Insect Behavior Final
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
foraging
food-obtaining behavior, recognizing, searching for, capturing, eating food items
all animals
carbohydrates, fats, amino acids, minerals, and vitamins are essential for
cholesterol (cannot synthesize), sodium (particularly important to herbivores)
essential nutrients that are specific to insects
sweat bees feeding on human sweat for sodium and other minerals
an example of an insect feeding for sodium
puddling: insects gather at the edge of a puddle for salt and amino acids
an example of insects gathering nutrients
surface texture, visual cues, chemical cues
how do insects recognize and accept their food?
some wasps (Trichogramma evanescens) will only parasitize objects that are firm enough for it to walk on
example of surface texture recognition
proper positioning for egg laying, physical contact assists with host suitability, relying on walking to explore a host is very efficient for small insects
why use surface texture in foraging?
tsetse flies are drawn to their host using a combination of visual and chemical cues: movement, dark color, shape of large mammals, CO2, sweat, body odors, heat
example of visual cues in foraging
potato beetle lives on plant that contains toxic alkaloids, larvae have not adapted to the alkaloids yet, rely on olfactory receptors to detect harmful alkaloids, if receptors (palps and antennae) are removed, they will eat the harmful alkaloids
example of chemical cues in foraging
insects make “perfect” foraging decisions
to test if insects balance their diet, you must assume that
age, previous experience, nutritional needs, development stage, etc
what are some factors to consider when testing insect foraging?
choice experiment of different types of pollen (yes they can)
how to test if insects can balance their diet?
reduced competition, efficient, may provide protection from predators through plant toxins, plant-insect coevolution, the plant serves as mating site (drawbacks: what if host goes extinct? environmental changes?)
most insects are herbivores and specialists, why?
favored
specialization is _____ by natural selection
specialists
(foraging) most insects are
single host (parasitic wasps, leaf mining larvae)
extreme specialists are limited to a
mosquito larvae feed on plankton, adult female = blood, adult male = nectar
example of different feeding behavior throughout life stages
leaves in sugar are tied up in cellulose (strong connections btwn cellulose and glucoses), pollen and nectar limited to certain flowers/hours/seasons, plants may have defense mechanisms
challenges of herbivorous insects
gut microbes
digestion of cellulose requires specific enzymes that are acquired by having
by licking the anus of the adults
how do young termites acquire symbiotic microbes?
must find a way to capture prey, such as actively hunting in dragonfly larvae or ambushing
challenges in carnivores
relatively rare in insects, difficult lifestyle, example = ants, use cooperative hunting
challenges in omnivores
saprophagous
feed on carrion, decayed plant, and animal material, biggest challenge is to find resources (“first come first serve”)
blood feeders
need to find the host, digest large amount of food at once, and resist potential pathogens
mouthparts (butterflies, bees)
adaptation of _____ helps in foraging
optimal foraging theory (OFT)
views foraging behavior as a compromise between benefits of nutrition and costs of obtaining food to maximize fitness (natural selection should favor foraging behavior that minimizes costs and maximizes benefits) (behavior may not always be optimal)
currency
(foraging) the “goal,” more food per unit time, must correlate with fitness, often maximize rate of net energy intake
contraints
factors that limit the forager’s ability to maximize the currency, intrinsic (limitations in ability, such as running speed, tolerances), extrinsic (imposed by environment, such as prey density)
decision
(foraging) maximizes the currency under the constraints of the environment, behavioral options such as pursuing prey or not
outputs of OFT
identifies currency and constrains (ex: number of food items, energy spent), makes assumptions explicit (ex: the more food items the better), generates quantitative and testable predictions (ex: count items, count fitness), suggests new hypotheses if model doesn’t fit, becomes more complicated as function of the number of constraints/currency
prey types (predators encounter various species, diff sizes etc), search times (time spent searching for prey), handling time (time spent subduing prey and consuming it), energy return (energy gained from consumption), optimal prey choice (model assumes predator will choose prey that maximizes gain and minimizes time/risk)
prey choice model basic principles (which prey to capture?)
patch choice model
when is the optimal time to leave a patch? decision = stay or leave a patch, currency = maximizing profitability, constraints = time spent searching patches or traveling between patches, we assume perfect knowledge (energy gain in a patch and patch locations are known)
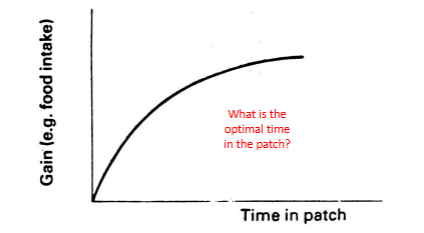
diminishing return
energy gain in patches shows ______ ______ but the optimal time in the patch also depends on the traveling time between patches
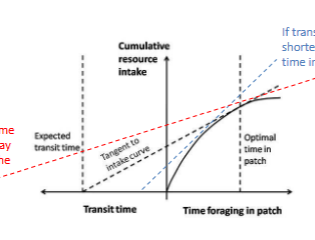
marginal value theorem (MVT)
stay in a patch until the benefit of staying is equal to the benefit of moving (if transit time is longer, stay in patch longer, if transit time is shorter, stay in patch less)
central place foraging
an extension of the marginal value theorem: insects typically leave a central place to forage and return to that place with food, insects needs to know when to leave patch and how much to carry back, the further the insect has to carry food, the longer it will remain in the patch and the more it will carry
larger loads require more energy (used weights and found that bees were in fact maximizing profitability)
larger load in nectar that bees carry shows diminishing returns because
termites, leaf cutter ants with fungus to digest cellulose, cockroaches with symbionts that are transferred across generations in eggs
examples of digestion using symbionts
red queen hypothesis
organisms must constantly increase their fitness to compete with other evolving organisms in a changing environment
insectivores, parasites, microscopic predators (and humans sometimes)
who eats insects?
no
is the exoskeleton of the Hercules beetle a behavioral defense?
passive messages (camouflage, mimesis, aposematism, mimicry, morphology couple with behavior is usually low energy cost, active messages (startling, jamming, behavioral defense, social defense)
defense strategies
seek the appropriate background or include motion shifting
static coloration is a behavioral anti-predator defense only if the insects
by dorso-ventral flattening
how is reducing shadows achieved?

countershading
light source makes the upper side look lighter, ability to hide/be seen in different angles
mimesis (orchid mantis disguised as orchid)
resembling an object in the environment that is uninteresting to the predator
skipper butterfly caterpillars eject feces from their hiding spots to make it harder for parasitic wasps to find them, beetle larvae shielding itself with feces
example of crypsis by sanitation

Batesian mimicry
aposematic inedible model has an edible mimic, only works if false mimic is rare (predators will eat safe one and begin to think all are safe)

Mullerian mimicry
a group of species benefit from each other’s existence because they are all warningly colored in the same manner and distasteful, like in Batesian mimicry, the mimics are not necessarily related
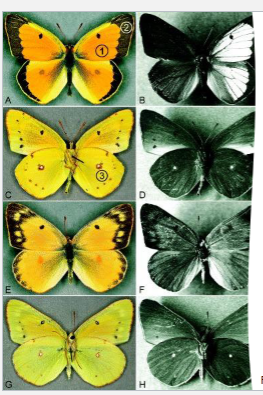
UV-reflecting scales on dorsal wing surface, brief flash of UV with each downstroke of the wing, different signals by different species, serves as mating signals for males
behavioral aspects in mimicry
behavioral mimicry
fly mimics vespid by smelling with front legs to mimic antennae
startle display
a display made by a cryptic insect upon discovery, involving exposure of a startling color pattern or display, such as eyespots
snake mimicry in caterpillar, snowberry flies resemble jumping spider
startle display/intimidation examples
jamming
disrupting the echolocation of bats by clicking
feigning death
beetles, particularly weevils, are especially fond of this sort of acting (defense)
delayed chemical defense (class 1 compounds, ex: monarch butterfly)
chemicals with delayed reactions, occur after the prey item has been consumed, found in the hemolymph or other internal tissue of the insect, are often accompanied by an immediate-acting chemical or aposematic coloring
class 2 compounds (formic acid in ants, spines on caterpillar)
immediate acting chemicals affect the predator as it is handling the potential prey item, chemicals are secreted externally, tend to be volatile
bombardier beetle mixes different chemicals from different glands then injects them into an explosion chamber containing mostly water, within chamber is catalase, causes explosive reaction, 100C water
example of chemical defense
lipids
aphids secrete ____ to gum up mouthparts of arthropod predators
chemical defense in termites
many termites secret chemicals that harden when in contact with air, impairs movement of predators, termites preyed upon by ants emit a class II mimic of ant alarm pheromone

gregarious insects
chemically defended, aposematic insects tend to cluster rather than spread out in environment, will orient themselves in the best manner for optimally disseminating chemicals, sometimes form aggregations in defensive circles
herd allows individuals to hide, downside: many individuals are easy to spot, most aggressive individuals get safest spot in center
sociality as an anti-defense mechanism
social defense in mayflies
dilution effect, predators saturation, the more females emerging per day, the less likely any individual mayfly was to be eaten by a predator
successful reproduction, appropriate microclimate for growth of juveniles, minimum inter and intra species competition, maximal food availability, maximal survival
the right habitat allows for
habitat destruction, climate change and humans are largely responsible for this
what is the main cause for species decline?
both landscape and species affects preference, results can be used to improve conservation
habitat preference in bumblebees
paper wasps, chew and glue plant material together to form cells, small variation in building pattern can result in large differences in nest shape: flat comb vs. string like nest
example of next construction and architecture

string-like nests
cells are started near the top of the previous cell, long string-like structures that look like dead sticks, often found on garden shrubs or fences
flat comb nests
cells are started near the base of the previous cell, open combs appearance, underside of leaves or overhangs
build, take it with them
some insects ____ their home and ____
territorial space
crickets have a _____ for the purpose of mating
stability, choice of materials (feces, saliva, mud, chewed-up plant), internal design (tunnels and chambers strategically placed to distribute weight evenly), moisture is regulated to prevent structure from becoming too brittle/soft, maintenance, chimney effect for passive airflow
functional architecture in termite nests
parasitic wasp find its host using innate (response to frass) and learned (response to fruit cue) responses, bumblebee choice of cavity is innate, cockroach preference for darkness is genetic
habitat selection: nature vs. nurture
aggressive competition with other individuals over nesting
if appropriate nesting sites are scarce, this leads to
ideal free distribution theory
the number of individual animals that will aggregate in various habitats is proportional to the resources available in each
habitats differ in the resource they contain, individuals are aware of this and try to maximize fitness, individuals are free to move to
ideal free distribution assumptions