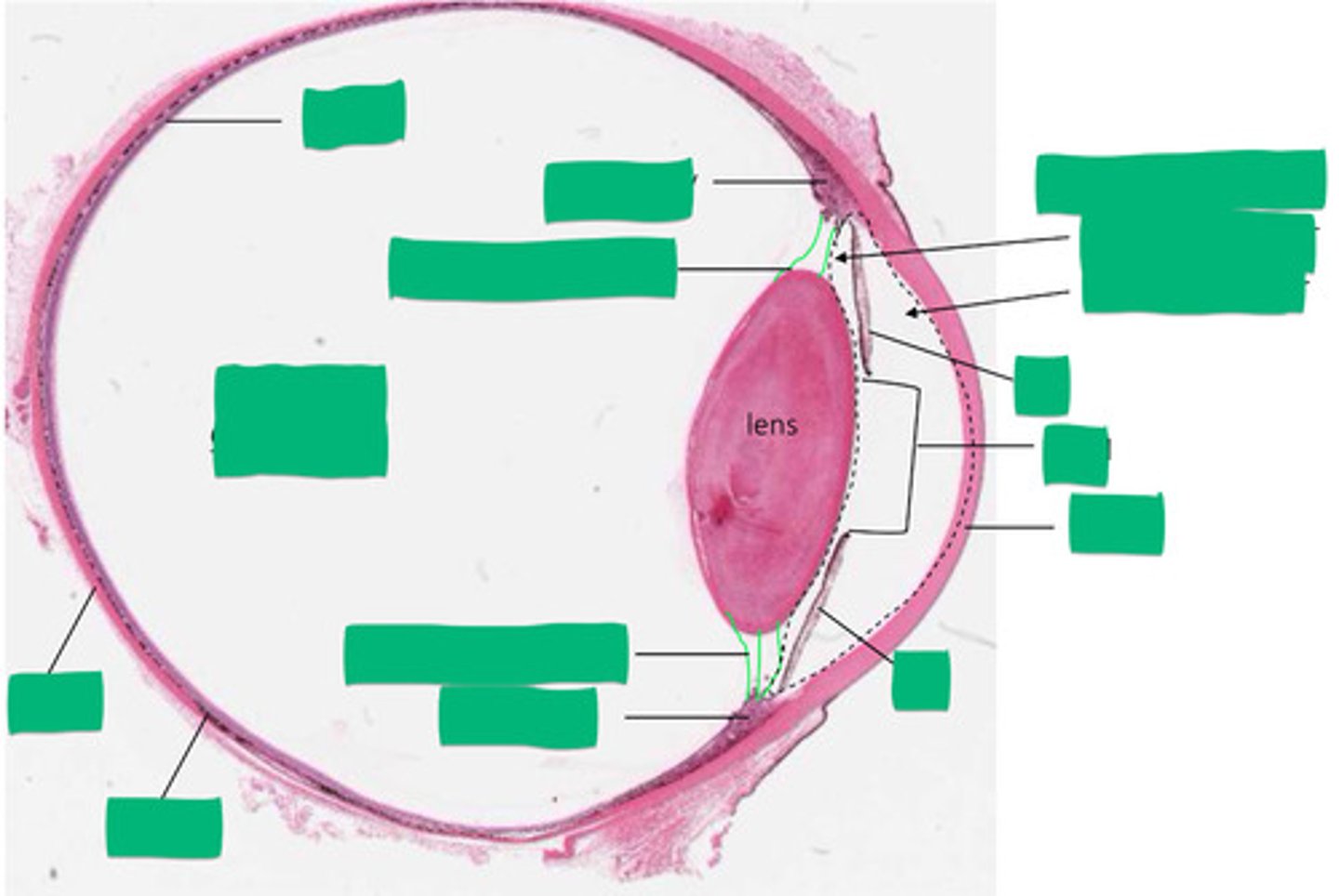
C
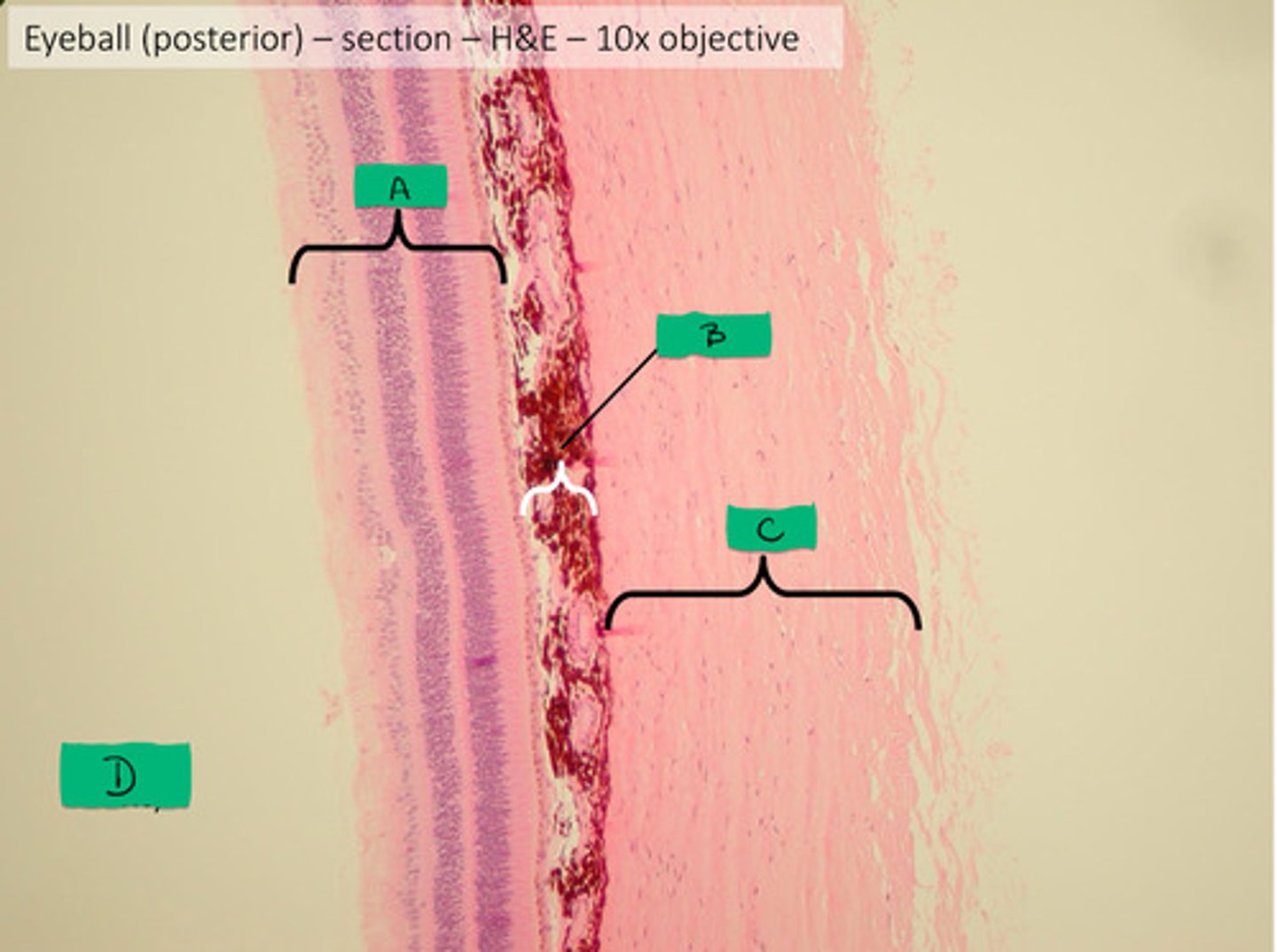
choroid histology
B
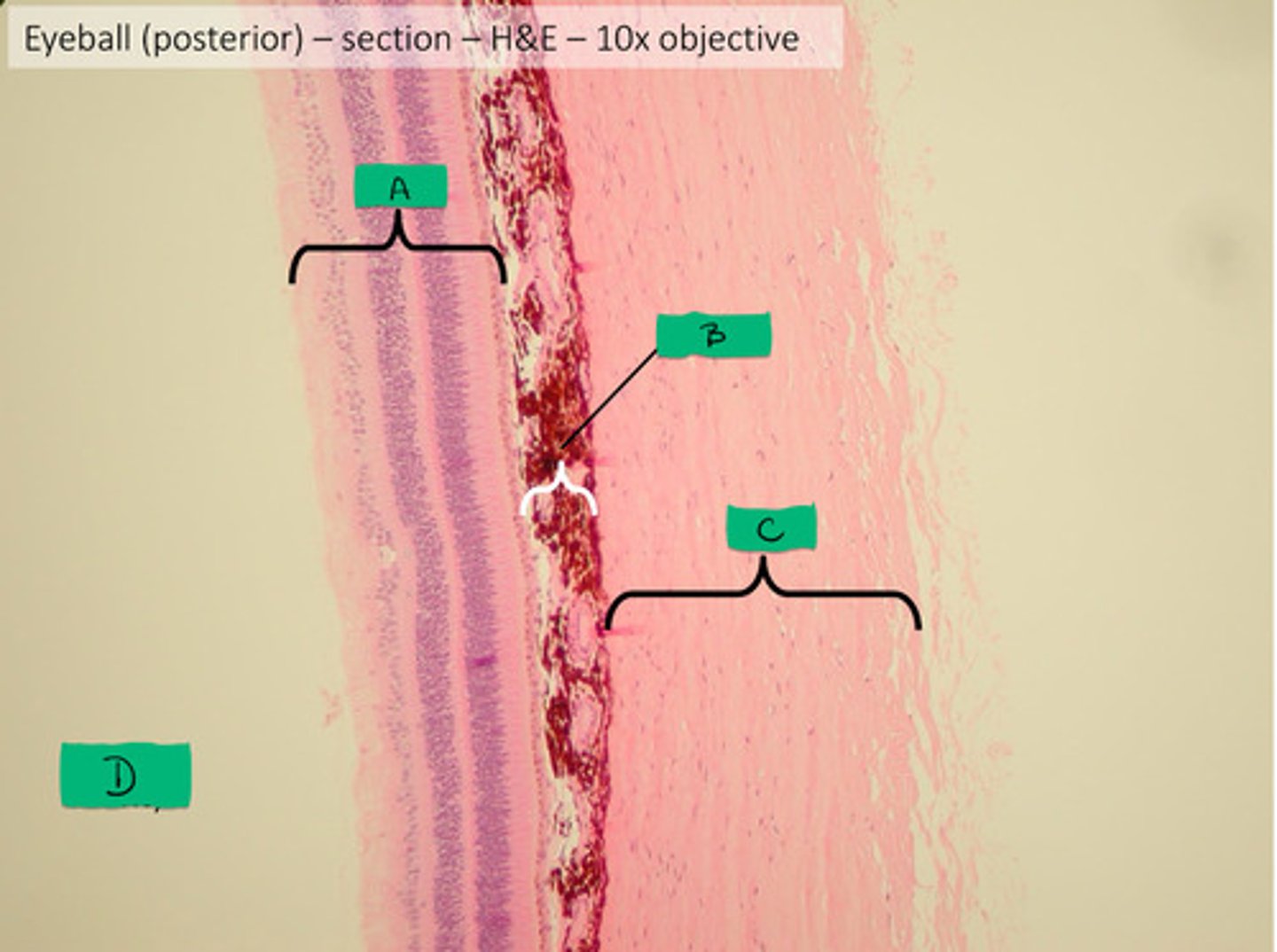
retina histology
A
ciliary body histology
E
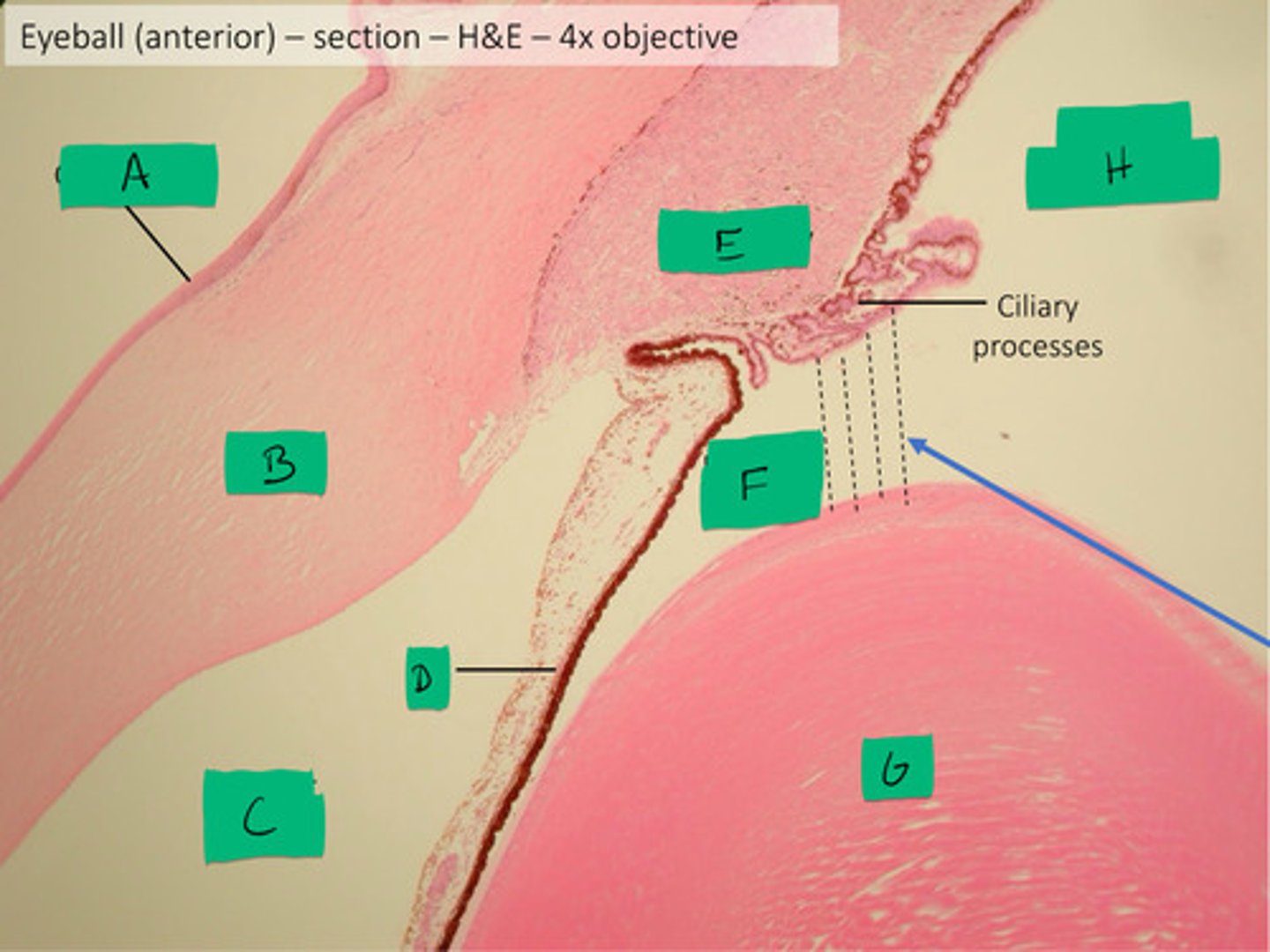
posterior compartment histology
H
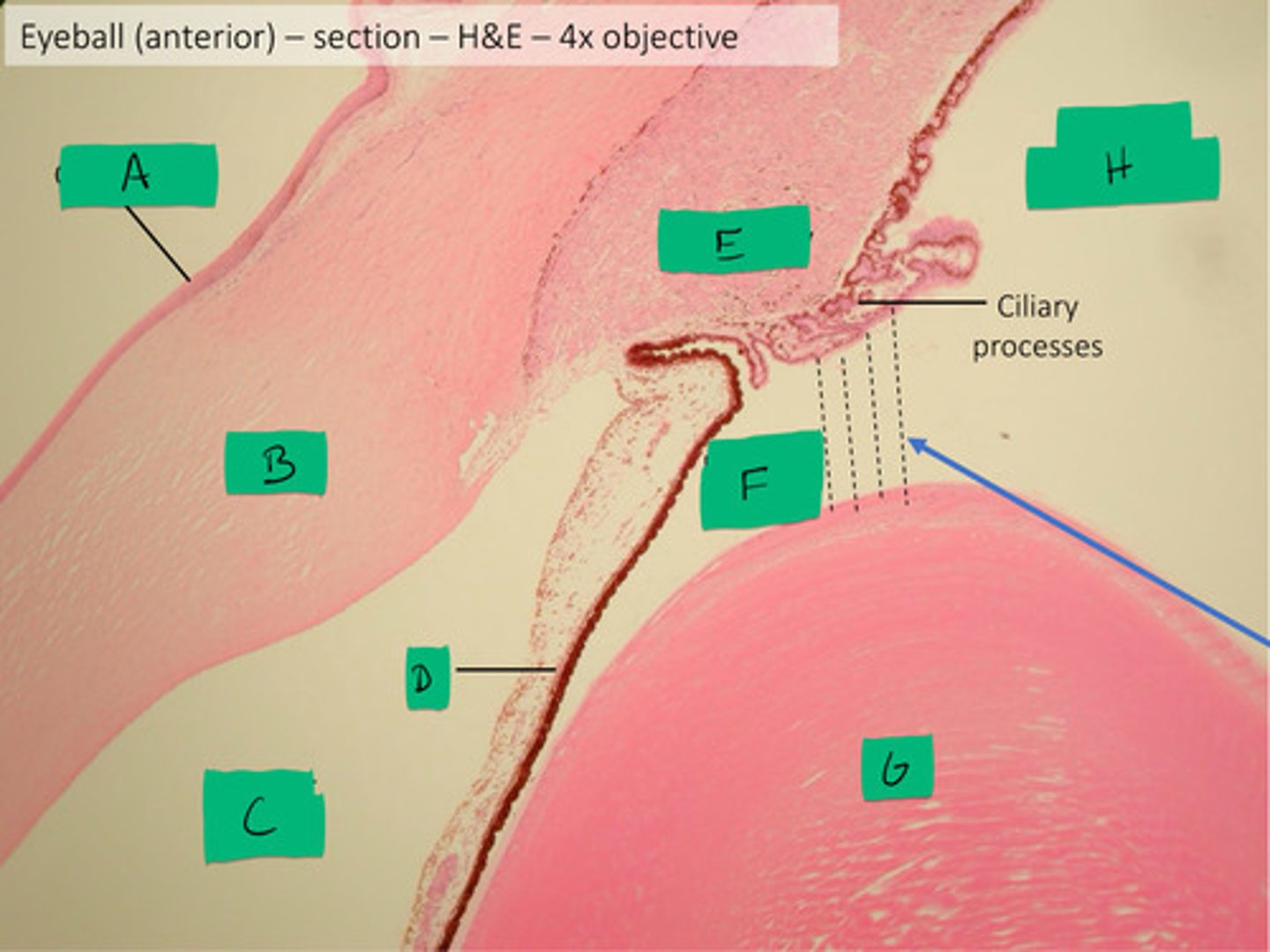
anterior compartment histology
Black dashed line
posterior chamber histology
F
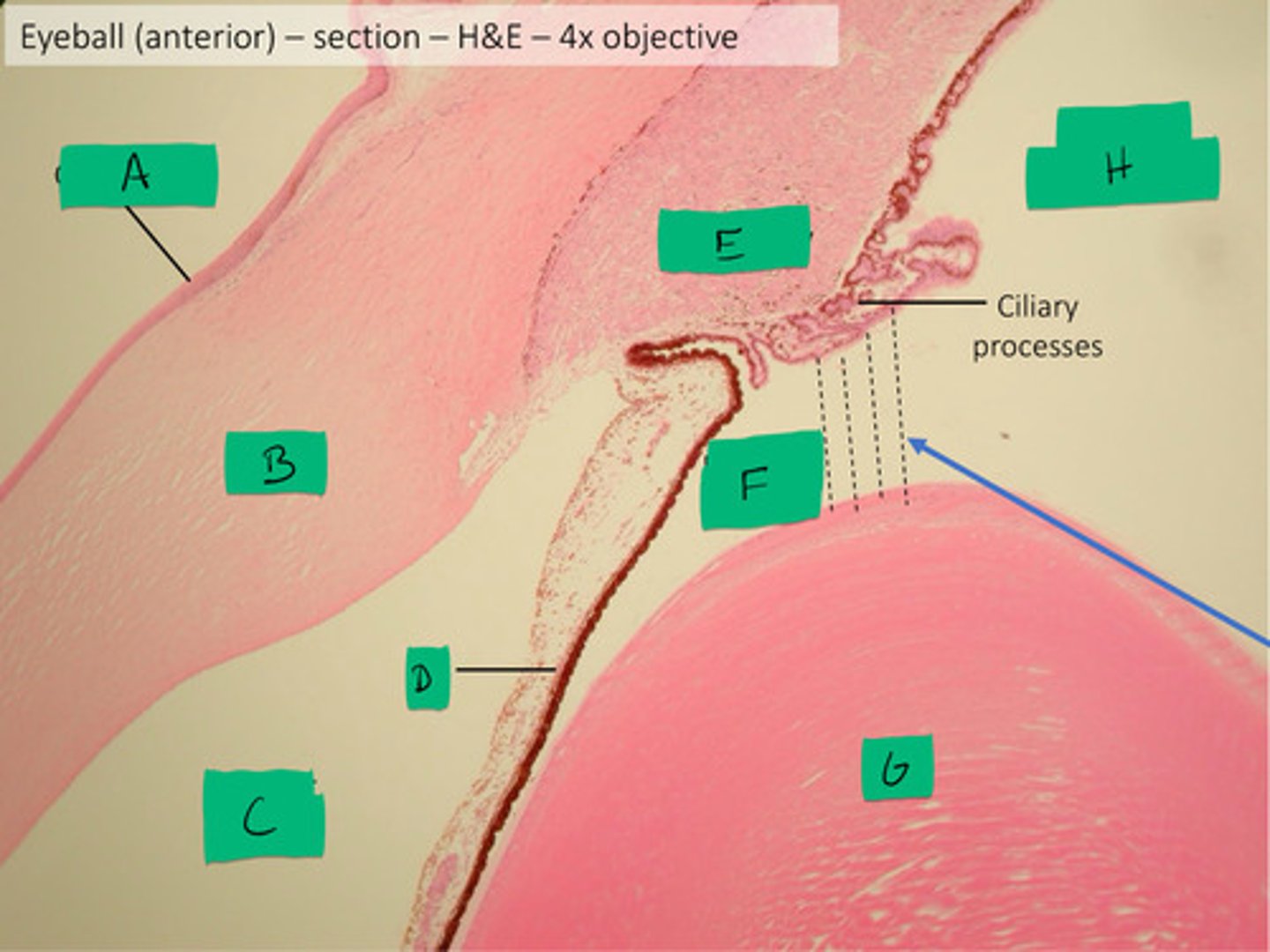
anterior chamber histology
C
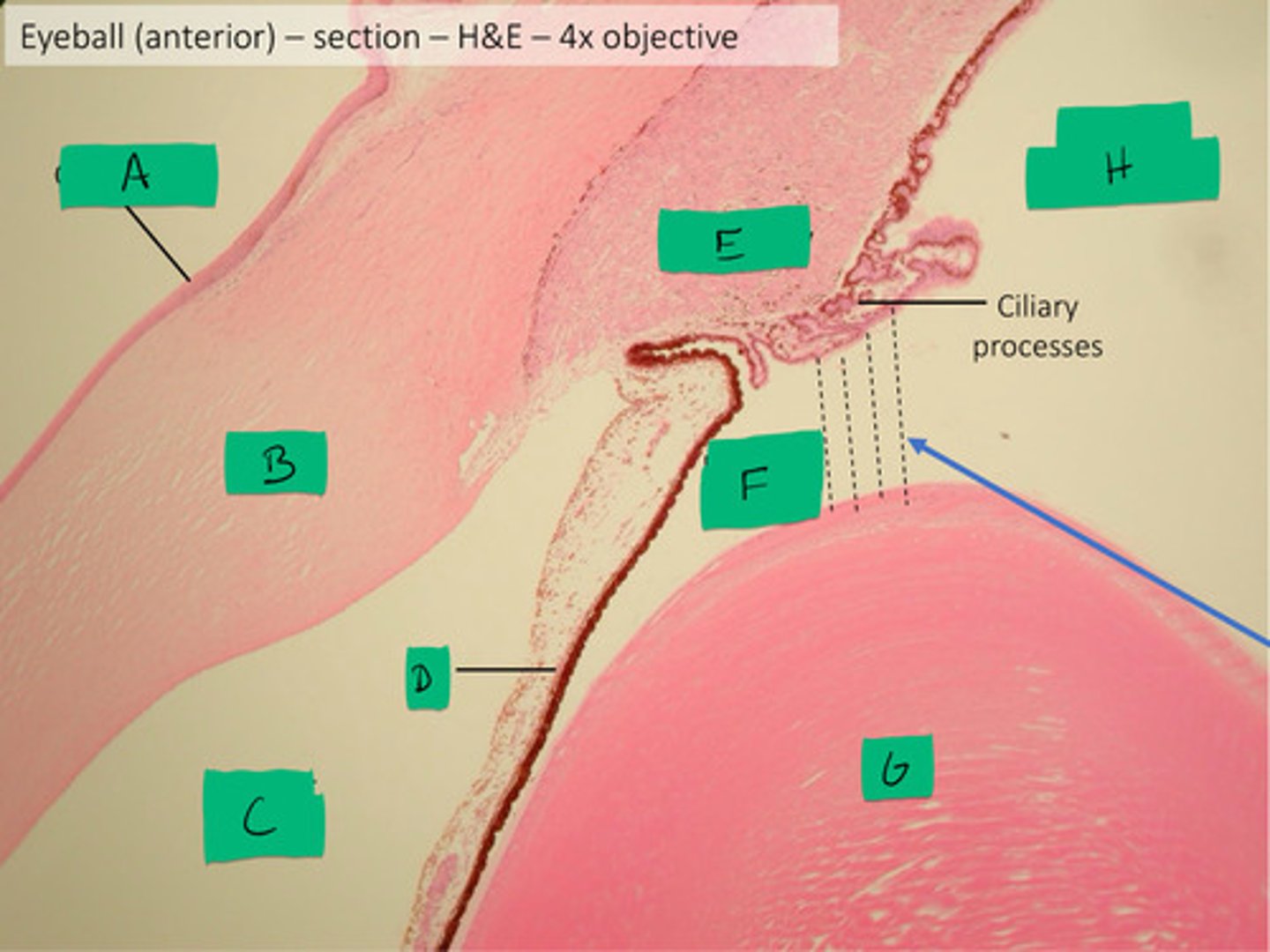
iris histology
D
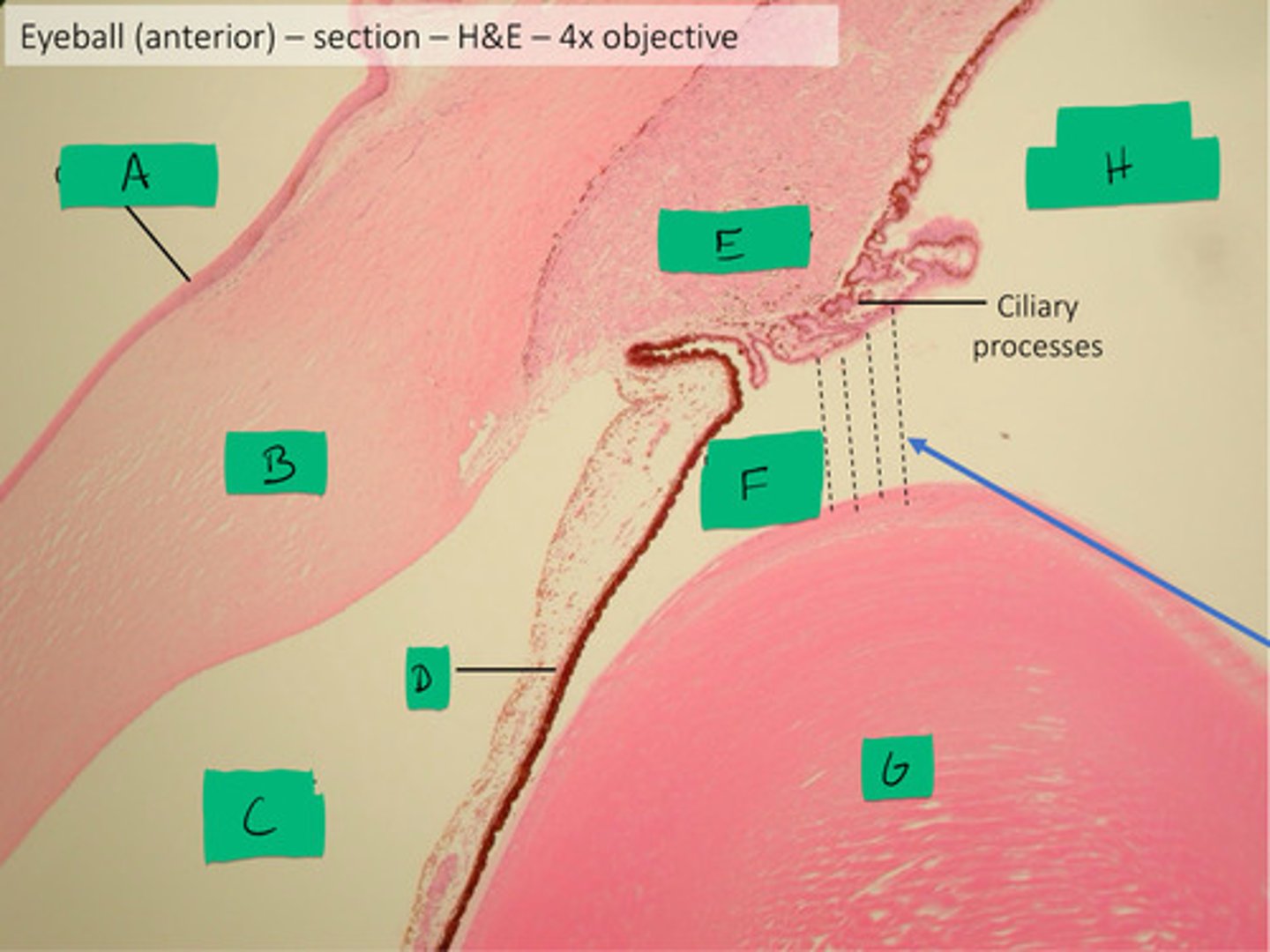
lens histology
G
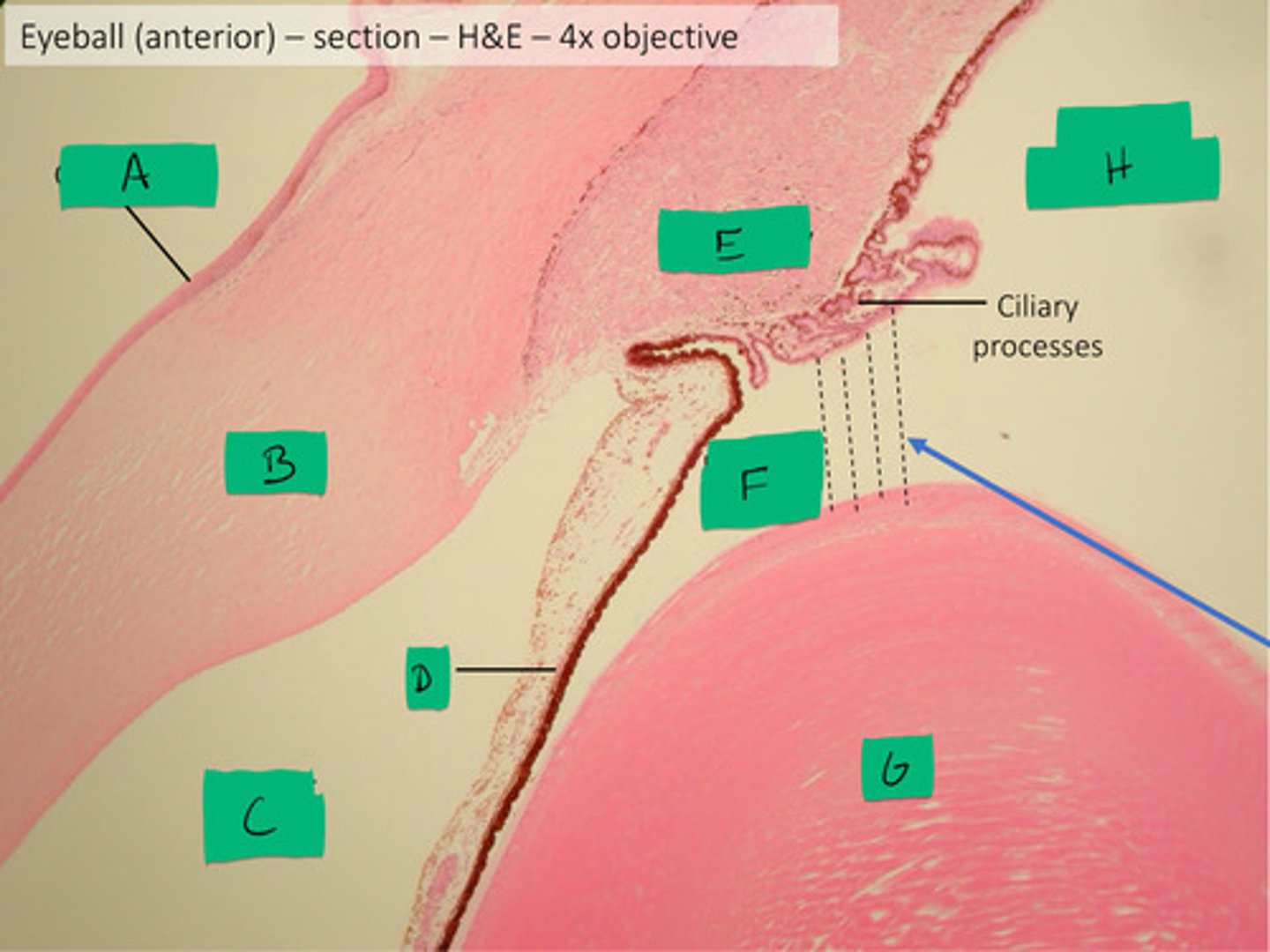
cornea histology
B
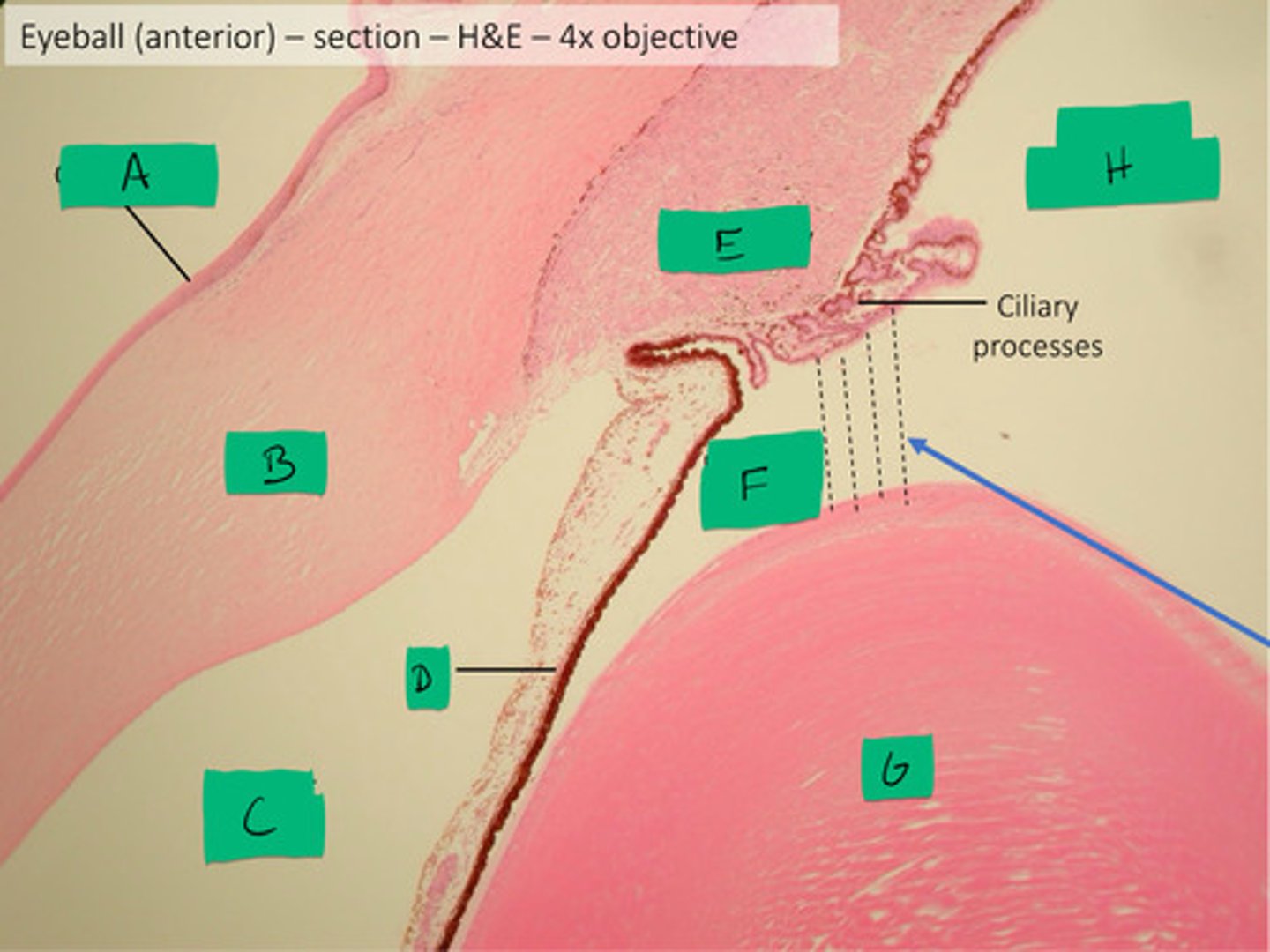
conjunctiva histology
A
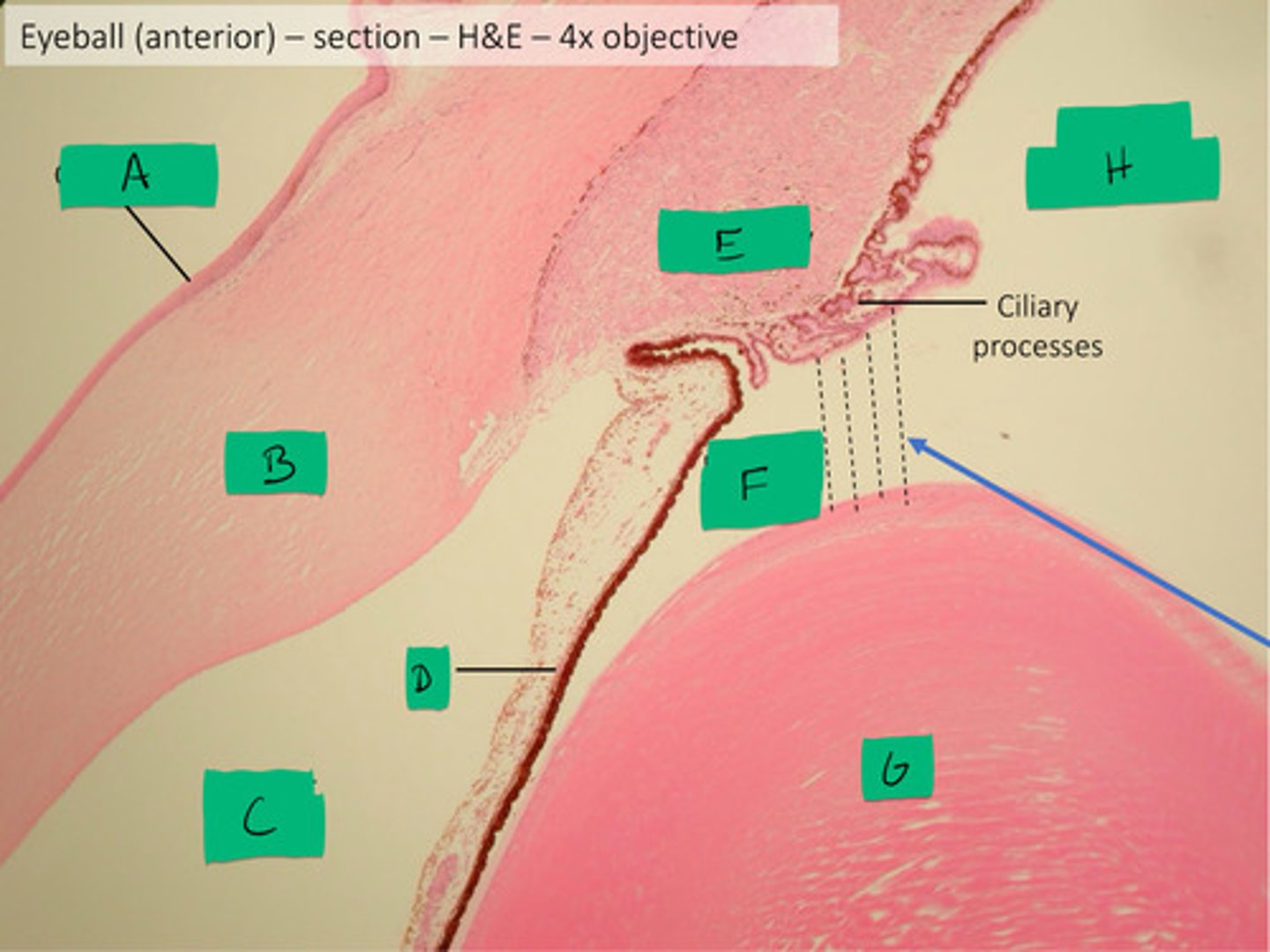
ciliary process histology
E
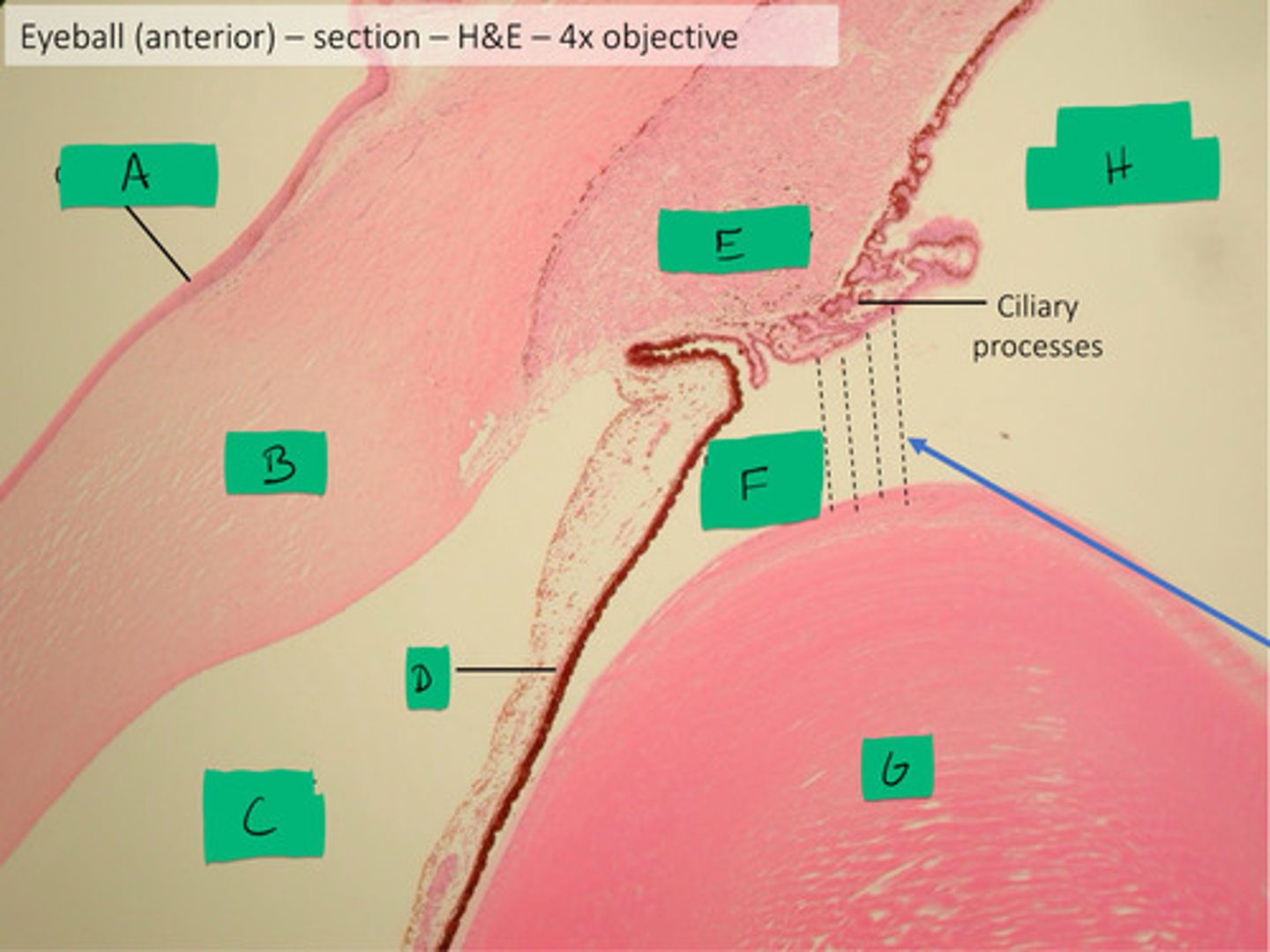
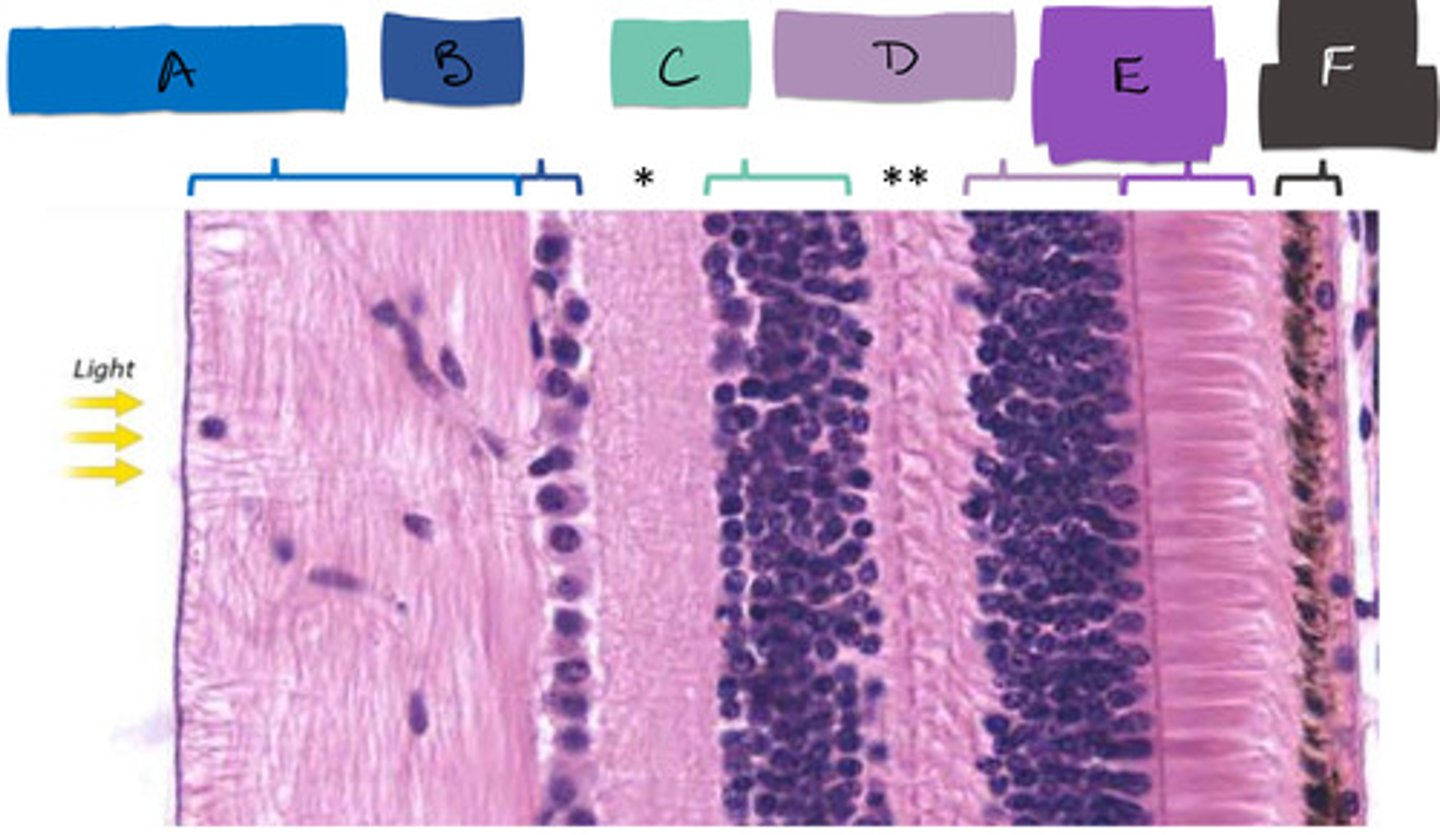
rod and cones segment (as one)
E
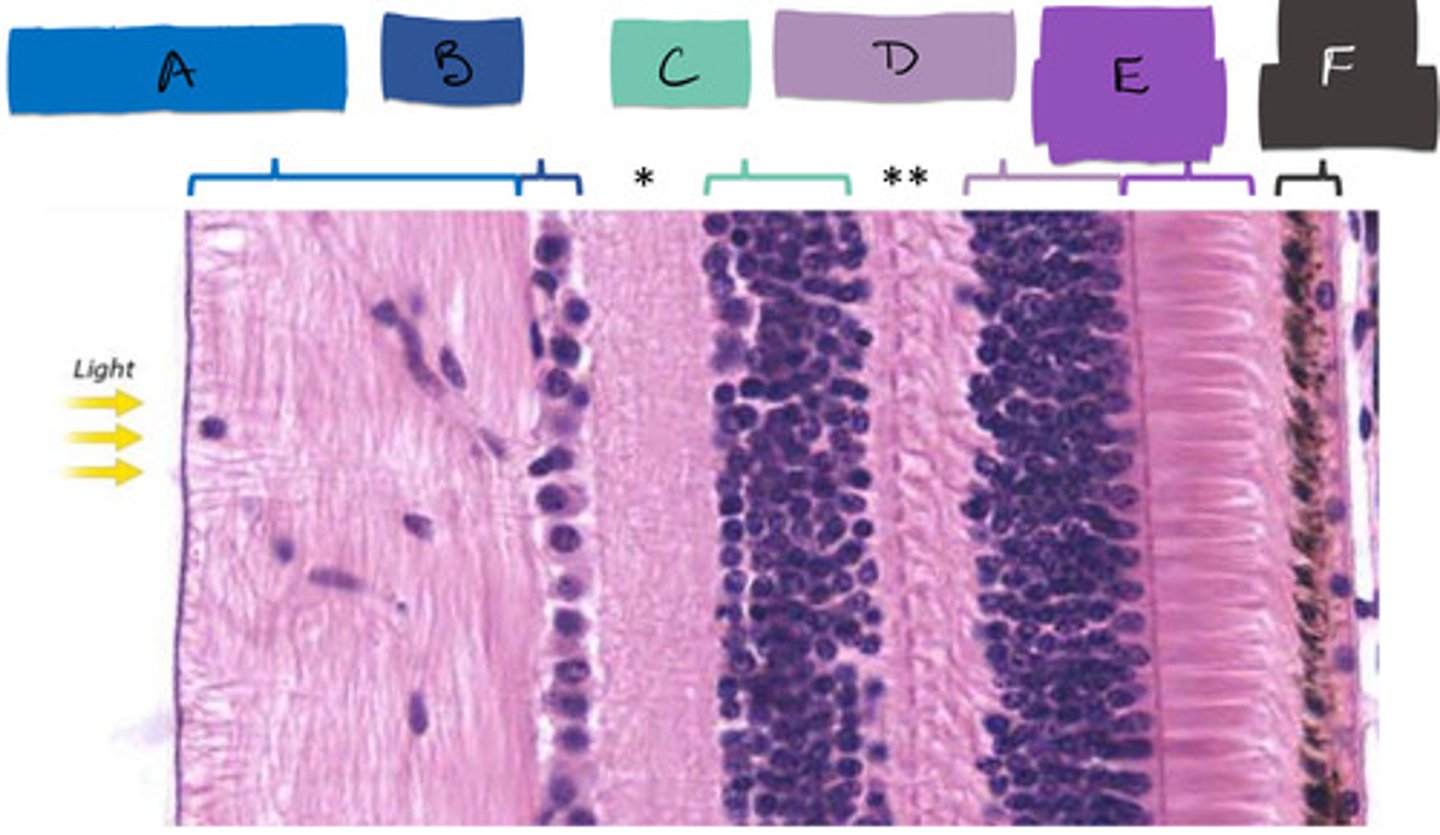
bipolar cells
C
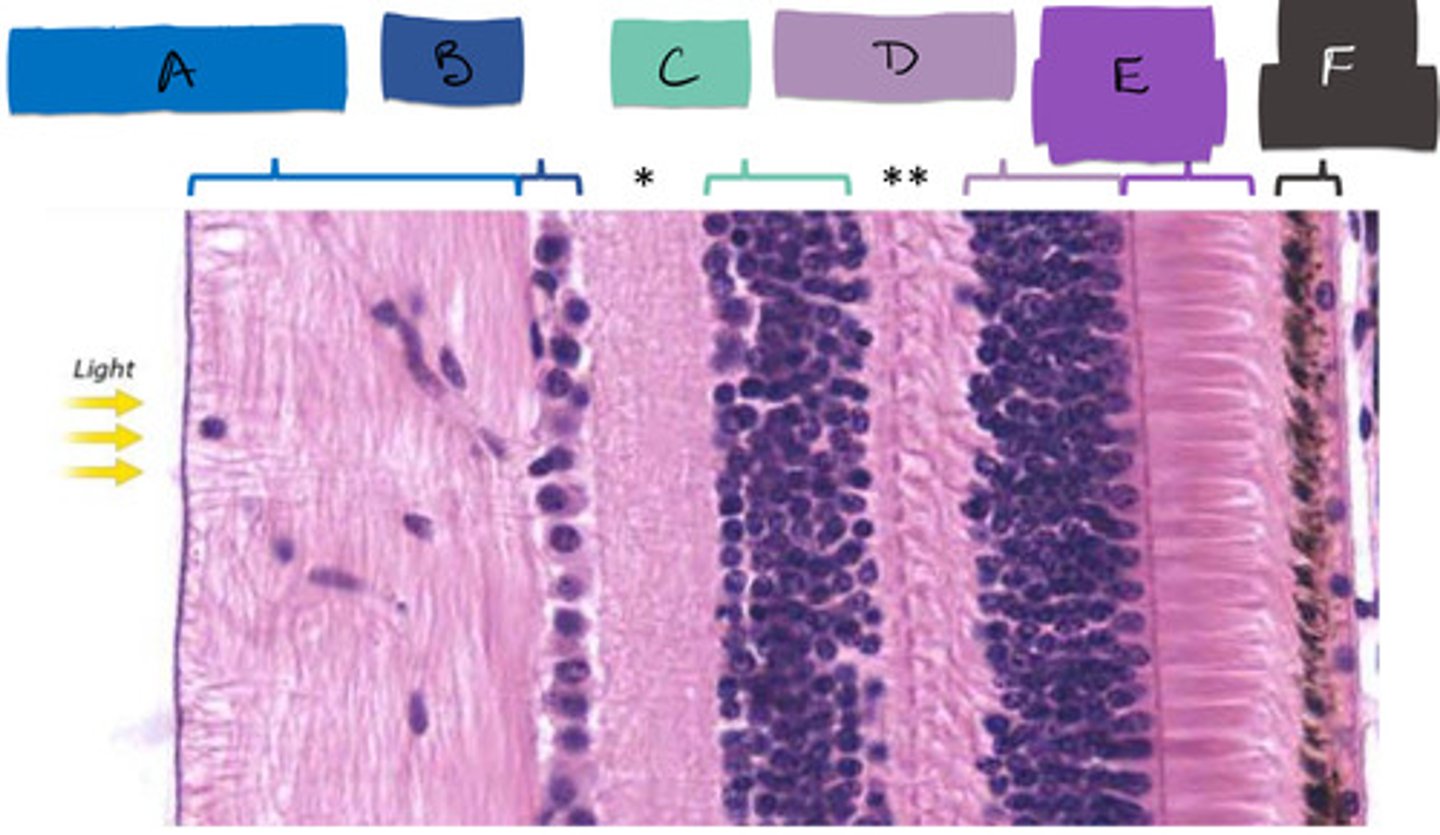
ganglion cells
B
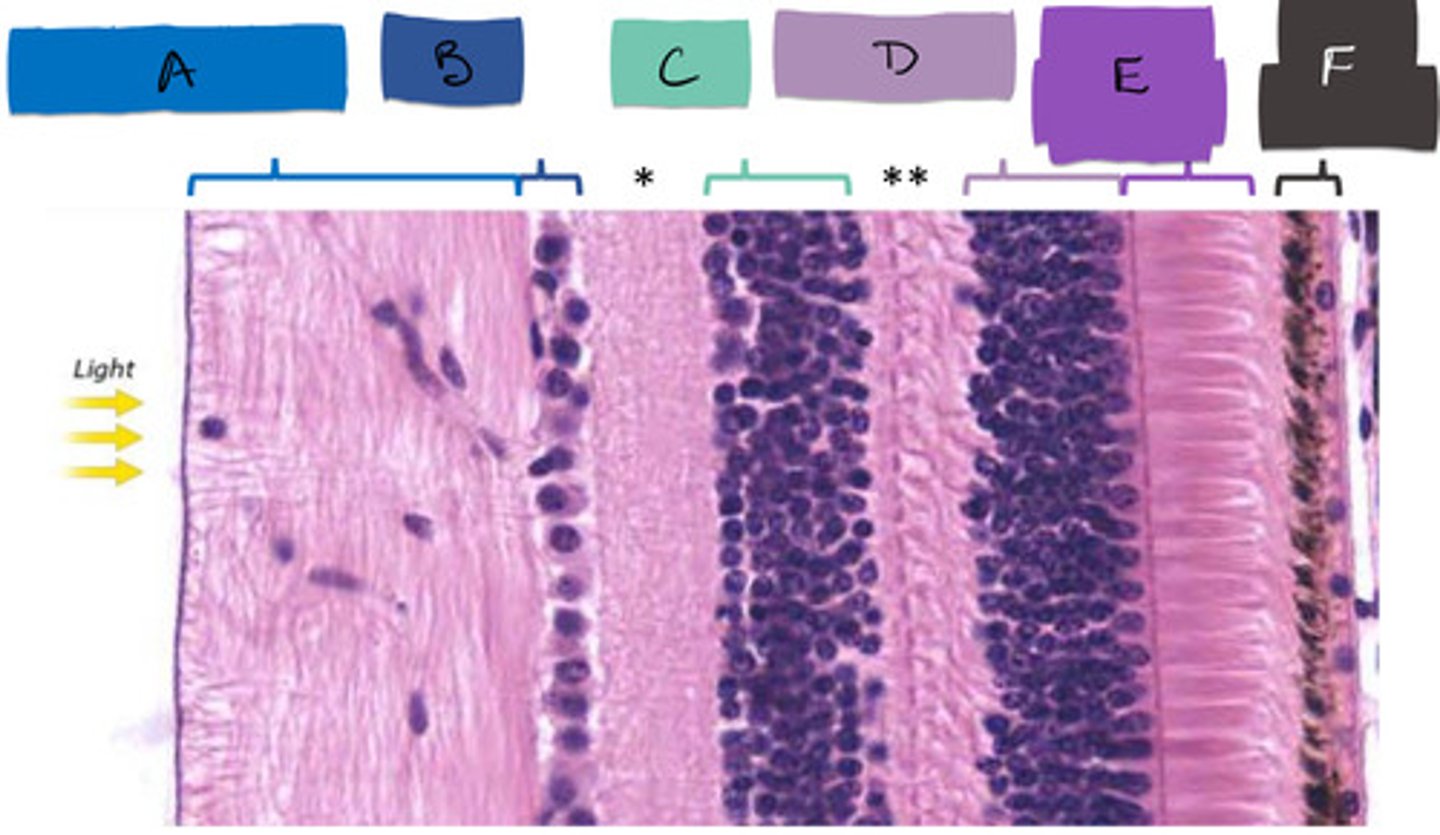
inner plexiform layer
*
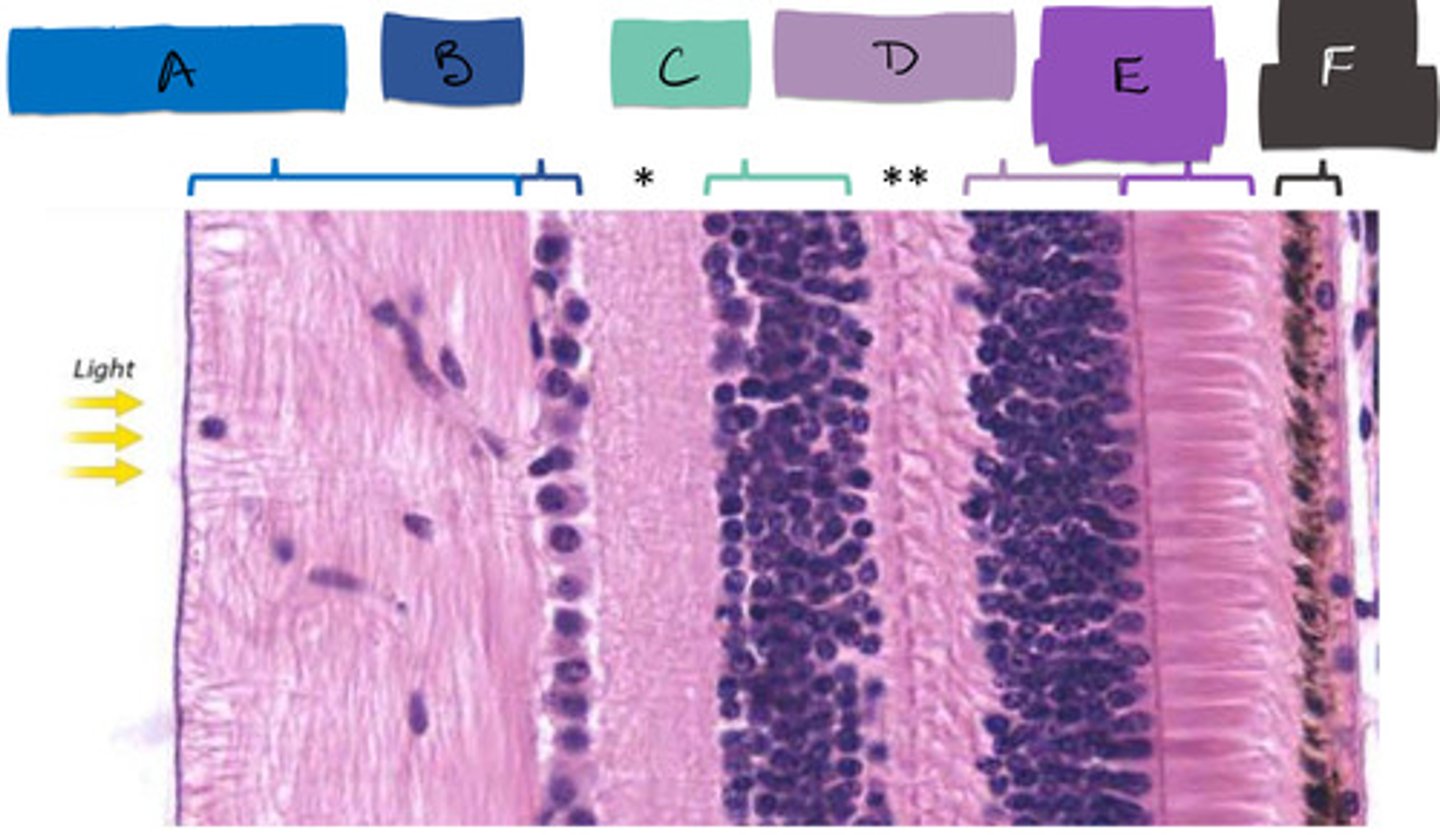
outer plexiform layer
**
What does vitreous body maintain?
the eye's shape and volume, keeps the retina and lens in their correct positions, and provides a clear optical pathway for light to reach the retina
Where does light bend in the eye?
the cornea
What converts light energy into neural signals?
rods and cones through phototransduction
direction of light
-front to back of retina
-ganglion cells --> bipolar cells --> photoreceptors
neural communication
-from back to front of retina
-photoreceptors --> bipolar cells --> ganglion cells --> brain