Written Exam 1 (Labs 5-8 Combined)
1/158
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
159 Terms
Which cranial nerve number is the olfactory nerve?
I (1)
Which cranial nerve number is the optic nerve?
II (2)
Which cranial nerve number is the oculomotor nerve?
III (3)
Which cranial nerve number is the trochlear nerve?
IV (4)
Which cranial nerve number is the trigeminal nerve?
V (5)
Which cranial nerve number is the abducens nerve?
VI (6)
Which cranial nerve number is the facial nerve?
VII (7)
Which cranial nerve number is the vestibulocochlear nerve?
VIII (8)
Which cranial nerve number is the glossopharyngeal nerve?
IX (9)
Which cranial nerve number is the vagus nerve?
X (10)
Which cranial nerve number is the accessory nerve?
XI (11)
Which cranial nerve number is the hypoglossal nerve?
XII (12)
Is the cranial olfactory I (1) nerve sensory, motor, or both?
Sensory
Is the cranial optic II (2) nerve sensory, motor, or both?
Sensory
Is the cranial oculomotor III (3) nerve sensory, motor, or both?
Motor
Is the cranial trochlear IV (4) nerve sensory, motor, or both?
Motor
Is the cranial trigeminal V (5) nerve sensory, motor, or both?
Both
Is the cranial abducens VI (6) nerve sensory, motor, or both?
Motor
Is the cranial facial VII (7) nerve sensory, motor, or both?
Both
Is the cranial vestibulocochlear VIII (8) nerve sensory, motor, or both?
Sensory
Is the cranial glossopharyngeal IX (9) nerve sensory, motor, or both?
Both
Is the cranial vagus X (10) nerve sensory, motor, or both?
Both
Is the cranial accessory XI (11) nerve sensory, motor, or both?
Motor
Is the cranial hypoglossal XII (12) nerve sensory, motor, or both?
Motor
What is the function of the cranial olfactory I (1) nerve?
Sense of smell (olfaction)
What is the function of the cranial optic II (2) nerve?
Vision
What are the functions of the cranial oculomotor III (3) nerve?
Motor to 4/6 extrinsic eye muscles and the upper eyelid for eyeball movement and opening of the eye
Changes the diameter of the pupil (constriction)
Changes the shape of the lens
What is the function of the cranial trochlear IV (4) nerve?
Motor to the superior oblique muscle for movement of the eye medially and inferiorly
What is the function of the cranial trigeminal V (5) nerve?
Sensory to the face
Motor to muscles of mastication and swallowing
What is the function of the cranial abducens VI (6) nerve?
Motor to the lateral rectus muscle for movement of the eye laterally
What is the function of the cranial facial VII (7) nerve?
Taste to the anterior half of the tongue
Stimulates lacrimal and salivary glands
Motor to the muscles of facial expression
Sensory to the external ear, palate, and nasal cavity
What is the function of the cranial vestibulocochlear VIII (8) nerve?
Equilibrium (vestibular branch)
Hearing (cochlear branch)
What is the function of the cranial glossopharyngeal IX (9) nerve?
Taste to the posterior third of the tongue
Stimulates salivation
Motor to the muscles of swallowing and speech
External ear and posterior pharynx sensation
What is the function of the cranial vagus X (10) nerve?
Taste and sensation to the pharynx
Parasympathetic innervation to viscera for blood CO2 detection
Swallowing and speech
Ear skin sensation
What is the function of the cranial accessory XI (11) nerve?
Motor to muscles that move the head, shoulders, and swallow
What is the function of the cranial hypoglossal XII (12) nerve?
Movement of the tongue during speech and swallowing
What is the main function of the sympathetic nervous system (SNS)?
“Fight or flight” during exercise, embarrassment, emotion, and emergency
Where are the nerve roots located in the sympathetic nervous system (SNS)?
Thoracolumbar portion of the spinal cord
Which neurotransmitters are released by the sympathetic nervous system (SNS)?
Norepinephrine (NE)
Epinephrine (E)
Acetylcholine (ACh)
What effect does the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) have on the heart?
Increases rate and force of contraction
What effect does the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) have on the bronchioles (airway passages of the lungs)?
Bronchodilation
What effect does the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) have on the blood vessels to abdominal organs and skin?
Vasoconstriction
What effect does the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) have on the blood vessels to skeletal muscle?
Vasodilation
What effect does the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) have on secretion from digestive glands?
Decreases secretion
What effect does the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) have on urine formation and micturition (urination)?
Decreases urine formation and inhibits imicturition
What effect does the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) have on the pupils of the eye?
Dilation
What is the main function of the parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS)?
“Rest and digest” during digestion, diuresis, defecation
Where are the nerve roots located in the parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS)?
Craniosacral nerves
Which neurotransmitter is released by the parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS)?
Acetylcholine (ACh)
What effect does the parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) have on the heart?
Decreases rate of contraction
What effect does the parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) have on the bronchioles (airway passages of the lungs)?
Bronchoconstriction
What effect does the parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) have on the blood vessels to abdominal organs and skin?
Vasodilation (indirect effect only)
What effect does the parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) have on the blood vessels to skeletal muscle?
Vasoconstriction (indirect effect only)
What effect does the parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) have on secretion from digestive glands?
Increases secretion
What effect does the parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) have on urine formation and micturition (urination)?
Promotes urine formation and micturition
What effect does the parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) have on the pupils of the eye?
Constriction
What is the pupillary response to a light shined into the left eye?
Left pupil constricts
Right pupil constricts
What is the pupillary response to light removed from the left eye?
Left pupil dilates
Right pupil dilates
What is the pupillary response to a light shined into the right eye?
Left pupil constricts
Right pupil constricts
What is the pupillary response to light removed from the right eye?
Left pupil dilates
Right pupil dilates

Example spinal reflex test:
Tap the subject’s patellar tendon and record the response
Give the subject a difficult math problem to work through and tap their patellar tendon again. How does the response change? Why?
The response is depressed (weaker) due to:
A decrease in facilitation from the higher brain centers because the subject’s attention is diverted

Which system dominates during exercise, the sympathetic or the parasympathetic nervous system? How do you know?
Sympathetic nervous system (SNS)
Increased blood pressure, heart rate, and force of contraction
Which system dominates during rest and after exercise, the sympathetic or the parasympathetic nervous system? How do you know?
Parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS)
Blood pressure and heart rate are lowest before and 5 minutes after exercise
Damage to which cranial nerve might produce an inability to move the tongue?
Hypoglossal XII (12)
Damage to which cranial nerve might produce an inability to see?
Optic II (2)
Damage to which cranial nerve might produce an inability to masticate (chew food)?
Trigeminal V (5)
Damage to which cranial nerves might produce an inability to swallow?
Glossopharyngeal IX (9)
Vagus X (10)

The herbal supplement bitter orange, also known as synephrine, mimics the effects of the neurotransmitters of the SNS on the heart and blood vessels serving the abdominal viscera and skin.
What effect would this would have on blood pressure?
Should this drug be given to people with hypertension (high blood pressure)?
Causes an increase in the rate and force of contraction of the heart and constriction of the blood vessels supplying the abdominal viscera and skin
Raises blood pressure
Not recommended for people with hypertension

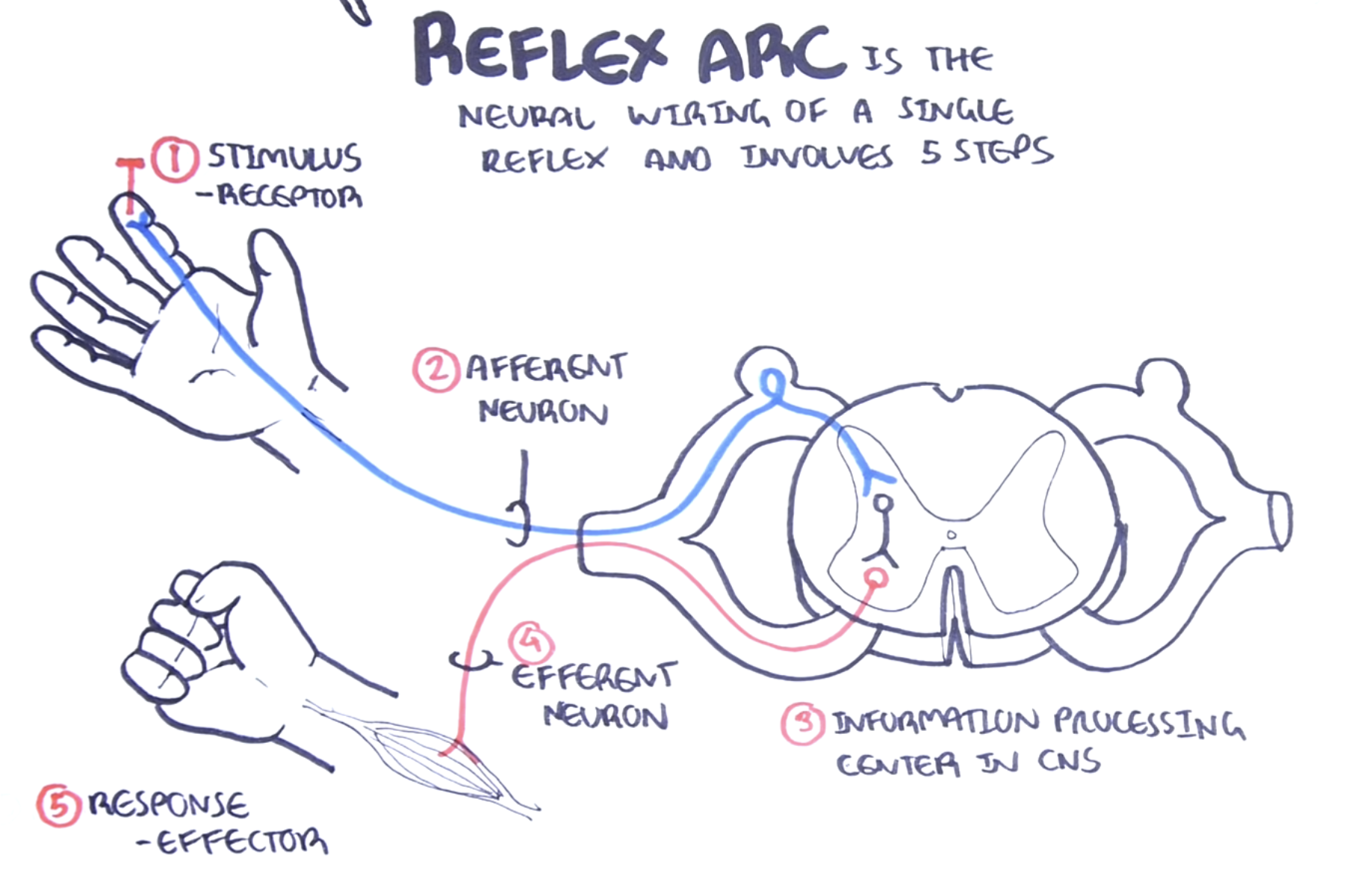
Draw and label the 5 steps of a reflex arc. (https://youtu.be/bY0oQnflmog)
Stimulus (receptor)
Afferent neuron
Information processing center in the CNS
Efferent neuron
Response (effector)
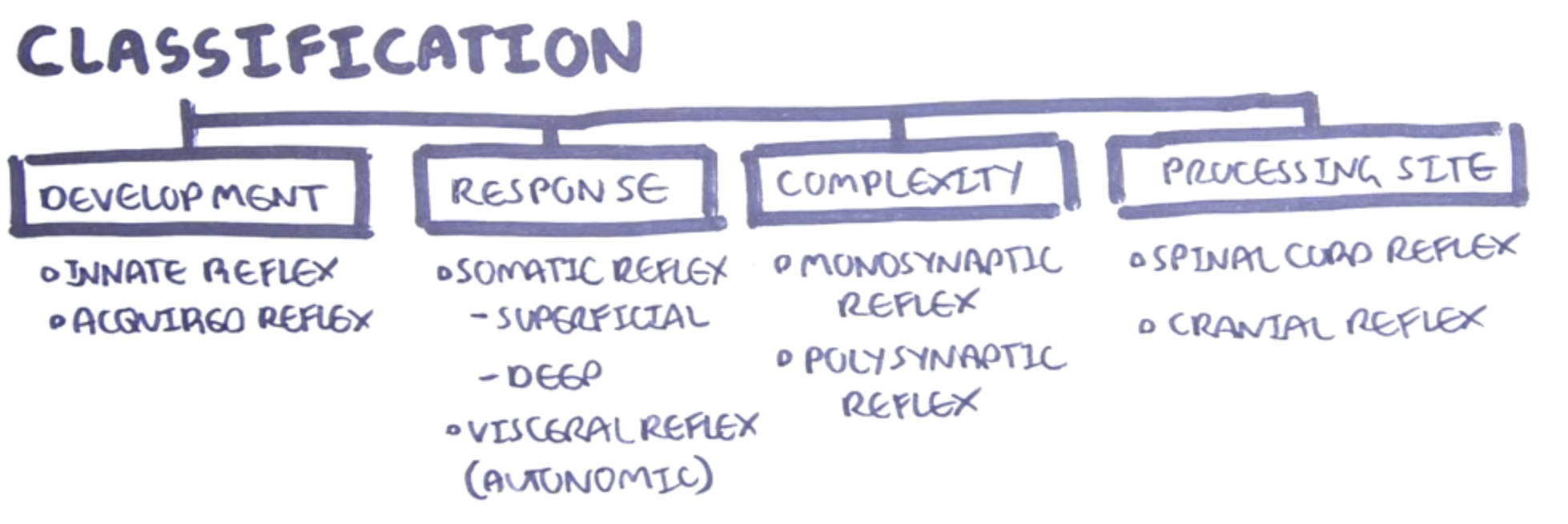
What are the 4 classifications of reflexes? (https://youtu.be/bY0oQnflmog)
Development - innate or acquired
Response - somatic or visceral
Complexity - monosynaptic or polysynaptic
Processing site - spinal cord or cranial
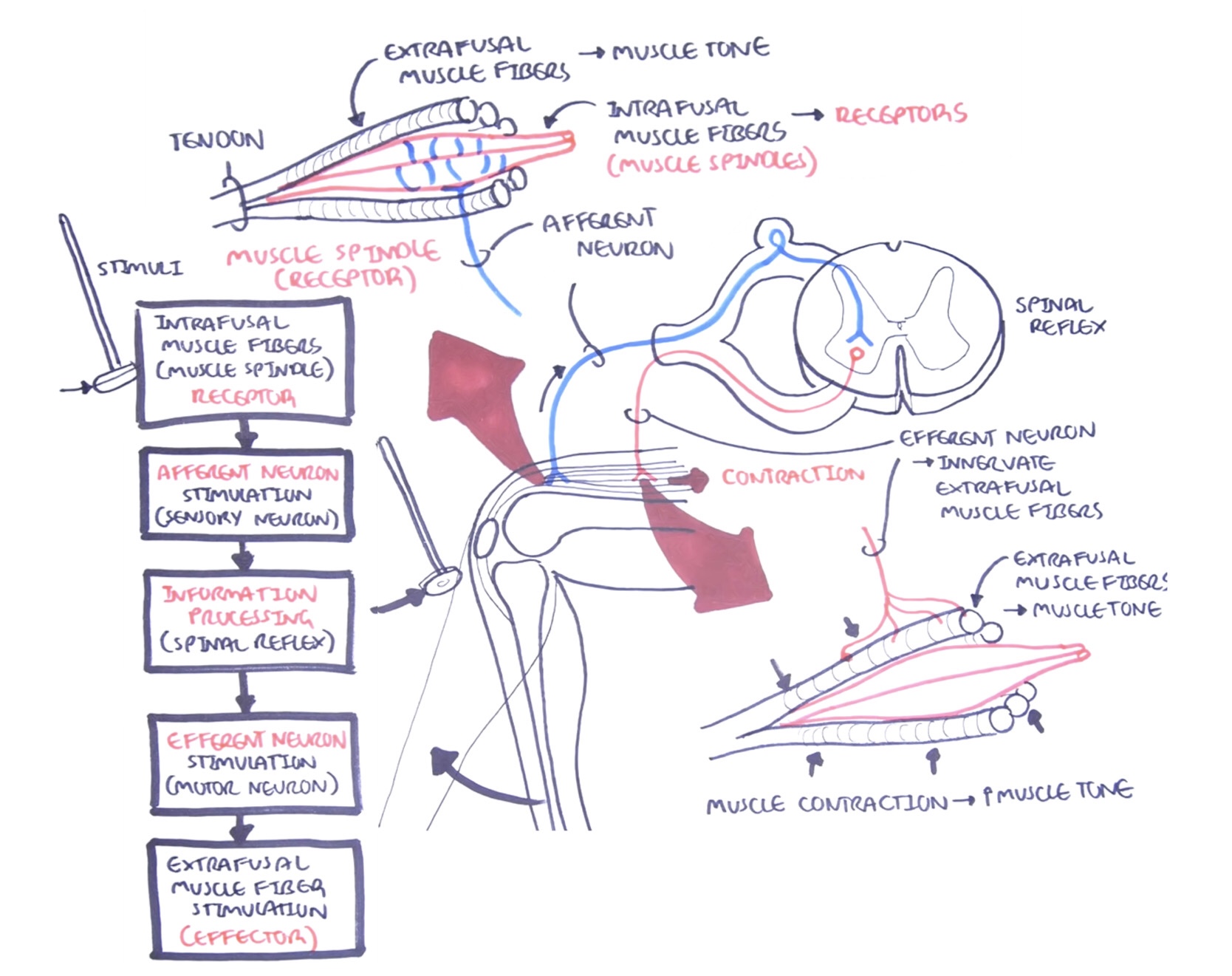
Draw and label the patellar reflex. (https://youtu.be/bY0oQnflmog)
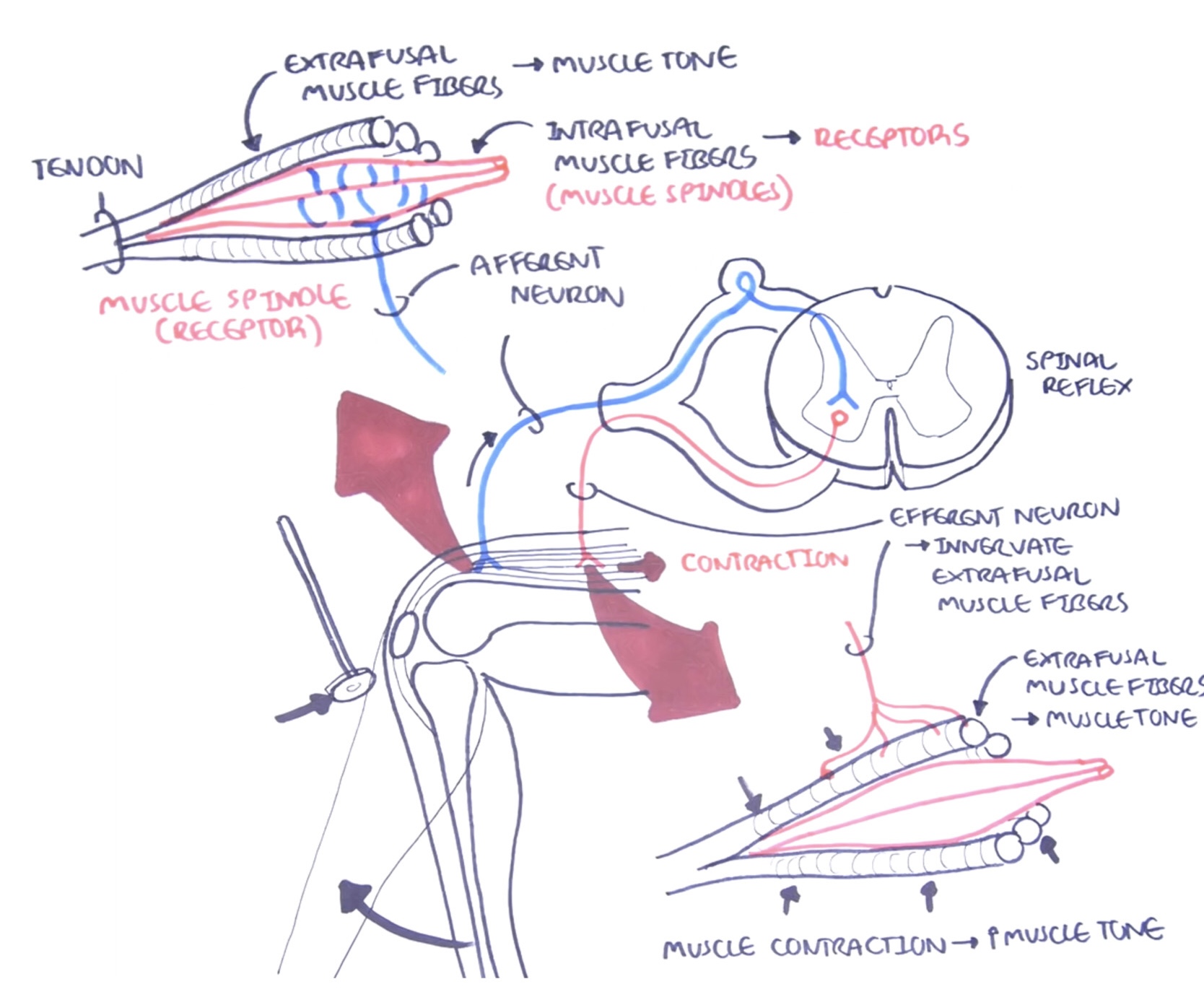
Outline the events of the patellar reflex. (https://youtu.be/bY0oQnflmog)
Stimuli travels to intrafusal muscle fibers, muscle spindles (receptor)
Afferent neuron stimulation (sensory neuron)
Information processing (spinal reflex)
Efferent neuron stimulation (motor neuron)
Extrafusal muscle fiber stimulation (effector)
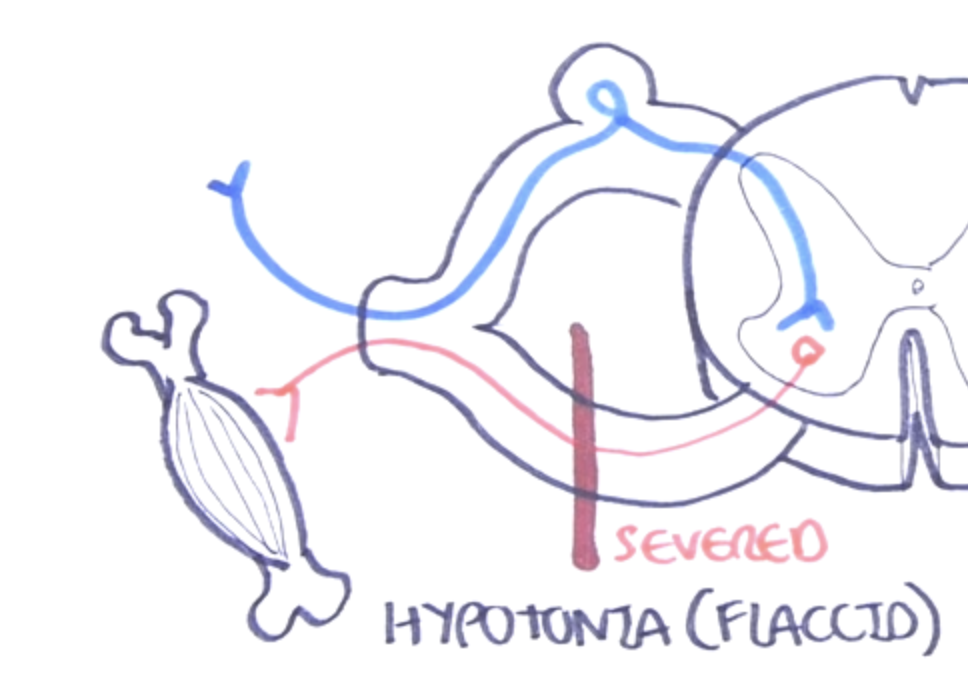
What may cause a hypotonic (flaccid) muscle? (https://youtu.be/bY0oQnflmog)
A severing of the area where efferent neurons deliver signals to the muscle
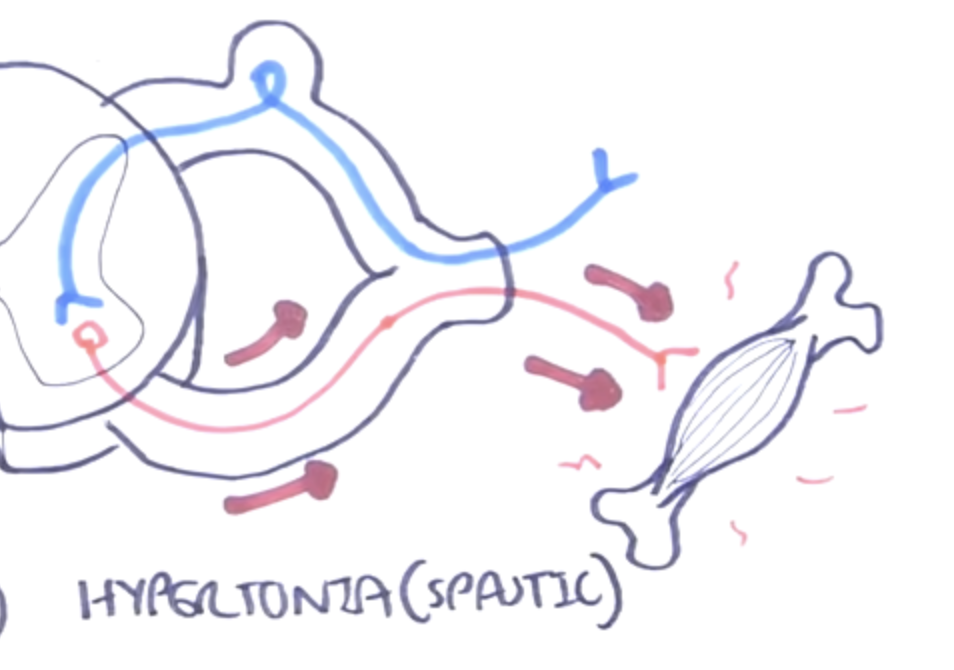
What may cause a hypertonic (spastic) muscle? (https://youtu.be/bY0oQnflmog)
A continuously firing efferent neuron with no inhibition continuously stimulates the muscle
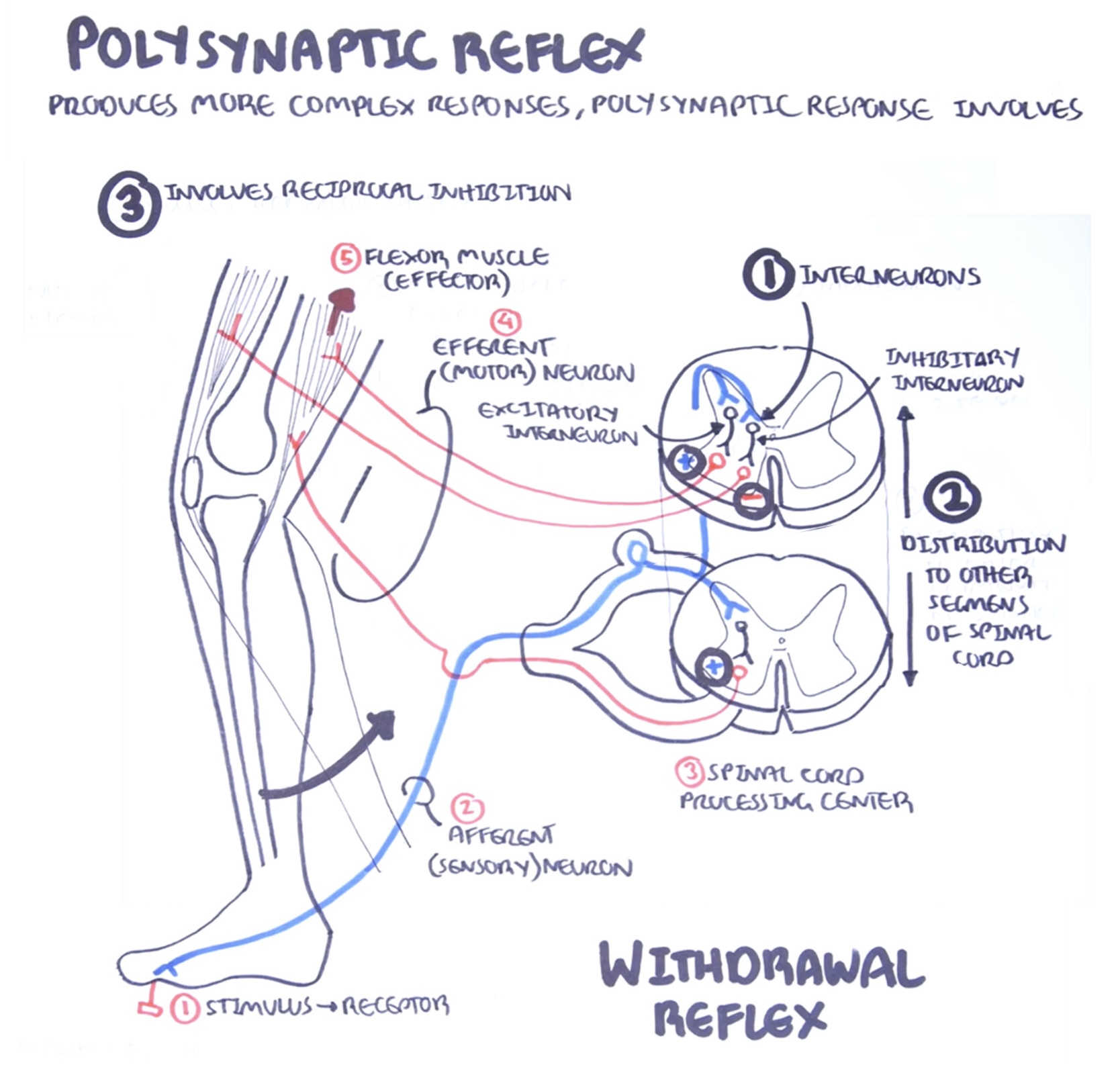
Draw and label the polysynaptic stretch reflex. (https://youtu.be/bY0oQnflmog)
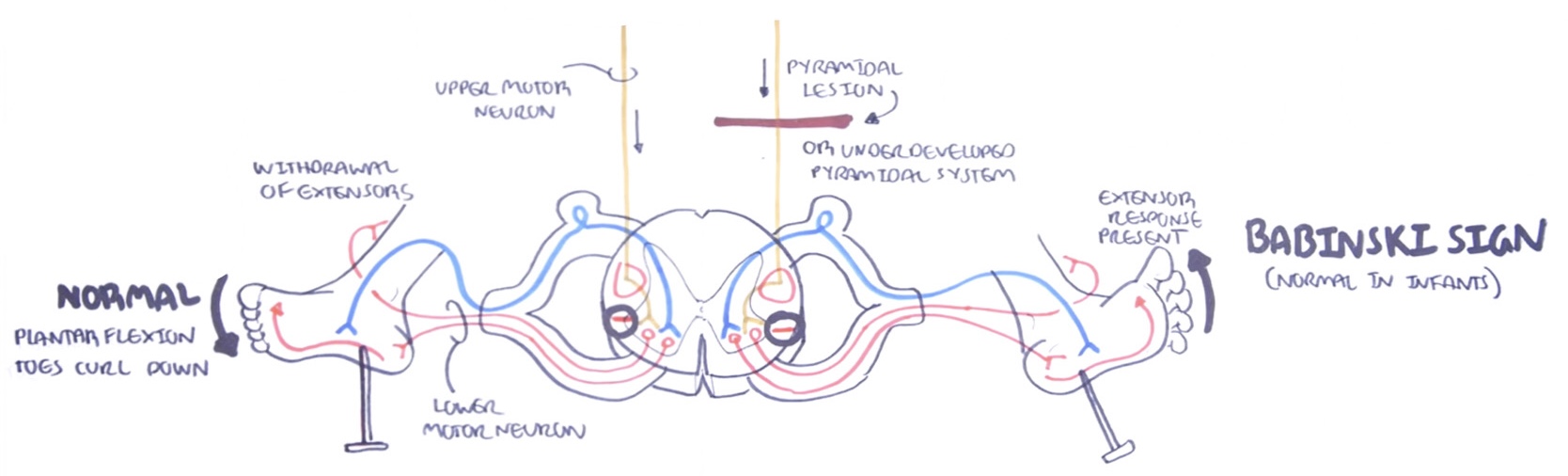
Explain the Babinsky reflex and the Babinsky sign. (https://youtu.be/bY0oQnflmog)
Pyramidal lesions (or an underdeveloped pyramidal system) cause upper motor neurons to NOT inhibit the extensor plantar muscles resulting in abnormal muscle contraction which fans the toes out and curls them upward
What 3 steps must be taken before performing a clinical cranial nerve examination?
Provide the patient privacy
Perform hand hygiene
Explain the procedure to the patient
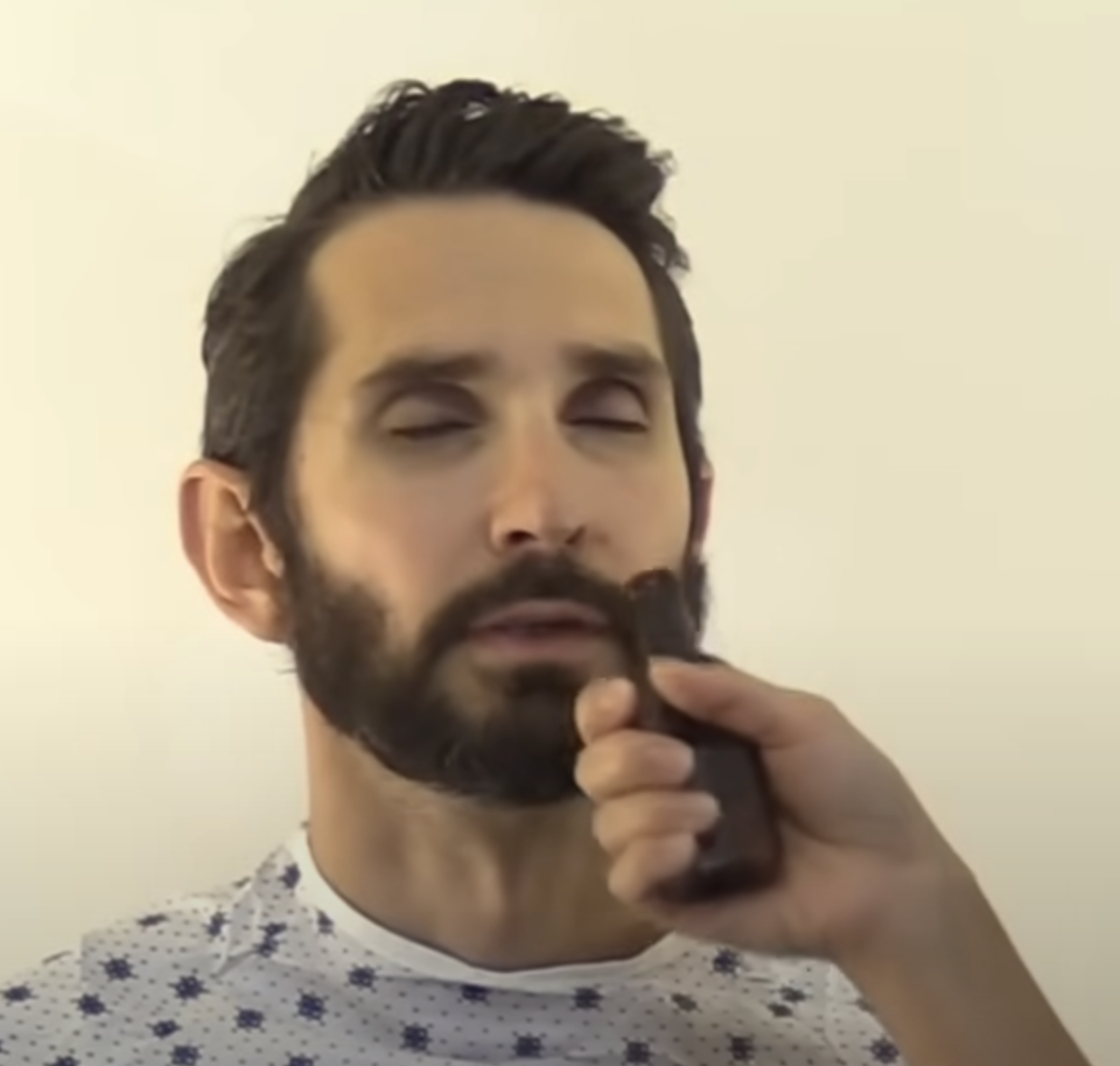
How can the cranial olfactory I (1) nerve be clinically examined and tested? (https://youtu.be/oZGFrwogx14)
Have the patient close their eyes
Put a scented object in front of the patient’s nose
Ask the patient to breathe in and identify the scent

How can the cranial optic II (2) nerve be clinically examined and tested? (https://youtu.be/oZGFrwogx14)
Confrontation visual field
Have the patient stand an arm’s length away
Ask the patient to cover their right eye
Cover your own right eye
Tell the patient to stare at your left eye
Use your fingers to hold up numbers in the top, middle, and lower visual fields
Ask the patient to identify the number of fingers shown and repeat with the opposite side
Visual acuity
Have the patient stand 20ft away from a snellen chart
Ask the patient to read the lowest line they are able to with their right eye covered
Repeat with the patient’s left eye covered
Repeat with neither of the patient’s eyes covered
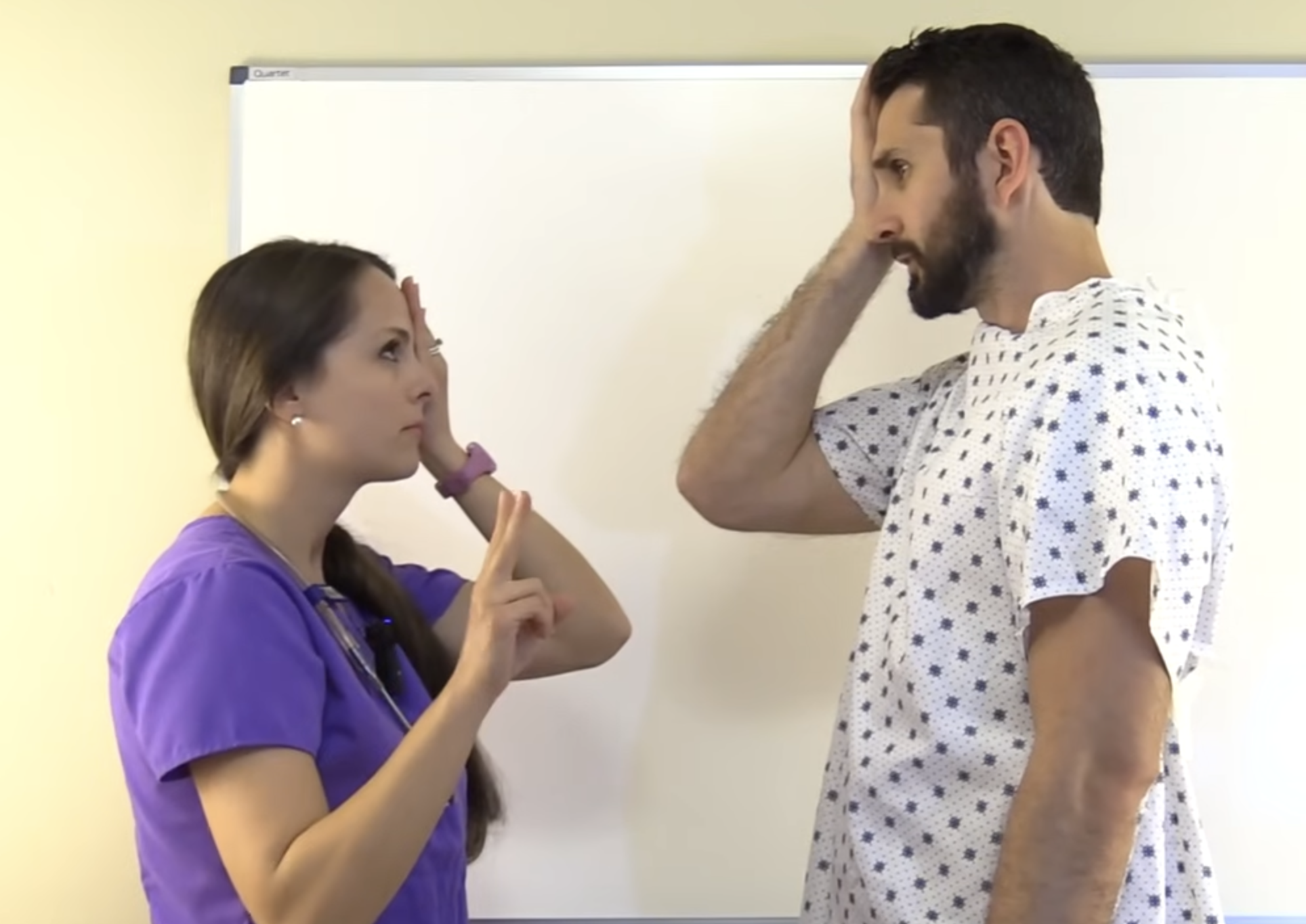

How can the cranial oculomotor III (3), trochlear IV (4), and abducens VI (6) nerves be clinically examined and tested? (https://youtu.be/oZGFrwogx14)
Test 1: Nystagmus
Hold a pen light 12in away from the patient’s nose
Ask the patient to keep their head still
Move the pen light around the 6 cardinal fields of gaze and ask the patient to watch with just their eyes
Assess any abnormal involuntary shaking of the eyes
Test 2: Pupil Reactivity
Ask the patient to stare at a distant object
Shine the pen light on one eye
Assess the ability of both pupils to simultaneously constrict and dilate
Test 3: Accommodation
Ask the patient to stare at a distant object
Move an object slowly toward the patient’s nose
Assess the ability of the pupils to constrict and and become crossed
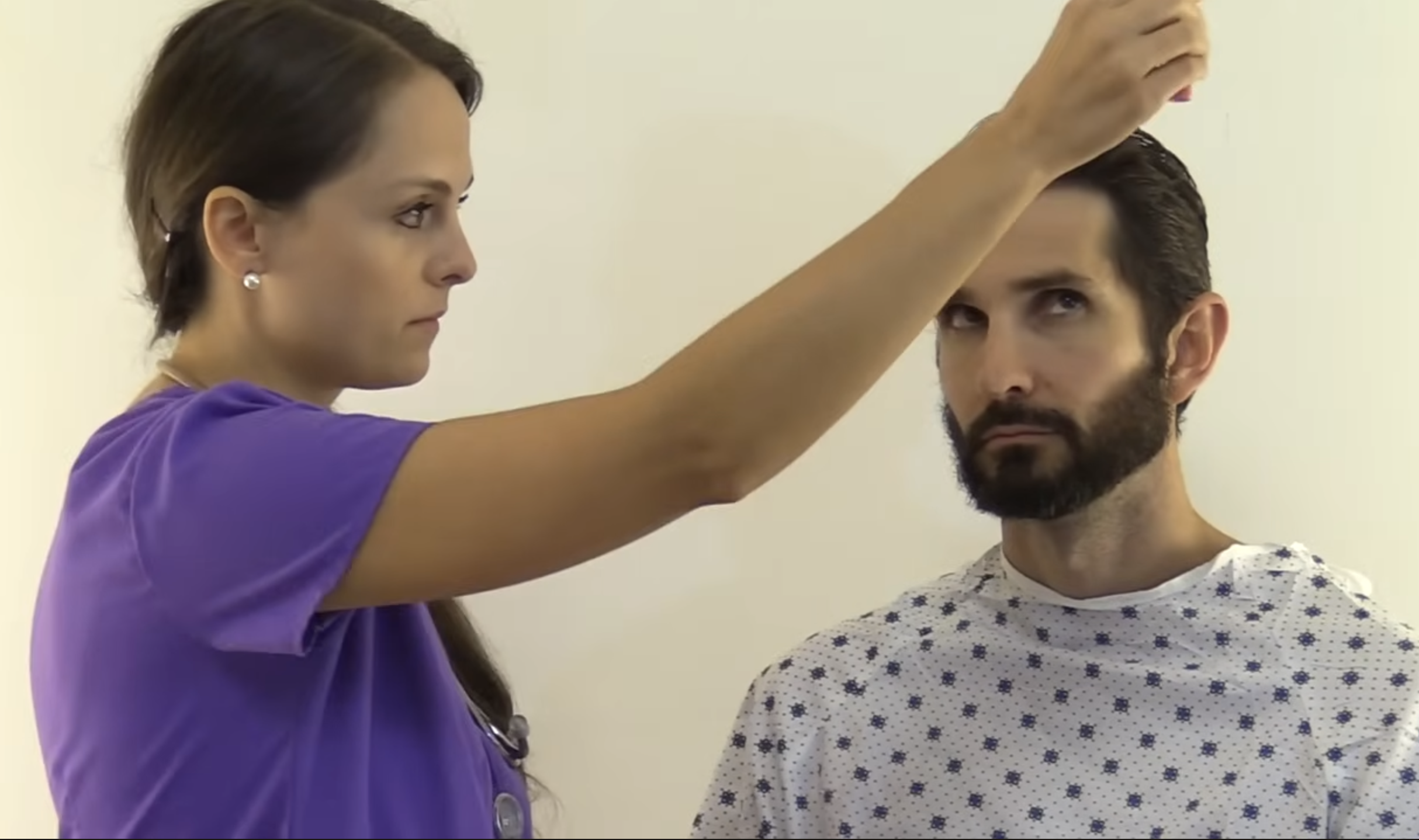

How can the cranial trigeminal V (5) nerve be clinically examined and tested? (https://youtu.be/oZGFrwogx14)
Ask the patient to clench their teeth
Feel the masseter and temporal muscles
Place fingers under the patient’s jaw and apply resistance
Ask the patient to open their jaw
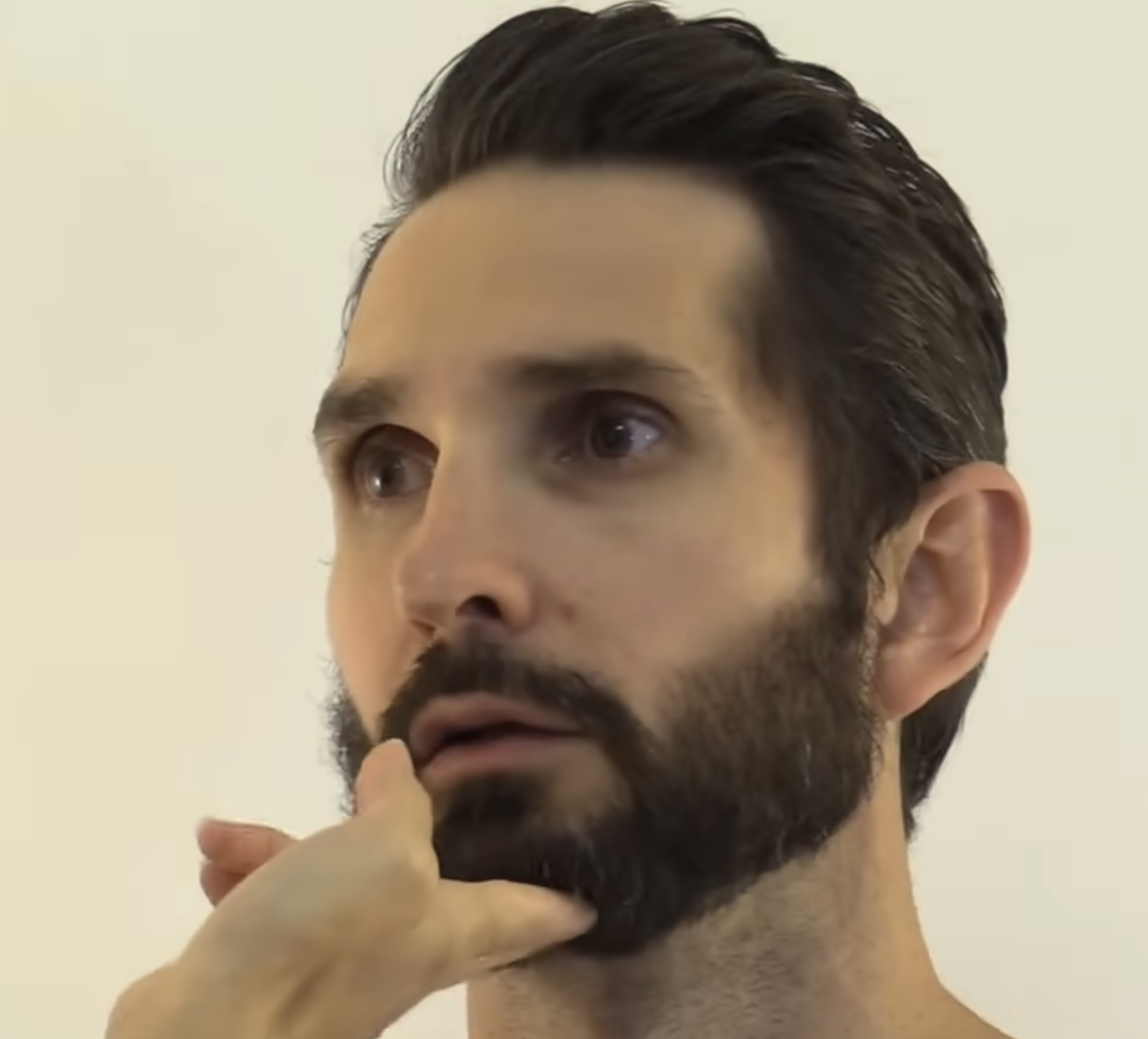

How can the cranial facial VII (7) nerve be clinically examined and tested? (https://youtu.be/oZGFrwogx14)
Ask the patient to close their eyes tightly and then reopen them
Ask the patient to smile
Ask the patient to frown
Ask the patient to puff their cheeks
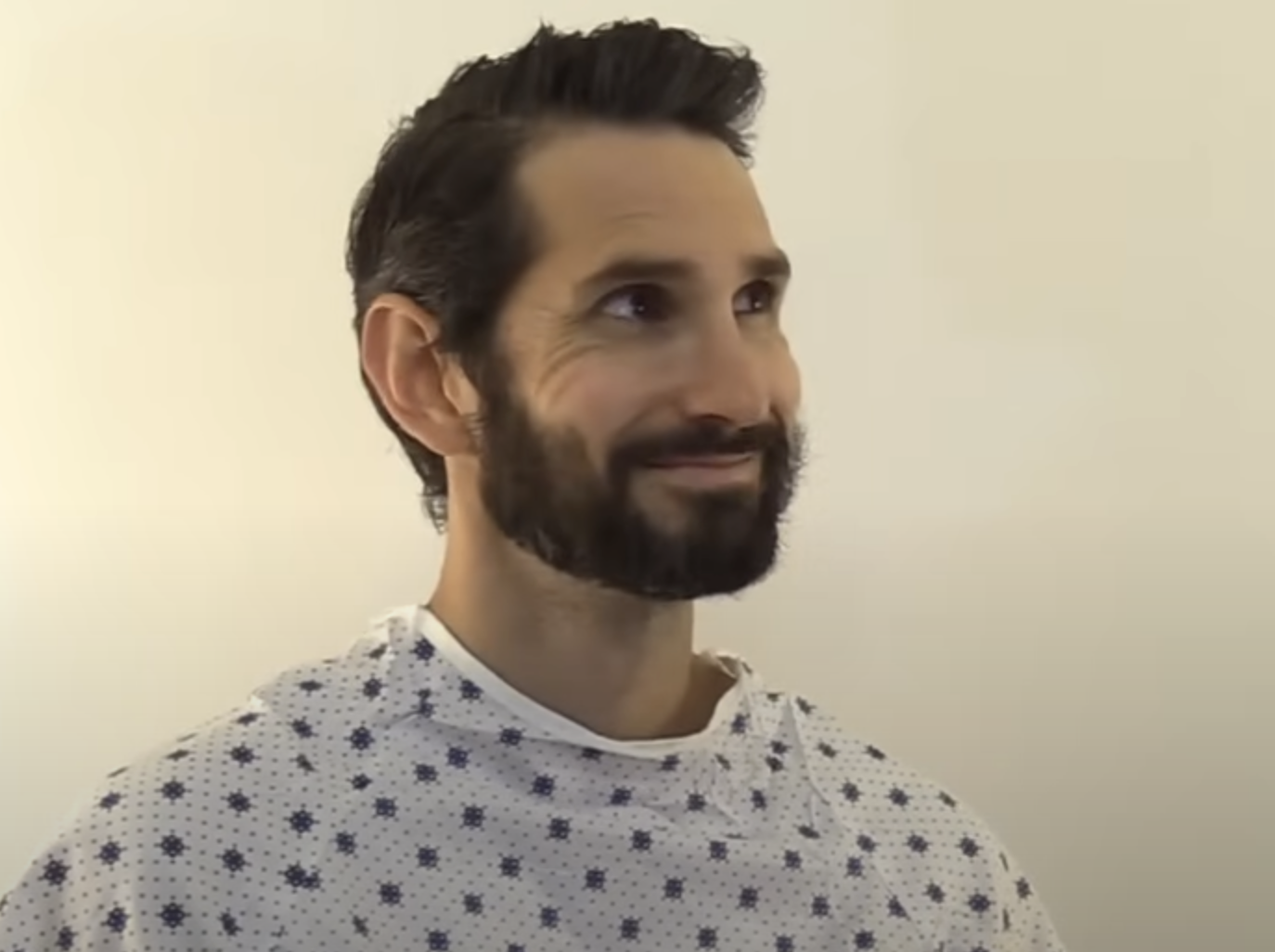

How can the cranial glossopharyngeal IX (9) nerve be clinically examined and tested? (https://youtu.be/oZGFrwogx14)
Ask the patient to open their mouth and say “ah”
Assess movement of the patient’s uvula
Use a tongue depressor to poke the back of patient’s mouth to elicit the gag reflex
How can the cranial vestibulocochlear VIII (8) nerve be clinically examined and tested? (https://youtu.be/oZGFrwogx14)
Cover one of the patient’s ears
Whisper something on the opposite side
Ask the patient to repeat what was said
Repeat on the opposite side
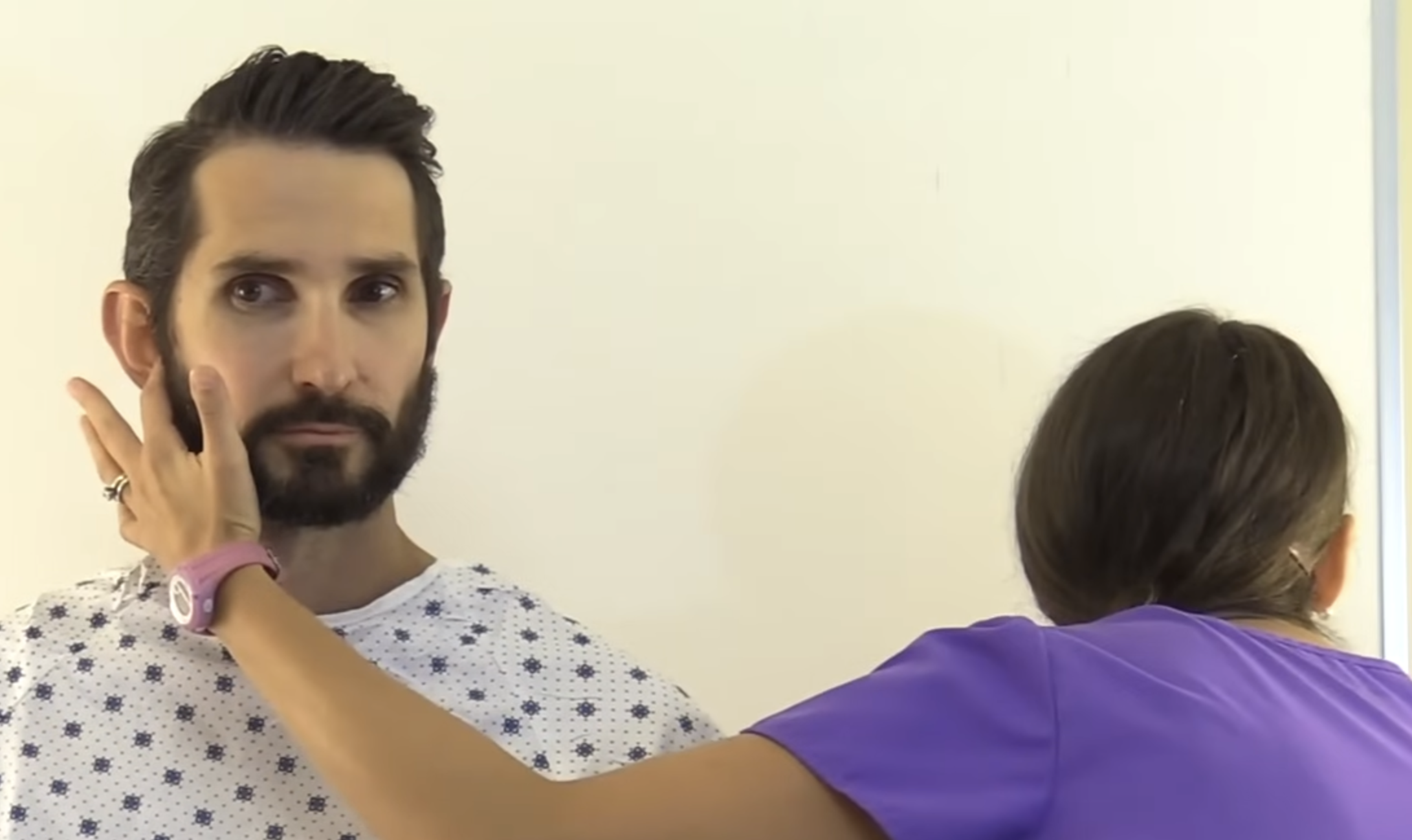

How can the cranial vagus X (10) nerve be clinically examined and tested? (https://youtu.be/oZGFrwogx14)
Assess that the patient can speak without hoarseness and swallow
How can the cranial accessory XI (11) nerve be clinically examined and tested? (https://youtu.be/oZGFrwogx14)
Ask the patient to move their head side to side and up and down
Apply resistance by placing your hands on the patient’s shoulders and ask them to shrug
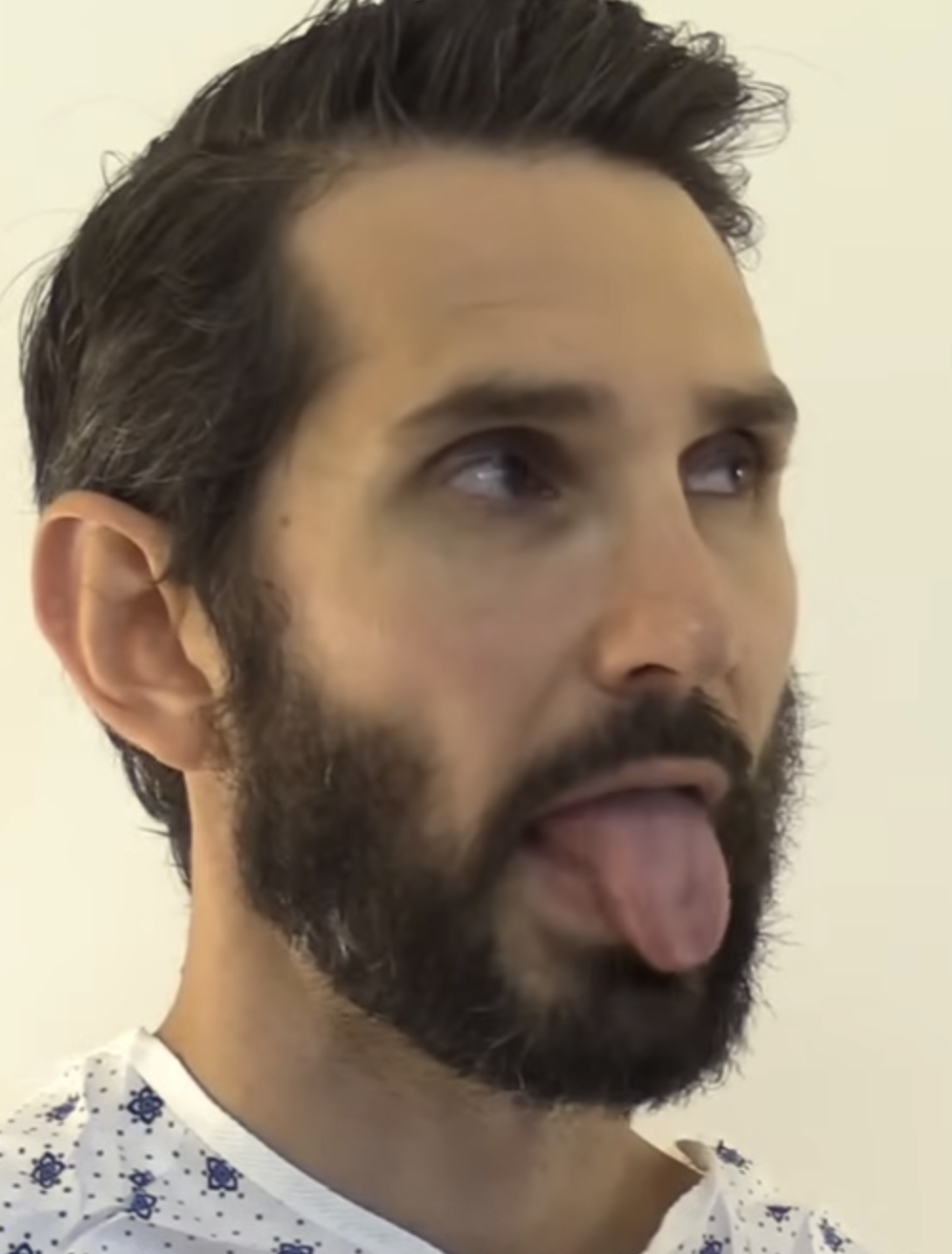
How can the cranial hypoglossal XII (12) nerve be clinically examined and tested? (https://youtu.be/oZGFrwogx14)
Ask the patient to stick out their tongue and move it side to side

What are the 6 basic digestive functions?
Ingestion
Secretion
Propulsion
Digestion
Absorption
Defecation
What is the function of the 1st basic digestive process ingestion?
Food and water are brought into the digestive system via the mouth
What is the function of the 2nd basic digestive process secretion?
Production of endocrine (hormones) and exocrine (mucus, enzymes and acid) products to aid digestion
What is the function of the 3rd basic digestive process propulsion?
Movement of food and liquids by peristalsis
What is the function of the 4th basic digestive process digestion?
Mechanical and chemical breakdown of food
What is the function of the 5th basic digestive process absorption?
Movement of nutrients through the alimentary canal wall into blood or lymphatic vessels
What is the function of the 6th basic digestive process defecation?
Exit of feces composed of non-digestible or unusable materials by body
What are organs within the peritoneal cavity called?
Intraperitoneal
What are organs outside of the peritoneal cavity called?
Retroperitoneal
Which organs are intraperitoneal?
SALTD SPRSS (“salted spurs”)
Stomach
Appendix
Liver
Transverse colon
Duodenum (first part)
Small intestines (jejunum and ileum)
Pancreas (tail only)
Rectum (upper third)
Spleen
Sigmoid colon
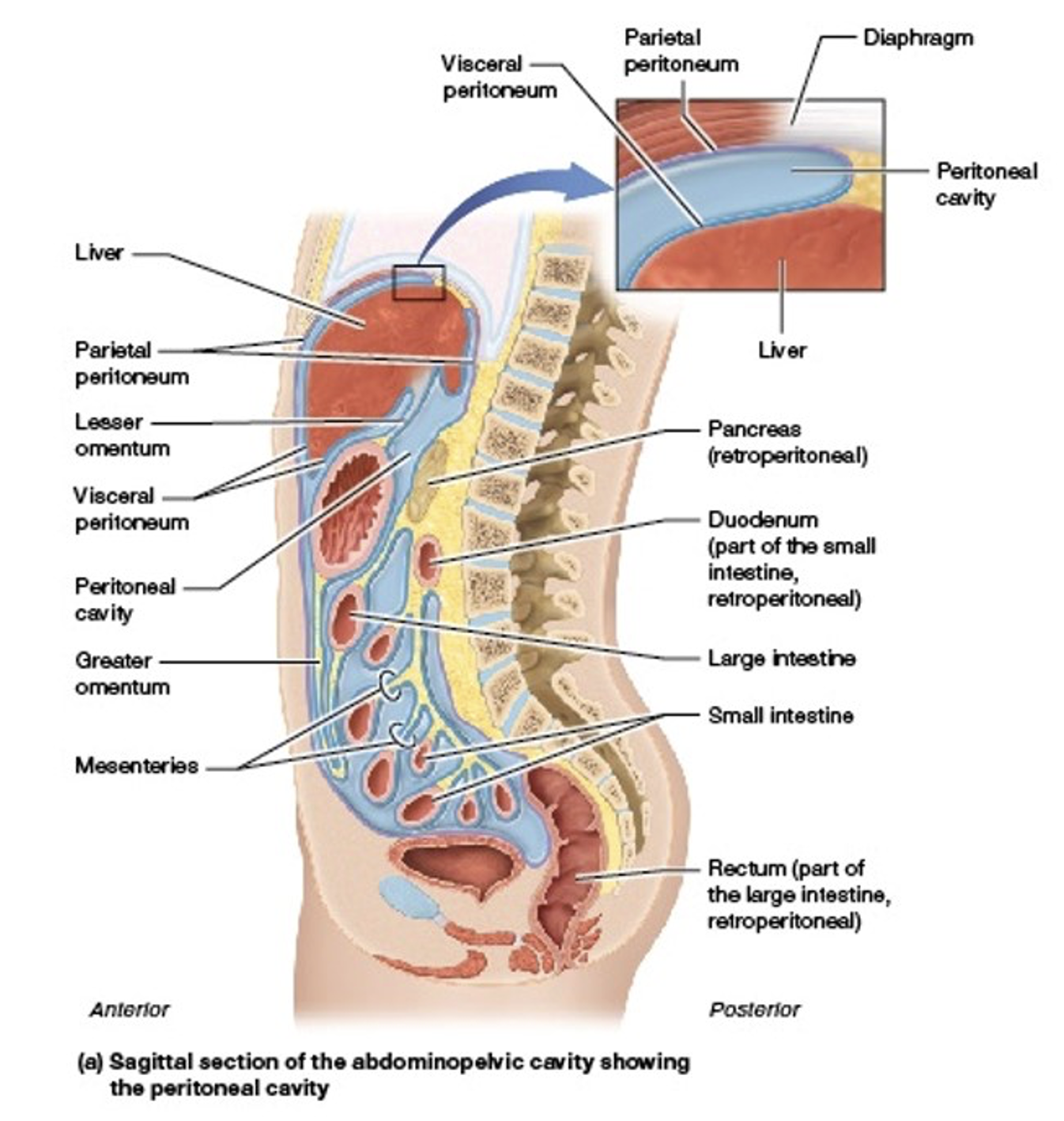
Which organs are retroperitoneal?
SAD PUCKER
Suprarenal adrenal glands
Aorta/Inferior vena cava
Duodenum (second, third, and fourth parts)
Pancreas (except the tail)
Ureters
Colon (ascending and descending)
Kidneys
Esophagus
Rectum (middle third)
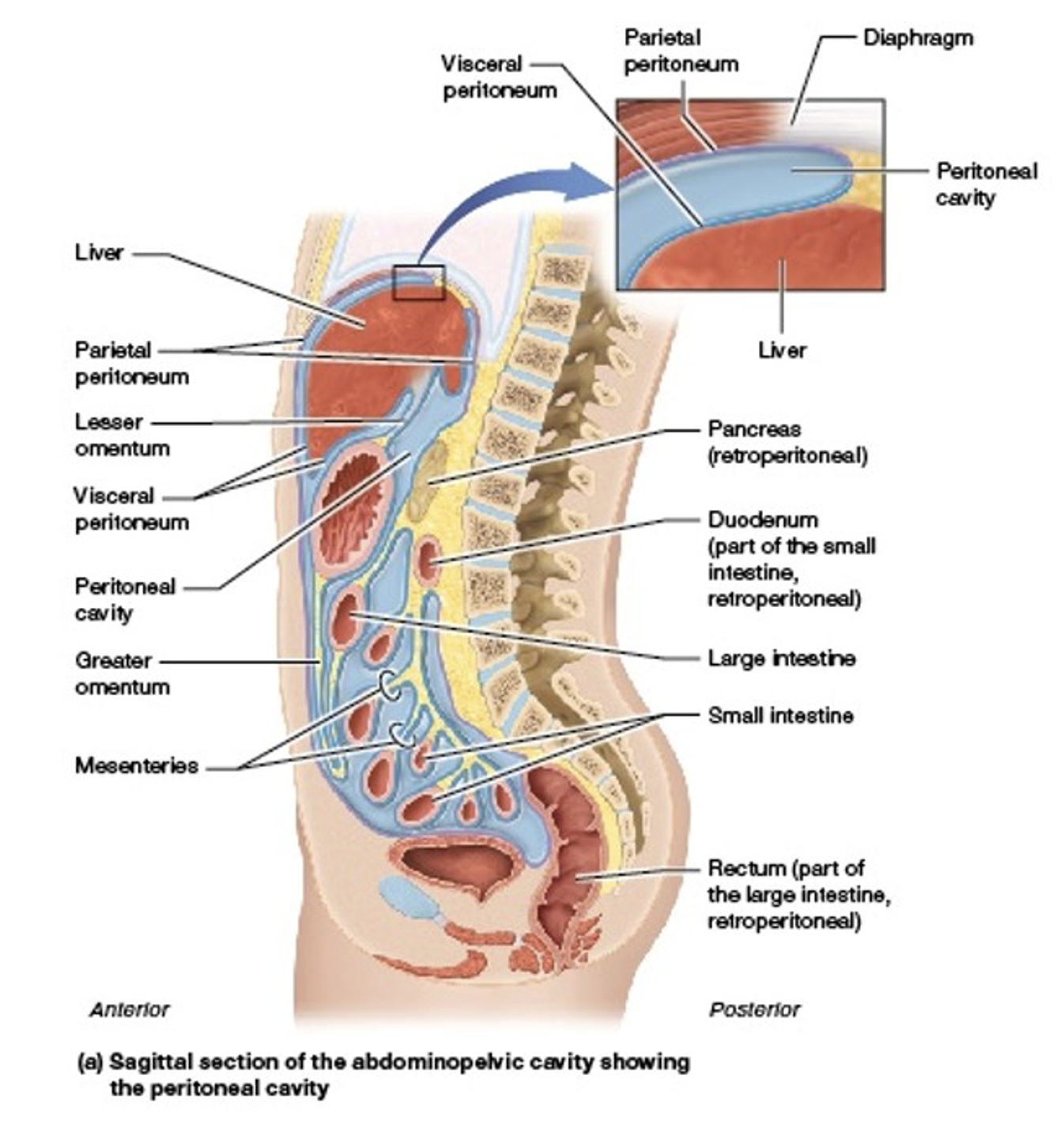
Which organs are both intraperitoneal and retroperitoneal?
Duodenum
Pancreas
Rectum
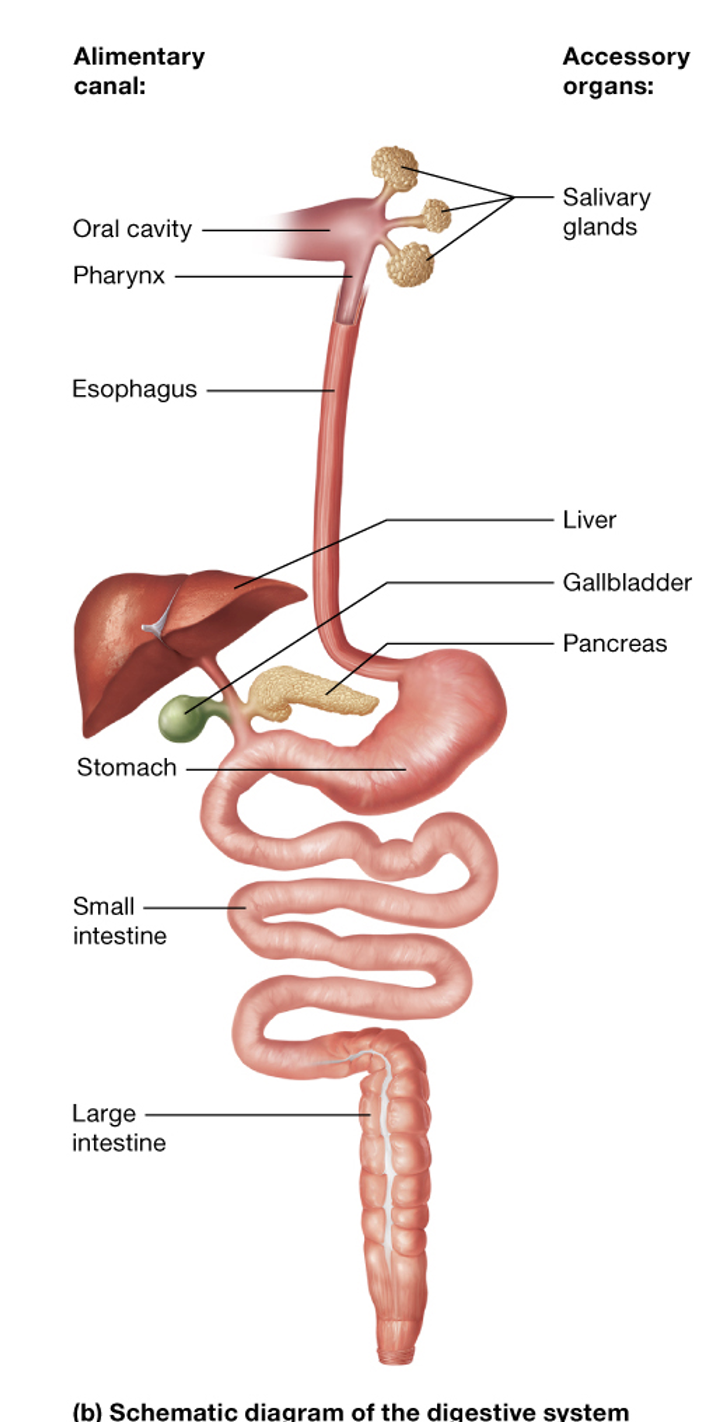
What is the pathway of food through the alimentary canal of the digestive system?
My purple elephant sits silently listening:
Mouth → Pharynx → Esophagus → Stomach → Small Intestine → Large Intestine