Ecology: Species Interactions and Biodiversity
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Specialists
Species with narrow ecological niches.
Generalists
Species with broad ecological niches.
Competition
Interaction where species vie for resources.
Predation
One species hunts and consumes another.
Herbivory
Consumption of plants by animals.
Parasitism
One organism benefits at another's expense.
Mutualism
Both species benefit from the interaction.
Commensalism
One species benefits; the other is unaffected.
Trophic Levels
Hierarchical levels in an ecosystem's food chain.
10% Rule
Only 10% of energy transfers between trophic levels.
Keystone Species
Species crucial for maintaining ecosystem structure.
Apex Predators
Top predators with no natural enemies.
Trophic Cascades
Chain reactions in ecosystems from predator removal.
Community Stability
Ability of a community to resist change.
Disturbances
Events that disrupt ecosystem structure or function.
Primary Succession
Ecological recovery on lifeless surfaces.
Secondary Succession
Recovery after disturbance in an existing ecosystem.
Climax Communities
Stable, mature ecological communities in equilibrium.
Biodiversity
Variety of life forms in an ecosystem.
HIPPCO
Acronym for biodiversity threats: Habitat loss, Invasive species, Pollution, Population growth, Climate change, Overexploitation.
Biodiversity Hotspots
Regions with high species diversity under threat.
Invasive Species
Non-native species that disrupt local ecosystems.
Endangered Species
Species at risk of extinction.
Threatened Species
Species likely to become endangered soon.
Endangered Species Act
U.S. law protecting threatened and endangered species.
Biomes
Large ecological areas with distinct climates and organisms.
Climatographs
Graphs showing temperature and precipitation of biomes.
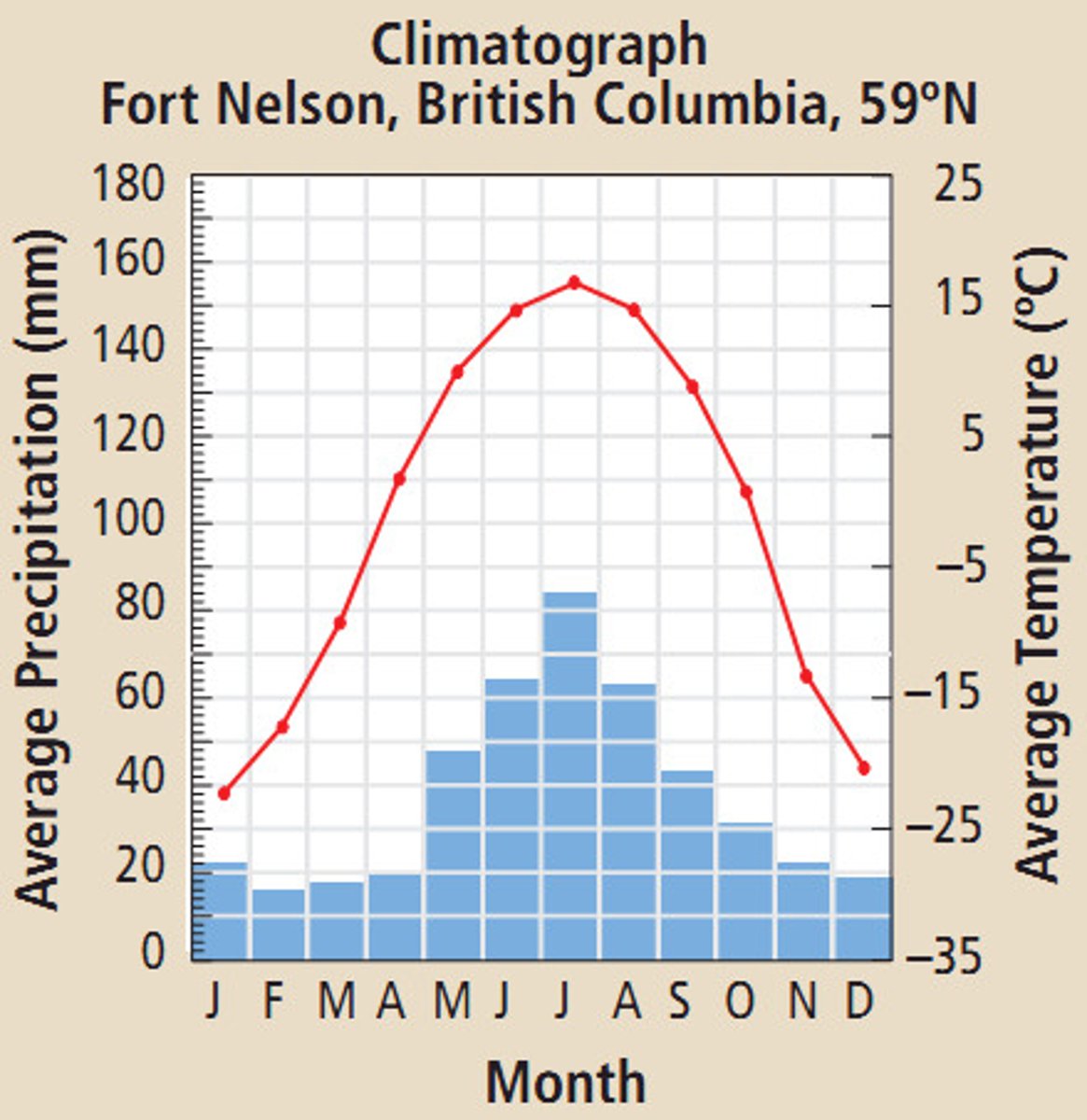
Factors Defining Biomes
Climate, soil, vegetation, and geography influence biomes.
Temperature and Precipitation Factors
Latitude, altitude, and ocean currents affect climate.