Chapter 7 Sexual Reproduction/Meiosis
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
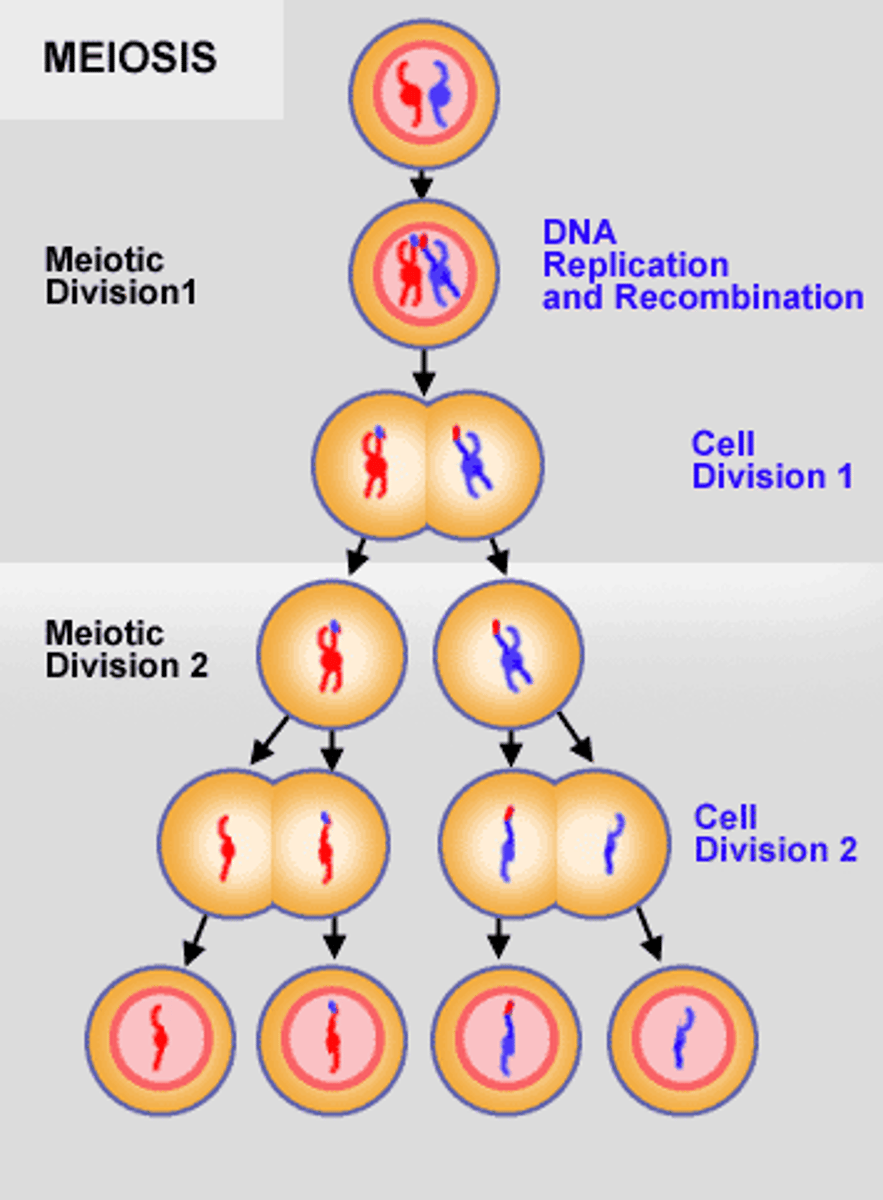
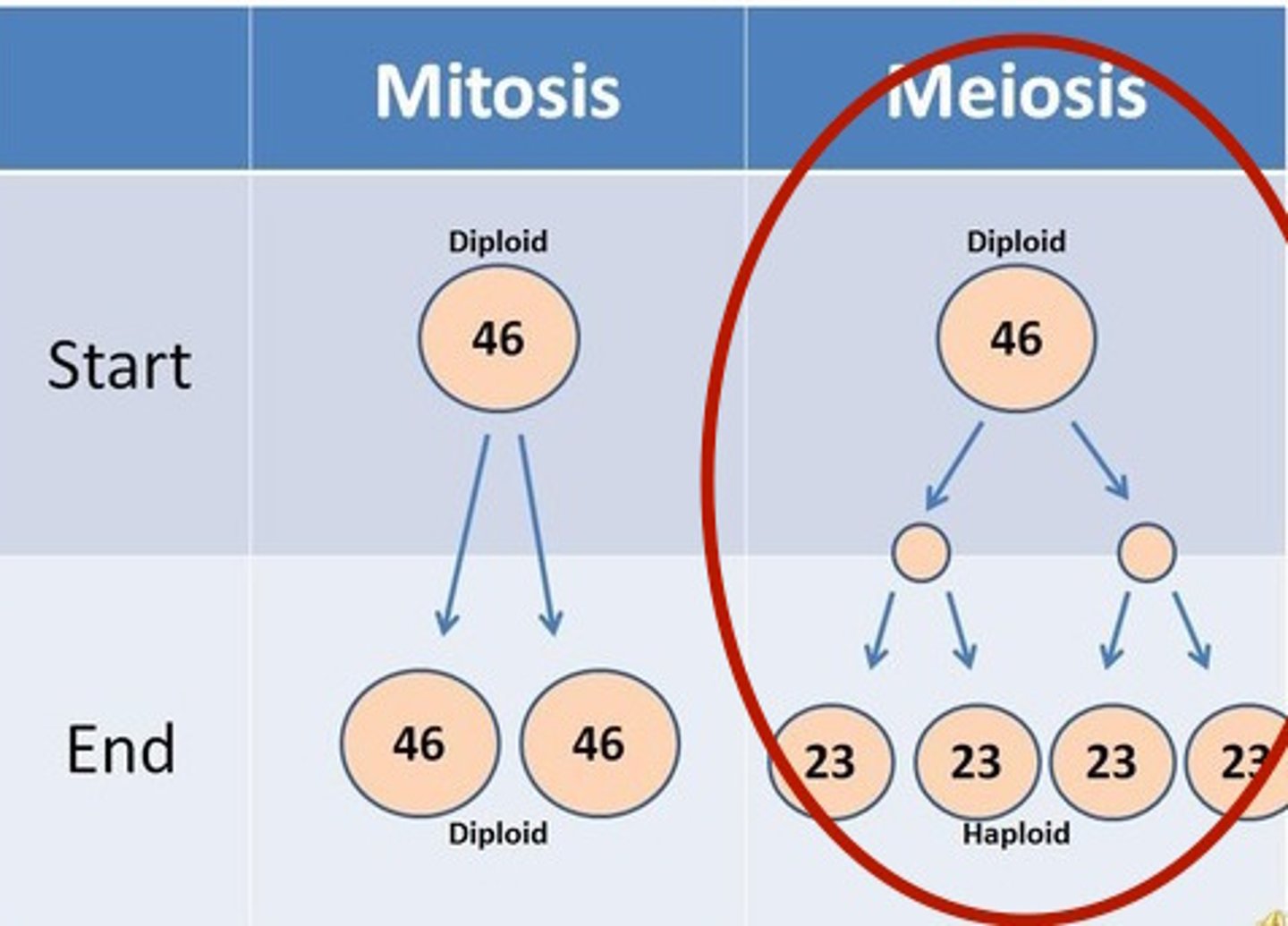
Main goal of meiosis
To cut the chromosome number in half
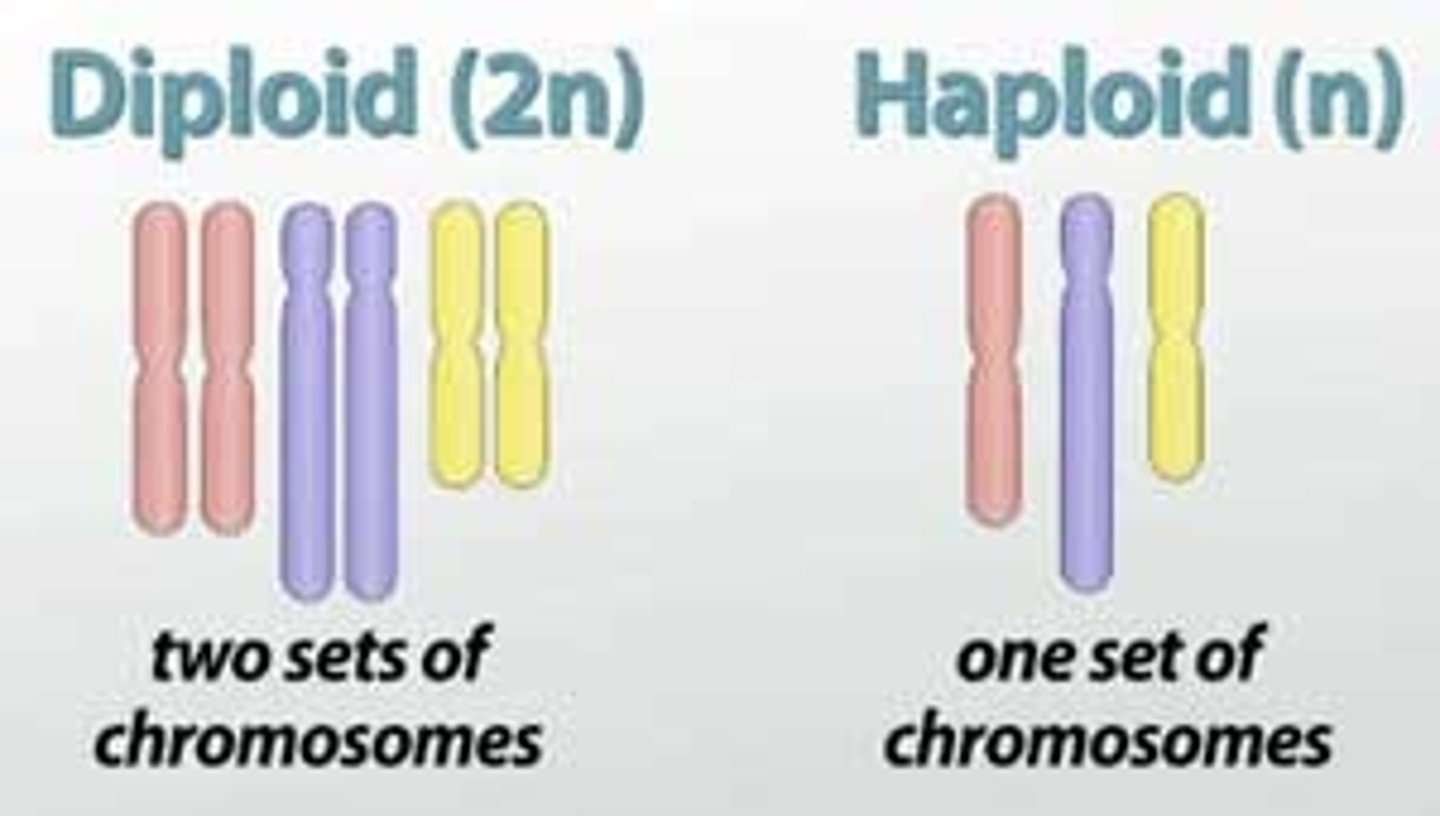
Contain a single chromosome set
Haploid cells
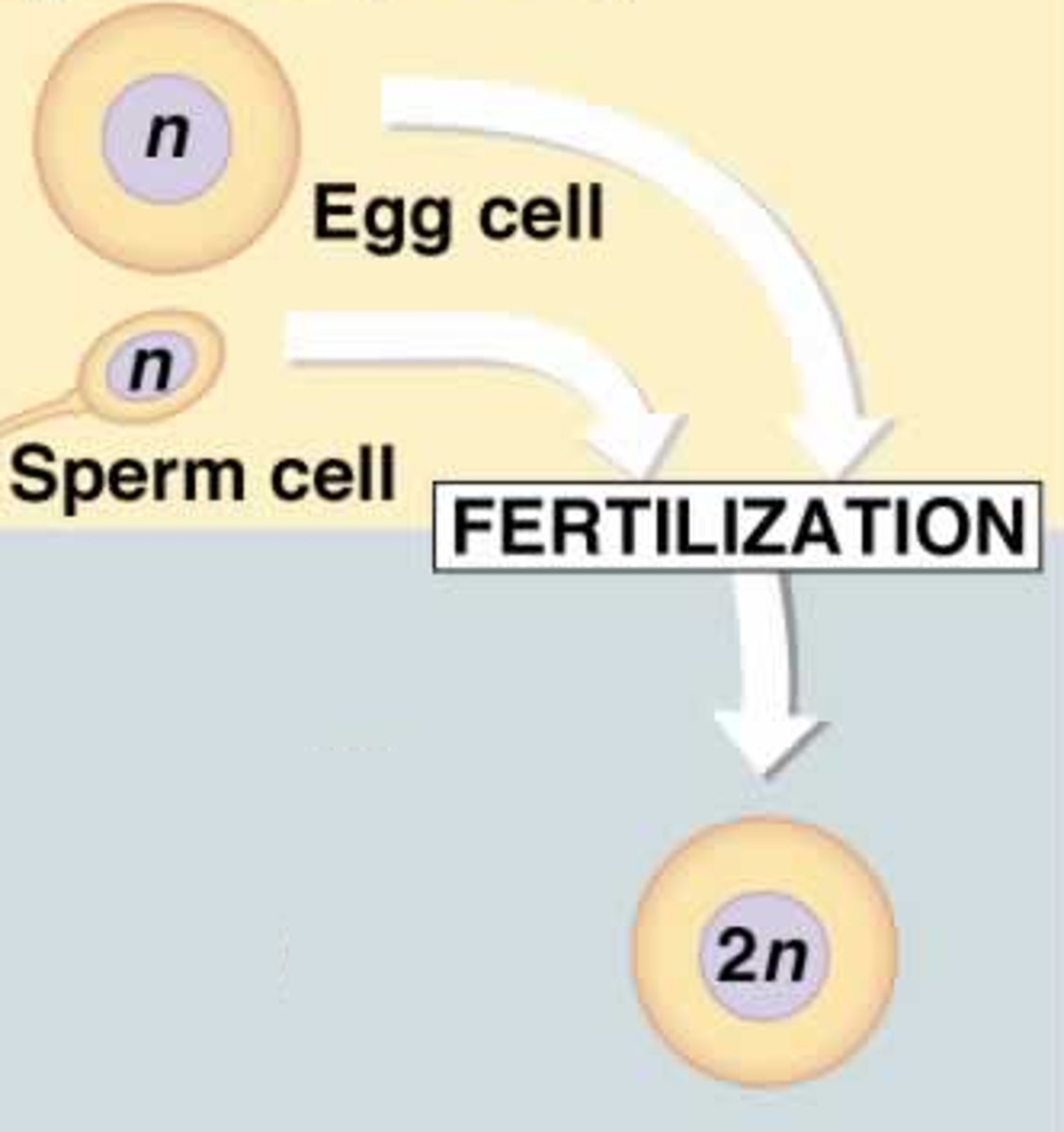
Two haploid cells combine to form a diploid zygote
Fertilization
Reduction division
The chromosome count is reduced by half
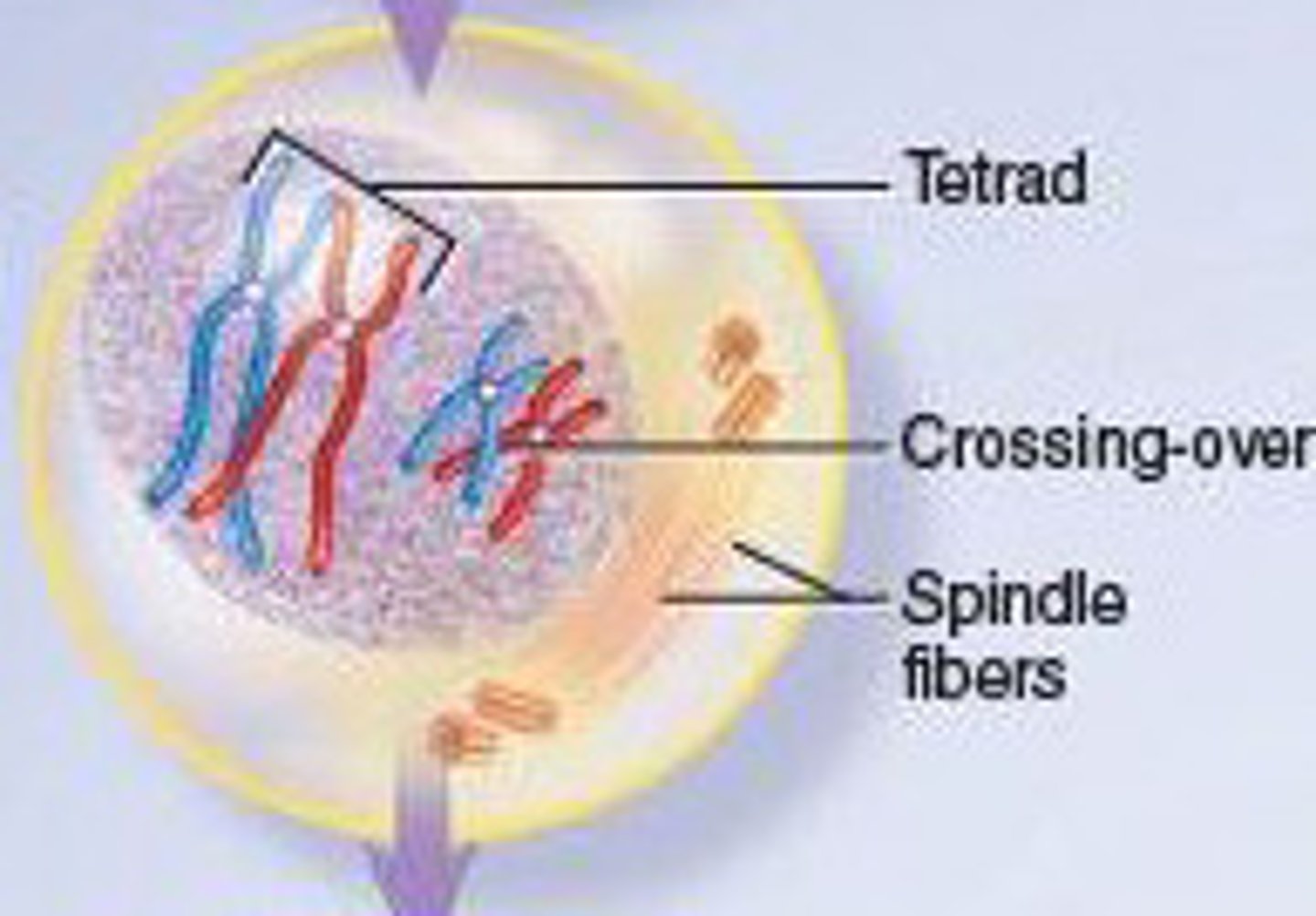
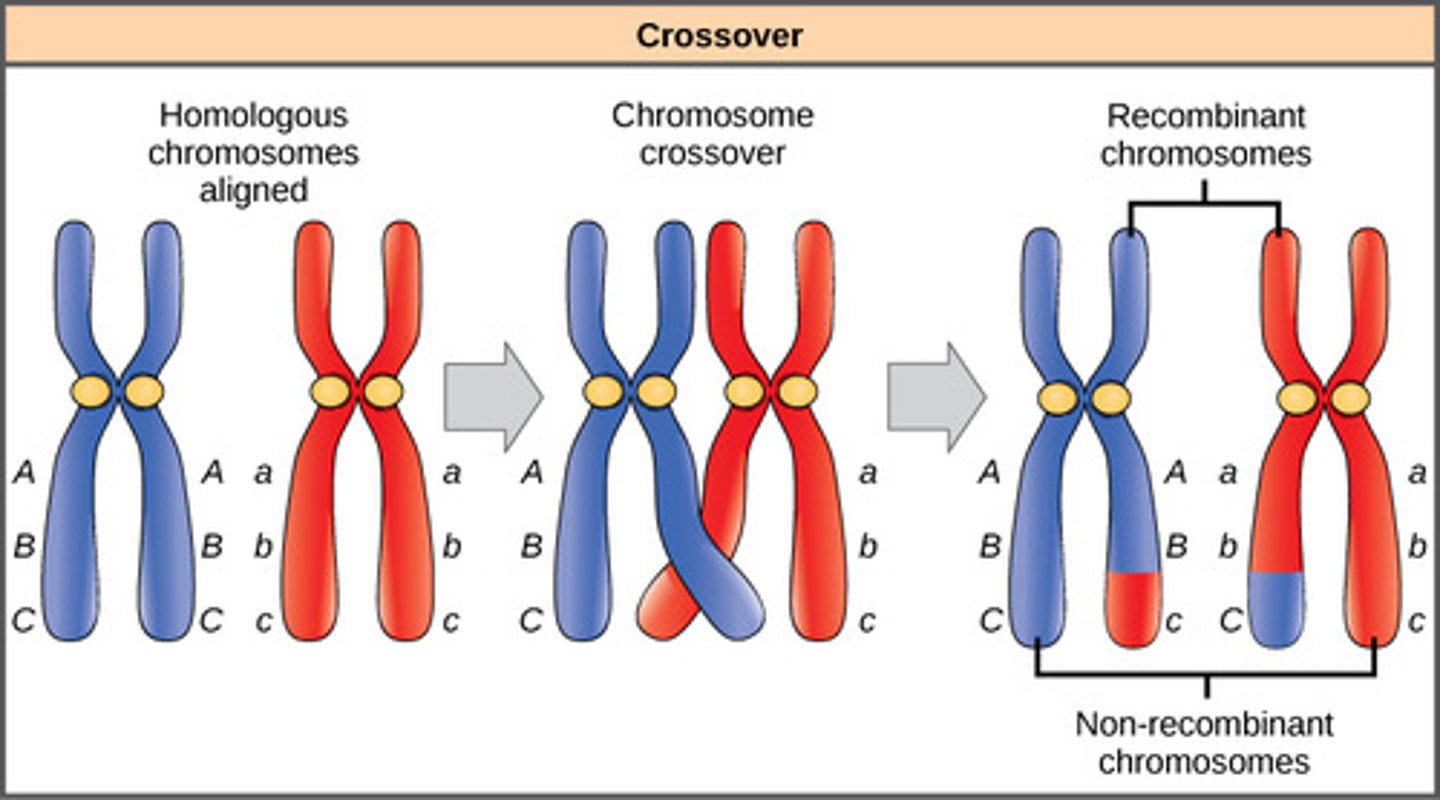
It creates genetic variation by exchanging genetic material
Significance of crossing over
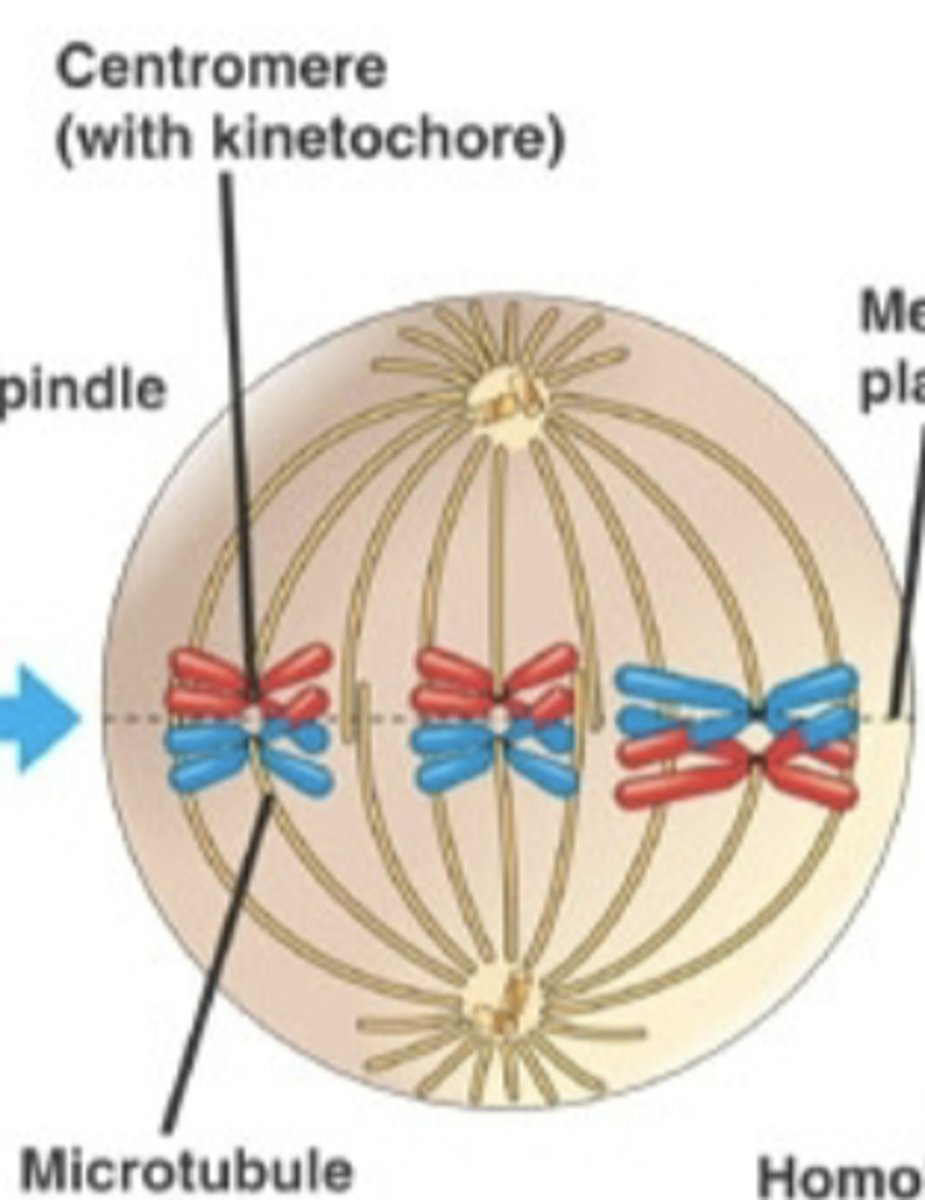
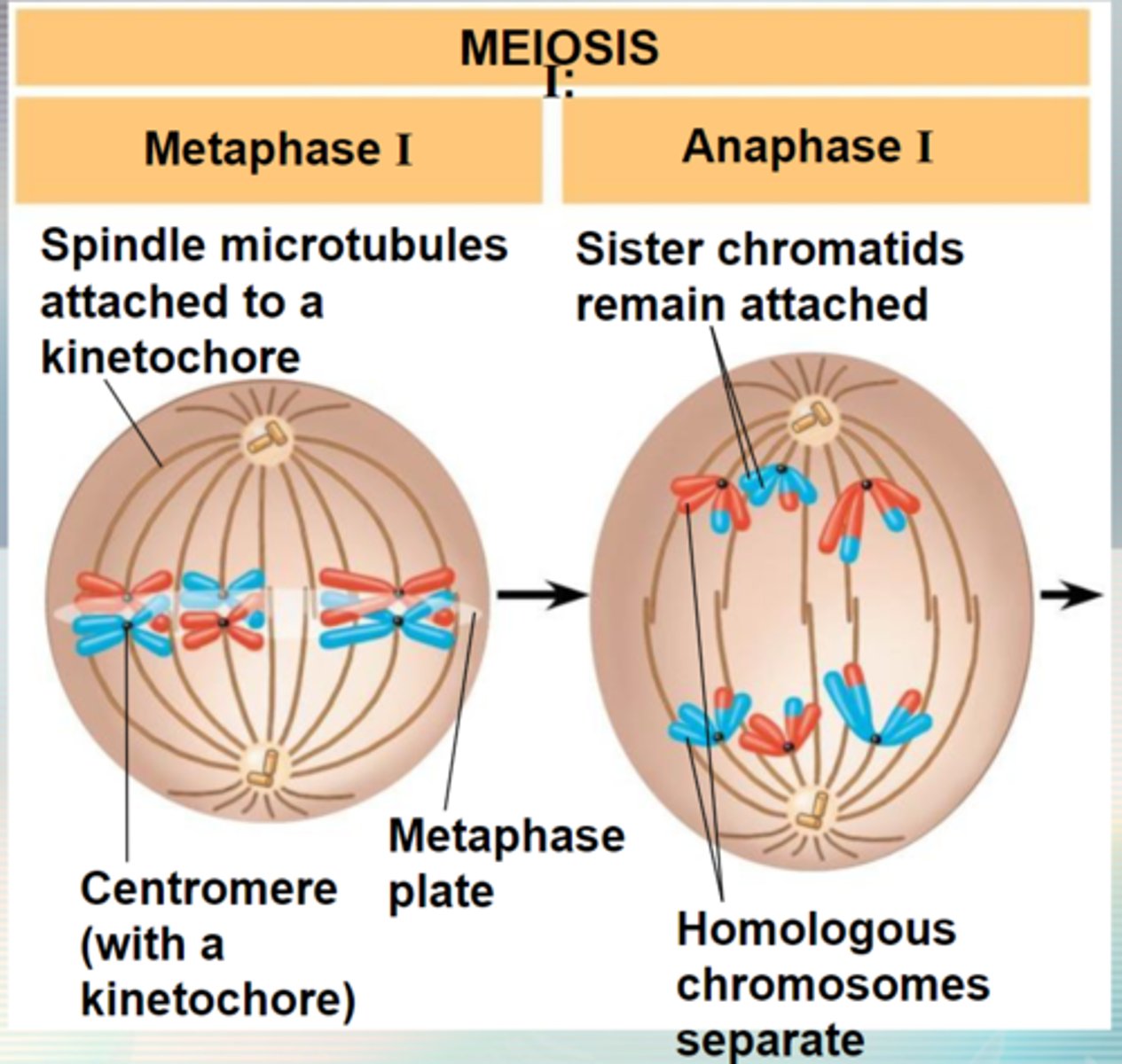
In metaphase 1 of meiosis, what happens?
the process where pairs of homologous chromosomes line up together during metaphase I of meiosis
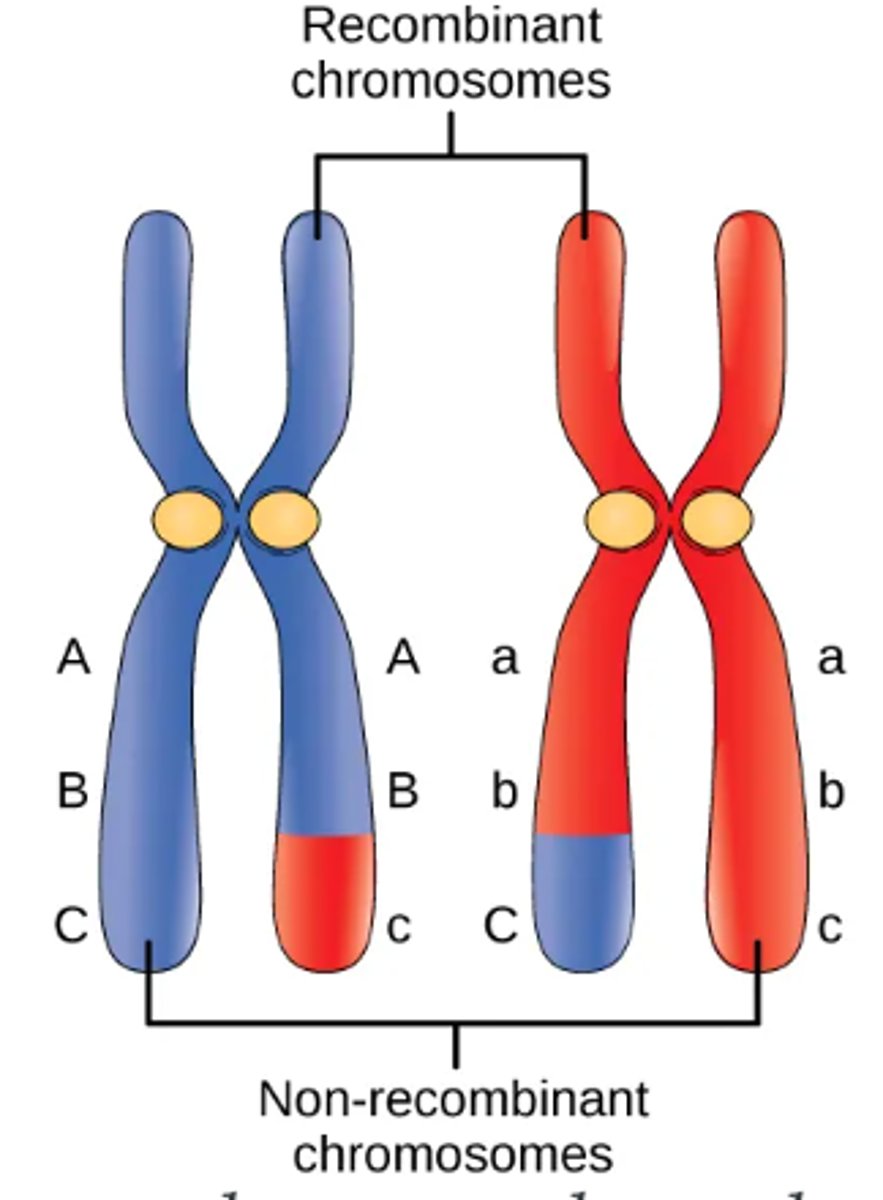
A chromosome that has gone through crossing over
Recombinant chromosome
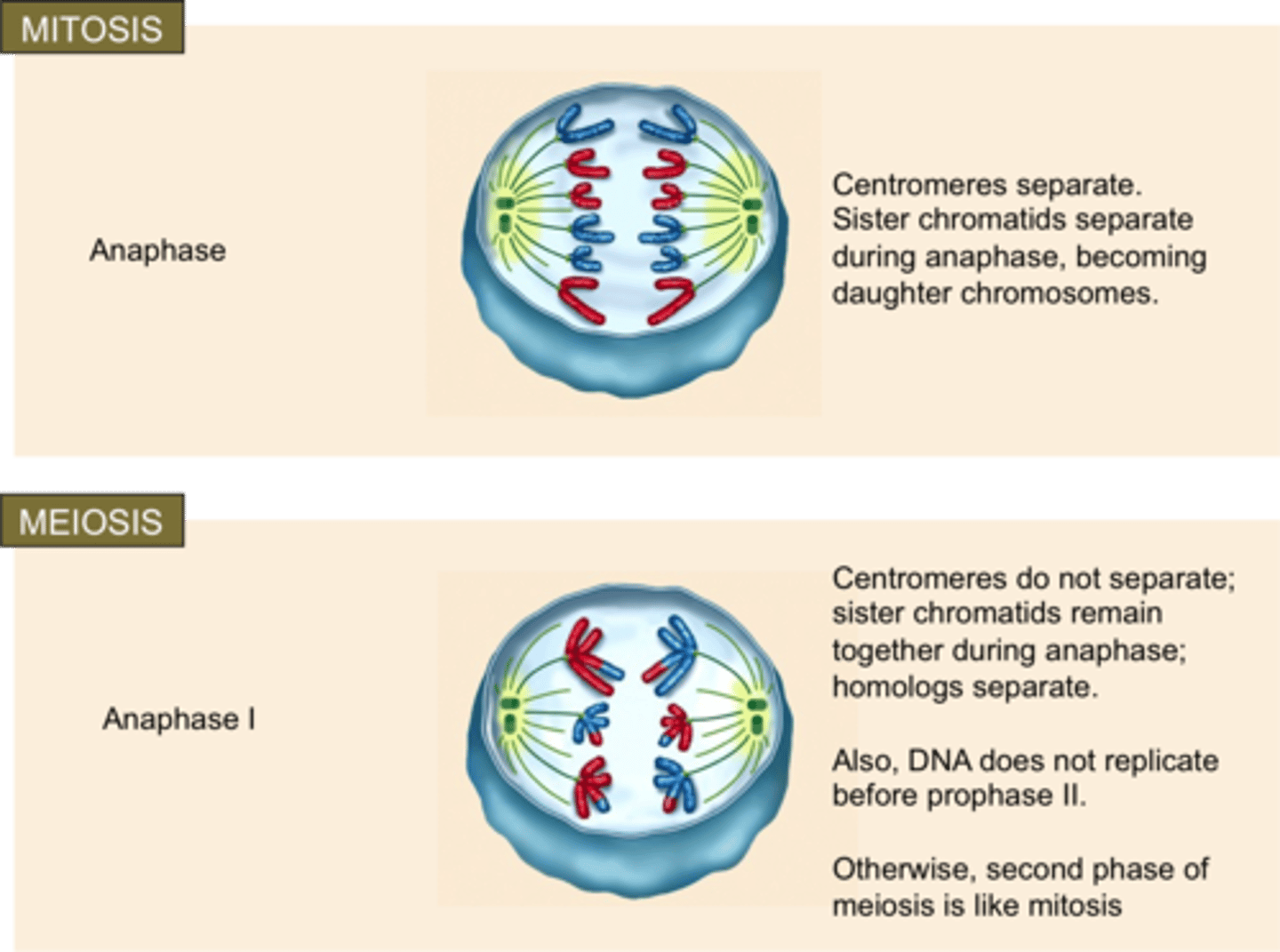
homologous chromosomes separate and move to opposite poles of the cell
Anaphase I (Meiosis)
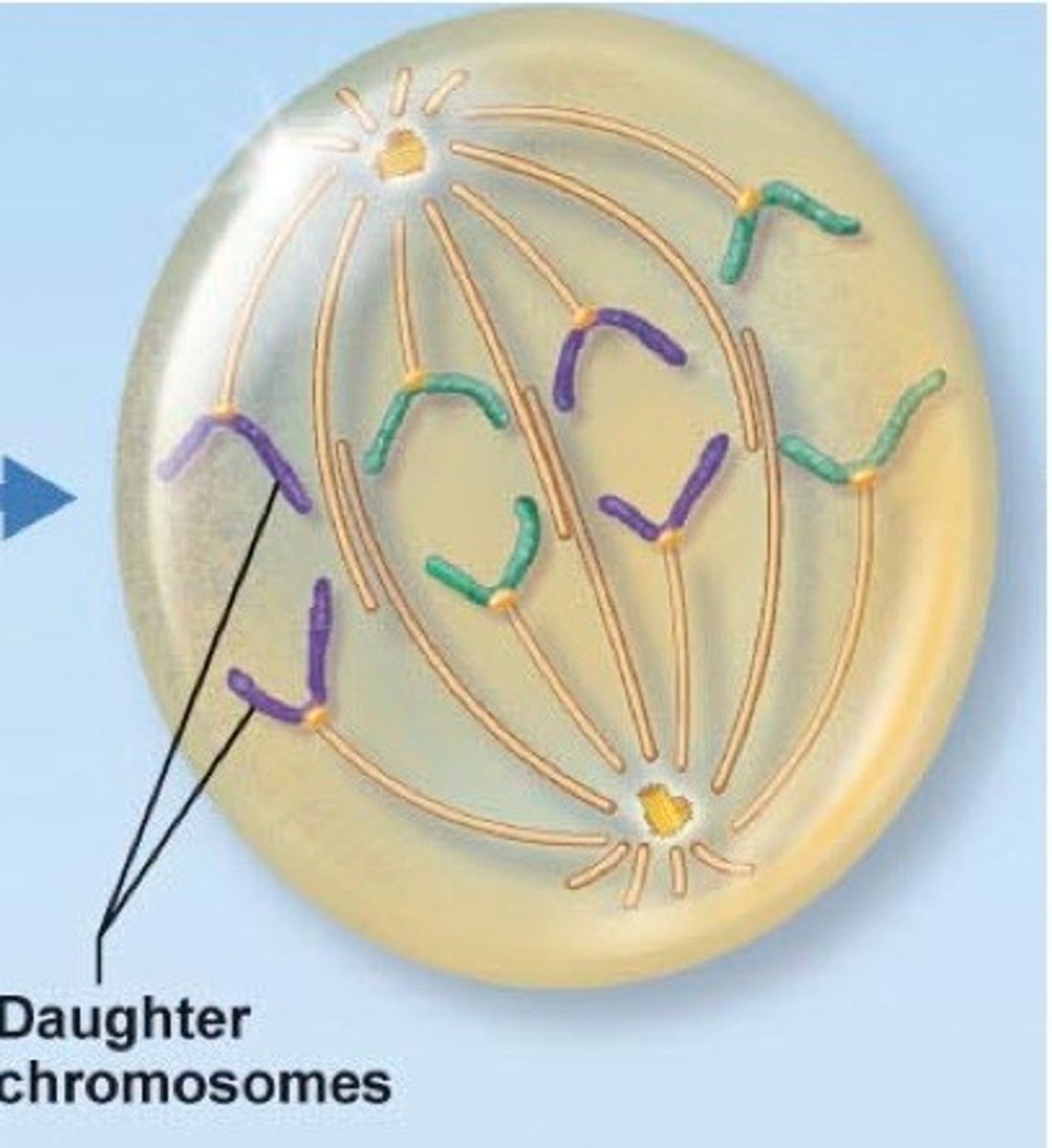
Anaphase II
sister chromatids separate from each other and are pulled toward opposite poles of the cell
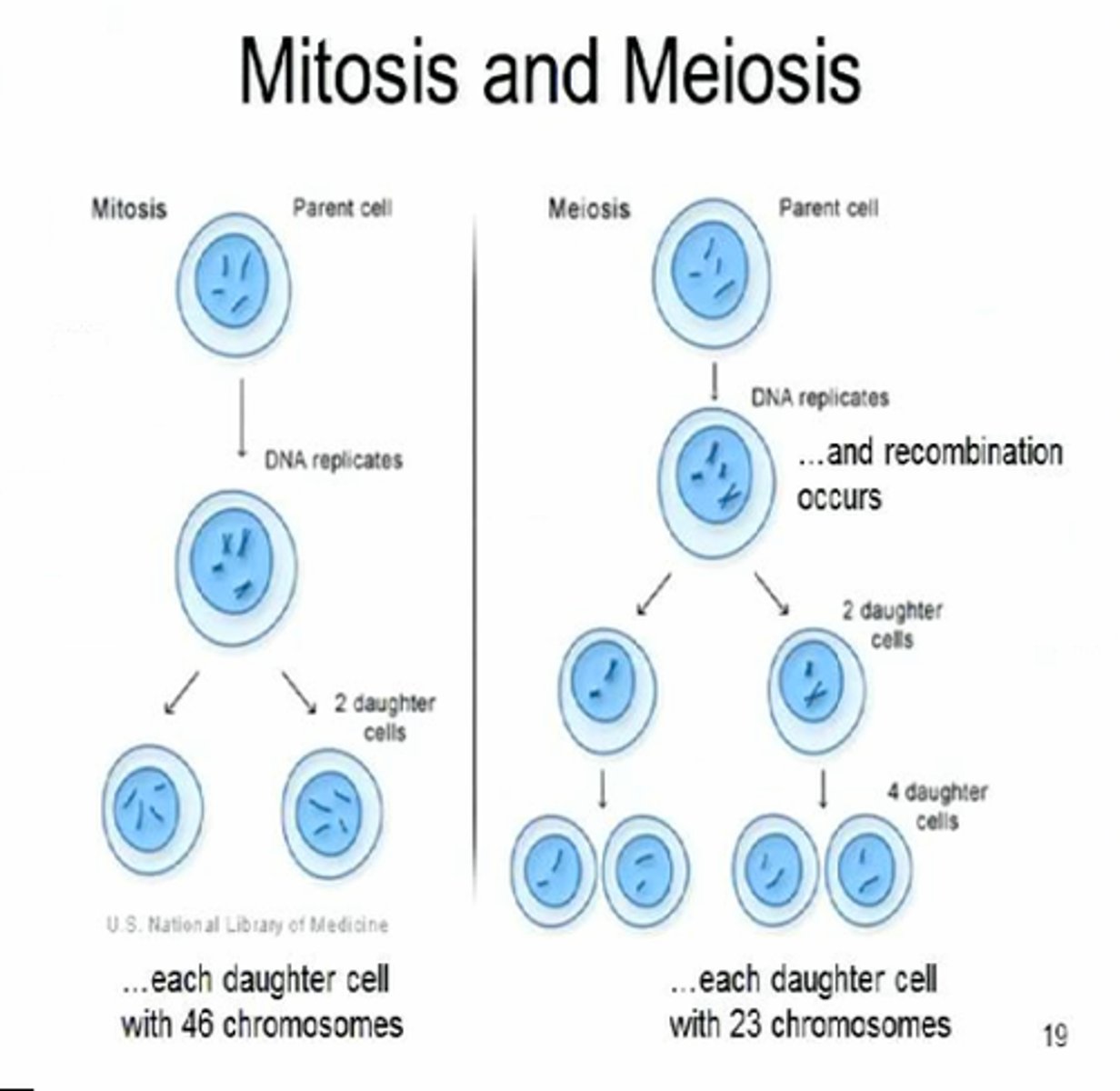
Cells resulting from meiosis
Four, and they are not identical
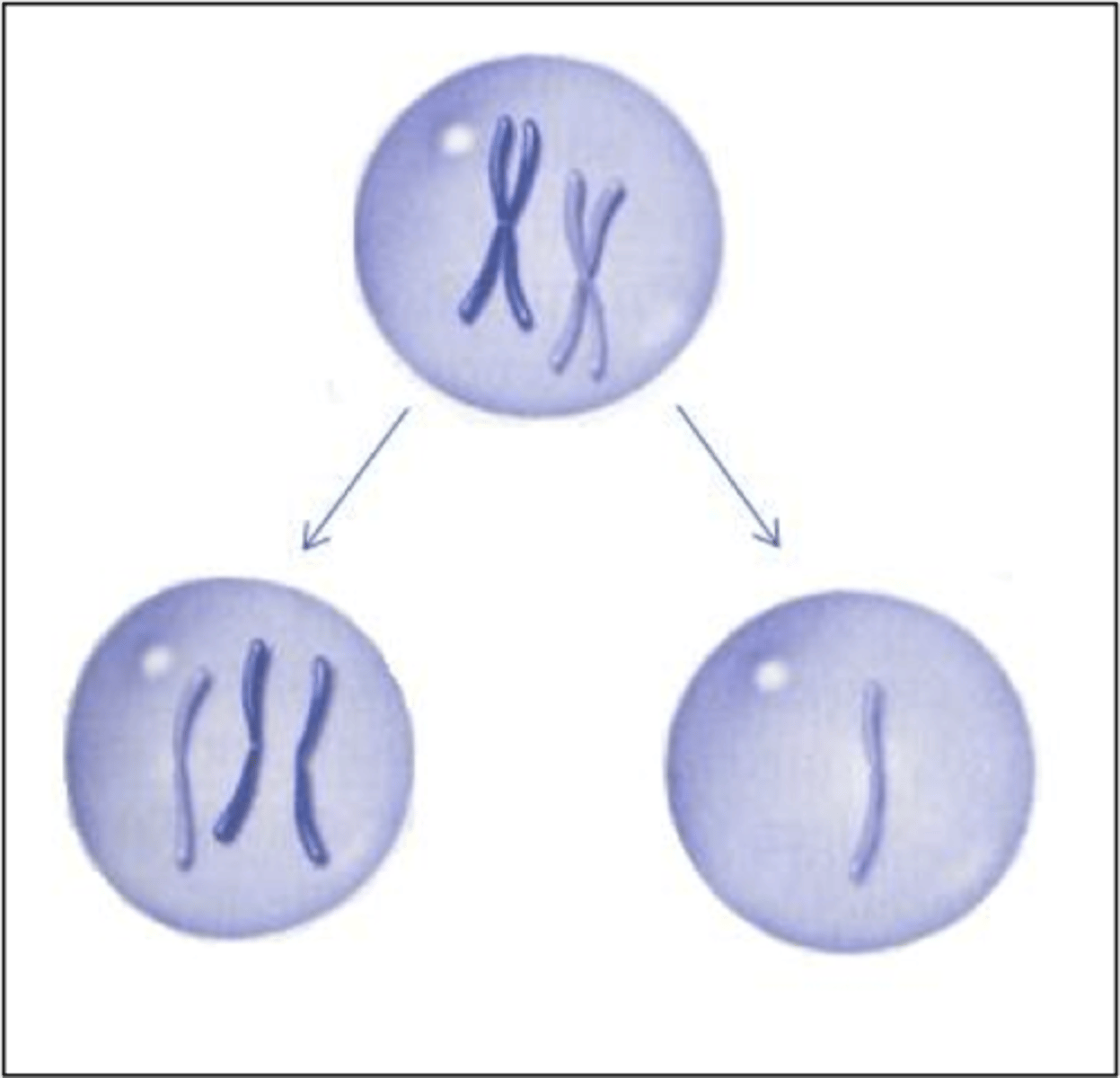
What is nondisjunction?
Nondisjunction is the failure of chromosomes to separate properly during cell division.
When can nondisjunction occur?
Nondisjunction can occur during anaphase of mitosis, meiosis I, or meiosis II.
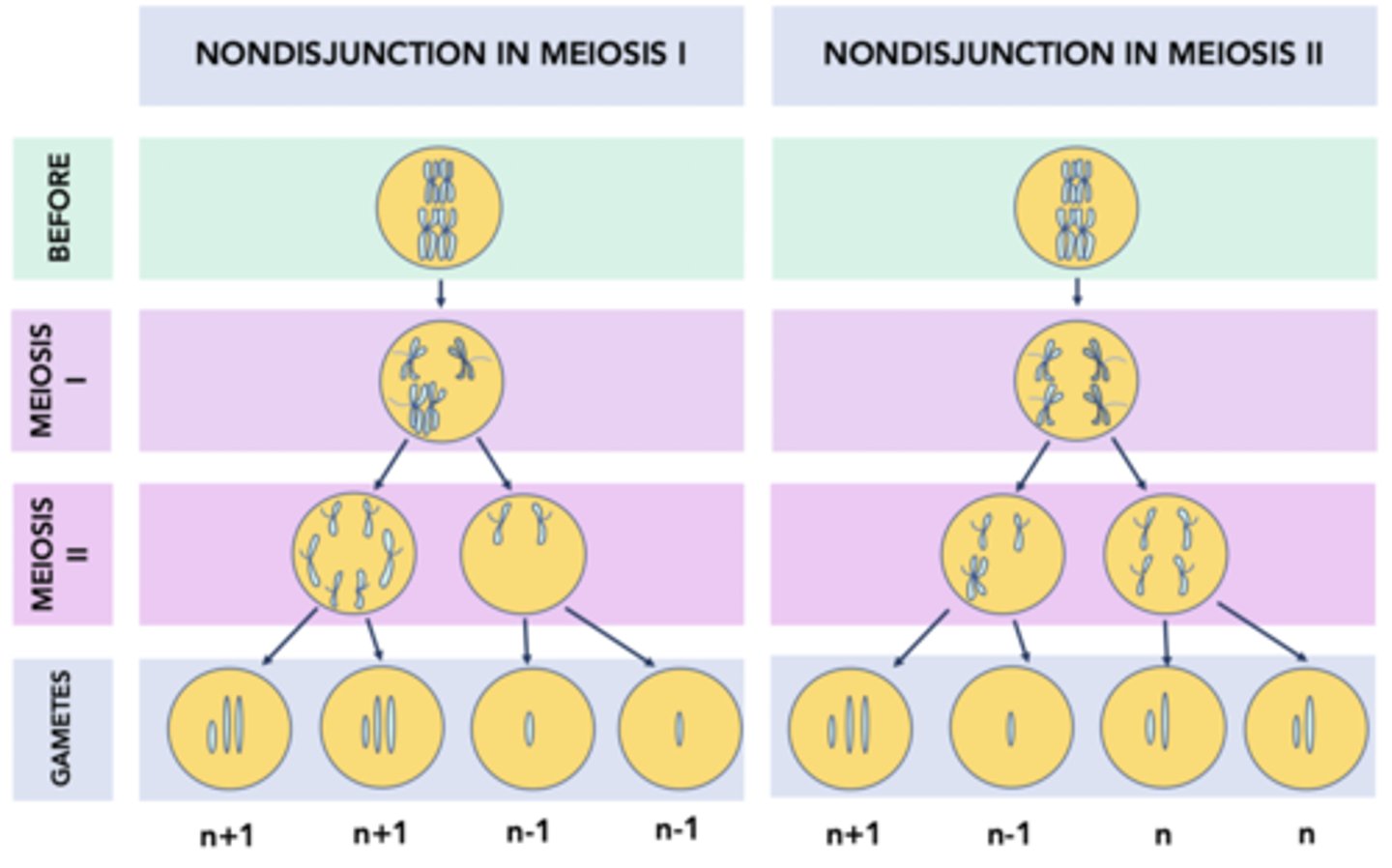
What happens during anaphase in relation to nondisjunction?
During anaphase, sister chromatids (or homologous chromosomes for meiosis I) fail to separate and move to opposite poles of the cell.
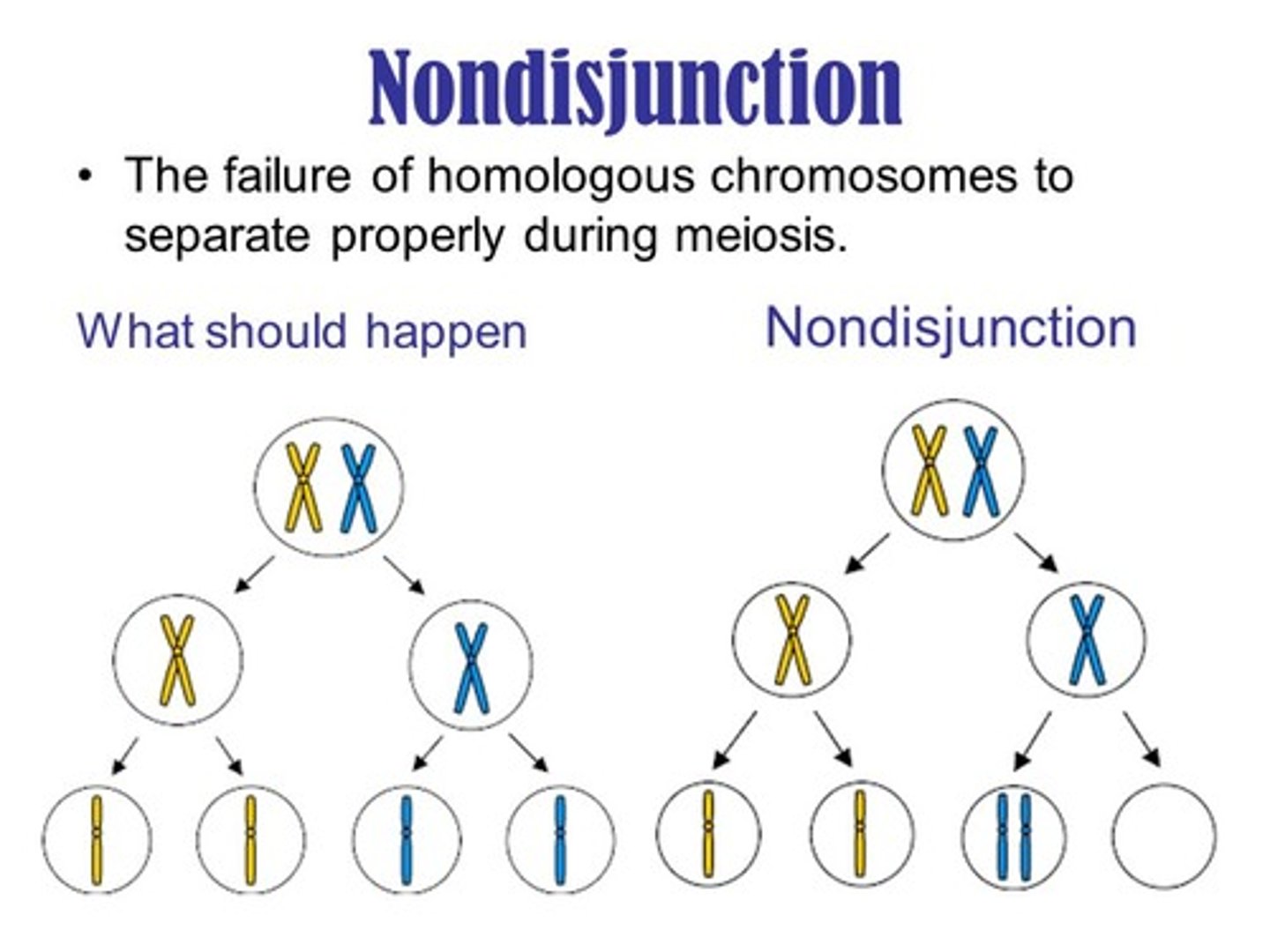
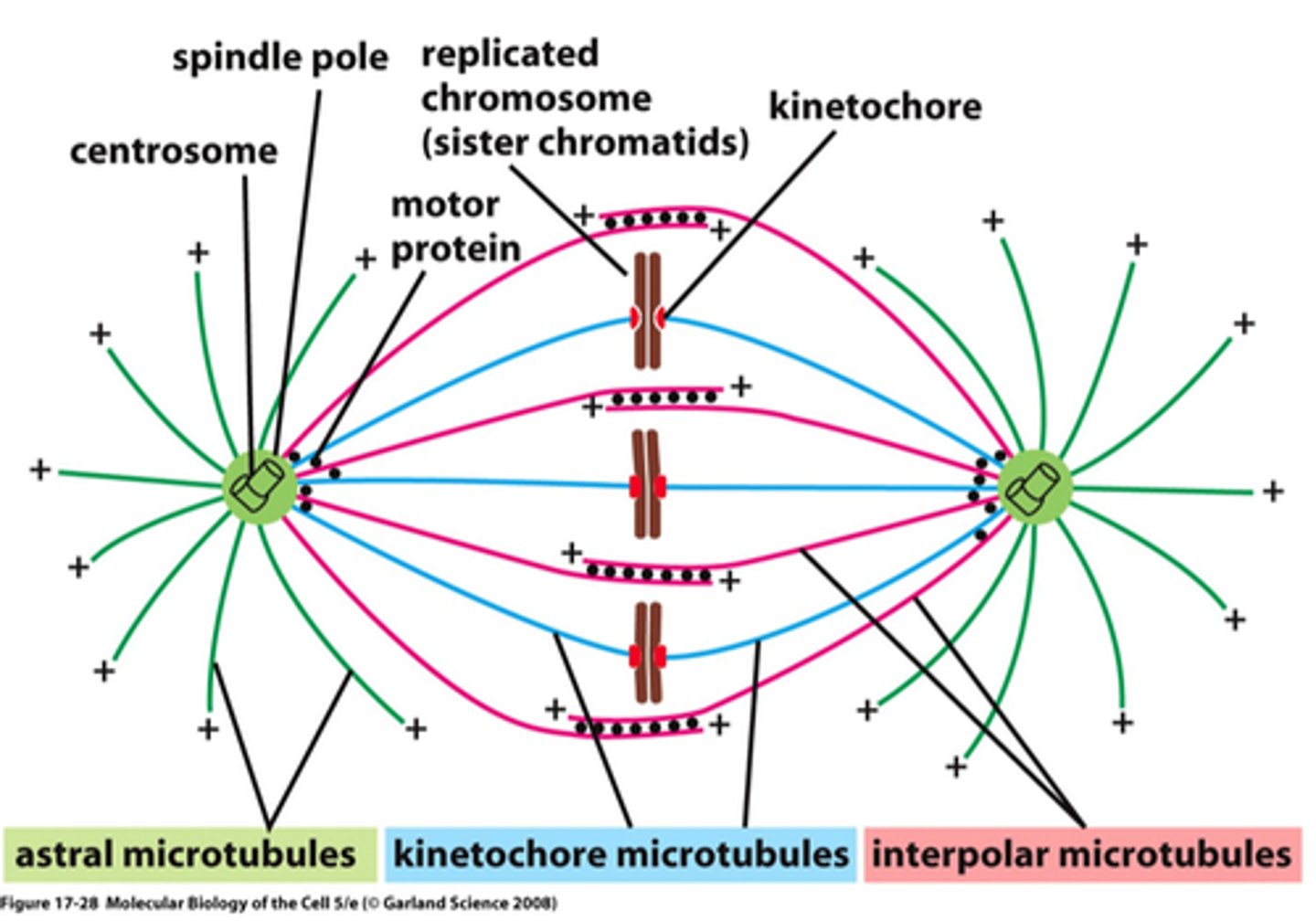
What pulls chromosomes to opposite poles during anaphase?
Microtubules
Nondisjunction consequence
Abnormal chromosome numbers
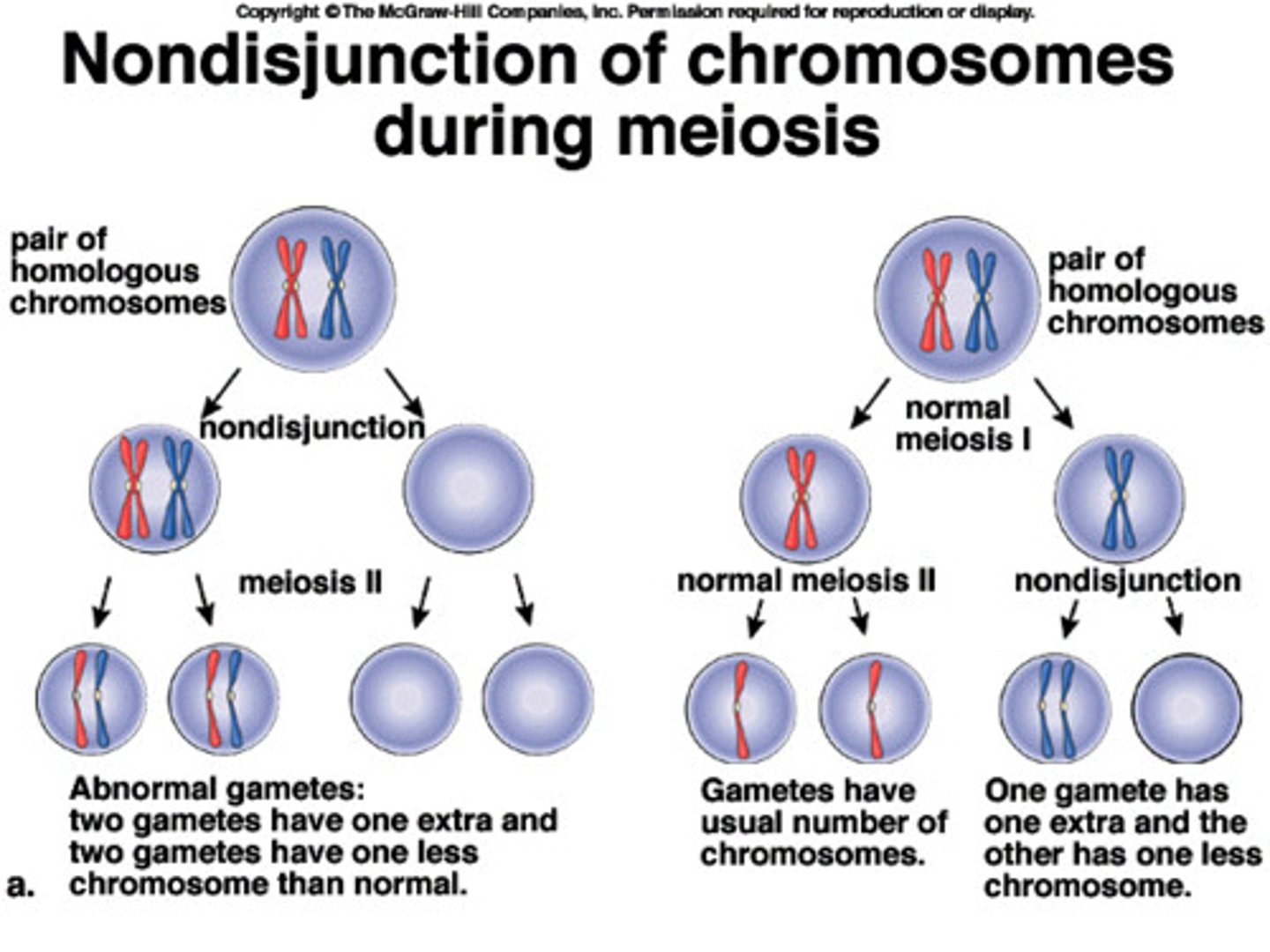
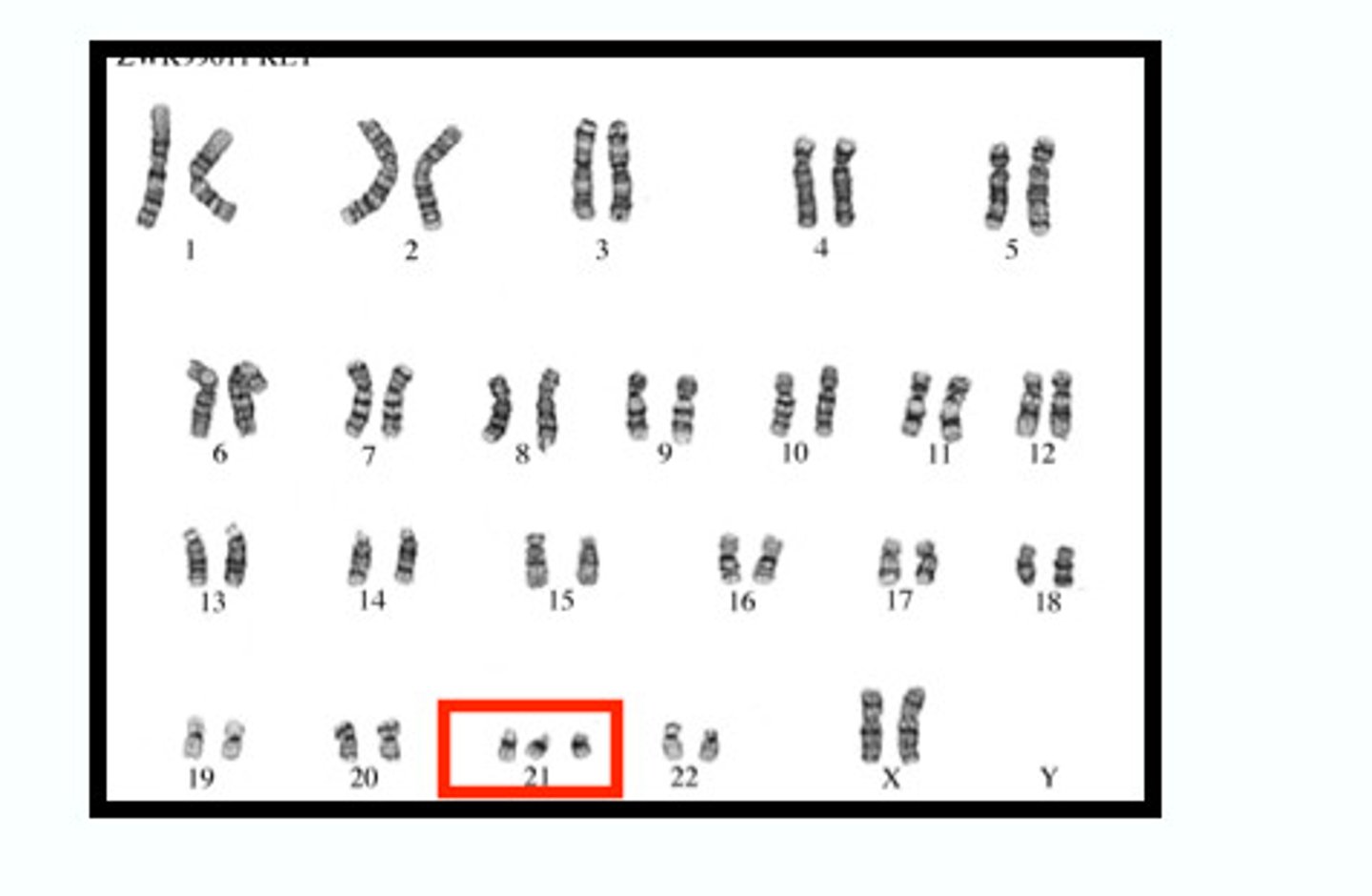
Genetic cause of Down syndrome
An extra copy of chromosome 21
Chromosomes randomly align, increasing genetic variation
Independent assortment
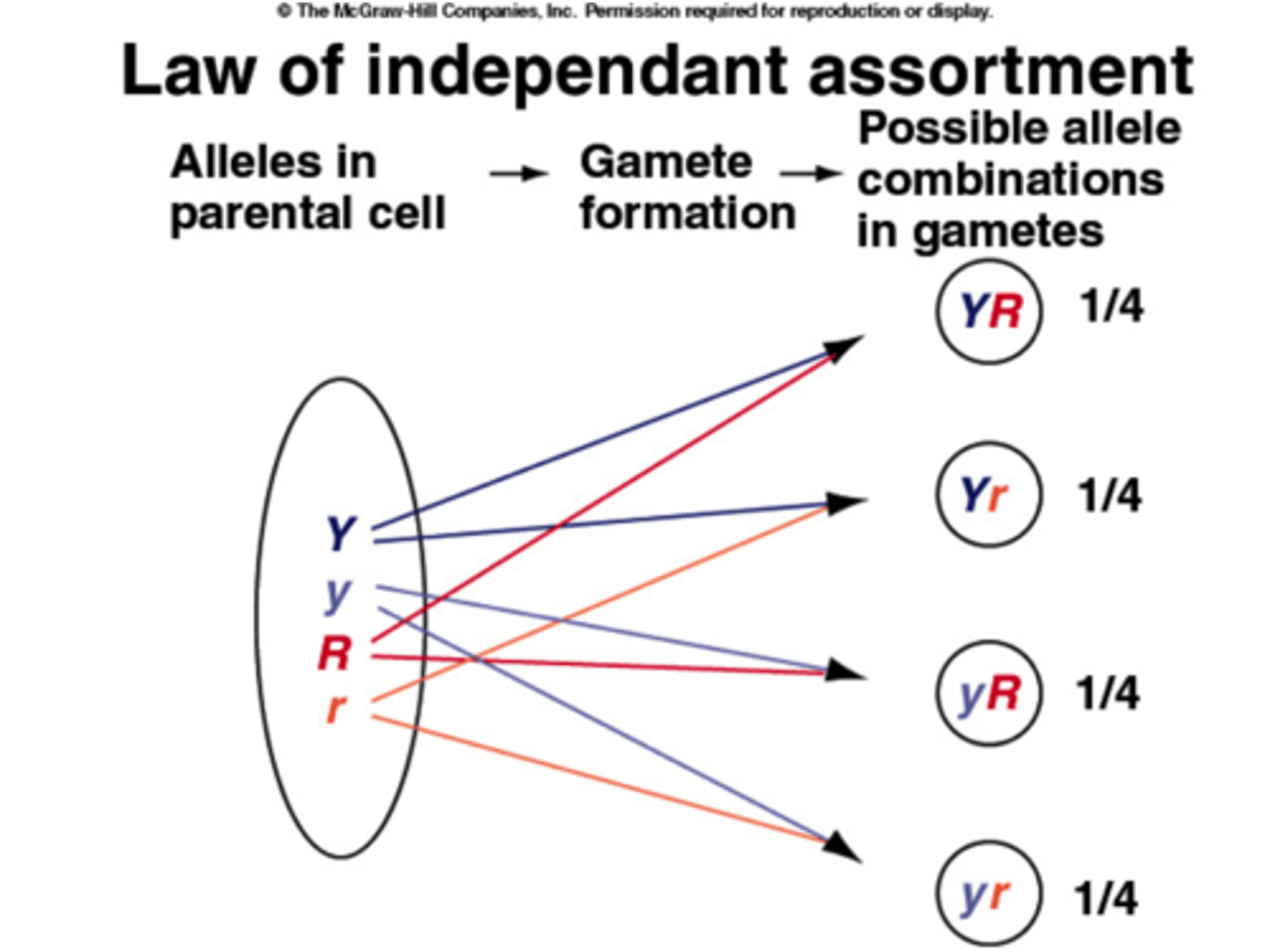
When does independent assortment occur?
metaphase I of meiosis I
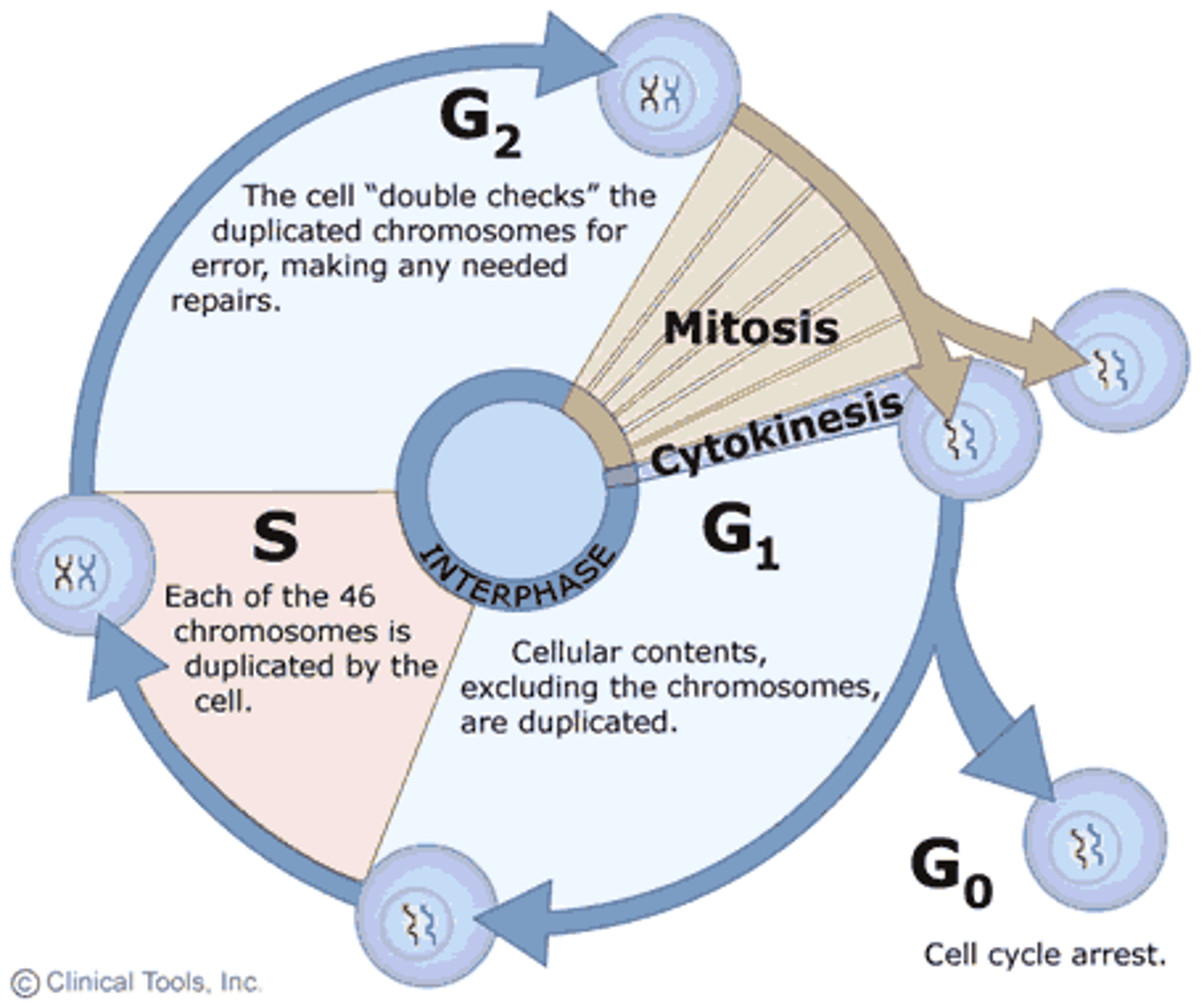
When does DNA replication occur?
Interphase. Meiosis is preceded by an interphase which is nearly identical to the interphase preceding mitosis. During interphase, the DNA of the chromosomes is replicated (during S phase).
What is the difference between recombinant and non recombinant gametes?
Two types of gametes are possible when following genes on the same chromosomes. If crossing over does not occur, the products are parental gametes. If crossing over occurs, the products are recombinant gametes.
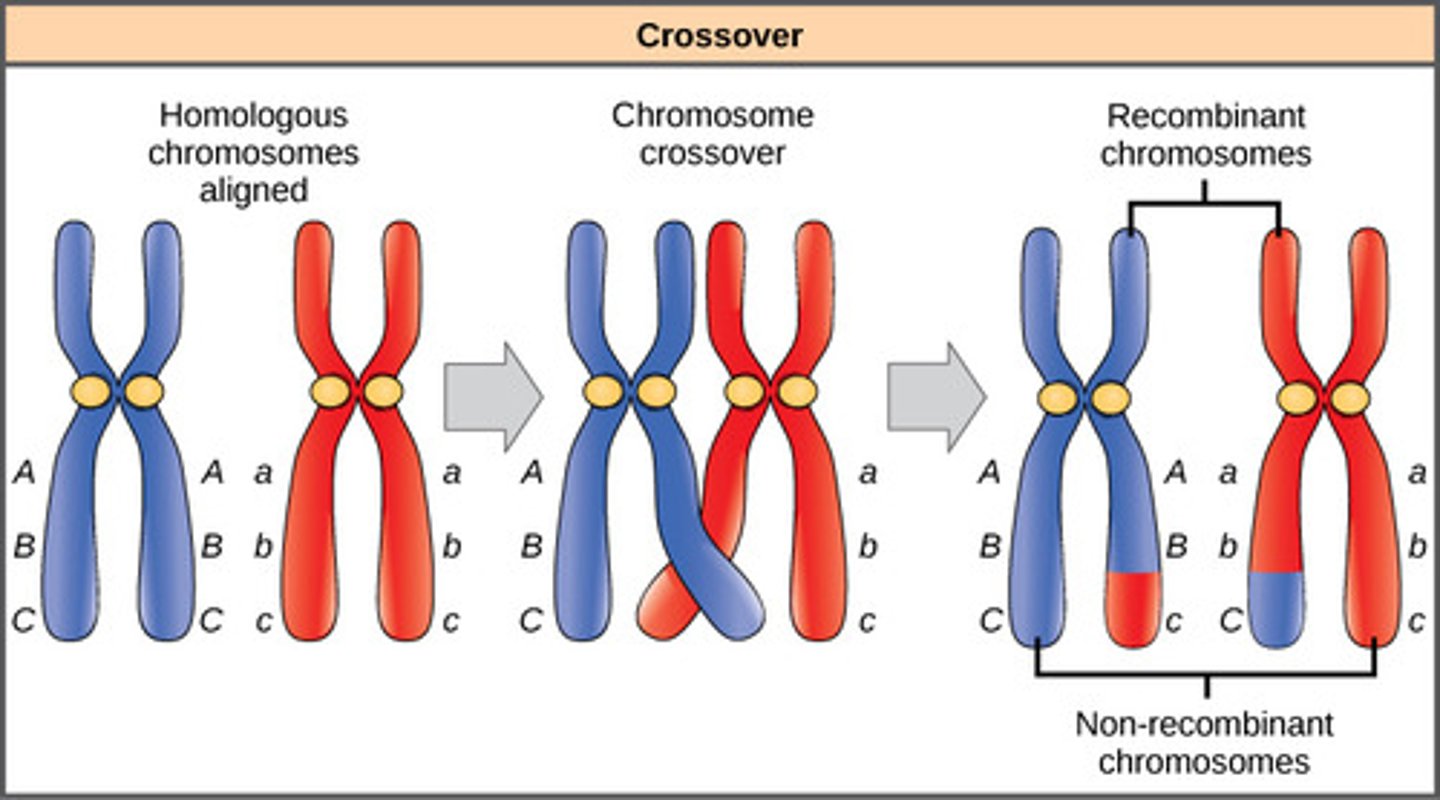
Processes contributing to genetic diversity
The primary processes contributing to genetic diversity are: mutation, gene flow (migration), random mating, crossing over (genetic recombination) during meiosis, and independent assortment of chromosomes during meiosis; essentially, any mechanism that generates new allele combinations or introduces new genetic material into a population, allowing for variation in traits among individuals within a species.

Do homologous chromosomes align in mitosis metaphase?
In mitosis, homologous chromosomes do not align with each other; instead, individual replicated chromosomes (sister chromatids) line up at the metaphase plate
Prophase I (Meiosis)
homologous chromosomes pair up and form tetrads, crossing over occurs