Carbonyls/ Carboxylic acids derivatives and esters (module 6 )
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
General equation for carboxylic acid reactions
RCOOH ⇌ H⁺ + RCOO⁻
Acid + carbonate reaction
Carbonate+ acid → salt + CO₂ + water
What are the acid + NH₃ products
RCOONH
what type of acids are carboxylic acids
weak acids (⇌ for partial dissociates)
what are acids
proton donors
what is carbon 1 in a carboxylic acid
carbon attached to the COOH
naming carboxylic acids ( image)
state carbon chain then add a dioic acid
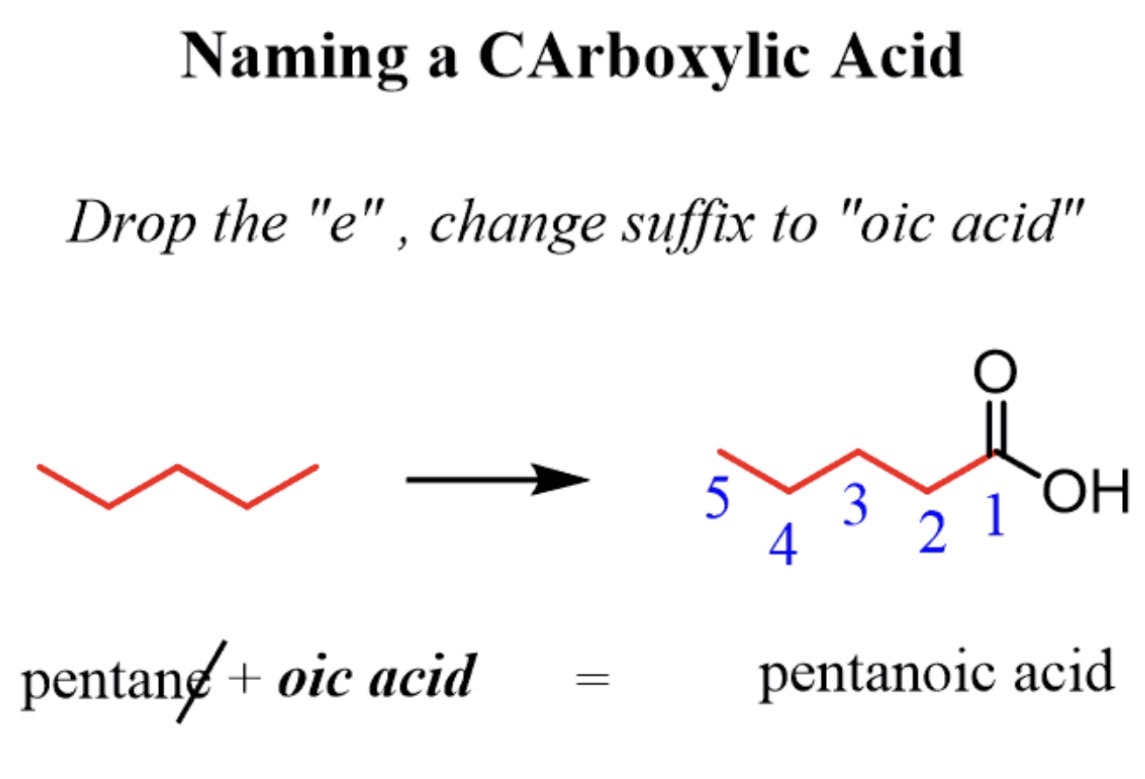
How to name 2 COOH groups ( image)
Add dioic acid

Why are carboxylic acids soluble
They can form hydrogen bonds with H₂O

Name this molecule
Benzene-1,2-dioic acid
Name of benzene with 1 COOH group
Benzoic acid
Trend of carboxylic acid solubility
Longer the carbon chain the less soluble
More of the non polar carbon skeleton
What are the first 4 carboxylic acid solubility
Dissolve completely in water ( they are misible)
name of ion formed when ethanoic acid dissociates
ethanoate ion → CH₃COO⁻
name of benzoic acid dissociation ( image)
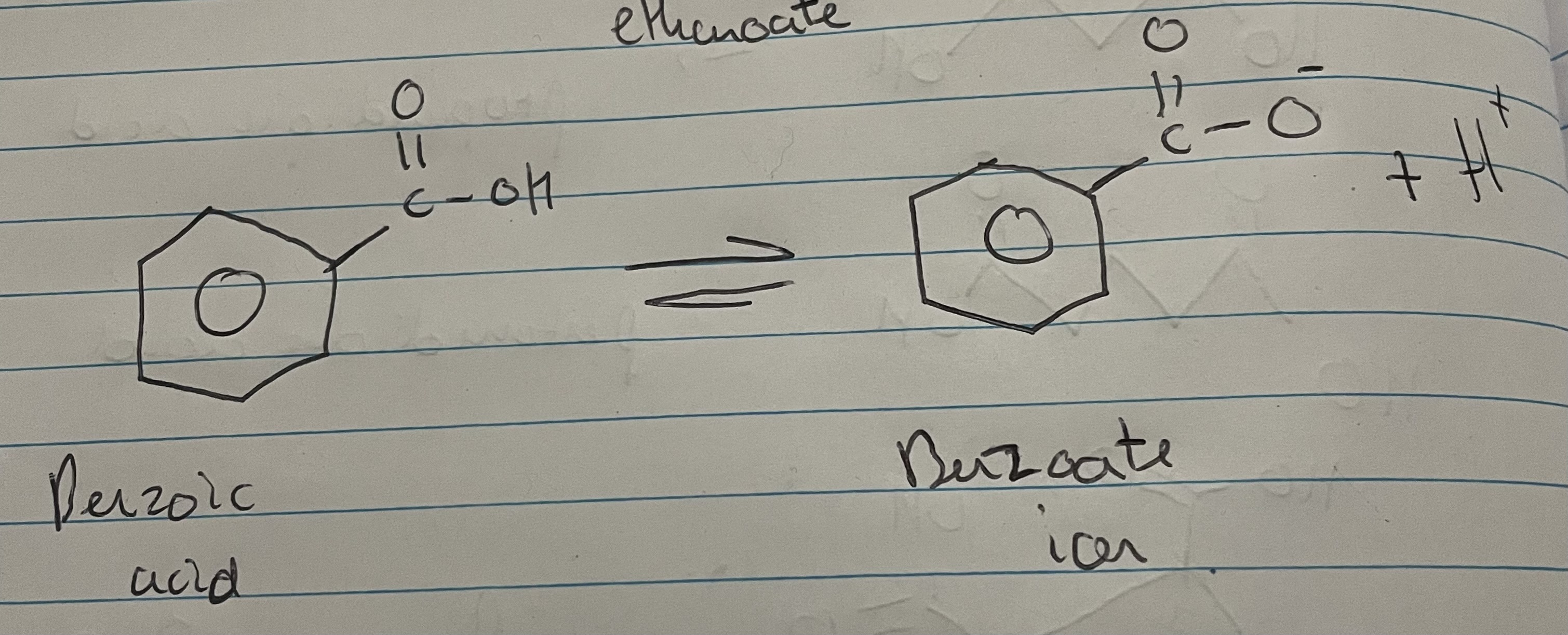
How do carboxylic acids react
Dissociate into a carboxylate ion and H⁺
general reactions of carboxylic acids
carboxylic acid + metal→ salt + H₂
carboxylic acids + carbonate → Salt + CO₂ + H₂O
carboxylic acids + Base → salt + H₂O
what is the salt that carboxylic acids forms
carboxylate ion + metal ion
methanoic acid + mg →
2HCOOH + Mg →(HCOO⁻)₂Mg + H₂
structure of a ester ( image)

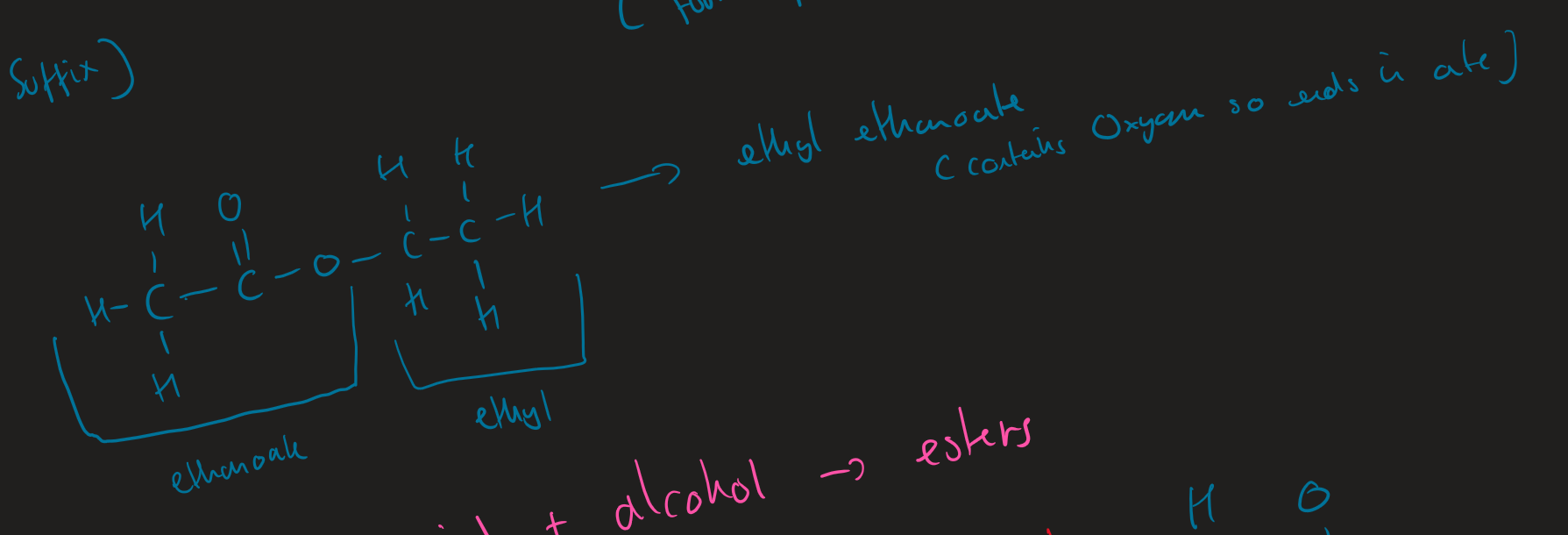
naming esters
prefix comes from alcohol ( alkyl)
suffix comes from carboxyl acid ( ends in oate)
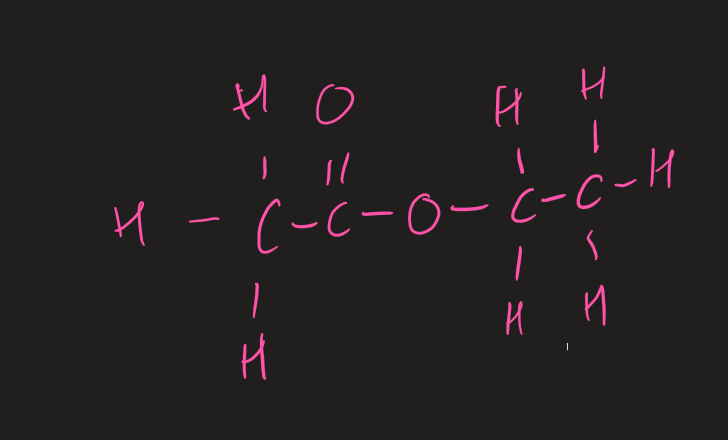
name this ester
what are the 3 ways to make a ester
carboxyl acid + alcohol → ester + H₂O
acid anhydride + alcohol → ester + carboxylic acid
Acyl chloride + alcohol → ester + HCl
conditions for esterification ( alcohol + carboxylic acid)
conc H₂SO₄
Heat
what happens during esterification
alcohol loses OH
carboxylic acid loses H
H₂O formed
what type of reaction is esterification
condensation reaction
esterification image
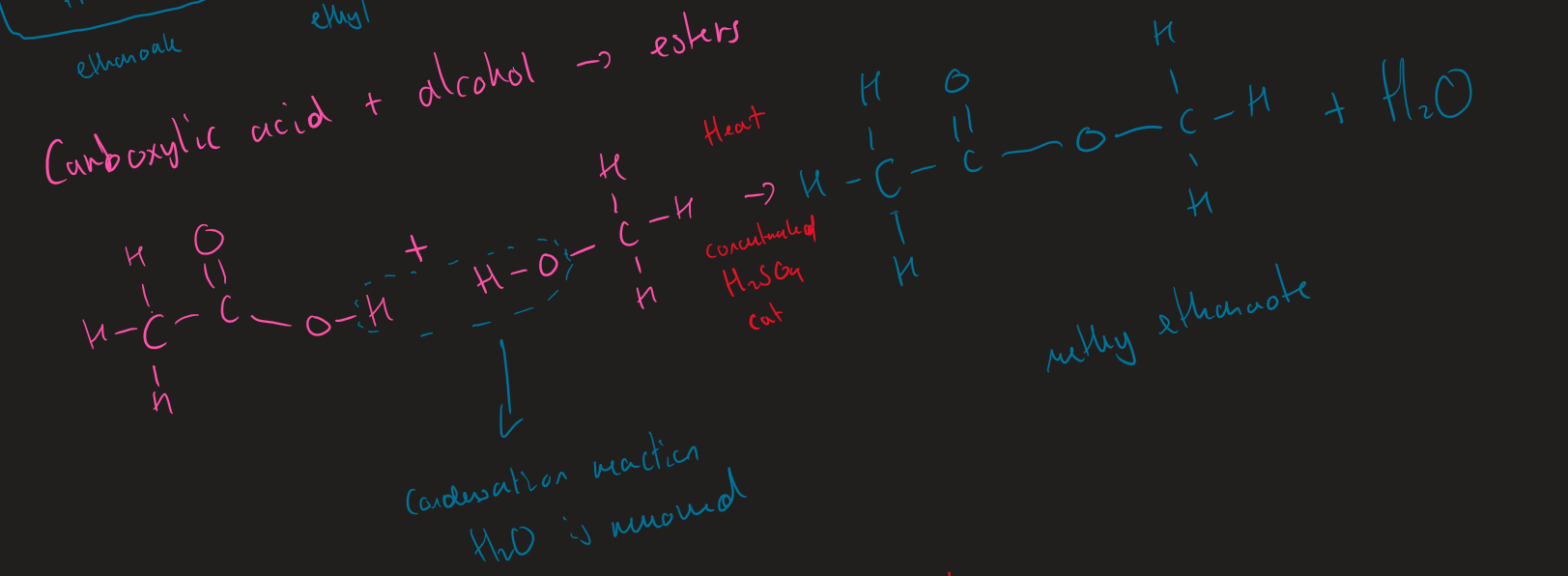
reactants of forming acid anhydrides
carboxylic acid + carboxylic acid
what is a acid anhydride
2 carboxylic acids joined together due to elimination of H₂O
acid anhydride forming ( Image)

structural formula of acid anhydrides
( identical R group)₂O
(R₁)(R₂)O
how do acid anhydrides form
esters
acid anhydrides + alcohol → esters + carboxylic acid
acid anhydride + alcohol reaction explained
alcohol ( hydroxyl group) loses H
carboxylic acid formed is R group gains H
how to name acid anhydrides
number of carbon in R group ( if 3)
propanoic anhydride
acid anhydride forming ester image

does making esters using acid anhydrides require catalyst
doesn’t require conc H₂SO₄
products of all acyl chloride reactions
all make HCl (g))
how do acyl chlorides react
HCl is removed ( H is always from OH)
disadvantages of acyl chlorides reactions
make HCl which is toxic
how to know if HCl is made in a acyl chloride reaction
misty/ white fumes is produced
products of acyl chloride + water ( hydrolysis) word equation
acyl chloride + H₂O → carboxylic acid + HCl
products of acyl chloride + water ( hydrolysis) symbol equation
R - COCL + H₂O → R- COOH + HCL
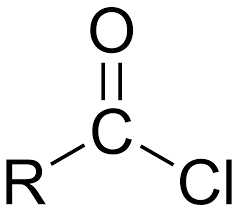
what is Acyl chloride
Derivative of carboxylic acid OH is replaced by Cl
acyl chloride structure
products of acyl chloride + alcohol / phenol word equation
acyl chloride + alcohol → ester + HCl
products of acyl chloride + alcohol / phenol symbol equation
R - COCL + R-OH → R -COO-R + HCl
advantages of using a acyl chloride to make a ester
Higher ester yield
products of acyl chloride + ammonia word equation
acyl chloride + ammonia → primary amide + HCl
products of acyl chloride + ammonia symbol equation
R-COCL + NH₃ → R-CONH₂ + HCl
products of acyl chloride + amide word equation
acyl chloride + amide → secondary amide + HCl
products of acyl chloride + amide symbol equation
R - COCl + R- NH₂ → R-CO- NH-R + HCl
how to form a acyl chloride
carboxylic acid + SOCl₂
carboxylic acid + SOCl₂ products
acyl chloride + SO₂ + HCl
effect of water on making acyl chloride
acyl chloride produced reacts with carboxylic acid
no water present
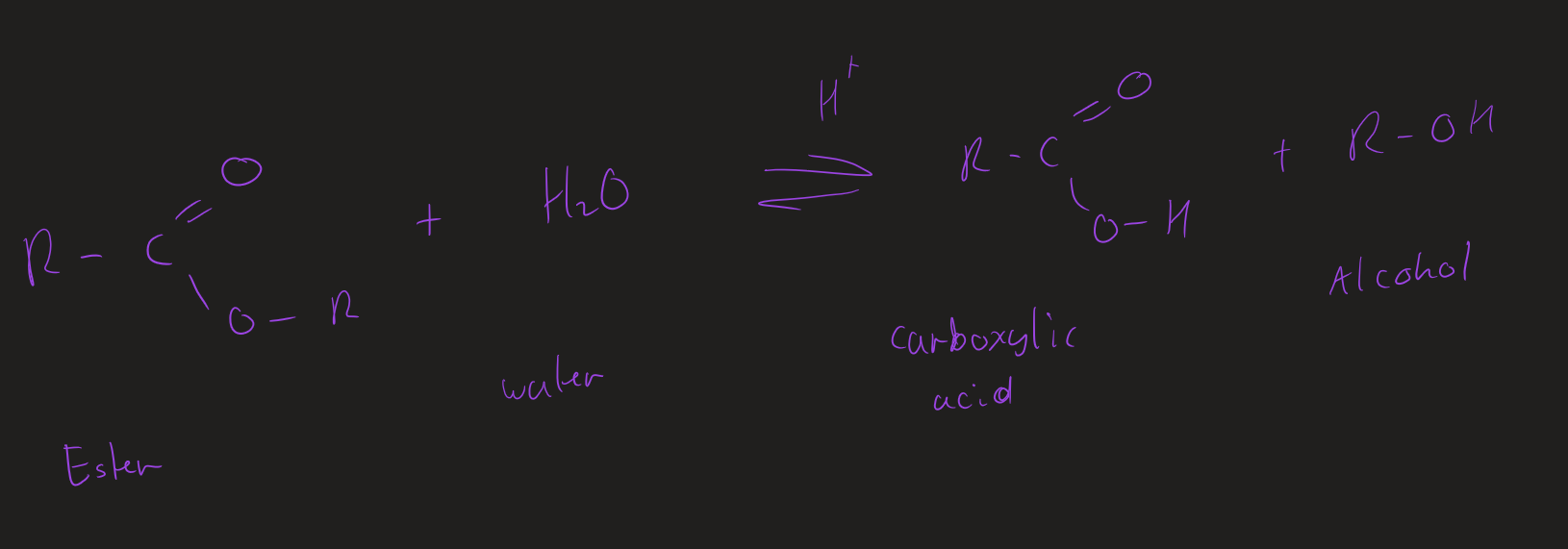
what are the two type of hydrolysis of esters
acid hydrolysis
base hydrolysis
conditions for acid hydrolysis
heat under reflux
dilute H₂SO₄ (aq)
products of acid hydrolysis
carboxylic acid + alcohol
Acid hydrolysis ( image)
Base hydrolysis ( image)
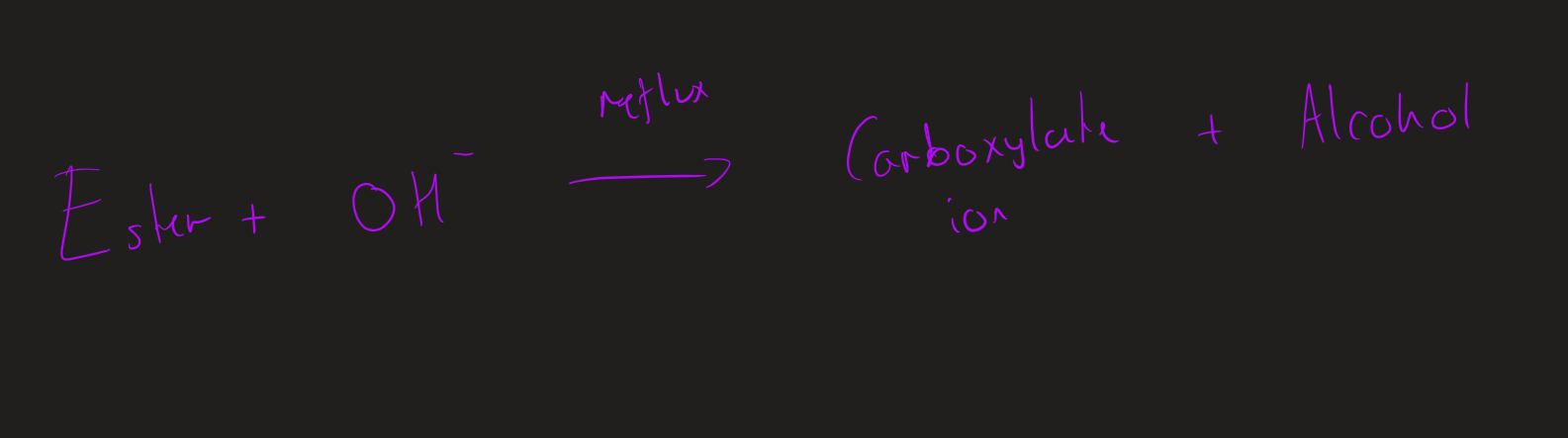
Conditions for base hydrolysis
heat under reflux
Dilute alkali ( NaOH)
acid hydrolysis reaction

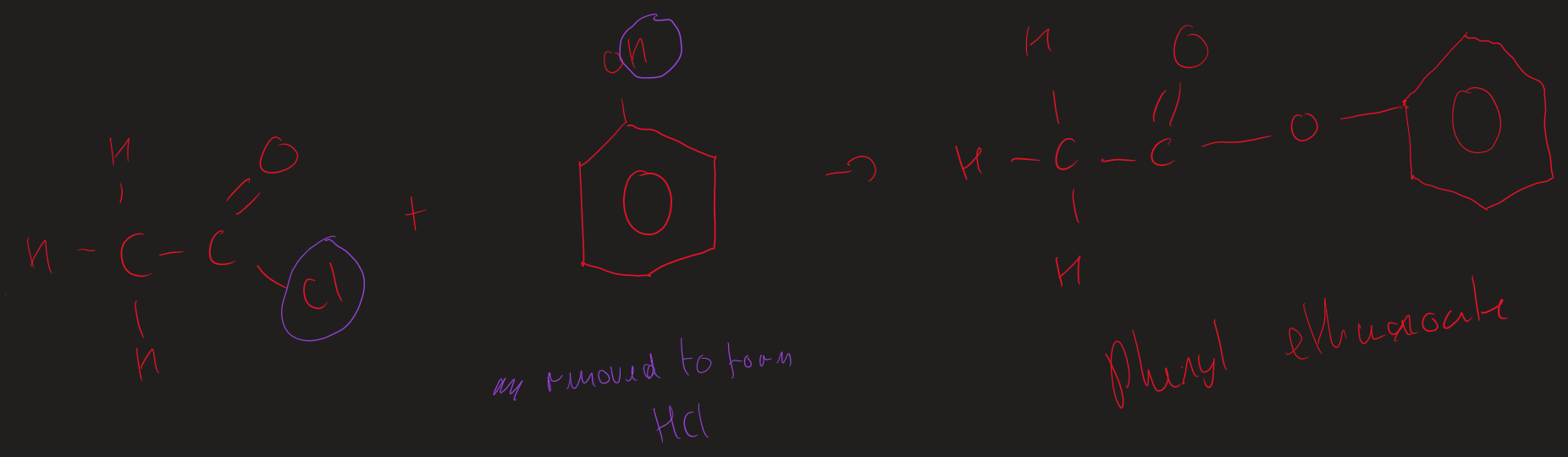
Phenols + acyl chloride image
how to convert nitrile group to carboxylic acid
react with H⁺ (aq)
Are esters polar molecules
YES due to carbonyl group