Redox , Rusting and Iron
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
3 definitions of oxidation
The gain of oxygen by a substance
The loss of hydrogen from a substance
The loss of electrons from a substance (OIL)
3 definitions of reduction?
The loss of oxygen from a substance
The gain of hydrogens by a substance
The gain do electrons by a substance ( RIG)
element combining with oxygen oxidation example
magnesium + oxygen → magnesium oxide
bright white light, forms white solid
2Mg + O2 →2MgO
sulfur + oyxgen -. sulfur dioxide
S + 02 → S02
the yellow solid sulfur melts to a red liquid which burns with a blue flame releasing heat and a colourless pungent and chocking gas called sulfur dioxide
combustion of fuels
oxygen is added and an oxide is produced, heat is also released
Carbon + oyxgen → carbon dioxide
C +02 → CO2
Black carbon (charcoal) is burned in a plentiful supply of oxygen and a colourless gas is formed
reduction reaction example
chlorine + hydrogen → hyrdogen chloride
Cl2 + H2 → 2HCl
reduction is gain of hydrogen, chlorine gains hydrogen therefore chlorine has been reduced
what is redox
A redox reaction involves both oxidation and reduction in the same reaction
what colour is copper oxide
black soild
what colour is copper
pink-brown solid
copper oxide reduction
CuO + H2 → Cu + H20
hyrdogen isg gaining oxygen so its oxidation
copper is losing oxygen soits reduction
the both make redox
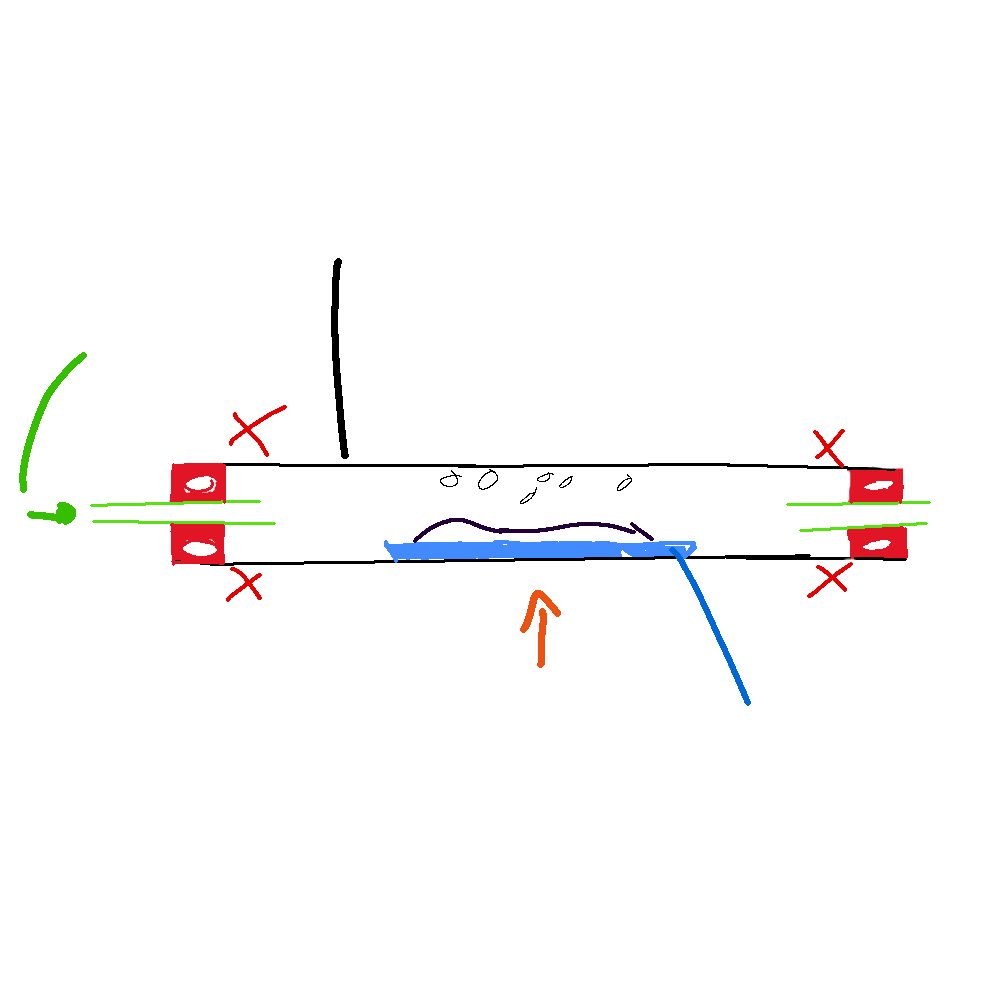
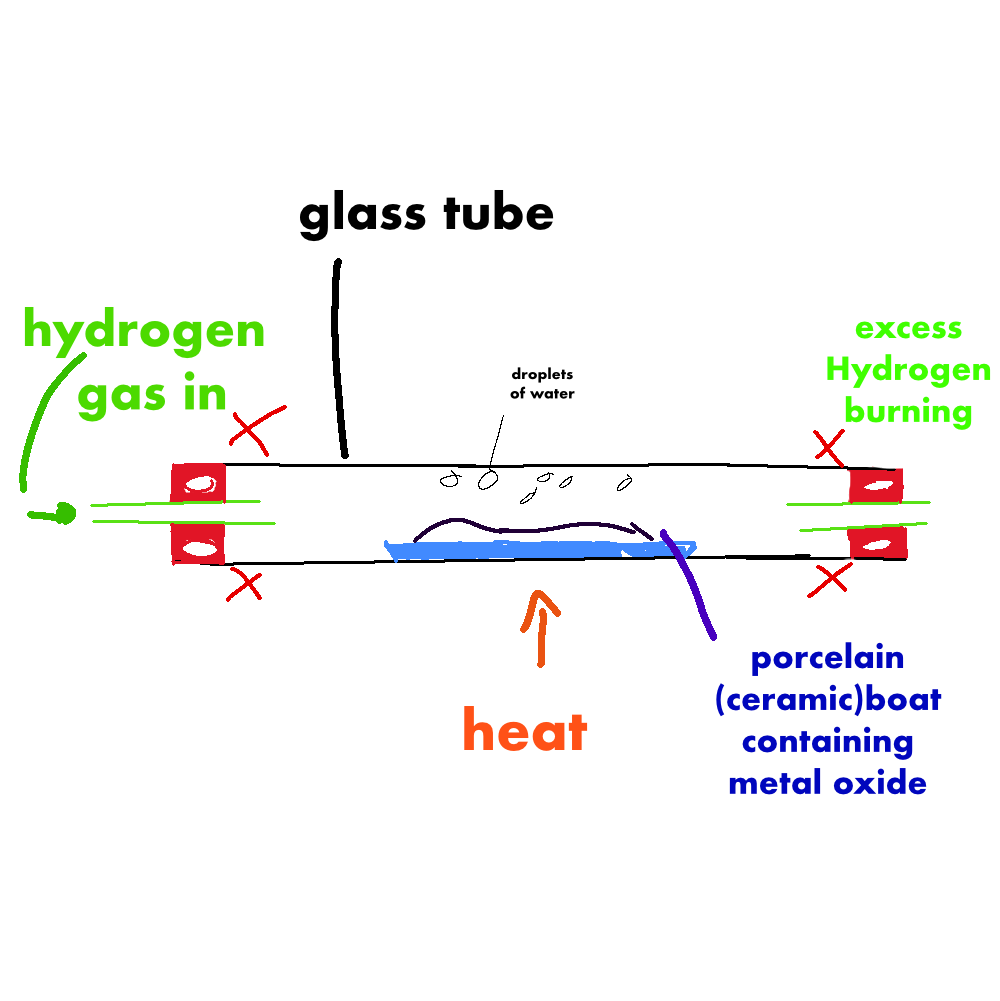
Balance symbol equation :
Zn + CuSO4 → Cu + ZnSO4
Ionic Equation :
Zn + Cu2+ → Cu +Zn2+
Why does the sulfate ion not appear
becuase it is a spectator ion
Balance symbol equation :
Zn + CuSO4 → Cu + ZnSO4
Ionic Equation :
Zn + Cu2+ → Cu +Zn2+
What type of reaction is this
Redox because zinc is losing electrons- oxidation and copper ion is gaining electrons electrons to become a copper atom - reduction
How does rusting occur
iron and steel rust when it comes into contact with oxygen and water
What type of reaction is rusting
Oxidation and is a form of corrosion
Rusting chemical name
Hydrated iron (III) oxide
describe what rust looks like
red-brown flaky solid
word equation for rust
iron + water + oxygen → hydrated iron (III) oxide
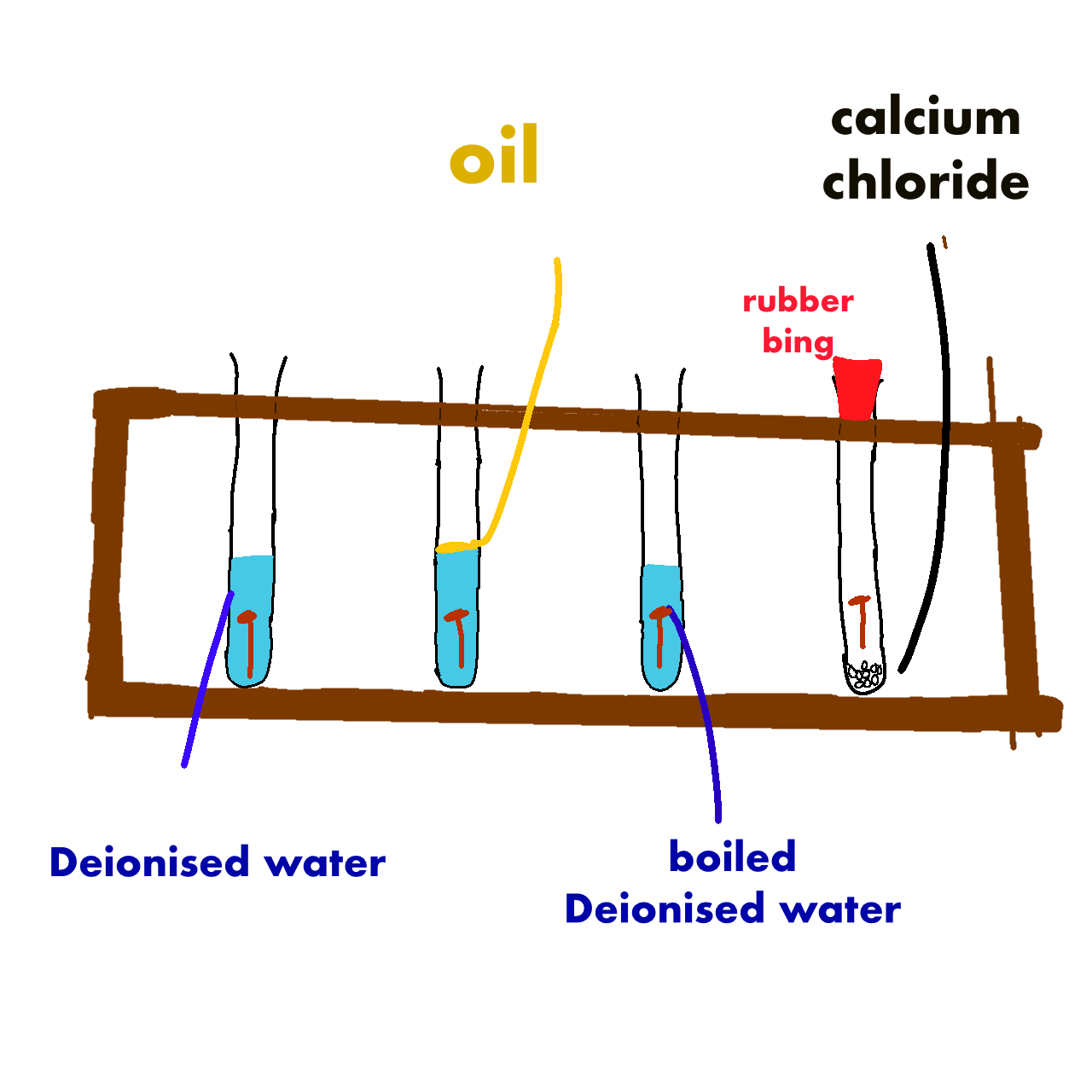
Test Tube | Present | Rusting observed | Reason |
A |
|
|
|
B |
|
|
|
C |
|
|
|
D |
|
|
|
Test Tube | Present | Rusting observed | Reason |
A | Ox, Wa, Fe | Yes | all present |
B | No ox, Wa, Fe | No | no oxygen |
C | Ox, Wa , Fe | Yes | all present |
D | Ox, No wa, Fe | No | calcium chloride removed water |
difference between corrosion and rusting
corrosion is the reaction of any metal with air(oxygen) / rusting is the speicific name given to the corrosion of iron/steel
1 method of preventing rust
Barrier method - preventing water and oyxgen from reaching ron , painting, oiling, plastic coasting e.g Cars, bridges, bicycle chains
2nd way of preventing rust
Metal covering/ plating - cover with another thin layer metal using electroplating. Acting as a barrier. E.g food cans are covered in tin (non reactive, non toxic), chromium used for car for shiny
What is galvanising
Galvanising involves iron being coated with zinc. E.g buckets/ chains are often galvanised
How does sacrifical protection work?
Iron is coated with a more reactive metal e.g magnesiumor a more reactive metal is attached to iron. This reacts instead of the iron with oxygen/ water.
Why is iron important
Used in bridges and structures due to its strength, cheap metal and abundant.
Purpose of blast furnace
to extract pure iron from iron ore and acidic sand impurities
Chemical name for iron ore, and formula
Haematite , Iron (III) Oxide, Fe2 O3
What are the raw materials that go into a blast furnace
Iron ore, coke(carbon), limestone (calcium carbonate)
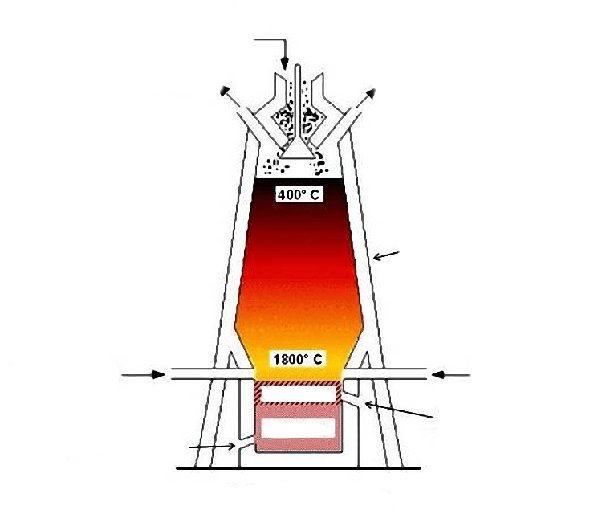
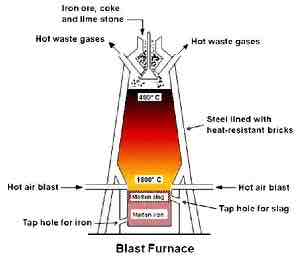
how do u form the reducing agent
hot air converts carbon into carbon dioxide and then carbon monoxide . Exothermic reaction
formation of reducing agent formula
Carbon + oxygen → carbon dioxide
C + O2 → CO2
Carbon dioxide + carbon → carbon monoxide
CO2 + C → 2CO
reduction of iron oxide to iron
carbon monoxide reduces iron oxide to iron (reduction )
reduction of iron oxide to iron formula
Iron (III) oxide + Carbon monoxide → Iron + Carbon dioxide
Fe2O3 +3CO → 2Fe + 3CO2
removal of impurity
limestone undergoes thermal decomposition and the calcium oxide produced reacts with the acidic impurities e.g sand/silicon dioxide) to produce molten slag. This falls to the bottom of the furnace ( used for tar road) . Molten iron is denser so it sinks below the slag. They are tapped off the base
removal of impurity formula
Calcium carbonate → calcium oxide + carbon dioxide
CaCO3 → CaO + CO2
Calcium oxide + silicon dioxide → Calcium sillicate
CaO + SiO2 → CaSiO3