plant sexual reproduction
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
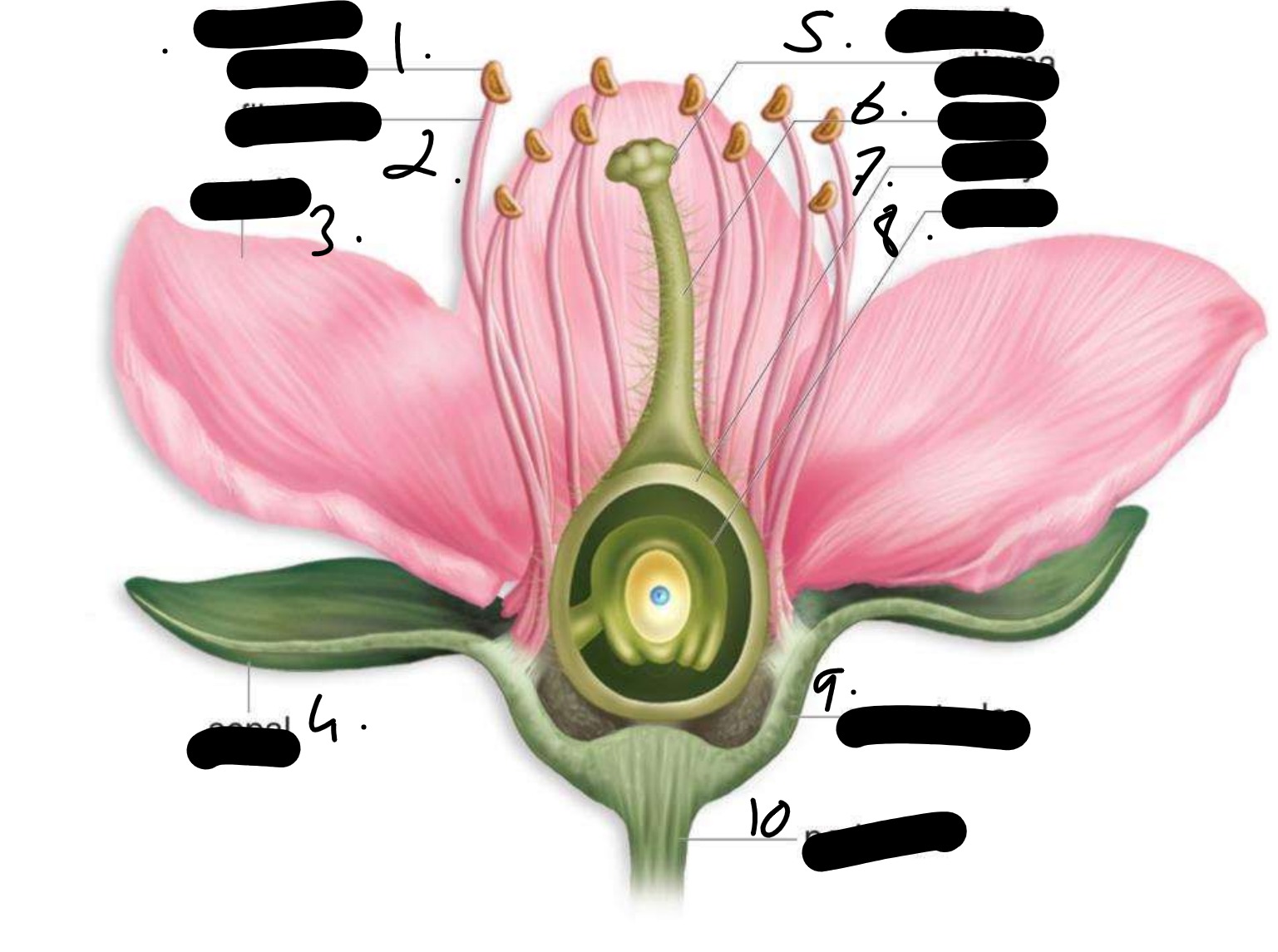
anther
filament
petal
sepal
stigma
style
ovary
ovule
receptacle
peduncle
what do the anther and filament make up
stamen
what do the stigma and style make up
the carpel
what is the name for a species that has both male and female gametes
bisexual or hermaphrodite
what are the male gametes and where do they come from
microspores produced by the anthers
what are the female gametes and where do they come from
megaspores produced in the ovule inside the ovary
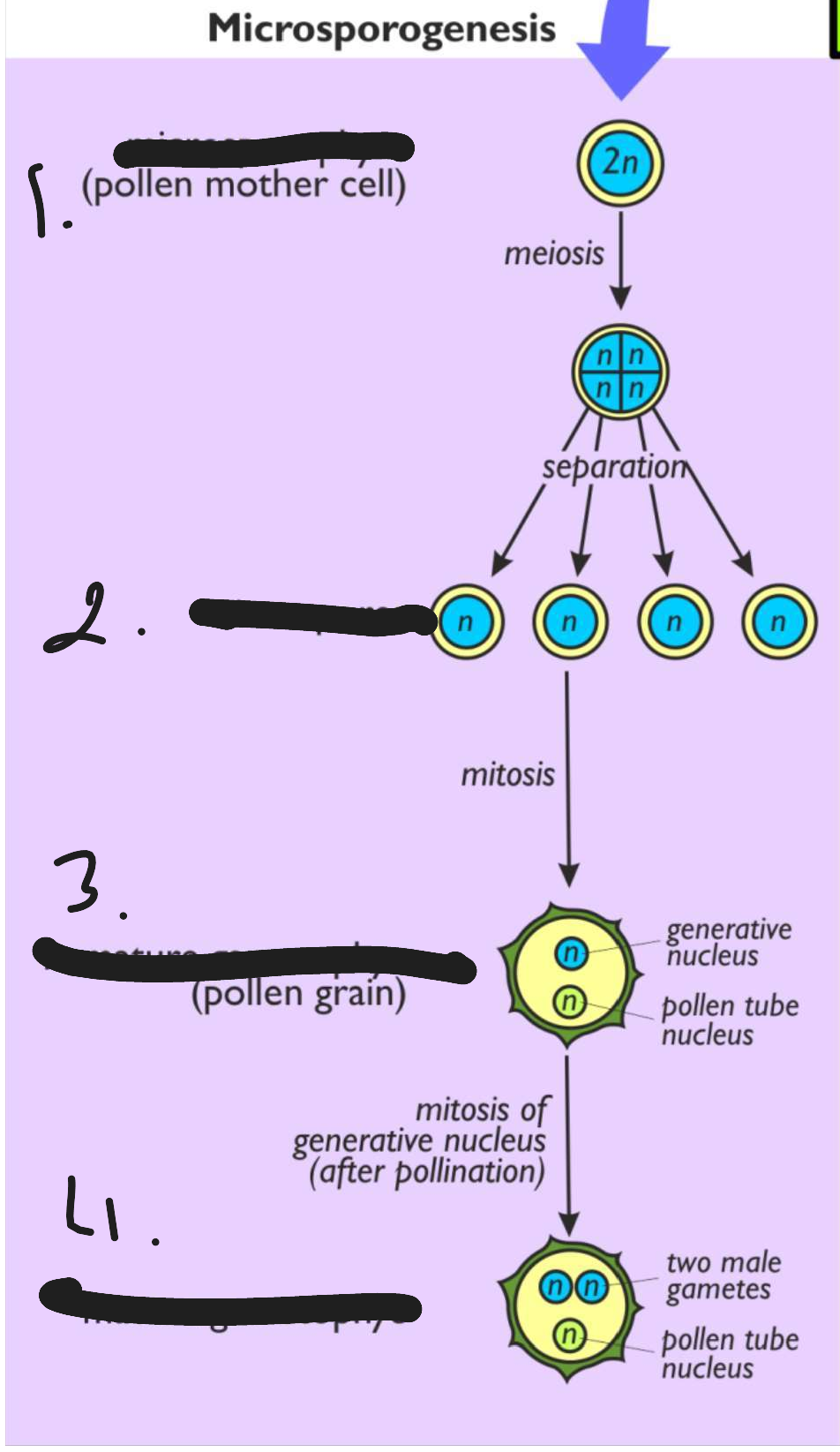
This process is called microsporogenesis
microsporophyte or pollen mother cell
microspores
immature gametophye pollen grain
mature pollen grain
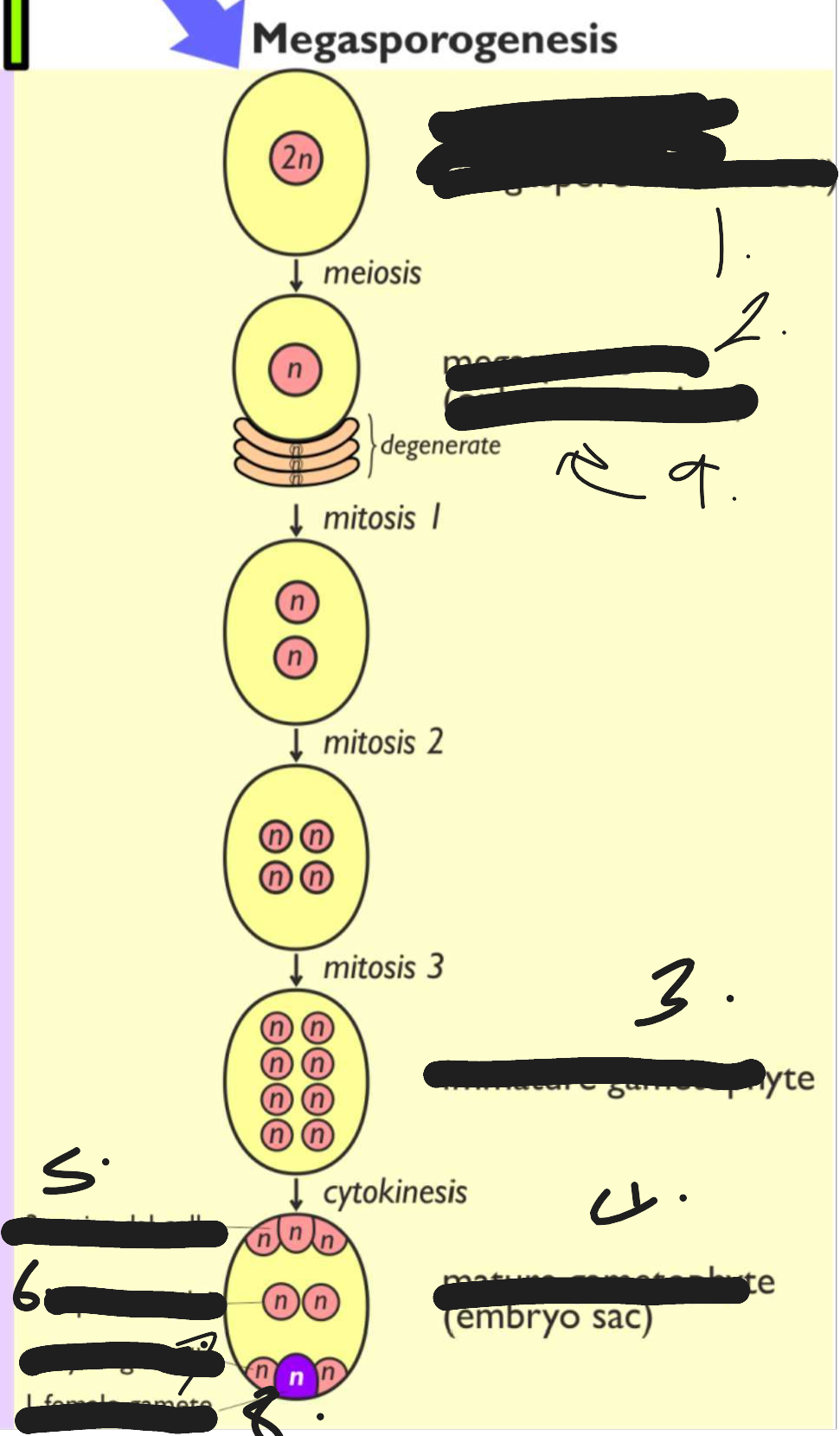
This process is called megasporogenesis
megaspores mega mother cell
megaspores
immature gametophyte
mature gametophyte embryo sac
3 antipodal cells
2 polar nuclei
2 synergid cells
1 female gamete
only one survives
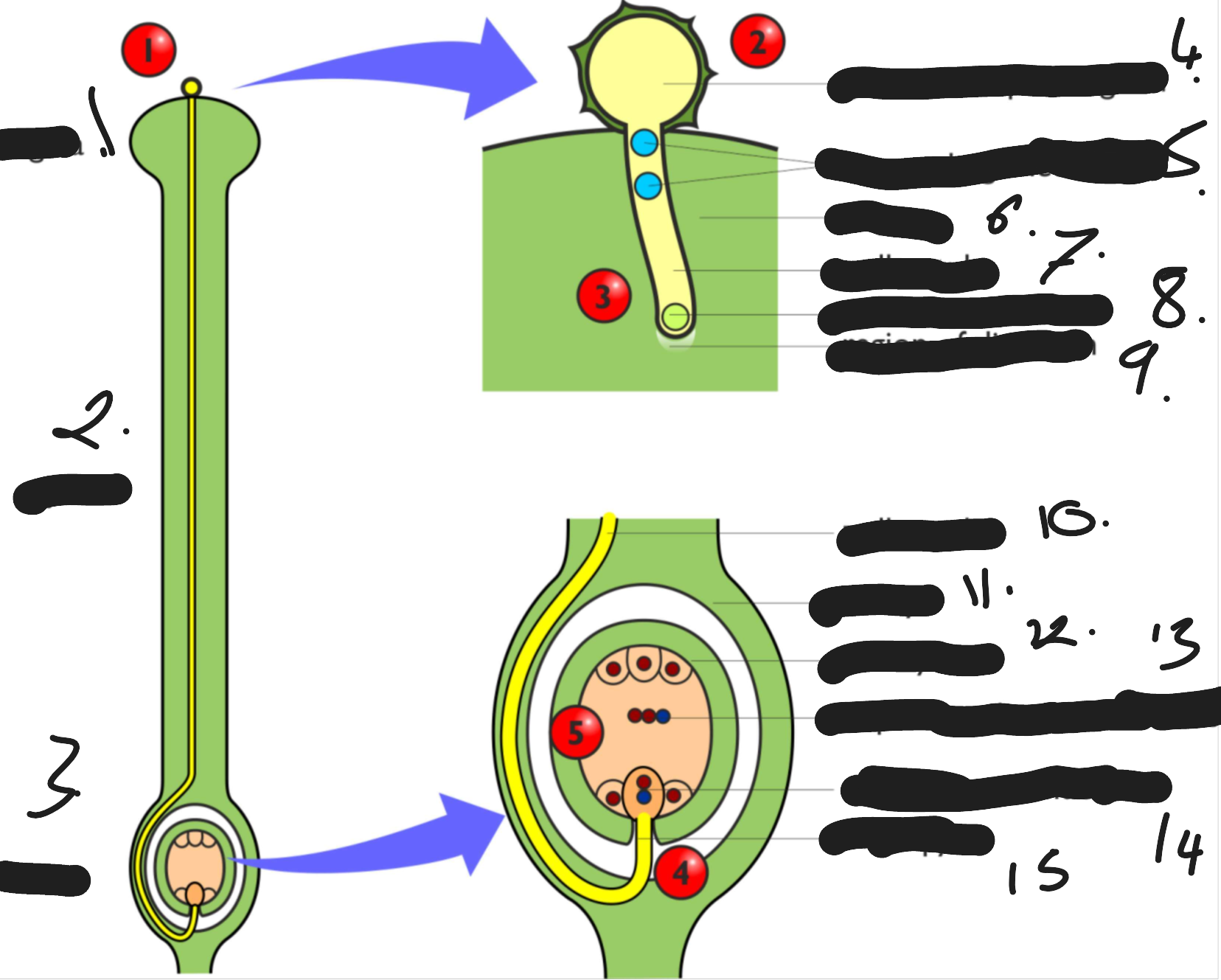
stigma
style
ovary
germinated pollen grain
2 male gamete nuclei
stigma
pollen tube nucleus
region of digestion
pollen tube
ovary embryo sac
triploid endosperm nucleus
diploid zygote nucleus
micropyle
explain plant fertilisation
The pollen grains (immature male gametophytes) are released from the anthers and dispersed by wind or insects to other flowers. If pollen lands on the stigma of a plant of the same species that plant is pollinated. Pollination can be done by the plant eg self-pollination or different plants cross-pollination
If the pollen grain has landed on a suitable stigma it will germinate by absorbing water swelling and splitting open. The generative nucleus divides by mitosis to form 2 haploid male gamete nuclei .The pollen grain is now a mature gametophyte.
A pollen tube emerges from the split and grows down the style towards the ovary. The pollen tube secretes enzymes to digest the tissue in front of it and uses these to digest products to grow. The pollen tube nucleus stays at the tips of the pollen tube controlling its growth. The 2 male gamete nuclei also move down the tube behind the pollen tube nucleus.
When the pollen tube reaches the ovary it enters the female embryo sac through a small opening called the micropyle. The pollen tube nucleus has now done its job degenerates while the 2 male gametes enter the embryo sac
both male gametes now fertilise female cells in the embryo sac in a process unique to sexual reproduction in flowering plants called double fertilisation. One male gamete fuses with the female gamete to form a diploid zygote. The other male gamete fuses with the 2 polar nuclei to form a triploid primary endosperm cell.
Following the fertilisation the flower develops into a seed that can survive in a dormant sate and be dispersed. This zygote develops into the embryo. Once it has dispersed it will germinate and form roots and shoot and eventually grow into a new plant. The primary endosperm grows and develops into a food store called the endosperm. This nourishes the developing embryo. Eg coconut meat. The embryo sac develops into the seed surrounding the embryo and protecting it during dispersal germination. The ovary wall develops into a fruit to aid the seed dispersal. different fruit have different properties depending on their method of seed dispersal
what type of enzymes digest the stigma and style allowing the pollen tube to form(hole)
the pollen tube secretes hydrolytic (digestive) enzymes
An investigation was carried out to study the effect of the concentration of a chemical called methylpurine on pollen tube growth. suggest why temp was kept the same
Idea that temperature is a controlled
variable
e.g. constant temperature removes
this variable, so temperature does
not affect {results / length of pollen
tube} ;
2. idea that (pollen tube) { growth /
enzymes / proteins /eq } affected by
temperature ;
3. idea that at this temperature {
enzymes / proteins } will not be
denatured / pollen not destroyed at
this temperature / 22.5°C optimum
temperature ;
4. idea that the investigation is valid
Methylpurine can inhibit messenger RNA (mRNA) synthesis. Suggest how this can cause the change in mean pollen tube length.
less / no } transcription / idea
of inhibition of RNA polymerase ;
2. { less / no } { translation /
protein synthesis/ protein made /
eq } ;
3. idea that protein needed for
(pollen tube) growth e.g. less
protein leads to reduced growth
(of pollen tubes) ;