Biomolecules Unit (REMASTERED)
1/61
Earn XP
Description and Tags
quarter test time
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
What elements do all organic molecules have?
Carbon (in all), Hydrogen, Oxygen
What is a substrate?
A molecule that binds with the enzyme to catalyze a chemical reaction.
What is the pH of an acid?
Under 7
What is the pH of a base?
Above 7
What does ‘denature’ mean?
When an enzyme breaks down or changes shape, causing it to not work.
What are enzymes?
Types of protein that speed up a chemical reaction.
What may cause an increase in the rate of an enzyme controlled reaction?
An increase in temperature (up to optimal temperature).
What do enzymes end in?
Enzymes: -ase
Why are high fevers dangerous?
High heat can denature enzymes.
What is the substrate at the end of a chemical reaction called?
Product
A substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction
Catalyst
What two environmental factors denature enzymes?
High temperature and extreme pH
The energy needed to get a reaction started
Activation Energy
If an enzyme graph is shown, which line would be the one with and without the enzyme?
The shorter line is with enzyme
The taller line is without an enzyme
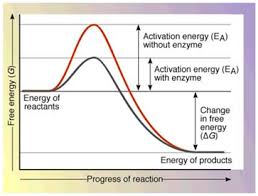
What would happen if there wasn’t a enzyme?
Chemical processes would slow down and would require more energy.
What is the monomer of an carbohydrate called?
Monosaccharide
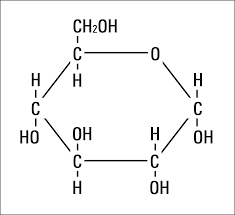
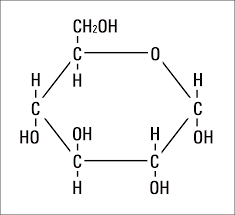
What elements do carbohydrates contain?
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio. (CHO)
Functions of carbohydrates?
Serves as rapidly available energy source and main energy source for all living things.
Quick energy source
Short-term energy storage
Makes up cell walls
What is the shape of a carbohydrate monomer?
Like a donut ring/stop sign
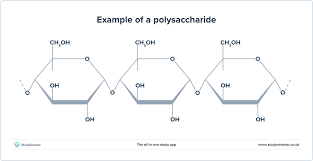
What are the five examples of carbohydrates?
Glucose
Starch (Plants)
Glycogen (Animals)
Cellulose (Plants)
Chitin (Fungi)
What is glucose?
Sugar that is produced during photosynthesis
What is starch?
Polysaccharide that plants cells store
What is glycogen?
Polysaccharide that animal cells store
What is cellulose?
Polysaccharide in a plant cell wall
What is chitin
Polysaccharide in a fungal cell wall
The names of most carbohydrates end in what suffix?
-ose
What are two monosaccharides combined called?
Disaccharide
What are three or more monosaccharides combined called?
Polysaccharide
What are simple sugars?
A type of carbohydrate composed of one or two sugar units. (Monosaccharide and Disaccharide)
What do carbohydrates and lipids both do?
Supply energy to living things
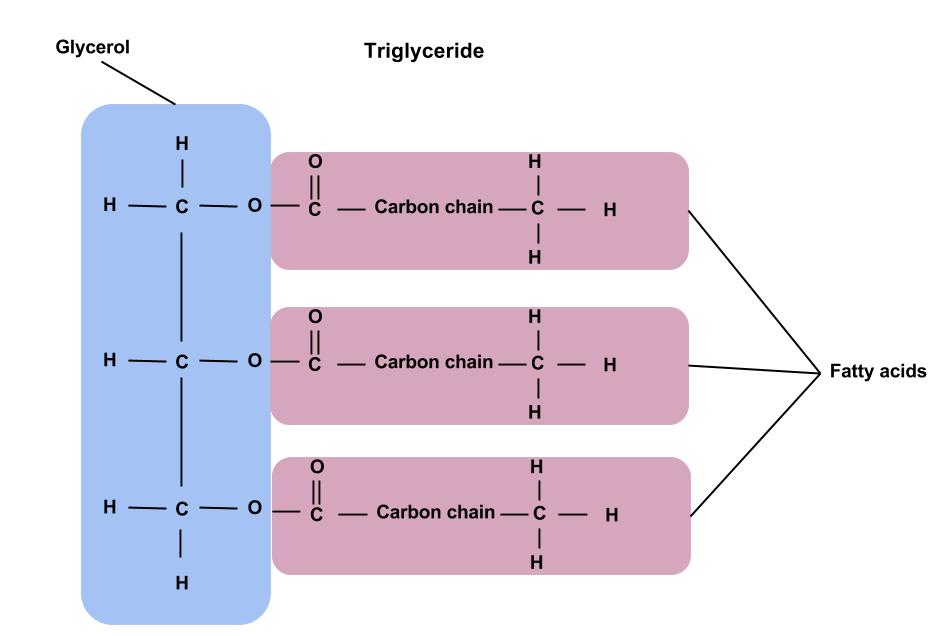
What are the monomers of lipids called?
Fatty Acids
Glycerol
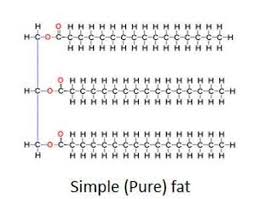
What elements do lipids contain?
Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen (A lot of carbon and hydrogen, and little oxygen) (CHO)
What are types of lipids?
Fats, oils, and waxes
Subunits of triglyceride (lipid)
1 glycerol and 3 fatty acids
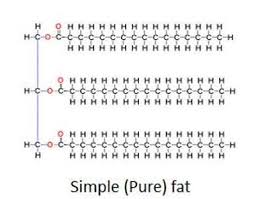
What is the shape of a lipid monomer?
The letter ‘E’ or a jellyfish
Function of lipids?
Insulation (Fats)
Long-term energy source (Fats)
Cushions organs (Fats)
Waterproofing (Oils and Waxes)
Makes up cell membrane (Phospholipids and cholesterol)
Steroid hormones ( Extra Credit: Estrogen and Testosterone)
Examples of lipids?
Fats
Oils
Waxes
Phospholipids
Cholesterol
Steroid hormones
What type of lipid is found on leaves to keep them from drying out?
Wax
What is fat (lipid)?
Lipid used on long term energy storage, insulation, and protection of organs.
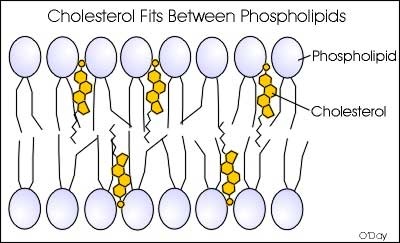
What lipids are commonly found in the cell membrane?
Phospholipids (makes up the structure)
Cholesterol (keeps the cell membrane fluid)
Saturated fatty acid vs. Unsaturated fatty acid
A saturated fatty acid only has a single bond and is solid at room temperature. While an unsaturated fatty acid has one or more double bonds and is liquid at room temperature.
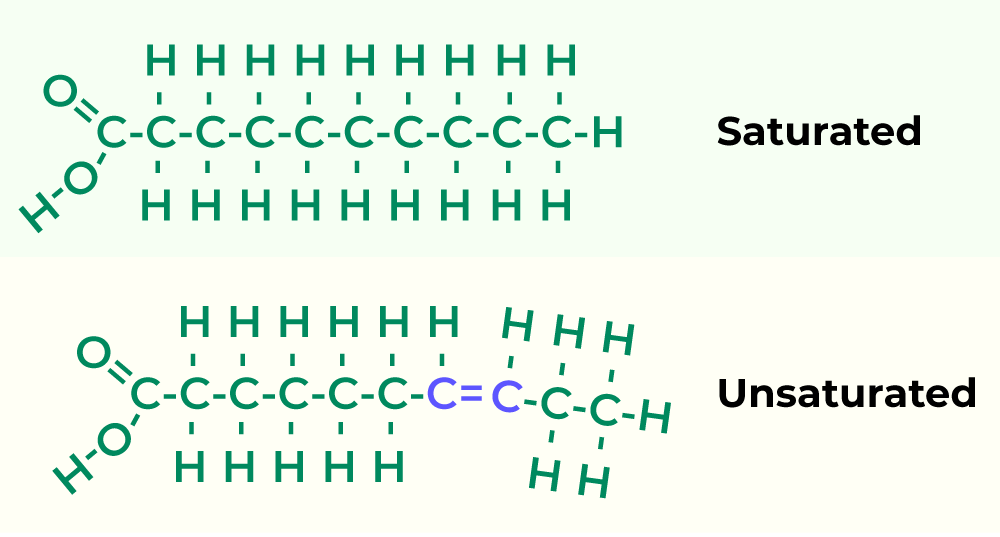
Are lipids hydrophobic?
ye
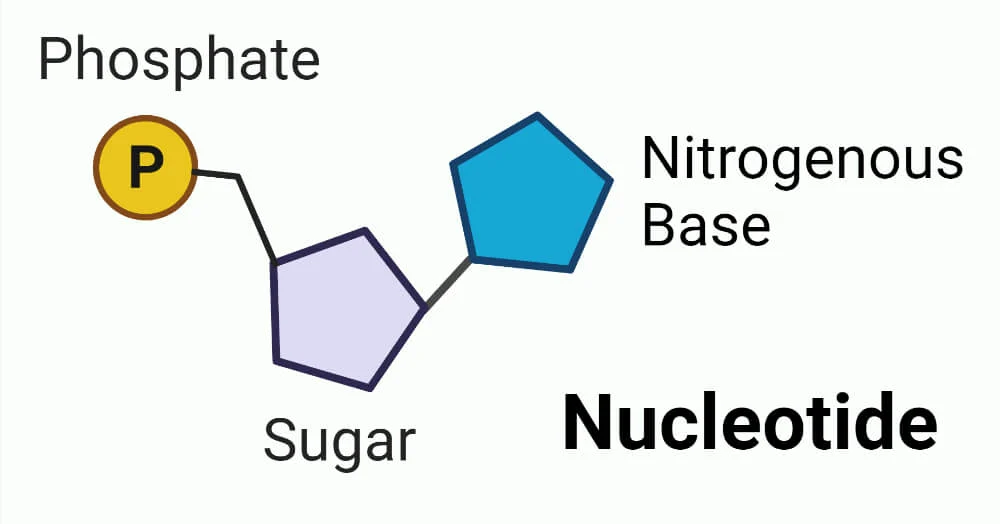
What is the monomer of nucleic acids?
Nucleotide
What elements do nucleic acids contain?
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus
What is the shape of a nucleic acid monomer?
House (sugar), flag (nitrogen base), pool (phosphate group)
What are the parts of a nucleotide?
A sugar group, phosphate group, and nitrogen base.
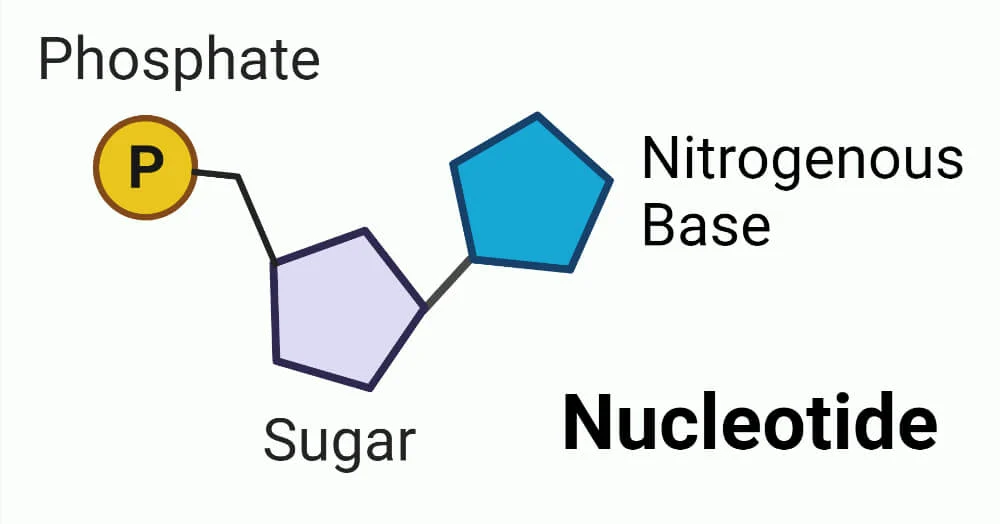
Examples of nucleic acid
DNA and RNA
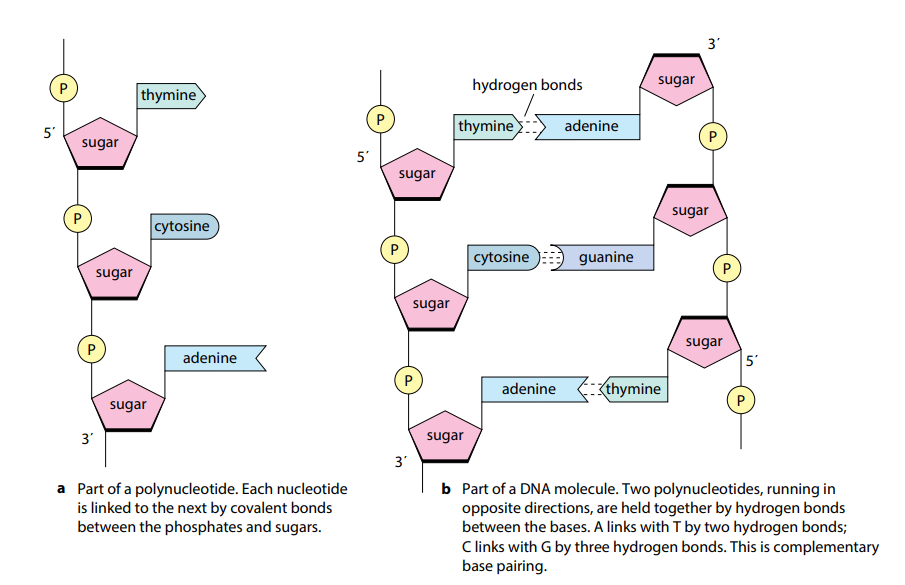
Functions of DNA vs. RNA
DNA: Stores protein recipes
RNA: Transmits protein recipe copy to build a protein (in the ribosomes)
What is the monomer of proteins?
Amino acids
What elements do proteins contain?
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur (sometimes)
What are the parts of an amino acid?
Amino group, carboxyl group, and side chain
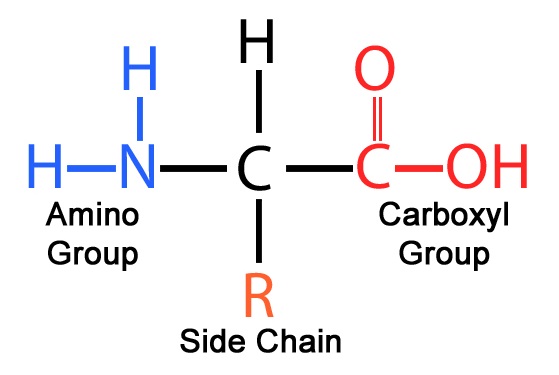
What is the shape of a protein monomer?
Butterfly
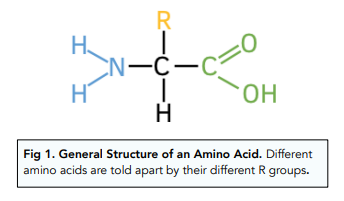
Functions of proteins?
Structure - Makes up skin, muscles, nails, and hair.
Transport (O2 and large charged particles)
Receptors for signals
Enzymes to speed up chemical reactions
Peptide hormones to help regulate body functions
Extra Credit: Builds microtubules (transporting and structural support organelles)
What are three examples of proteins?
Insulin
Hemoglobin
Enzyme
What is hemoglobin?
A protein in red blood cells that helps carry oxygen throughout the body
What is insulin?
A protein that helps regulate blood sugar levels
What are enzymes? (yes its here again)
A protein that helps speed up chemical reactions
What suffix does amino acids end in?
-ine
If a picture is shown of multiple circle looking thingies connected together, what is it?
Chain of amino acid, protein.
What kind of bond holds two amino acids together?
Peptide
How do amino acids differ from each other?
In the identity of the ‘R’ group (side chain)
What is a lactase?
An enzyme that helps speed up the breakdown of lactase, the sugar in milk