Edexcel iGCSE Biology
1/233
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
234 Terms
Processes of living organisms
Movement, reproduction, sensitivity, control, growth, respiration, excretion, nutrition
Types of living organisms
Animal, Plant, Bacteria, Protoctist, Fungi, Virus
Structure of Animal Cells
Cell Membrane, Cytoplasm, Nucleus
Characteristics of Animals
Multicellular, feed on other organisms, carbohydrates as glycogen
Example of Animals
Human or Mosquitos
Invertabrates
Animals which lack a backbone. E.g. Worms
Vertabrates
Animals with a backbone. E.g. Humans
Structure of Plant Cells
Cellulose cell wall, Cell membrane, Cytoplasm, Chloroplasts, Sap Vacuole, Nucleus
Characteristics of Plants
Multicellular, contain chloroplasts to carry out photosynthesis, cellulose cell walls, carbohydrates as starch or sucrose
Example of Plants
Flowering plants: maize, herbaceous legumes: peas
Structure of Fungi
Chitin cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, vacuole, nucleus
Characteristics of Fungi
Multicellular or unicellular, hyphae structures, no photosynthesis, nutrition by secreting digestive enzymes on dead organisms (heterotrophic), carbohydrates as glycogen
Example of Fungi
Multicellular: Mushrooms, Unicellular: Yeast
Characteristics of Protoctists
Microscopic, usually unicellular, can resemble plants or animals
Example of Protoctists
Amoeba, Chlorella
Structure of Bacteria
Cell wall made of peptidoglycan, cell membrane, no nucleus but circular chromosome of DNA, capsule, plasmids (DNA/extra genes), chloroplasts, flagellum
Characteristics of Bacteria
Unicellular, small organisms, circular DNA instead of nucleus, some can photosynthesis others are saprotrophic feeding
Example of Bacteria
Lactobacillus bulgaricus, Pneumoccus
Structure of Virus
Membrane from host cell, protein coat, DNA or RNA
Characteristics of Virus
Smallest organisms, non cellular, parasitic pathogens
Example of Viruses
Influenza, HIV
Pathogens
Organisms which cause disease, usually fungi or bacteria
Levels of organisation
Organ systems, Organs, tissues, cells, organelles
Organ systems
A group of organs that work together to perform a particular function
The organ systems
Digestive, respiratory, circulatory, excretory, nervous, hormonal, reproductive
Organs in the Digestive system
Oesophagus, stomach, intestines
Function of the Digestive system
Digest and absorb food
Organs in the Respiratory system
Lungs and trachea
Function of the Respiratory system
Gas exchange
Organs in the Circulatory system
Heart and bloods vessels
Function of the Circulatory system
Carry oxygen and food around the body
Organs in the Excretory system
kidney's, bladder, liver
Function of the Excretory system
Remove wastes and toxins
Organs in the Nervous system
Brain, spinal cord, nerves
Function of the Nervous system
Send messages and responses around the body
Function of Skeletal and Muscle systems
Movement, support and protection
Organs in the reproductive system
Ovaries and Testes
Function of reproductive system
Produce an offspring
Tissues
Cells with a similar function that are grouped together
Organs
A group of tissues acting together to perform a particular function
Cells
Structural units of organisms
Organelles
Structures inside cells like cytoplasm and cell membranes
Nucleus
Largest organelle containing chromosomes which carry genetic material
Cell Membrane
thin, flexible barrier around a cell; regulates what enters and leaves the cell
Cytoplasm
a jellylike fluid inside the cell where the organelles are found
Cell wall
Layer of freely permeable material, cellulose or chitin, outside the cell membrane that keeps the cell's shape
Chloroplasts
Absorb light energy to make food in the process of photosynthesis; green due to presence of chlorophyll
Vacuole
Filled with cell sap, a store of dissolved sugars, mineral ions and other solutes. Permanent in plants
Function of Nucleus
To control the activities of the cell and hold the genetic material
Function of Cell membrane
Controls what enters and leaves the cell
Function of Cytoplasm
Where chemical reactions take place
Function of Cell Wall
Provide the cell with support and protection
Function of Vacuole
Store molecules like amino acids and sugars
Function of Chloroplasts
Where photosynthesis occurs
Chemical elements in carbohydrates
Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
Chemical elements in proteins
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen
Chemical elements in lipids
Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
Simple molecules of carbohydrates
Starch and glycogen made up of simple sugars
Simple molecules of protein
Long chains of amino acids
Simple molecules of lipids
Chains of glycerol and fatty acids joined together
Test for glucose
Add Benedict solution to a solution of dissolved glucose. Heat to observe color change blue to orange
Test for starch
Iodine solution goes brown to blue-black
How do enzymes work as biological catalysts
Reaction occurs faster and under moderate conditions. Turns substrate into product through lock and key, enzyme remains unchanged and can repeat
Enzymes as biological catalysts
Enzymes provide a route with lower activation energy to turn substrates into products without extreme heat or ph that could damage cells
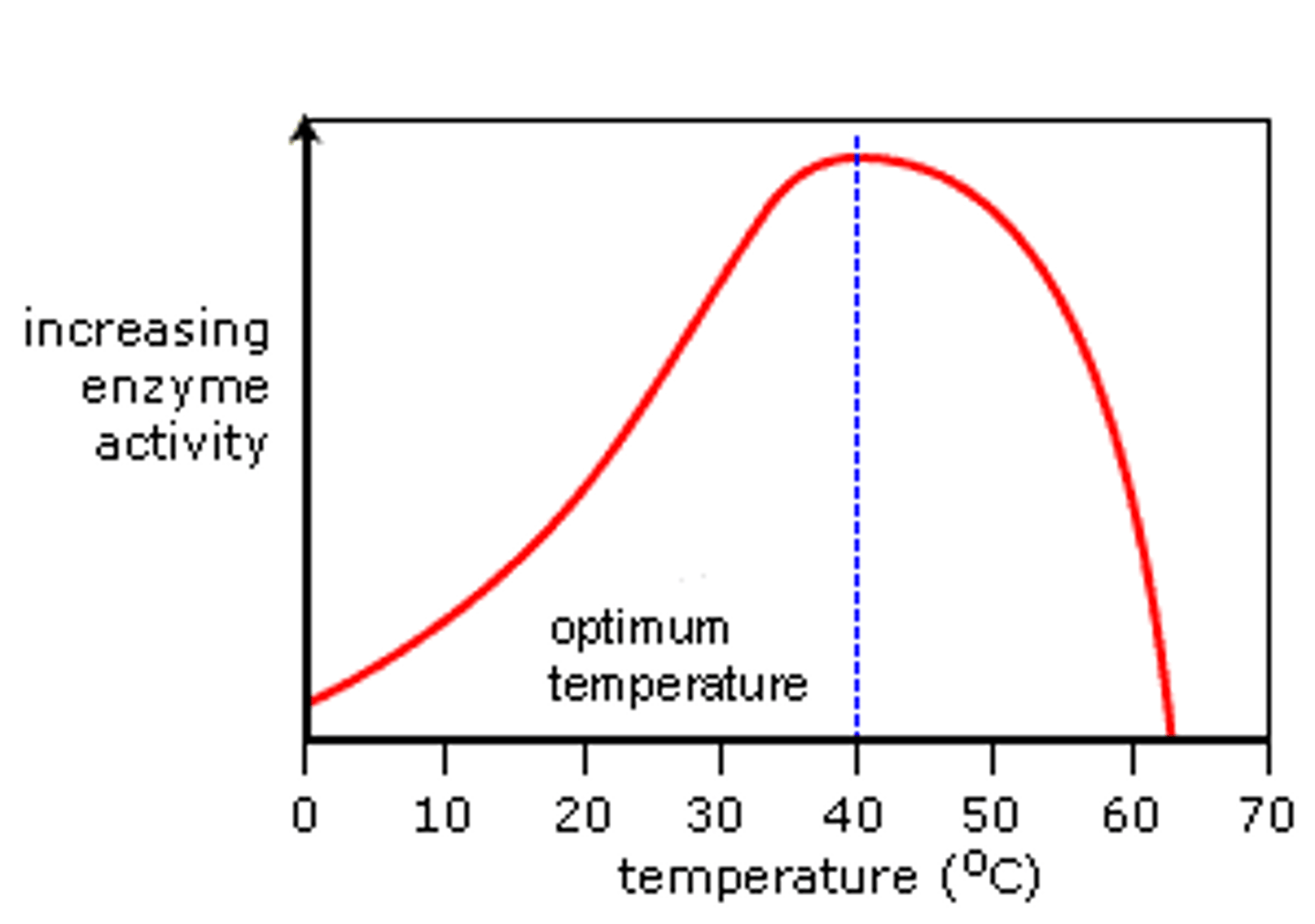
Temperature effect on enzymes
Extremely high or low temperatures can denature enzymes
pH effect on enzymes
Acidic or Alkali conditions change the shape of the active site which slows the reaction. Optimum pH depends on the enzyme
Diffusion
The movements of particles down a concentration gradient from an area of high concentration to low until concentration is uniform
Osmosis
The movement of water across a semi permeable membrane down a concentration gradient from dilute to concentrated
Active transport
Movement of molecules from an area of low concentration to high concentration with an energy requirement
Factors that affect rate of movement of substances in and out of cells
Surface area to volume ratio, temperature and concentration gradient.
How surface area to volume ratio affects rate of movement
Increase surface area with same volume increase rate of movement
How temperature affects rate of movement
Temperature is average kinetic energy so a high temperature increases kinetic energy therefor increased rate
How concentration gradients affects rate of movement
A high concentration gradient increases rate of diffusion into cells
Photosynthesis equation
6CO₂+6H₂O→C₆H₁₂O₆+6O₂
Photosynthesis
The process of converting light energy into chemical energy
Factors affecting the rate of photosythesis
Concentration of carbon dioxide, light intensity, temperature
How carbon dioxide affects the rate of photosythesis
Increasing carbon dioxide levels through hydrocarbonate solution will increase the rate until constant
How light intensity affects the rate of photosythesis
More light, through a lamp or direct sunlight, increases the light energy to the chloroplast until constant
How temperature affects the rate of photosynthesis
Enzymes in the process of photosynthesis work at an optimum temperature
Leaf adaptations for photosynthesis
Large surface area to collect, thin for diffusion, palisade cells in upper section, chloroplasts containing chlorophyll, stomatal pores allowed in, space in mesophyll for diffusion of CO₂ and movement of water, xylem transports water, phloem translocates sugars.
Why do plants need mineral ions
For growth, magnesium ions for chlorophyll and nitrate ions for animo acids
Carbohydrates in the diet
Starches and sugars for energy stores
Balanced diet
correct proportions of the food groups
Why do humans need food
energy to respire and matter for cells and tissues
Water in the diet
needed in the semi liquid cytoplasms to allow movement of particles and allow chemical reactions to occur
Fats in the diet
Long term energy stores and insulation layer
Proteins in the diet
growth and repair of muscle tissues, make up hair, muscles and enzymes
Fibre in the diet
Allows for peristalsis, aids digestive system and increases roughage
Sources of carbohydrates
Bread, Pasta
Sources of proteins
Fish, meat, leafy vegetables
Sources of lipids
Dairy, nuts
Vitamin A in the diet
Creates visual pigment in retina and prevents night blindness
Sources of Vitamin A
Carrots, meat, fish
Vitamin C in the diet
Makes connective tissue to heal wounds and prevent scurvy
Scurvy
A disease caused by a lack of vitamin C. Symptoms of gums bleeding, wounds not healing and loose internal organs
Vitamin D in the diet
promotes calcium absorption, prevents rickets and oestoperosis
Sources of Vitamin C
Citrus fruits
Sources of Vitamin D
sunlight, fatty fish
Calcium in the diet
Normal growth and maintains teeth and bones.
Osteoporosis
Deficiency in calcium leading to bones weakening and thinning