Week 2: Introduction to Endocrine Disorders and Disorders of the Posterior Pituitary Gland (SIADH and DI)
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)/Vasopressin
-potent vasoconstrictor (RAISES BP)
-regulates fluid volume
When is ADH released?
-high serum osmolality
-when BP is LOW
-when blood volume is LOW
-releases when water needs to be absorbed
Relationship with Serum osmolality
ELEVATED = Diabetes Insipidus
DECREASED = SIADH
Relationship with Urine osmolality
ELEVATED = SIADH
DECREASED = Diabetes Insipidus
Diabetes Insipidus and ADH
UNDERPRODUCTION of ADH hormone
Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH) and ADH
OVERPRODUCTION of ADH hormone
S/s of Diabetes ADH
-polyuria
-polydipsia (thirst)
-fluid loss
-serum hyperosmolality
-hypernatremia
-dilated urine (light urine)
S/s of SIADH
-fluid retention
-hypoosmolality
-hyponatremia
-concentrated urine (dark urine)
Relationship between ADH and water absorption
LOW ADH = LESS water absorbed
HIGH ADH = HIGH water absorbed
Types of Diabetes Insipidus (DI)
-NOT enough ADH
-neurogenic: underproduction of ADH from hypothalamus or pituitary
-nephrogenic: renal tubules dont respond to ADH
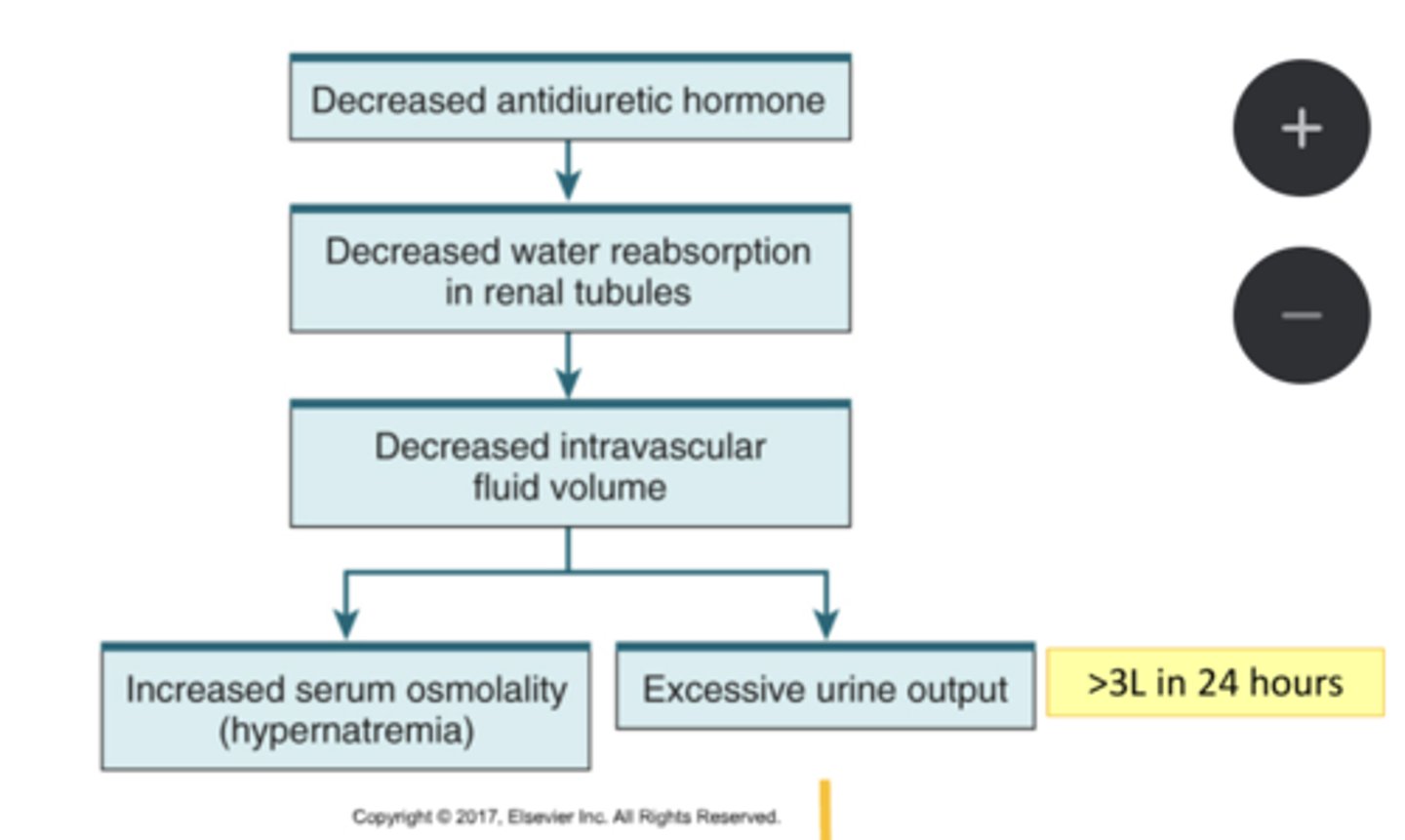
S/s of hypernatremia:
-hypovolemia and dehydration
-muscle weakness
-mental status changes
-hallucinations (especially elderly)
How to treat hypernatremia?
HYPOTONIC IV FLUIDS
-restore fluid balance
S/s of excessive urine output?
-thirst
-dehydration
-hypovolemic shock
--tachycardia, hypertension
How to treat excessive urine output?
MAINTAIN ADEQUATE HYDRATION
Nursing considerations for Diabetes Insipidus:
-monitor I&O
-administer hydration (HYPOTONIC IV fluid)
-monitor for hypovolemic shock (tachycardia, hypertension)
-monitor electrolytes and osmolality
-monitor LOC (think Na)
Vasopressin/Desmopressin (DDAVP)
synthetic replacement of Vasopressin
-reduces urine production
-increases BP in patients w/shock
can only be used in central or neurogenic DI
Nursing considerations for DDAVP:
-monitor for water intoxication (i.e too much absorption)
-monitor for seizures or change in LOC
-can increase BP in patients w/shock
-monitor for HTN, tachycardia, chest pain
Specific gravity range:
1.005-1.030
-higher means urine is very concentrated = less water more solutes
Serum osmolality range:
275-295
dehydration = high osmolality
overhydration = low osmolality
Function of hypothalamus vs pituitary gland:
hypothalamus: releases hormones that target pituitary
pituitary: releases actual hormone itself with direction of hypothalamus
3 Hormones released by thyroid:
-Thyroxine (t4) most of this hormone
-Triiodothyronine (t3)
-Calcitonin
T3 and T4 functions:
-stimulate energy use
-stimulate the heart
-promote growth and development
think getting everything moving!
Calcitonin function:
decreases Ca plasma levels
-inhibits resorption of Ca from bone
-increases calcium excretion by kidneys
think tone it down (the calcium)
PTH function:
-high Ca=low PTH
-low Ca=high PTH
-regulates serum calcium levels
-stimulates renal conversion of vitamin D
Causes of SIADH:
-shock, trauma, stress, pain, nausea, surgery
-chronic like cancer or genetic disorders
S/s of hyponatremia
-SEIZURES
-loss of energy, mental status changes
-muscle weakness
-headache (cerebral edema)
Sodium reference range
135-145
Nursing considerations for hyponatrema:
-treat underlying cause
-replace lost sodium
-water restriction (typically for dilutional hyponatremia)
-seizure precautions
Nursing considerations for SIADH:
-daily weights, monitor I&O, assess lung sounds
-fluid restriction of 800-1000mL/day
-HOB elevated no more than 10 degrees
-administer hypertonic saline infusion (3% NaCl)
-offer distractions for fluid restriction
-monitor serum sodium and osmolality
-monitor urine specific gravity
ANP function
opposite of ADH
-results in higher fluid and sodium excretion
Why does keeping the HOB below 10* important?
-higher chance of stimulating ANP release
-aids in fluid and sodium release
-helpful for patients with SIADH and their excess fluid
Potassium reference range
3.5-5.0
Adverse effects of DDAVP:
-water retention
-hyponatremia
-cerebral edema
-headache is most common
When a patient has Diabetes Insipitus, what kind of fluids should they be getting? Avoiding?
-replace with 5% Dextrose in water (D5W)
-avoid hypertonic and excess sodium
Two types of hyponatremia:
-dilutional hyponatremia
-depletional hyponatremia
Euvolemic hyponatremia
-no edema
-occurs during SIADH
-total body water is increased
-total body sodium is normal
Cancer and ADH relationship:
cancer cells can produce and release ADH
Severe hyponatremia range
less than 125
Moderate hyponatremia range
125-130
Mild hyponatremia
130-135