Ch. 25, Part Two: Leaves
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/93
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
1
New cards
leaf functions
-main photosynthetic organ of plants
-transpiration
-transpiration
2
New cards
transpiration definition
movement of H2O (water) through plant and evaporation via the leaves
3
New cards
leaf morphology
-more variable in size, shape, arrangement, and other factors than the roots and stems
-variations relfect evolutionary adaptations to different environments, herbivores, and photosynthetic needs
-variations relfect evolutionary adaptations to different environments, herbivores, and photosynthetic needs
4
New cards
maxing leaf surface area pros
catches more light -> more photosynthesis / food production
5
New cards
maxing leaf surface area cons
loses water faster
6
New cards
blade
flat part of the leaf
7
New cards
blade alternate name
lamina
8
New cards
petiole
stalk of the leaf that attaches to the stem
9
New cards
stipule
at base of petiole, appendages
10
New cards
sessile
no petiole, has a sheath instead
attached directly to the stem
attached directly to the stem
11
New cards
sheath
"coat" from the blade that wraps around the stem
12
New cards
leaf arrangement definition
leaf arrangements on a stem in an ordered and predictable pattern
13
New cards
leaf arrangement function
maxes sun exposure
14
New cards
three basic patterns of leaf arrangement
alternate
opposite
whorled
opposite
whorled
15
New cards
alternate leaf arrangement
1 leaf per node
16
New cards
alternate leaf arrangement types
spiral
distichous
distichous
17
New cards
spiral arrangement
leaves spiral/helixes around the plant, no columns
18
New cards
distichous arrangement
leaves arranged in two vertial columns on opposite sides of the stem
(think 180 degrees)
(think 180 degrees)
19
New cards
opposite leaf arrangement
2 leaves per node
20
New cards
opposite leaf arrangement type
decussate
21
New cards
decussate arrangement
adjacent leaves pairs above and below are oriented 90 degrees differently
22
New cards
whorled leaf arrangement
3 or more leaves per node
23
New cards
leaf types
simple
compound
compound
24
New cards
simple leaves
have one leaf blade per petiole
25
New cards
compound leaves
have more than one leaf blade per petiole (leaflets)
26
New cards
compound leaf types
palmately compound
pinnately compound
bipinnately compound
pinnately compound
bipinnately compound
27
New cards
palmate compound leaf
think of a hand, leaflets originate from one center
28
New cards
pinnate compound leaf
has a center rachis and leaflets come off of it
29
New cards
rachis
axis of a compound leaf or compound inflorescence
30
New cards
petiolule
the stalk of a leaflet
31
New cards
How can you tell if a leaf is a compound leaf and not multiple simple leaves?
look for axillary bud, that's the connection of petiole to the stem
AND
leaves are on the same plane, and not going out in different directions
AND
leaves are on the same plane, and not going out in different directions
32
New cards
bipinnate compound leaves
leaves compound twice (once on the rachis, and then another time on the petiolule)
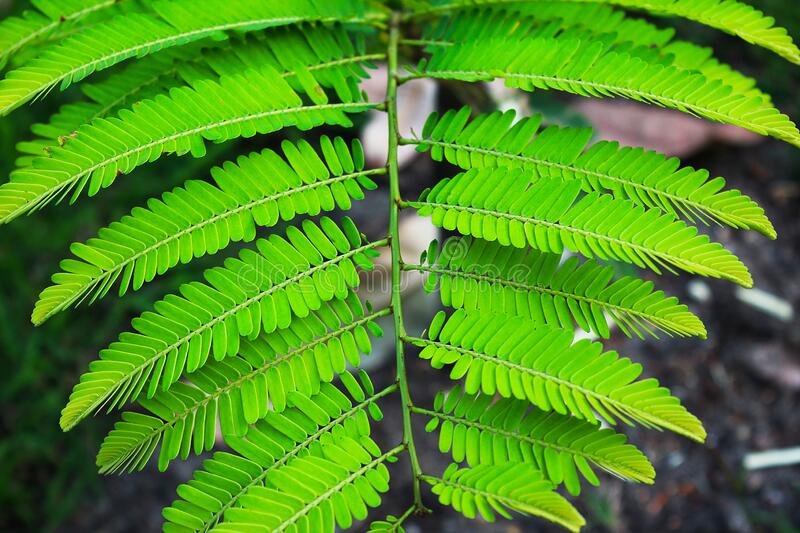

33
New cards
advantages of compound leaves
advantage in windy environments (less continuous surface area to catch wind and break or become damaged)
reduces transpiration
reduces transpiration
34
New cards
venation definition
the arrangement of veins in a leaf
35
New cards
venation types
pinnate
parallel
palmate
parallel
palmate
36
New cards
pinnate venation
main central vein, with veins coming off of that
37
New cards
pinnate venation found in...
eudicots
38
New cards
parallel venation
parallel veins that don't intersect
39
New cards
parallel venation found in...
grasses, monocots
40
New cards
palmate venation
palm-like vein spread from a center point
41
New cards
palmate venation found in...
eudicots
42
New cards
leaf margins
edges of the leaf
43
New cards
leaf margin types
smooth/entire
serrate/toothed
serrate/toothed
44
New cards
smooth/entire margin
rounded leaf margin
45
New cards
serrate/toothed margin
leaf margin with "teeth"
46
New cards
Why are the shapes and sizes of leaves generally more variable than for stems and roots?
environmental adaptation,
herbivore deterrent,
photosynthesis
herbivore deterrent,
photosynthesis
47
New cards
leaf origin
leaf primordia
48
New cards
leaf primordia
form near apical meristems
forms leaves
forms leaves
49
New cards
leaf primordia composition
protoderm
procambium
ground meristem
procambium
ground meristem
50
New cards
Mature leaves usually lack ___________, which means, when they reach maturity, ___________.
primary meristems, that is their final size
51
New cards
leaf major tissues
leaf epidermis
mesophyll
vascular tissue
mesophyll
vascular tissue
52
New cards
leaf epidermis functions
protects against bacteria/fungi
water retention
gas exchange
water retention
gas exchange
53
New cards
leaf epidermis origin
protoderm
54
New cards
leaf epidermis composition
single cell layer
cuticle
trichomes
guard cells w/ stomata
cuticle
trichomes
guard cells w/ stomata
55
New cards
trichome functions
sunlight protection (UV)
keeping water off of plant
herbivory protection
excessive heat protection (insulation)
keeping water off of plant
herbivory protection
excessive heat protection (insulation)
56
New cards
True or false: Cuticle does NOT affect gas exchange in a leaf.
True; the stomata are responsible for gas exchange
57
New cards
True or false: In most plants, water enters leaves via stomata
False; water can leave through stomata, however.
58
New cards
mesophyll
ground tissue of a leaf
59
New cards
mesophyll compostion
parenchyma cells with chloroplasts
60
New cards
mesophyll types
palisade parenchyma/mesophyll
spongy parenchyma/mesophyll
spongy parenchyma/mesophyll
61
New cards
palisade parenchyma
columnar, tightly packed cells
main source of photosynthesis in leaves (lots of chloroplasts)
main source of photosynthesis in leaves (lots of chloroplasts)
62
New cards
spongy parenchyma
spherical, aeration/holes between cells
where gas exchange occurs, needs room for gases to move around
where gas exchange occurs, needs room for gases to move around
63
New cards
vascular tissue difference in leaves, comparing to stems / roots
in one leaf, vascular tissue can branch out or merge.
64
New cards
vascular tissue alternate name in leaves
leaf veins
65
New cards
vascular tissue general arrangement
layered on top of one another, rather than a bundle like in roots and stems
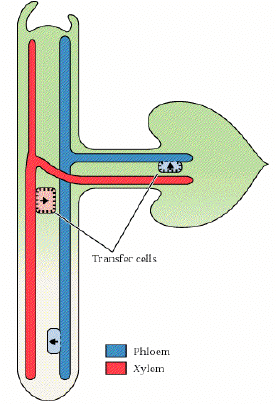
66
New cards
In different types of plants, vascular tissue arrangement...
can differ based on water availability
67
New cards
mesophytes
plants that require mesic environment
68
New cards
mesic
having or characterized by moderate or a well-balanced supply of moisture
69
New cards
mesophyte example
lilacs (Syringa)
70
New cards
mesophyte unique features
more stomata on bottom of leaf for water retention
single layer of lower and upper epidermis cells
single layer of lower and upper epidermis cells
71
New cards
hydrophytes
plants needing a large supply of water
72
New cards
hydrophyte example
water lily (Nymphaeaceae)
73
New cards
hydrophyte unique features
sclereid for structural support
stoma present on sides where air is accessable
large number of intracellular spaces to float on the water (for water lilies)
less vascular tissues
stoma present on sides where air is accessable
large number of intracellular spaces to float on the water (for water lilies)
less vascular tissues
74
New cards
xerophytes
plants adapted to arid condition
75
New cards
xerophyte example
oleander (Nerium)
76
New cards
xerophyte unique features
stomatal crypt w/ sunken stoma
hides stoma where it's less dry to further water retention
sometimes has trichomes in the crypt
hides stoma where it's less dry to further water retention
sometimes has trichomes in the crypt
77
New cards
grass leaves found in...
C3 and C4 photosynthesis pathways
78
New cards
grass leaf unique features
bulliform cells
79
New cards
bulliform cells
huge cells part of upper epidermis that inflate with water, flattening/closing the leaf from environmental changes
80
New cards
difference in sun exposure leads to...
sun and shade leaves
81
New cards
sun leaves morphology changes
thicker, more palisade, but smaller overall leaf
more vascular tissue extensiveness
thicker epidermis
more vascular tissue extensiveness
thicker epidermis
82
New cards
sun leaf function
photosynthesis focusing on more sun exposure
main photosynthesis source
main photosynthesis source
83
New cards
shade leaf morphology
less palisade parenchyma, but larger overall leaf
flimsy
larger surface area
not as much energy put into them
flimsy
larger surface area
not as much energy put into them
84
New cards
shade leaf function
photosynthesis focusing on less sun exposure
secondary photosynthesis source
secondary photosynthesis source
85
New cards
leaf abscission definition
process of leaves separating from the stem
86
New cards
abscission layer
enzymes break down middle lamella
builds up suberin on the stem side once the leaf breaks off
builds up suberin on the stem side once the leaf breaks off
87
New cards
leaf abscission reason
from an environmental trigger (day length)
88
New cards
leaf abscission features
reusable ions and molecules are returned to stem
occurs near base of petiole at abscission zone
broken down chloroplasts show other pigments (carotenoids)
occurs near base of petiole at abscission zone
broken down chloroplasts show other pigments (carotenoids)
89
New cards
leaf modication types
tendrils (either stem or leaf mods)
spines (either leaves or stipules)
bracts
bulb (underground leaves)
insectivorous leaves
spines (either leaves or stipules)
bracts
bulb (underground leaves)
insectivorous leaves
90
New cards
tendrils
either stem or leaf mods
for grappling / supporting
grape vines
for grappling / supporting
grape vines
91
New cards
spines
modded leaves / stipules
protection against herbivory
cacti
protection against herbivory
cacti
92
New cards
bracts
attracts pollinators
poinsettas
poinsettas
93
New cards
bulb
underground leaves
storage
onions
storage
onions
94
New cards
insectivorous leaves
obtains nitrogen from insects and digest them
pitcher plants, sundew, Venus fly trap
pitcher plants, sundew, Venus fly trap