comp eng notes
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/176
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:12 AM on 1/18/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
177 Terms
1
New cards
3 biggest saftey hazards
electrical
falling
fire
falling
fire
2
New cards
Avoid falling
disconnect cables
dont climb
keep clean
dont climb
keep clean
3
New cards
avoid electrical
* 0.1-0.2 amps = lethal
* don’t mix with water
* report cabling problems
* treat as live cables
* switch off before connecting/disconnecting cables
* Don't place electrical equipment near combustible materials
* Never use w/ wet hands
* Use type C(electrical) or ABC fire extinguishers
* Wear gloves with high voltage
* If comp. smoking/sparking - unplug and dont touch case/pwr. button
* don’t mix with water
* report cabling problems
* treat as live cables
* switch off before connecting/disconnecting cables
* Don't place electrical equipment near combustible materials
* Never use w/ wet hands
* Use type C(electrical) or ABC fire extinguishers
* Wear gloves with high voltage
* If comp. smoking/sparking - unplug and dont touch case/pwr. button
4
New cards
Explosive hazards
* Lithium ion batteries explode violently if over charged/over loaded
* Wiring dead battery = in closed circuit w/ fully charged battery cause fire/explosion
* Wiring dead battery = in closed circuit w/ fully charged battery cause fire/explosion
5
New cards
poison/toxic hazards
* Lead solder = toxic
* Rubbing alcohol - flammable and toxic
* Rubbing alcohol - flammable and toxic
6
New cards
Environmental hazards
* Comp parts create toxic/harmful envion
* Old electronics - e waste bins
* Old batteries - not thrown in garbage
* Old electronics - e waste bins
* Old batteries - not thrown in garbage
7
New cards
Compressed/corrosive hazards
* Clearing solvent = acidic and chemical burn
* Always wear Personal Protective Equipment
* Always wear Personal Protective Equipment
8
New cards
Laser hazards
* In optical drives - sufficient pwr. To cause eye injury w/out direct exposure
* Blue ray - hot enough to start fire
* Unshielded cathode tube rays emit high level ultraviolet radiation
* Smoke detectors have radioactive materials emitting ionizing radiation
* Electrons generate magnetic fields dangerous to digital devices
* Blue ray - hot enough to start fire
* Unshielded cathode tube rays emit high level ultraviolet radiation
* Smoke detectors have radioactive materials emitting ionizing radiation
* Electrons generate magnetic fields dangerous to digital devices
9
New cards
Binary
* base 2 system
* each new digit hv value greater than symbol to the rightpositio
* each new digit hv value greater than symbol to the rightpositio
10
New cards
positional notation
related to the next by a constant multiplier
11
New cards
alphanumeric
using alphabet to replace numbers
* base 32 - capitals and numbers
* base 32 - capitals and numbers
12
New cards
URL shorteners
using base 62
* capital letters, lowercase and numbers
\
* capital letters, lowercase and numbers
\
13
New cards
Microtransistors
on/off - count using switches
14
New cards
1 bit
1 transistor
15
New cards
byte
8 transistors
16
New cards
ASCII
American Standard Code Information Interchange
* convert numbers to letters
* 225 symbols/letters (1 byte)
* convert numbers to letters
* 225 symbols/letters (1 byte)
17
New cards
Arduino
open source hardware and software company
\
programmable with any PC - using USB cable
coded with C++
\
programmable with any PC - using USB cable
coded with C++
18
New cards
reset button
resets ATmega microcontroller
19
New cards
USB port
* powering arduino
* uploading sketches
* communing with sketches
* uploading sketches
* communing with sketches
20
New cards
TX and RX LEDS
show that Arduino and computer are communicating
21
New cards
Power Pins
distribute power to input and output
22
New cards
Analog In
receive analog value
23
New cards
ATmega microcontroller
heart and brain of Arduino Uno
24
New cards
Power LEDS
indicates that its receiving power
25
New cards
Digital Pins
send and receive digital signals
26
New cards
Pin 13 LEDS
built in LED
27
New cards
LAN - Local Area Network
w/out external connect
* no internet
* no internet
28
New cards
WAN - Wide Area Network
connects with computers not in the same building - internet access
29
New cards
WLAN - Wireless Local Area Network
radio to transmit data across local network
30
New cards
MAC address - Media Access Control Address
* physicals address on hardware
* never changed
* included on sticker attached to network devices
* never changed
* included on sticker attached to network devices
31
New cards
IP - Internet Protocol Address
* mailing address on internet
* Subnet number - IP issued to LAN devices
* geographically traced
* Subnet number - IP issued to LAN devices
* geographically traced
32
New cards
Data Packet
* thing being transmitted
* broken down into smaller structure of data before transmission
* then reassembled to original chunk once reaching destination
* sent receipt for each - allowing to determine if any dropped
* broken down into smaller structure of data before transmission
* then reassembled to original chunk once reaching destination
* sent receipt for each - allowing to determine if any dropped
33
New cards
Hub
* simple connection
* repeat data to any devices connected
* slower
* no security
* repeat data to any devices connected
* slower
* no security
34
New cards
Switch
* connected to LAN
* remembers MAC address
* read destination of all devices connected and send packet to specific intended computer
* faster
* security
* remembers MAC address
* read destination of all devices connected and send packet to specific intended computer
* faster
* security
35
New cards
Router
* connected between LAN and WAN (local to outside)
* built in switches - smaller LANS
* send data packet to other routers attaches to outside networks
* built in switches - smaller LANS
* send data packet to other routers attaches to outside networks
36
New cards
Modem
* convert digital signals for transmission across long distances
* modulates and de modulates
* built into most routers
* modulates and de modulates
* built into most routers
37
New cards
soldering
joining process of metals by melting together (alloy melted with hot iron/gun)
heated to 200 degrees Celsius
heated to 200 degrees Celsius
38
New cards
Soldering gun
heavy work, heavy weight and heats quickly
39
New cards
soldering iron
used for fine work, light weight and takes long to heat up
40
New cards
sponges
clean soldering iron/gun tips
41
New cards
flux
prevents oxidation/rust and creates cleaner soldering connection
42
New cards
Lead solder
high quality and easier to work with
43
New cards
soldering lead precautions
* ventilated areas
* fume extraction system'
* filtered breathing protection
* safety glasses
* neoprene/latex gloves
* fume extraction system'
* filtered breathing protection
* safety glasses
* neoprene/latex gloves
44
New cards
ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer)
* first programmable general purpose electronic digital computer
* building hydrogen bombs
* vacuum instead of transistors
* programmed with combination of wired plug board and switches
* building hydrogen bombs
* vacuum instead of transistors
* programmed with combination of wired plug board and switches
45
New cards
evolution of a cpu
1800% increase of processing power, less expensive and less power consumption
46
New cards
How a cpu works
bit transmitted and voltage levels
1. fetch
2. decode
3. execute
1. fetch
2. decode
3. execute
47
New cards
Fetch
* gets instructions from memory
* software instruction/data stored in ram
* each instruction provided in blocks of data
* program counter, instruction register, bus, address
* software instruction/data stored in ram
* each instruction provided in blocks of data
* program counter, instruction register, bus, address
48
New cards
Instruction register
instructions being executed and held
49
New cards
program counter
keeps track of instructions that hv been completed and where in RAM is stored
50
New cards
Bus
multilane between CPU and RAM
* data bus and address bus
* data bus and address bus
51
New cards
decode
* bitfields - opcode and operand code
* takes instructions and convert unto useable form for CPU
* into compatible languages - RISC, ARM, x86
* takes instructions and convert unto useable form for CPU
* into compatible languages - RISC, ARM, x86
52
New cards
Execute
completes instructions
* result sent to register for placement in system memory
ALU - carry over, over flow, 0, less than flags
* result sent to register for placement in system memory
ALU - carry over, over flow, 0, less than flags
53
New cards
CPU (computer processing unit
* electronic circuitry that executes the instruction that make up a computer program
* basic math, logic, controlling and input/output
* basic math, logic, controlling and input/output
54
New cards
Boolean logic and logic gates
true/false
55
New cards
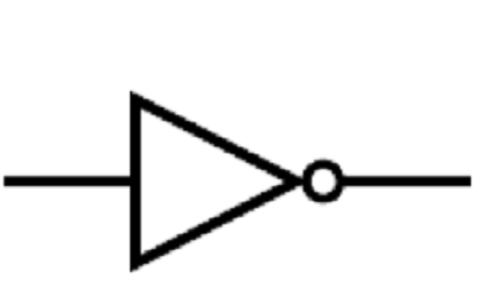
\
NOT gate
56
New cards
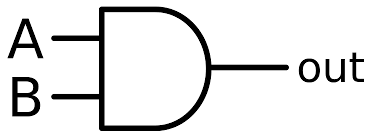
AND Gate
57
New cards
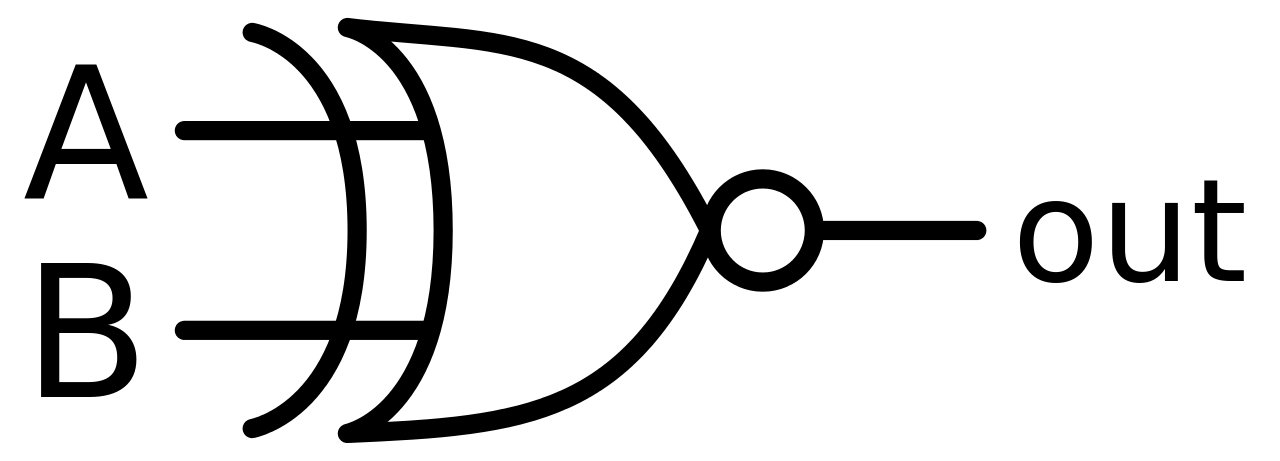
XNOR
58
New cards
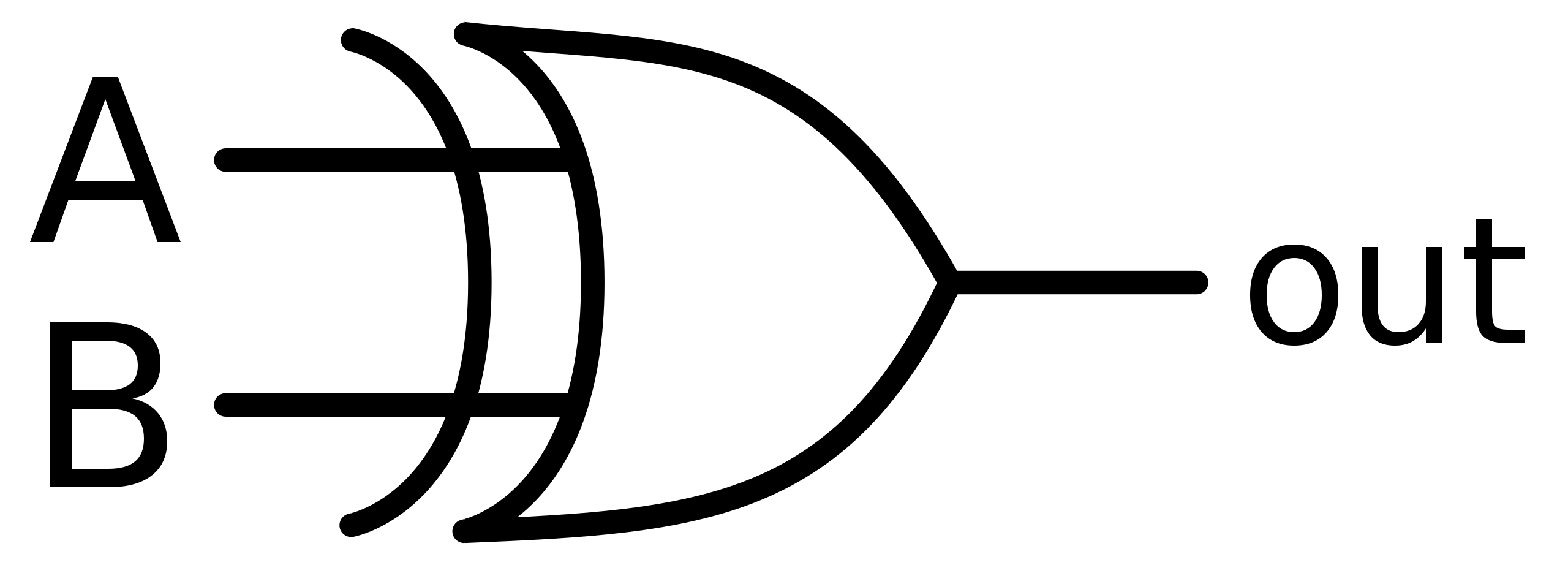
XOR
59
New cards
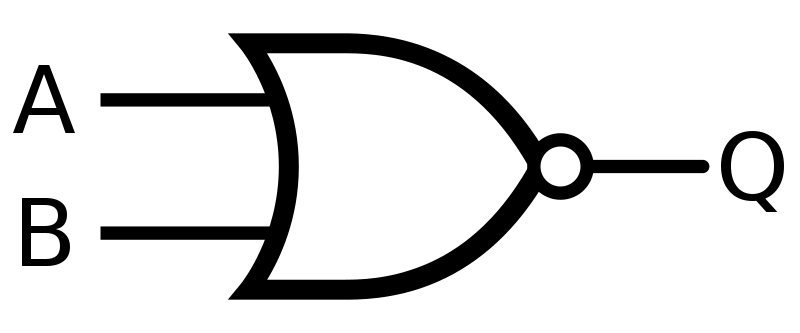
NOR
60
New cards
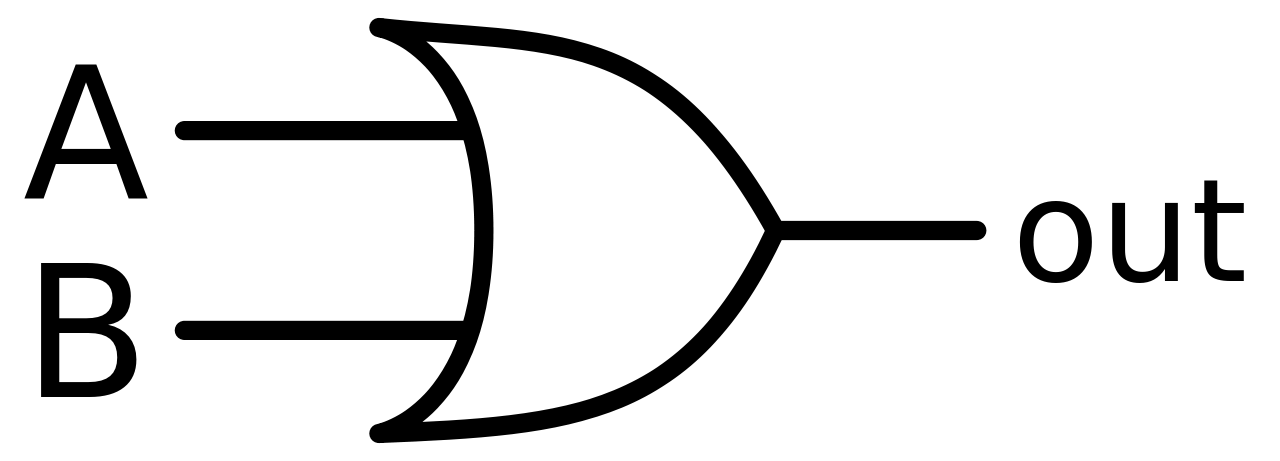
OR
61
New cards
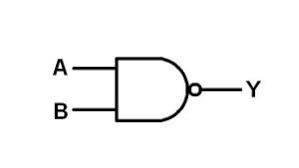
NAND
62
New cards
Amps
current - amount of electricity flowing through wire
63
New cards
volts
pressure electricity is under
64
New cards
resistance
how hard a martial is to pass electricity through
65
New cards
watts
measure of power
66
New cards
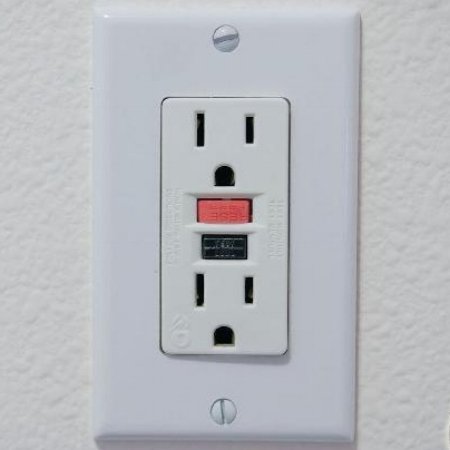

ground fault circuit interrupter
67
New cards

120V outlet
68
New cards
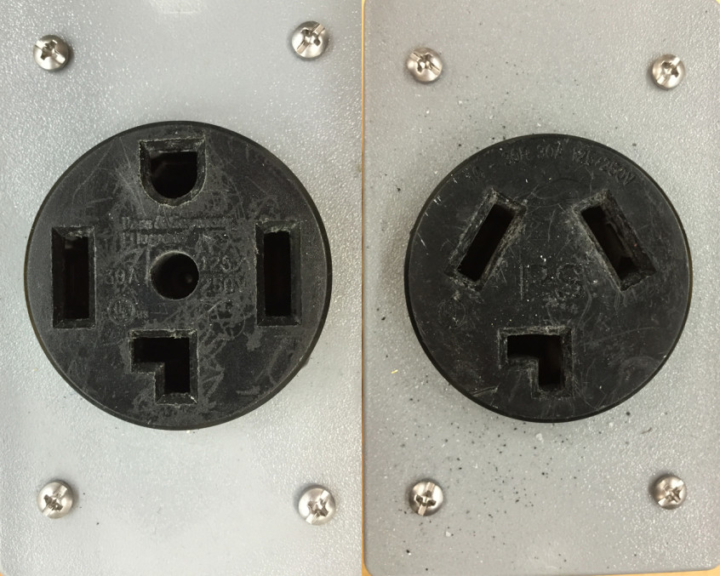
240 V outlet
69
New cards
orange outlet
isolated ground
70
New cards
red outlet
emergency generator supply
71
New cards
blue outlet
surge supply
72
New cards
series circuit
double volts
73
New cards
parallel circuit
double amps
74
New cards
battery safety
connecting batteries - connection cables to be equal length and resistance
75
New cards
wires
* Typical cylinders or braided strands of metal (or other highly conductive material) used to conduct electricity.
* Typically encased in non-conductive material called insulation. This insulation may also contain shielding (typically strands of metal such as copper) to protect from signal leakage or interference.
* Typically encased in non-conductive material called insulation. This insulation may also contain shielding (typically strands of metal such as copper) to protect from signal leakage or interference.
76
New cards
breadboard
* Also known as a Solderless Circuit Board or a Protoboard.
* Used to quickly construct and test electrical circuits
* Used to quickly construct and test electrical circuits
77
New cards
resistors
passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. In electronic circuits, resistors are used to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, to divide voltages, bias active elements, and terminate transmission lines, among other uses.
78
New cards
transistors
semiconductor device used to amplify or switch electrical signals and power
at least 3 terminals for connection to electronic circuit
at least 3 terminals for connection to electronic circuit
79
New cards
NPN transistor
current flows between collector to emitter when the positive supply is given to the base
80
New cards
PNP transistor
charge carrier flows from the emitter to collector when negative supply is given to the base
81
New cards
Silicon-Controlled Rectifier
react to the amount of voltage being applied. There has to be sufficient voltage to open/close the “gate”.
maintain their “gate” state until power is is cycles off and on again
MOSFETs (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor-Field-Effect-Transistor) function in largely the same was as SCRs but have very different construction and are better suited to voltage control than current switching
maintain their “gate” state until power is is cycles off and on again
MOSFETs (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor-Field-Effect-Transistor) function in largely the same was as SCRs but have very different construction and are better suited to voltage control than current switching
82
New cards
diodes
semiconductor device that essentially acts as a **one-way switch** for current. It allows current to flow easily in one direction, but severely restricts current from flowing in the opposite direction.
\n aka. rectifiers because they change alternating current (ac) into pulsating direct current (dc).
\n aka. rectifiers because they change alternating current (ac) into pulsating direct current (dc).
83
New cards
LED
semiconductor device that emits light when an electric current is passed through it. Light is produced when particles that carry current (electrons) combine together within the semiconductor material.
84
New cards
Capacitors
**energy-storing devices** available in many sizes and shapes. They consist of two plates of conducting material (usually a thin metal) sandwiched between an insulator made of ceramic, film, glass or other materials, even air.
As compared to batteries, capacitors have much lower storage capacity but much higher discharge/recharge speeds
As compared to batteries, capacitors have much lower storage capacity but much higher discharge/recharge speeds
85
New cards
Photocell
**resistor that changes resistance depending on the amount of light incident on it**. A photocell operates on semiconductor photoconductivity: the energy of photons hitting the semiconductor frees electrons to flow, decreasing the resistance.
More light = less resistance.
More light = less resistance.
86
New cards
potentiometer
form of **variable resistor**. It is a three-terminal resistor with a sliding or rotating contact that forms an adjustable voltage divider.
87
New cards
speaker
electrical energy into mechanical (kinetic) energy. The mechanical motion produces sound waves in air by vibrating a thin diaphragm.
This is done by varying an electrical current through copper windings (Coil) to create an electromagnet. The electromagnet is then attracted or repelled by the permanent magnet in rapid vibrations that create sound waves.
This is done by varying an electrical current through copper windings (Coil) to create an electromagnet. The electromagnet is then attracted or repelled by the permanent magnet in rapid vibrations that create sound waves.
88
New cards
push button
type of electric switch which closes a circuit when pressed and opens it when released
89
New cards
555 - Integrated circuits
timer/pulse generator
steady
steady
90
New cards
4011 - Integrated circuits
4 NAND gates - each has 2 inputs
91
New cards
4029 - Integrated circuits
counts in 10s - switches between binary and decimals
contains multiple flip flops to convert
contains multiple flip flops to convert
92
New cards
cpu types
* Mobile (ultralight)
* Laptop
* Desktop
* Workstation
* Server
* Laptop
* Desktop
* Workstation
* Server
93
New cards
cpu architecture
basic design rules of a CPU, the way it is organized internally and how it communicates externally. Architecture also refers to the way in which binary data is processed, in what order it is executed and where it is stored in memory.
94
New cards
x86 (16/32 bit)
* backwards compatibility
* high clock speeds
* custumizable - BIOS allows fine tuning/expandability
* more vulnerable and potentially less reliable
* open pathways for malicious software and opportunities for inept users to damage their own systems.
* more powerful but power hungry
* needs active cooling and larger power supply. (280+ Watts of power
* good for gaming
* high clock speeds
* custumizable - BIOS allows fine tuning/expandability
* more vulnerable and potentially less reliable
* open pathways for malicious software and opportunities for inept users to damage their own systems.
* more powerful but power hungry
* needs active cooling and larger power supply. (280+ Watts of power
* good for gaming
95
New cards
x64 (64 bit)
* same basic architecture as x86, however the processor Fetches, Decodes and Executes 64-bit blocks (words) of data rather than 16 (8086) or 32 (i386)
* improved processor performance only if the software has been optimized
* switch for the memory
* improved processor performance only if the software has been optimized
* switch for the memory
96
New cards
x86 vs x64
* more than 4GB of memory.
* The CPU industry is still years away from being able to take full advantage of the maximum memory potential of 64-bit systems.
* x64 processors are backwards compatible, meaning can run software that was written for an x86 system.
* The opposite is not true; x86 processors cannot run software written for a x64 systems.
* The CPU industry is still years away from being able to take full advantage of the maximum memory potential of 64-bit systems.
* x64 processors are backwards compatible, meaning can run software that was written for an x86 system.
* The opposite is not true; x86 processors cannot run software written for a x64 systems.
97
New cards
clock speed
* aka. frequency
* how many cycles(instruction) completed per second per CPU core
* multicore - capable of more instructions than single core
* does not always equate to more performance. Software needs to be optimized to take advantage of multiple cores.
* Ghz (gigahertz) = 1 billion cycles per second
* change based on usage and temperature.
* how many cycles(instruction) completed per second per CPU core
* multicore - capable of more instructions than single core
* does not always equate to more performance. Software needs to be optimized to take advantage of multiple cores.
* Ghz (gigahertz) = 1 billion cycles per second
* change based on usage and temperature.
98
New cards
core counts
* **ALUs.**
* **Multi Core = faster, more reliable, far superior at multitasking and generally results in reduced power consumption.**
* **Individual applications may not benefit from multi Core CPUs if not optimized for them**
* **Some old or poorly written software may slow down all processes on a multi-core system.**
* **Multi core - need more memory and BUS resources.**
* **Multi Core = faster, more reliable, far superior at multitasking and generally results in reduced power consumption.**
* **Individual applications may not benefit from multi Core CPUs if not optimized for them**
* **Some old or poorly written software may slow down all processes on a multi-core system.**
* **Multi core - need more memory and BUS resources.**
99
New cards
ARM (Advanced RISC Machines)
* company that designs CPUs and SOCs (system on a chip) and sells their designs to other companies for manufacture.
* ARM processors use RISC architecture (Reduced Instruction Set Computer) which provides greatly increased efficiency and simplicity at the cost of reduced performance and compatibility.
* not good at multitasking. Most ARM operating systems can only run one program (or have 1 open window) at a time
* closed hardware - Meaning there is no BIOS in which to customize systems.
* Simplistic linear coding makes programming easier and more energy efficient.
* Rarely suffer catastrophic errors
* ARM processors use RISC architecture (Reduced Instruction Set Computer) which provides greatly increased efficiency and simplicity at the cost of reduced performance and compatibility.
* not good at multitasking. Most ARM operating systems can only run one program (or have 1 open window) at a time
* closed hardware - Meaning there is no BIOS in which to customize systems.
* Simplistic linear coding makes programming easier and more energy efficient.
* Rarely suffer catastrophic errors
100
New cards
SOC
system on a chip
* single chip that contains all components find in a computer (even storage)
* interior volume of most modern smartphones and tablets is dominated by the battery
* single chip that contains all components find in a computer (even storage)
* interior volume of most modern smartphones and tablets is dominated by the battery