BISC 207 UDEL EXAM #1
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
Characteristics of living things
Reaction to or interact with the environment, Reproduce, Cellular Respiration (use energy), Growth/Development, Complex Structure, Evolves
Protist
a single cell eurkaryote
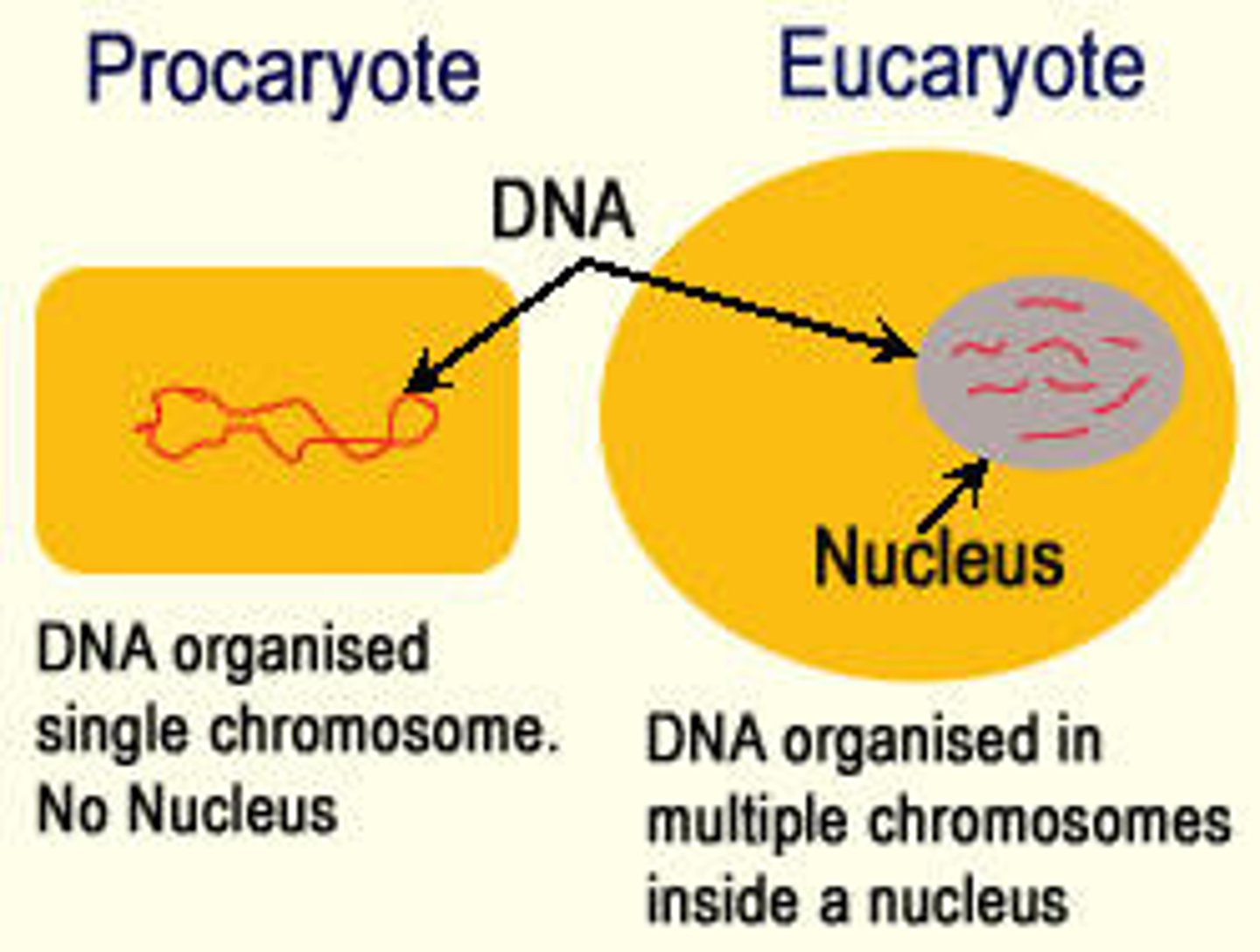
Eurkaryotic Cell
more complex, larger (yeast)
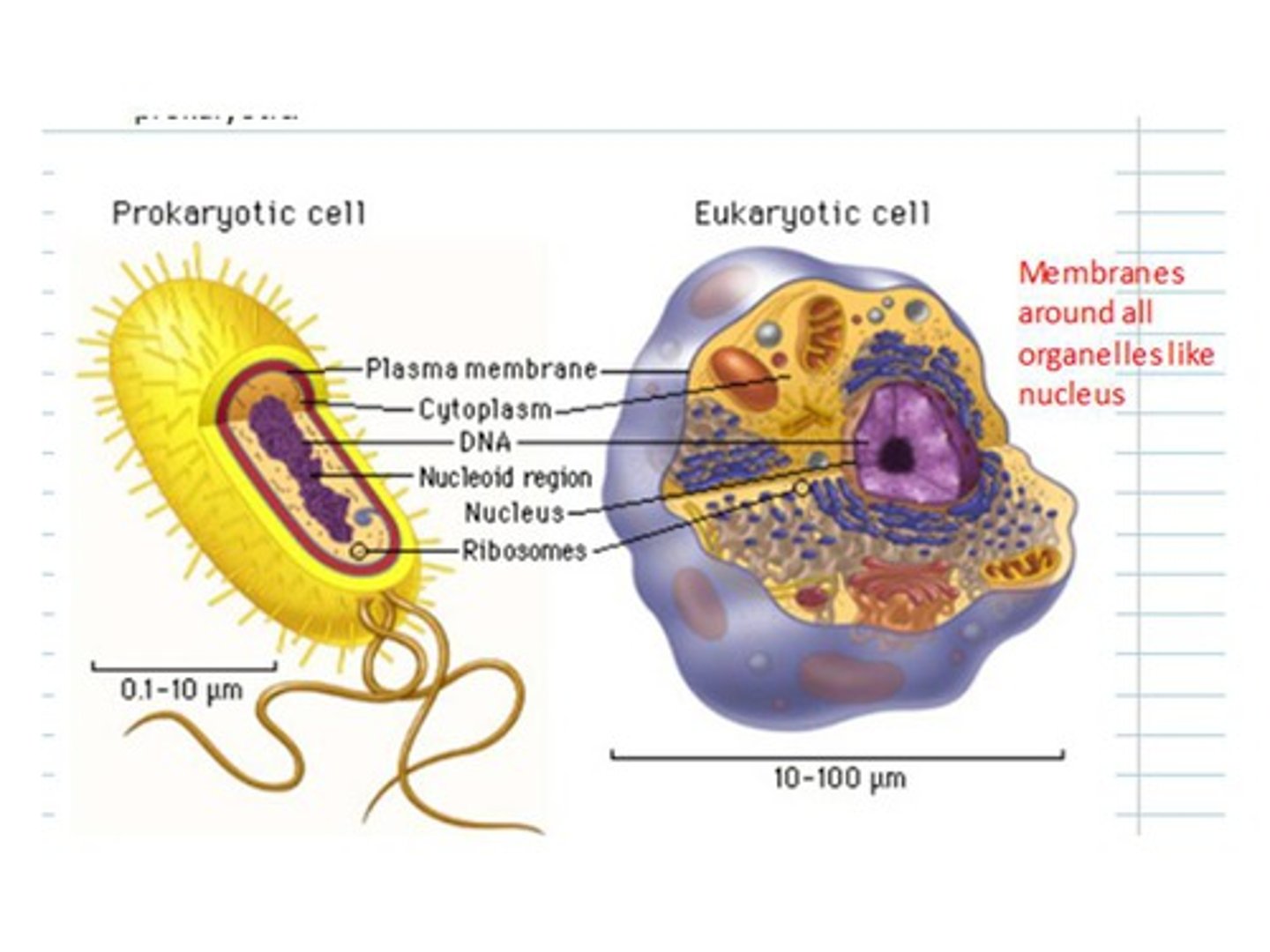
Prokaryotic Cell
simple, small (bacteria)
Cell Functions
Contain and use info, are bounded by a plasma membrane, obtain and use energy from the environment
Nonpolar Covalent Bonds
electrons shared equally between the bonding atoms
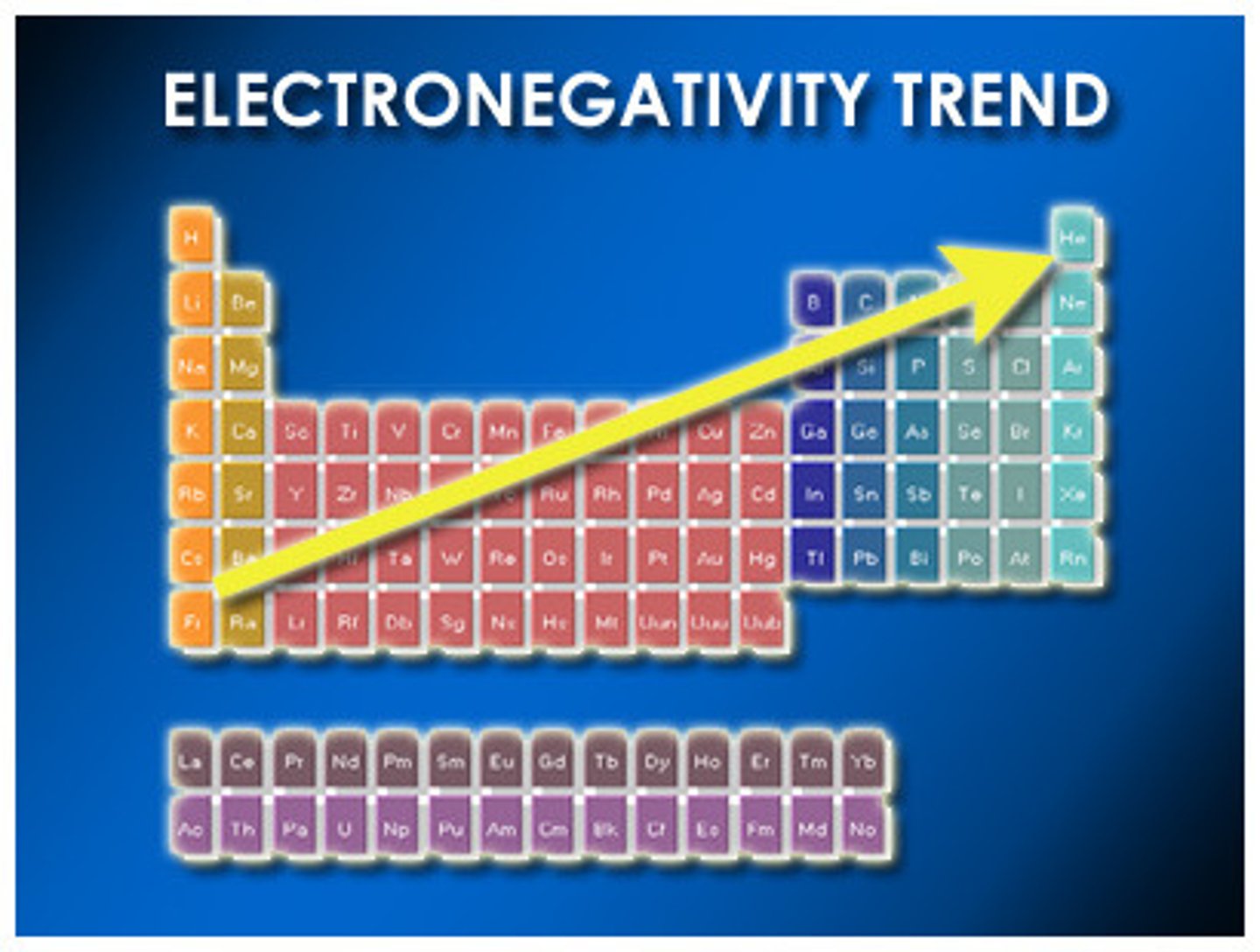
Electronegativity
an atom's ability to attract electrons. Scales .7-4.0
H=2.1, C=2.5, N=3.0, O=3.5
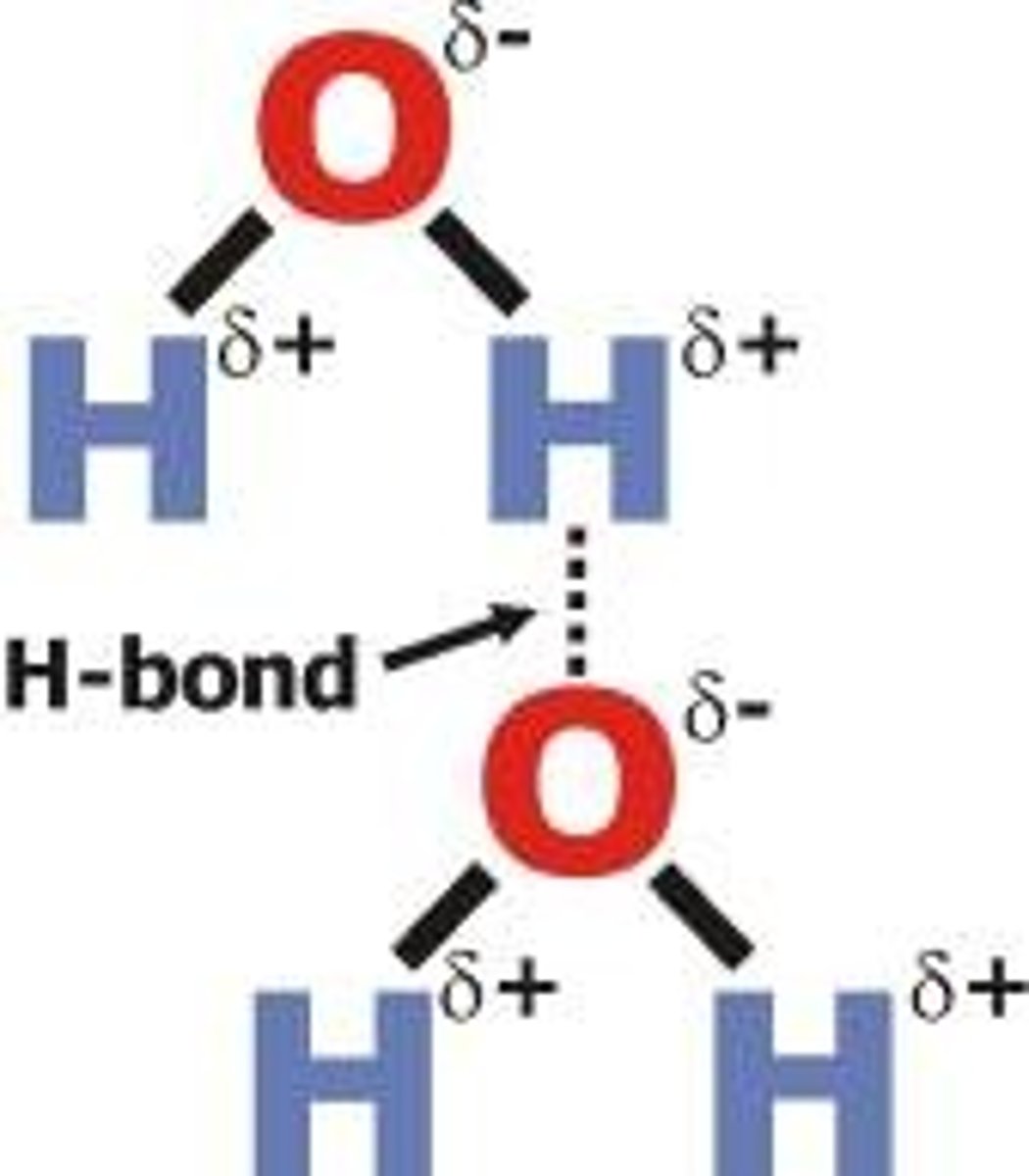
Hydrogen
in a polar molecule attracts an electronegative atom in another polar molecule. Weak bonds, many H bonds are strong.
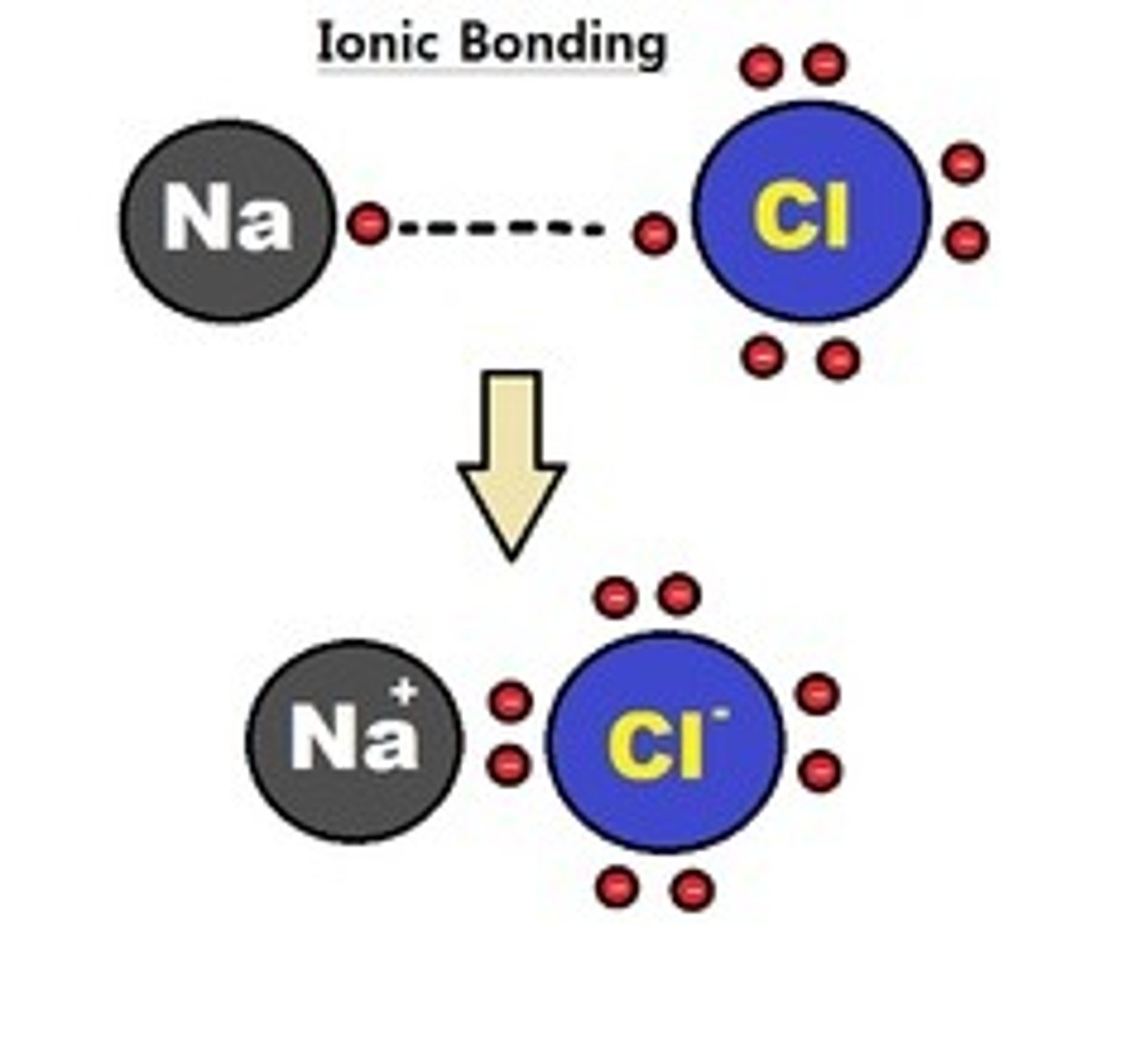
Ionic Bonds
EN- 2.0-2.3. Atoms interact because of the attraction of opposite charges. High EN atom attracts an atom from the low EN atom
Water
Dipole-charge distribution across the molecule. H bonds form between molecules. Primary solvent. Thermally stable, hard to change its temperature. Freezing/Boiling point changes when solute added
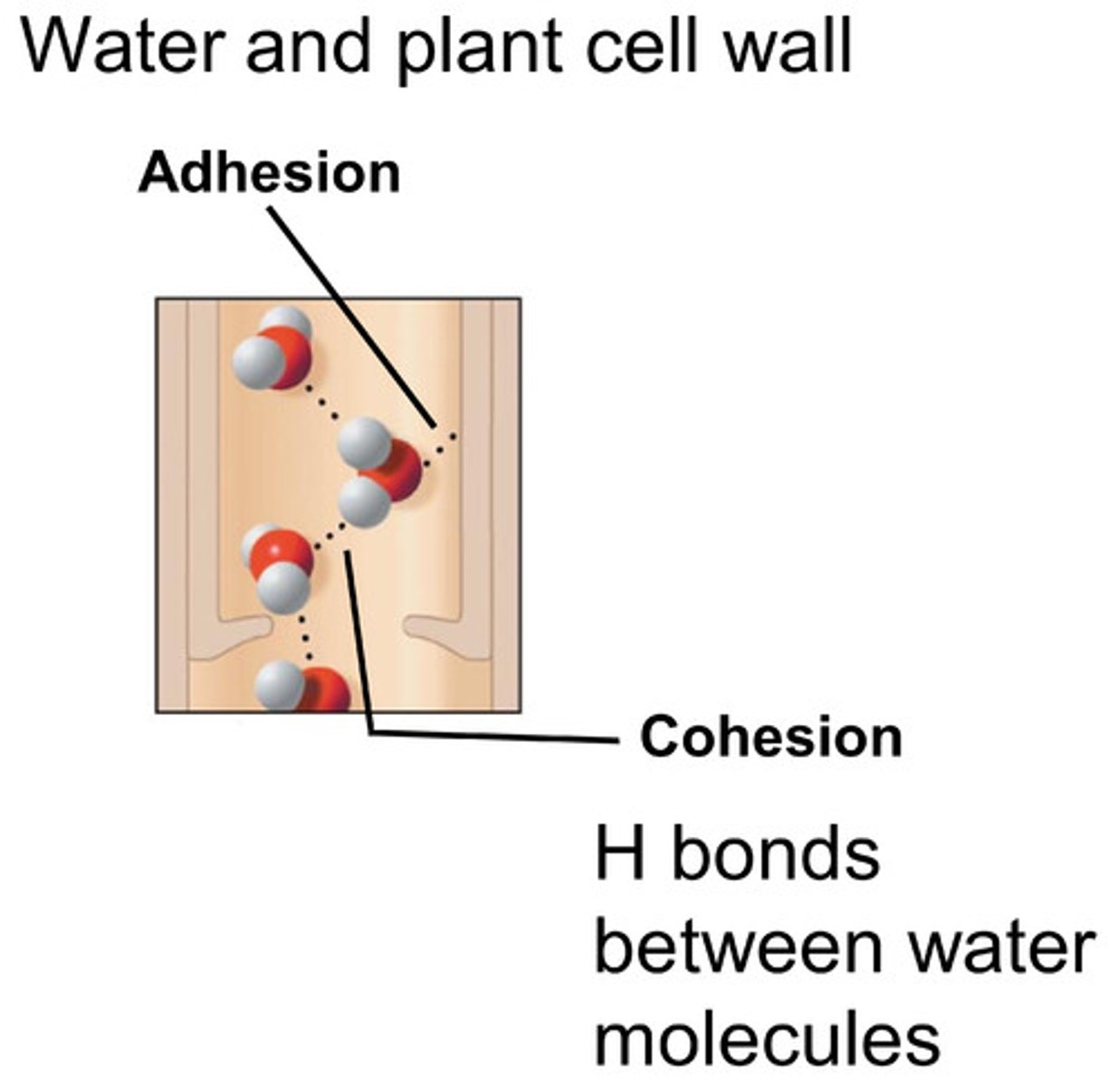
Cohesion
water molecules are attracted to each other
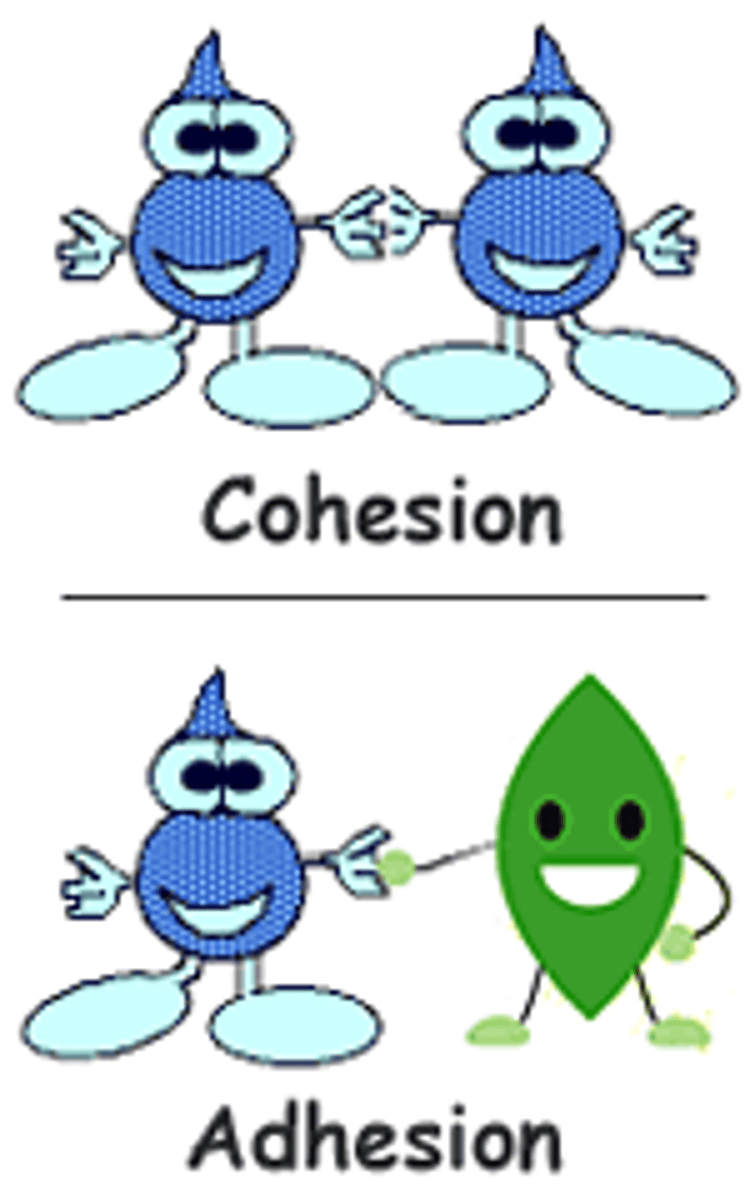
Adhesion
Water molecules are attracted to other types of molecules
Hydrophilic Molecules
contain many polar bonds. Like to interact with water
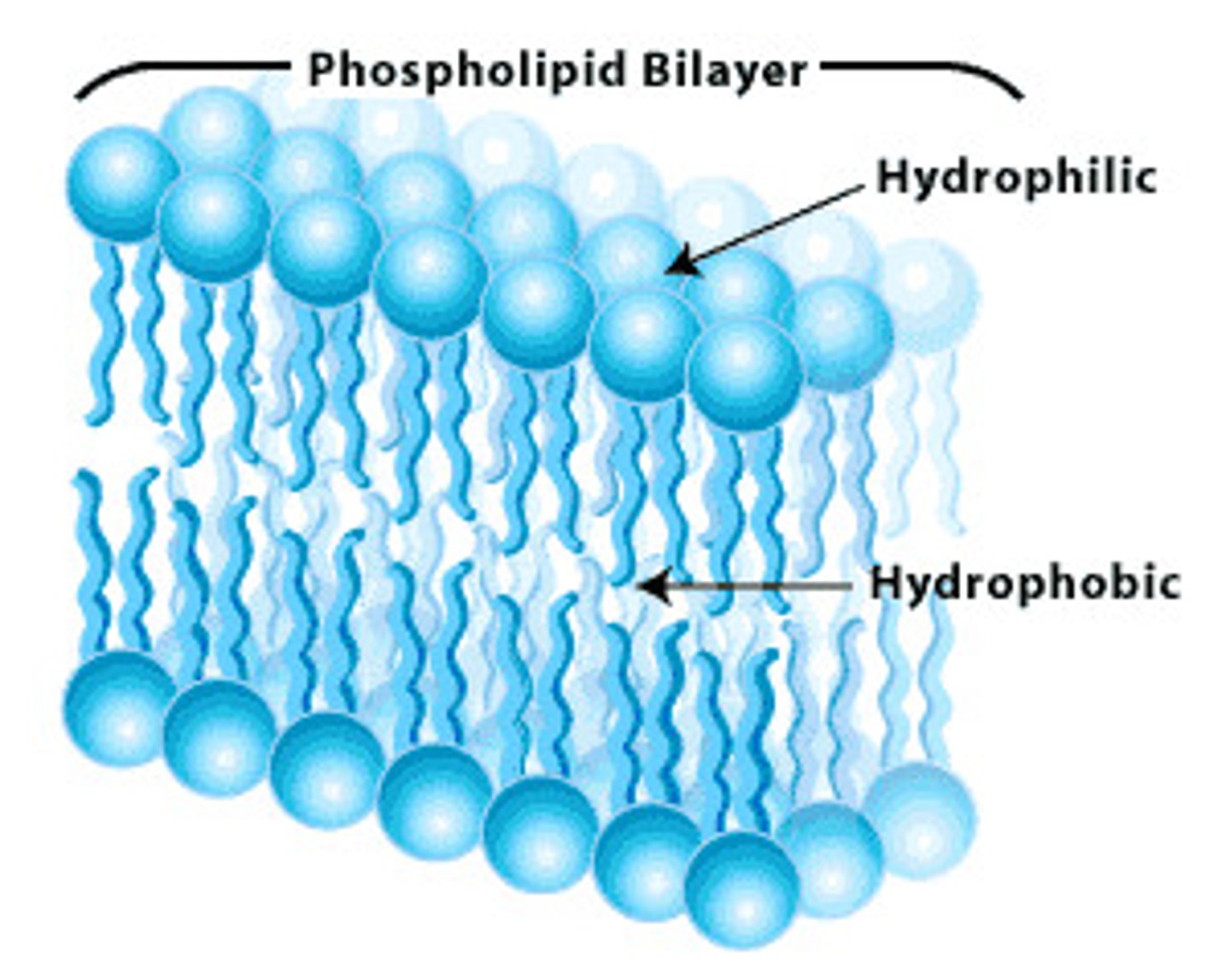
Hydrophobic Molecules
don't contain many polar bonds. Don't like to interact with water
pH
-log[H+]. Organisms regulate pH. Can vary within different cell compartments
Acids
add H+ into the solution
Bases
lower H+ concentration in solution
Organic molecules
4 types: proteins, nucleic acids, carbs, lipids
C-C & C-H bonds
nonpolar
C-O & O-H bonds
polar
Isomers
molecules that have the same chemical formula but different structures
Proteins
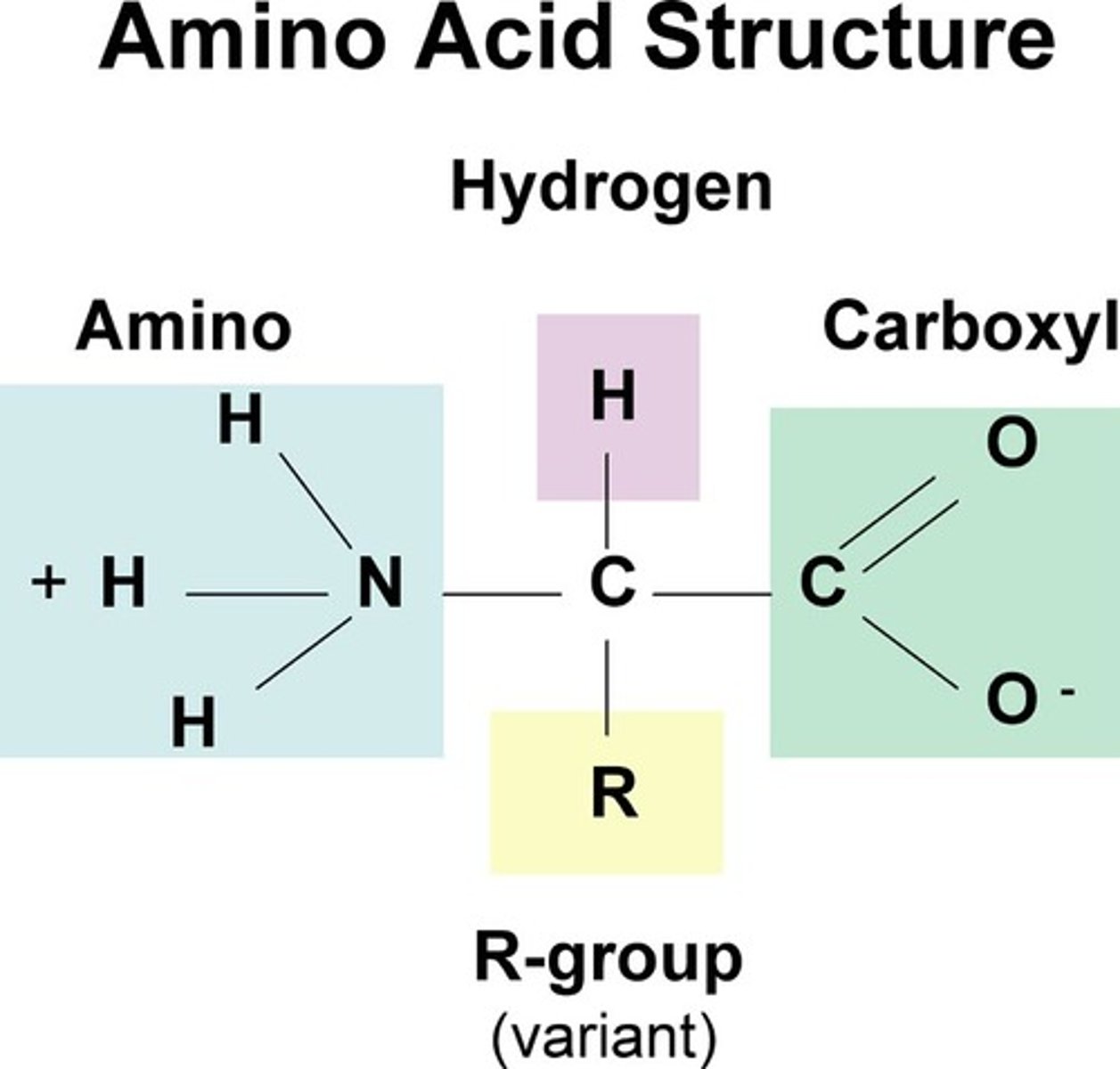
contain C,H,N,O & S. pH=7. Amino group=accepts a H+ (base). Carboxyl group donates a H+ (acid). Polymer
Polypeptide
a linear chain of COVALENTLY liked amino acids. Amino (N)-Terminus, Carboxyl (C)-Terminus attach to end of polypeptide
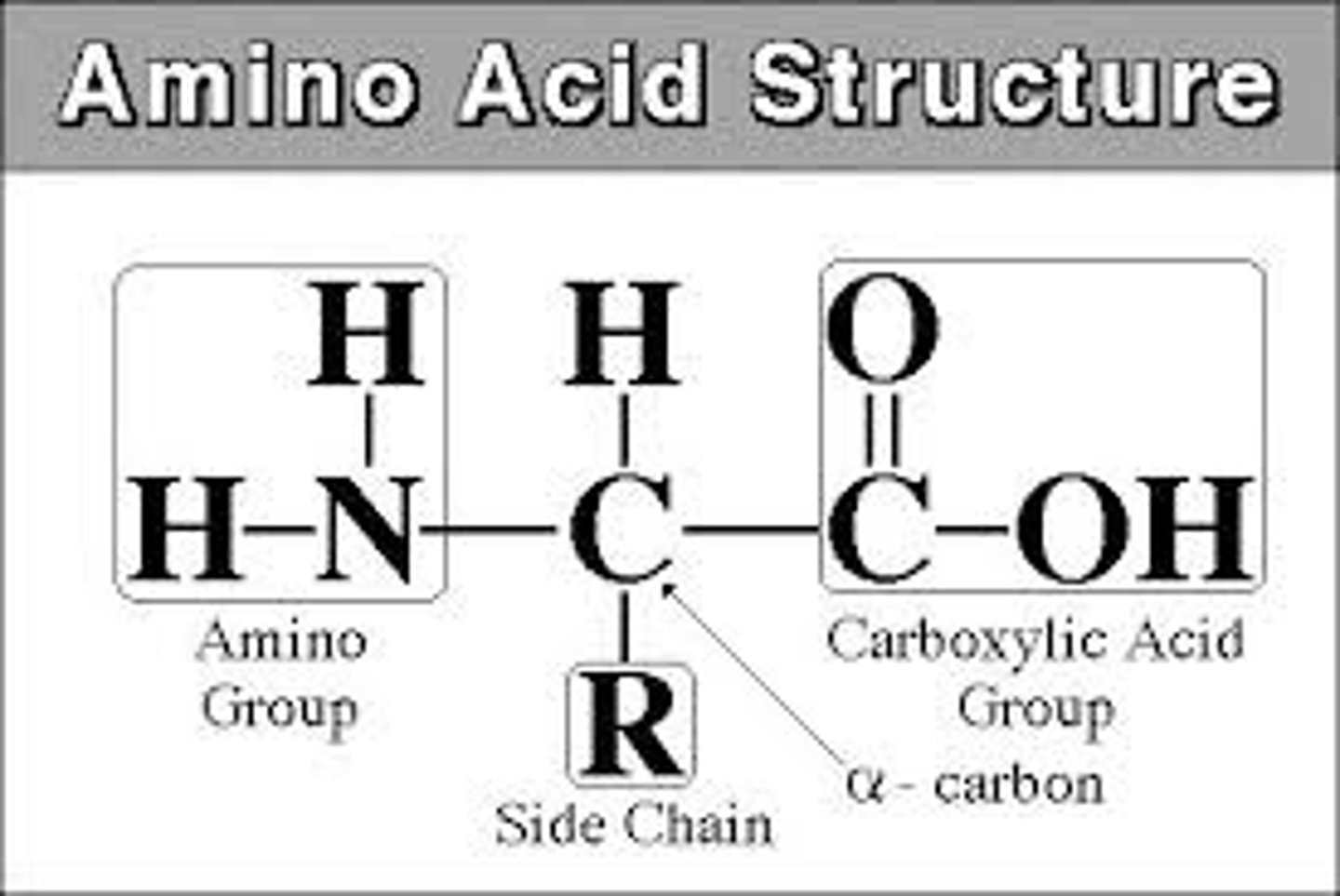
Amino acid
monomer of proteins. Tetrahedral Shape. 20 types. Made up of an amino group, side chain (R group), alpha carbon, carboxyl group
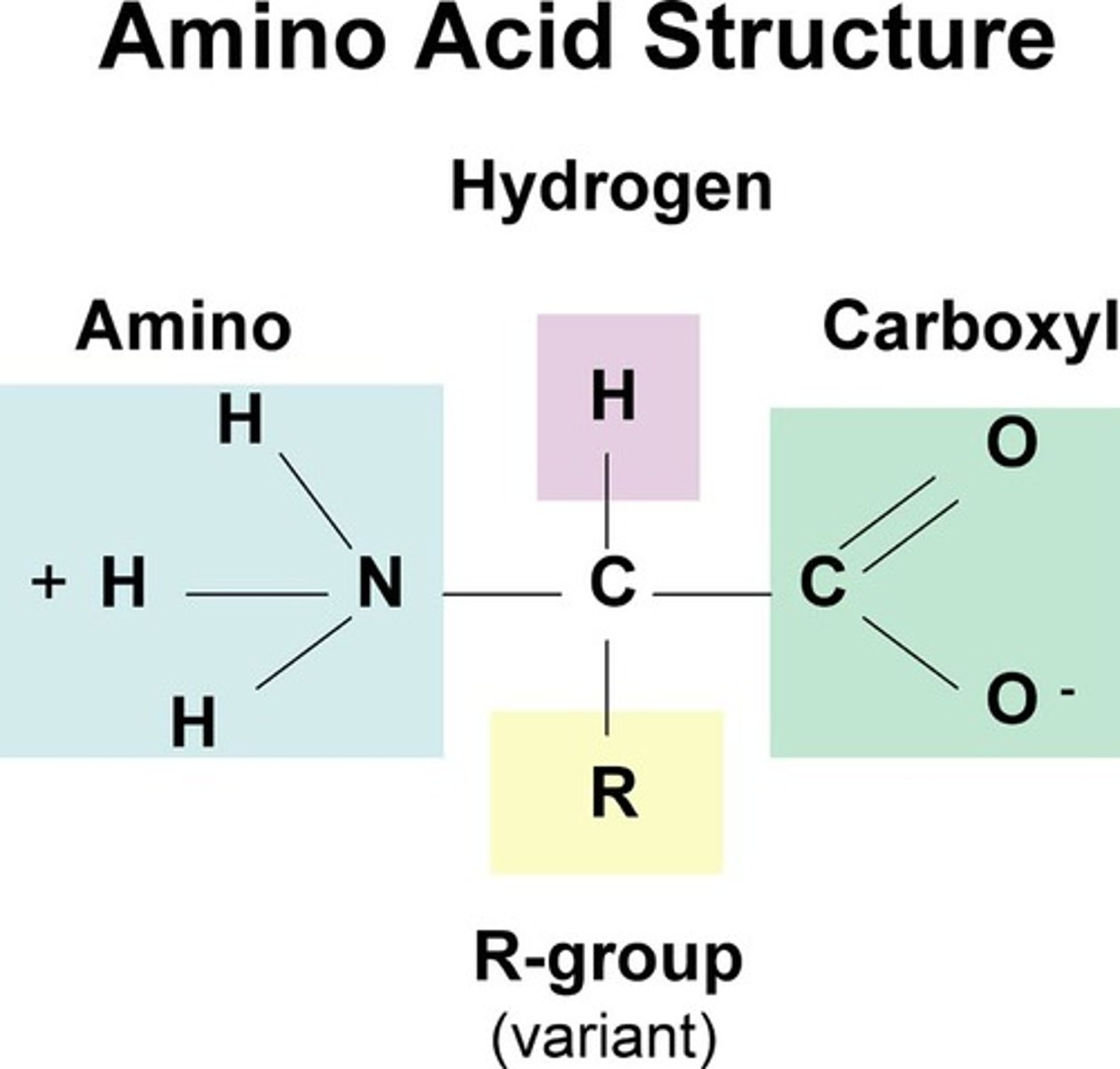
Side Chains (R Group)
make amino acids different. use electronegativity to determine polarity of the amino acid side chains. can point in different directions
Nucleic Acid
polymer. store, express, transmit genetic information
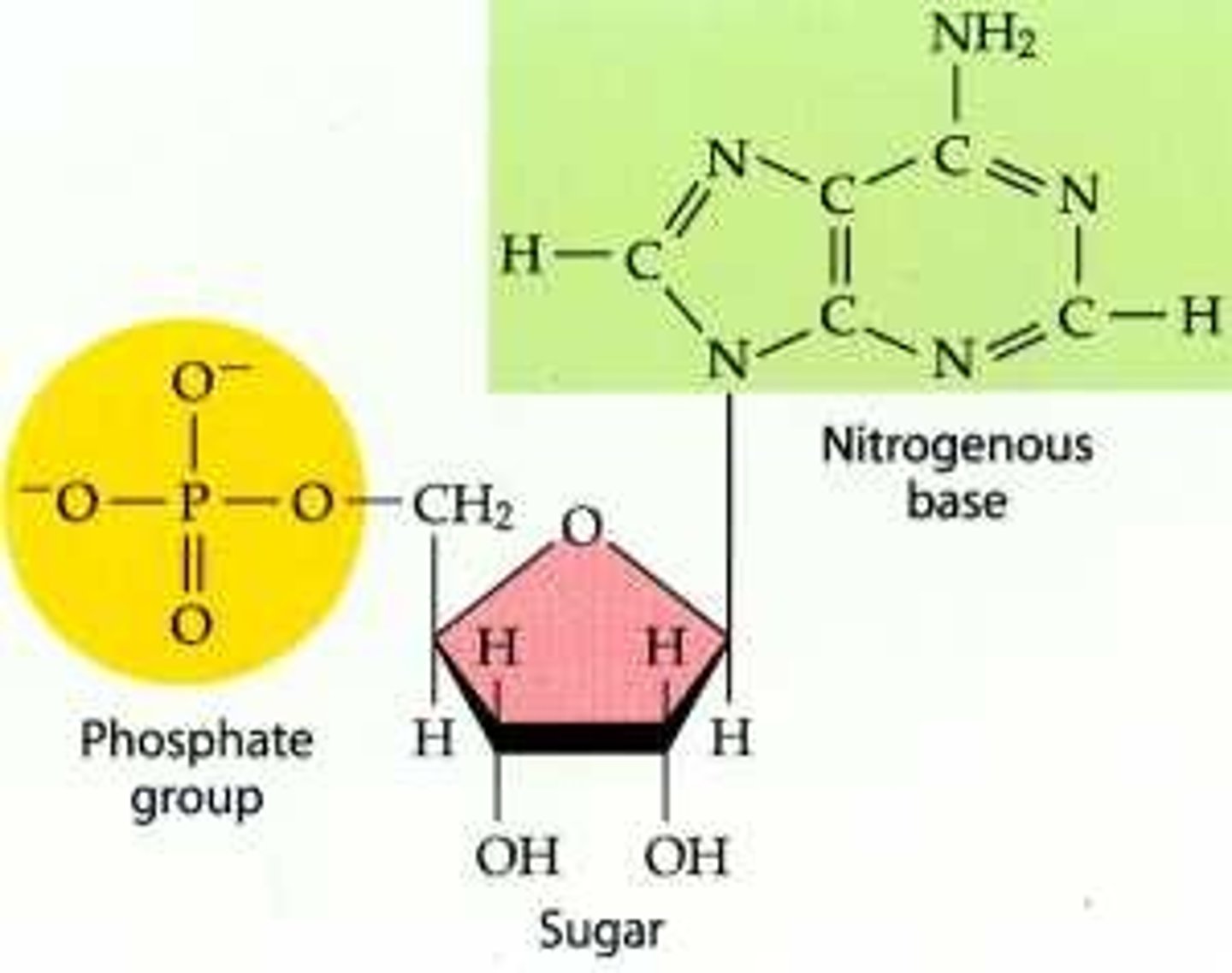
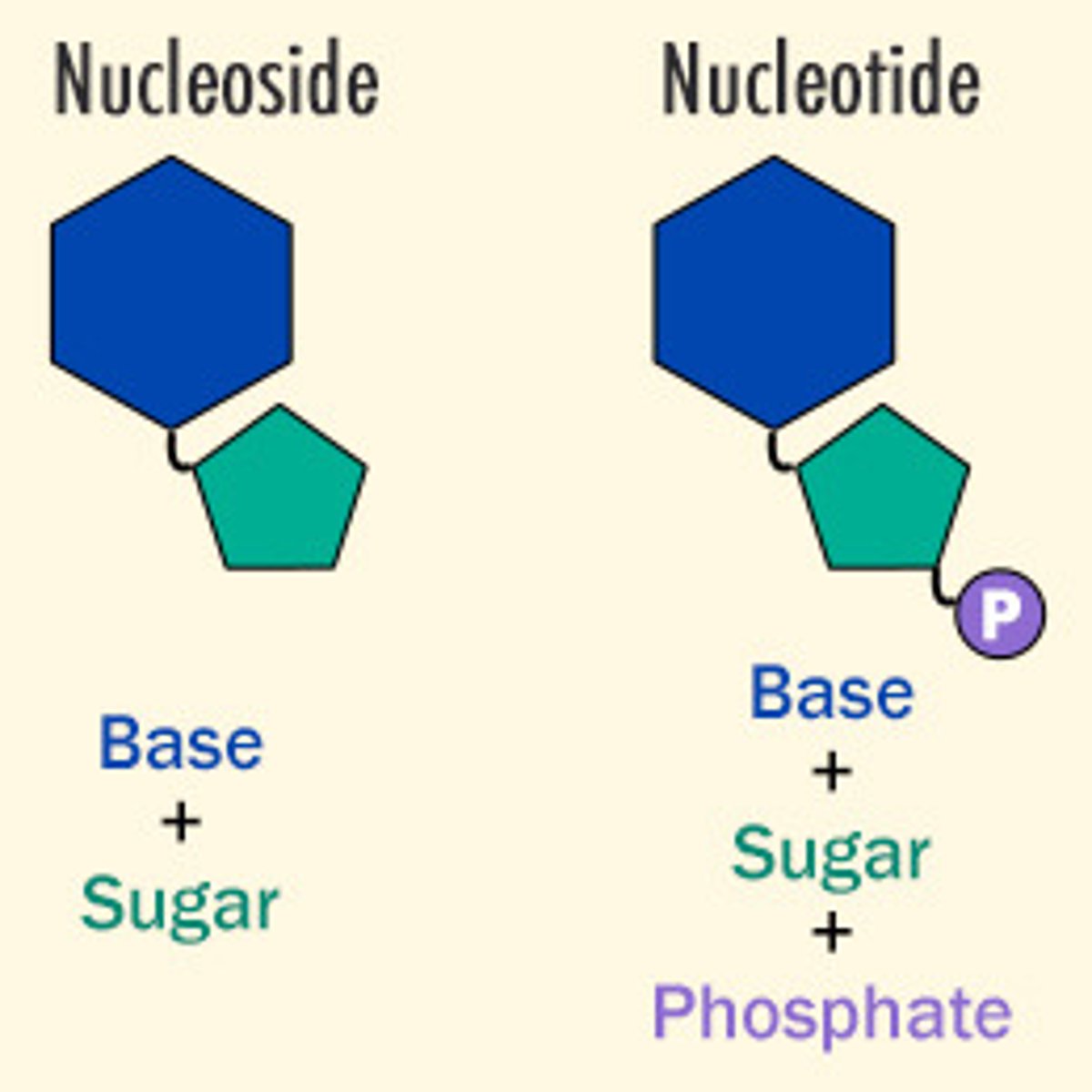
Nucleotide
Monomer. 3 parts: phosphate group, 5 carbon (deoxyribose) sugar, N-base
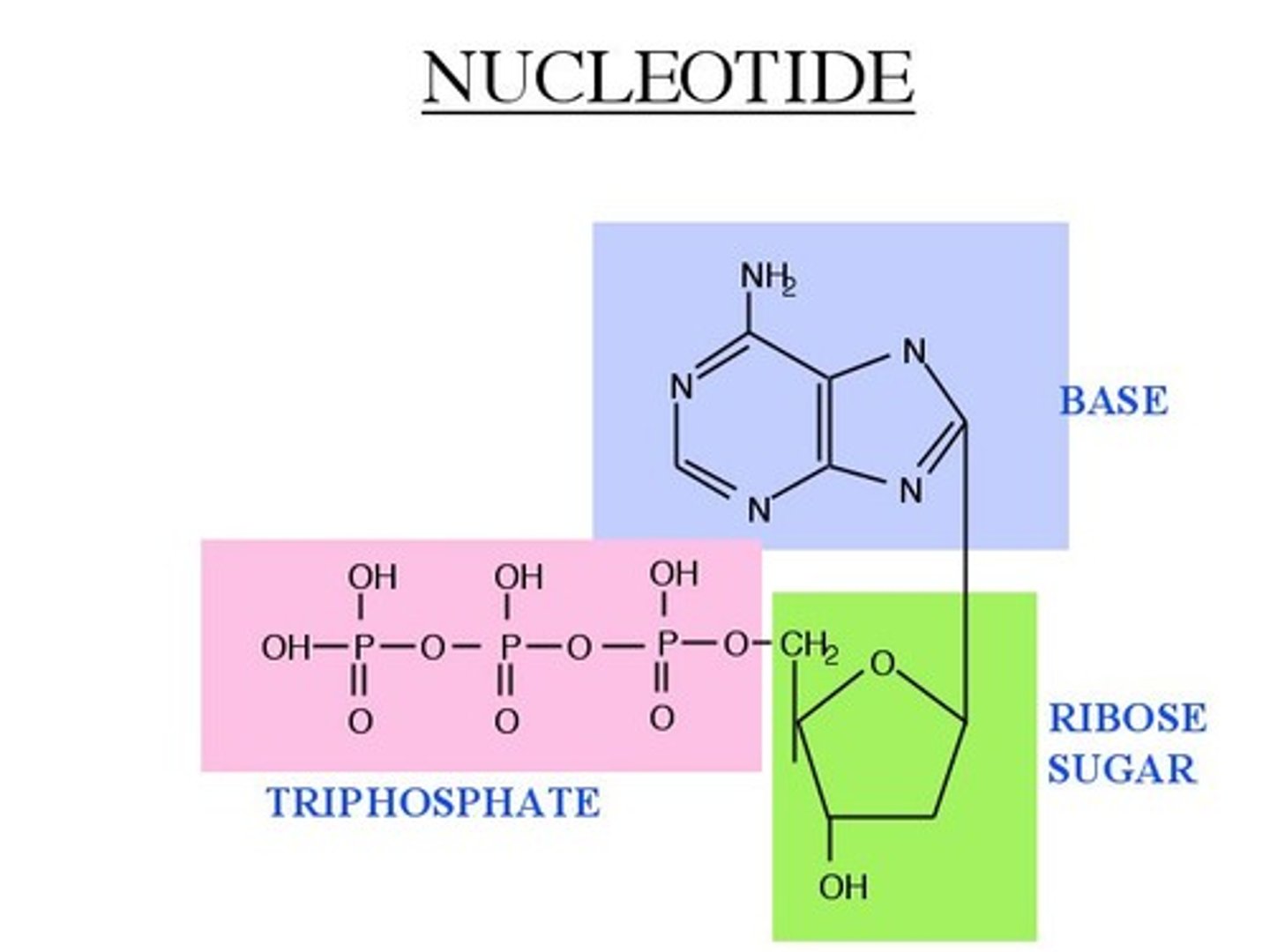
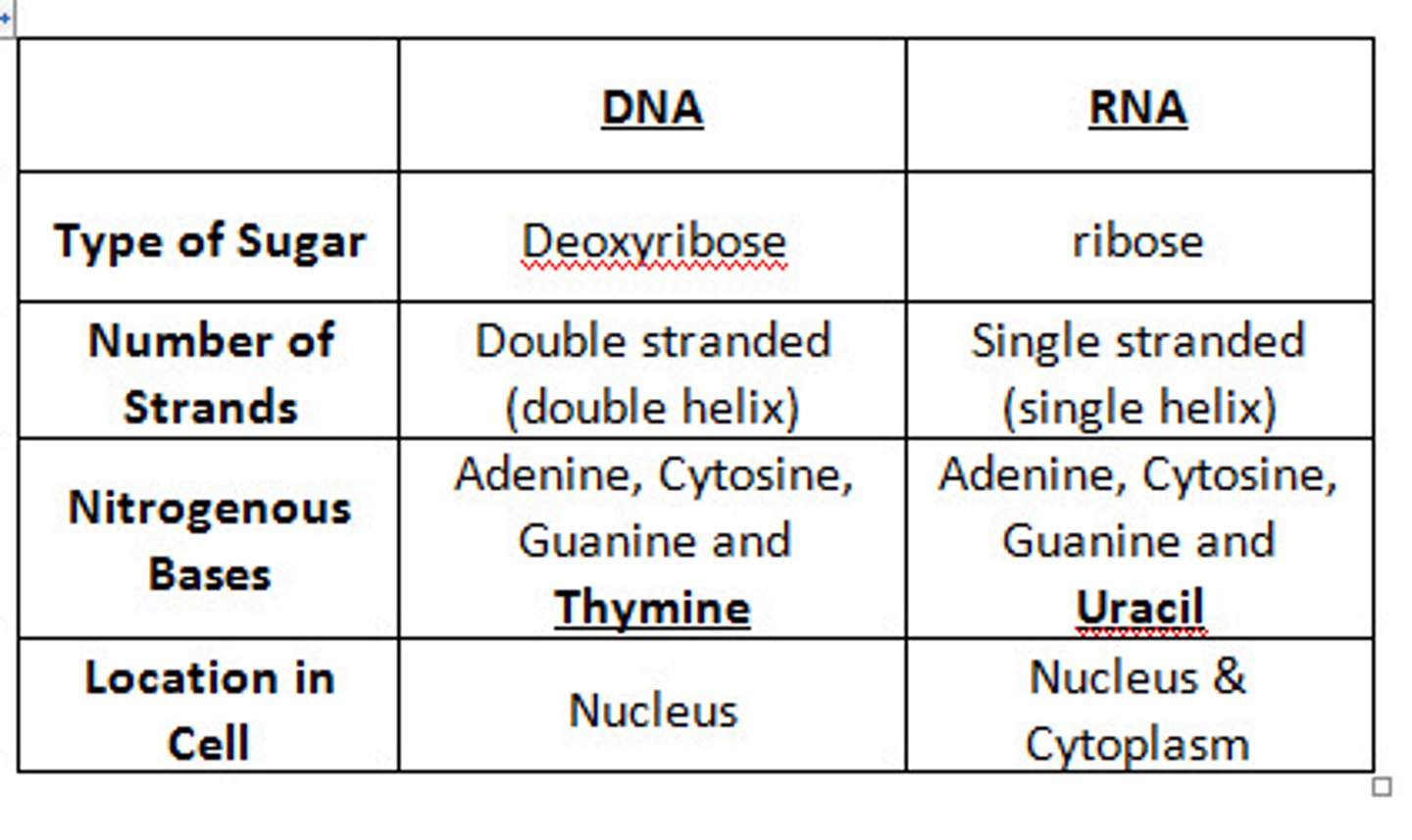
DNA & RNA
polymers made from nucleotides
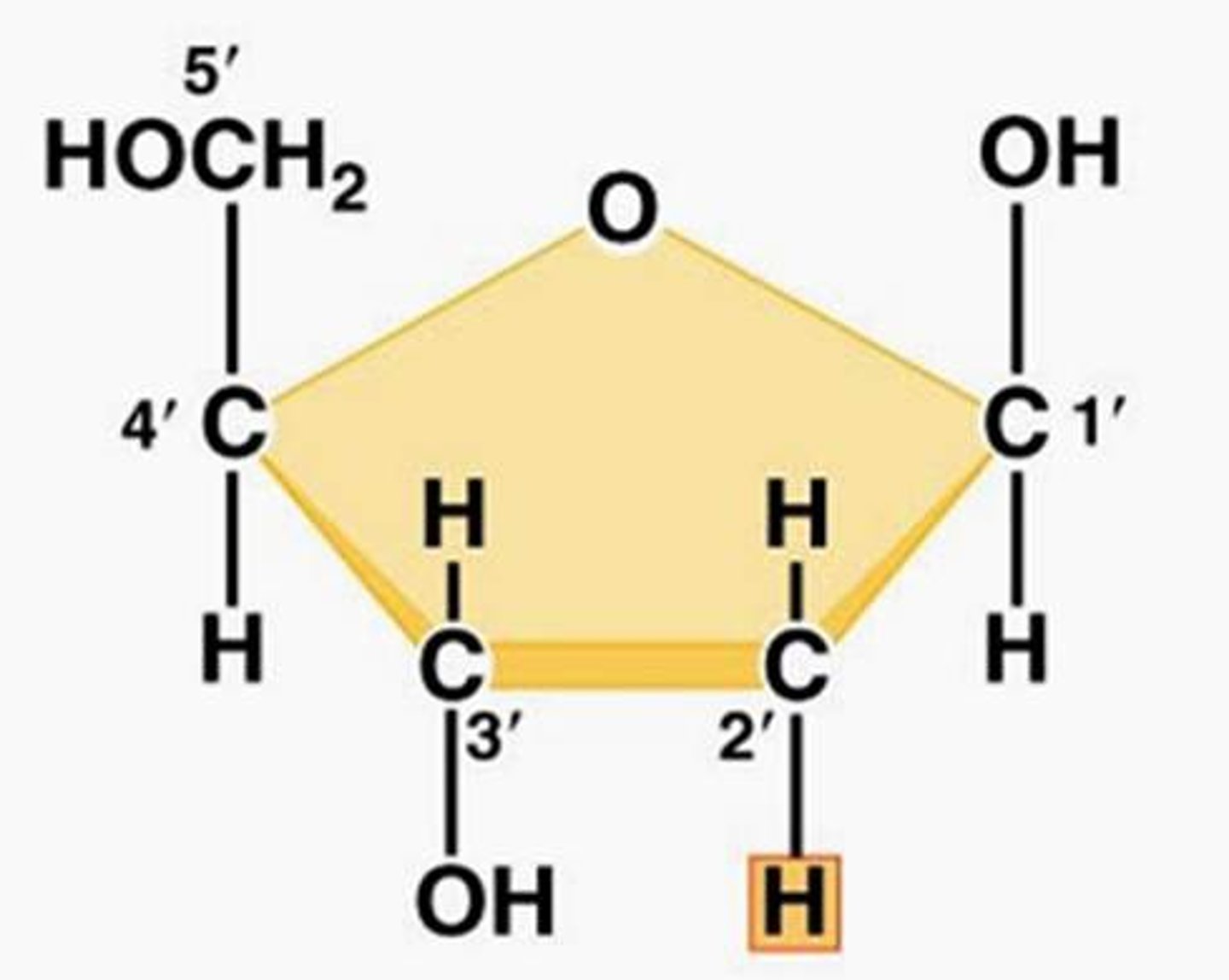
5-Carbon Sugar
Carbons labeled 1', 2', 3', 4', 5' clockwise
1'- forms COVALENT bond with base
2' on DNA- missing oxygen
5'-COVALENTLY bonded to a phosphate group
pyrimidines
single ring bases, cytosine, thymine, uracil
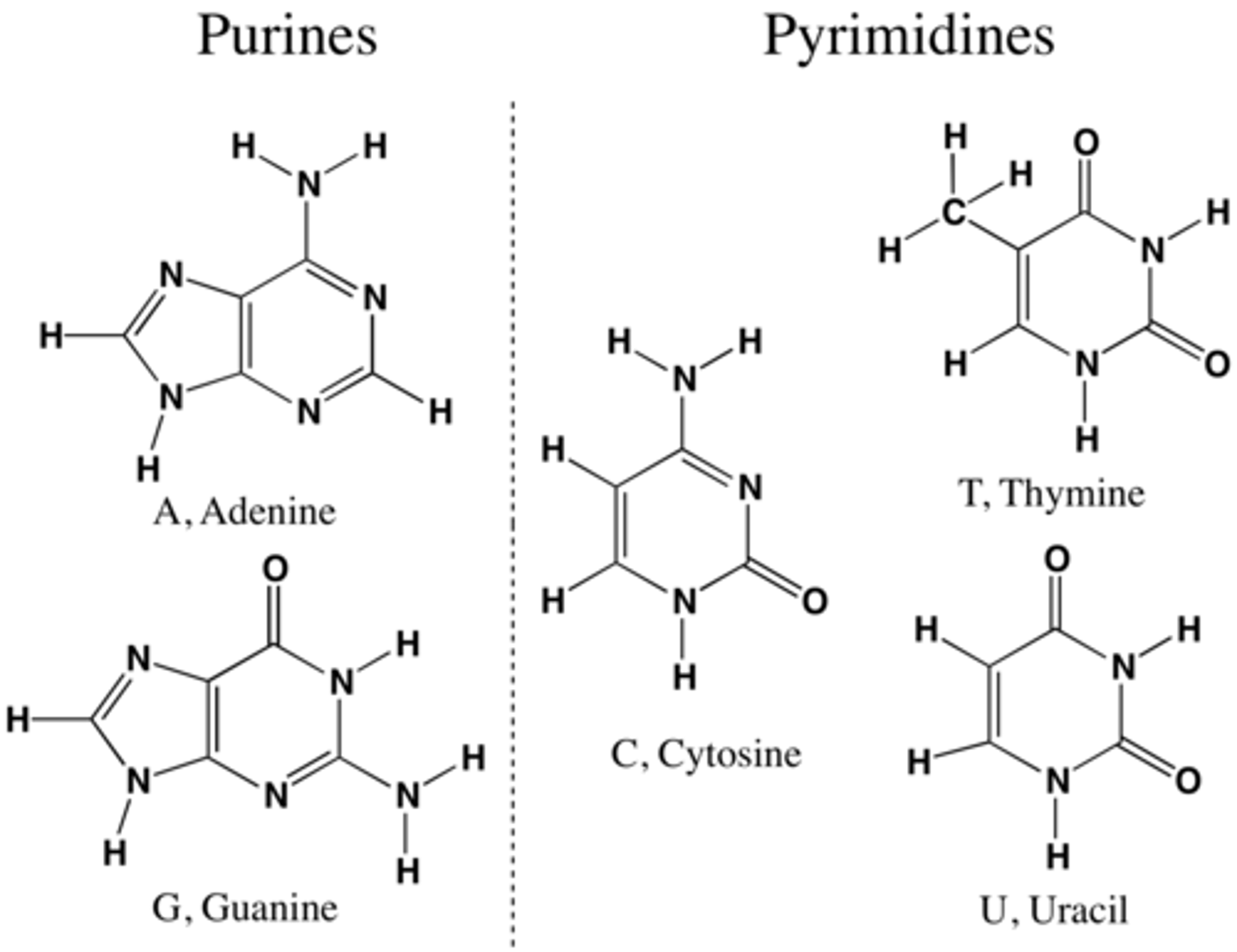
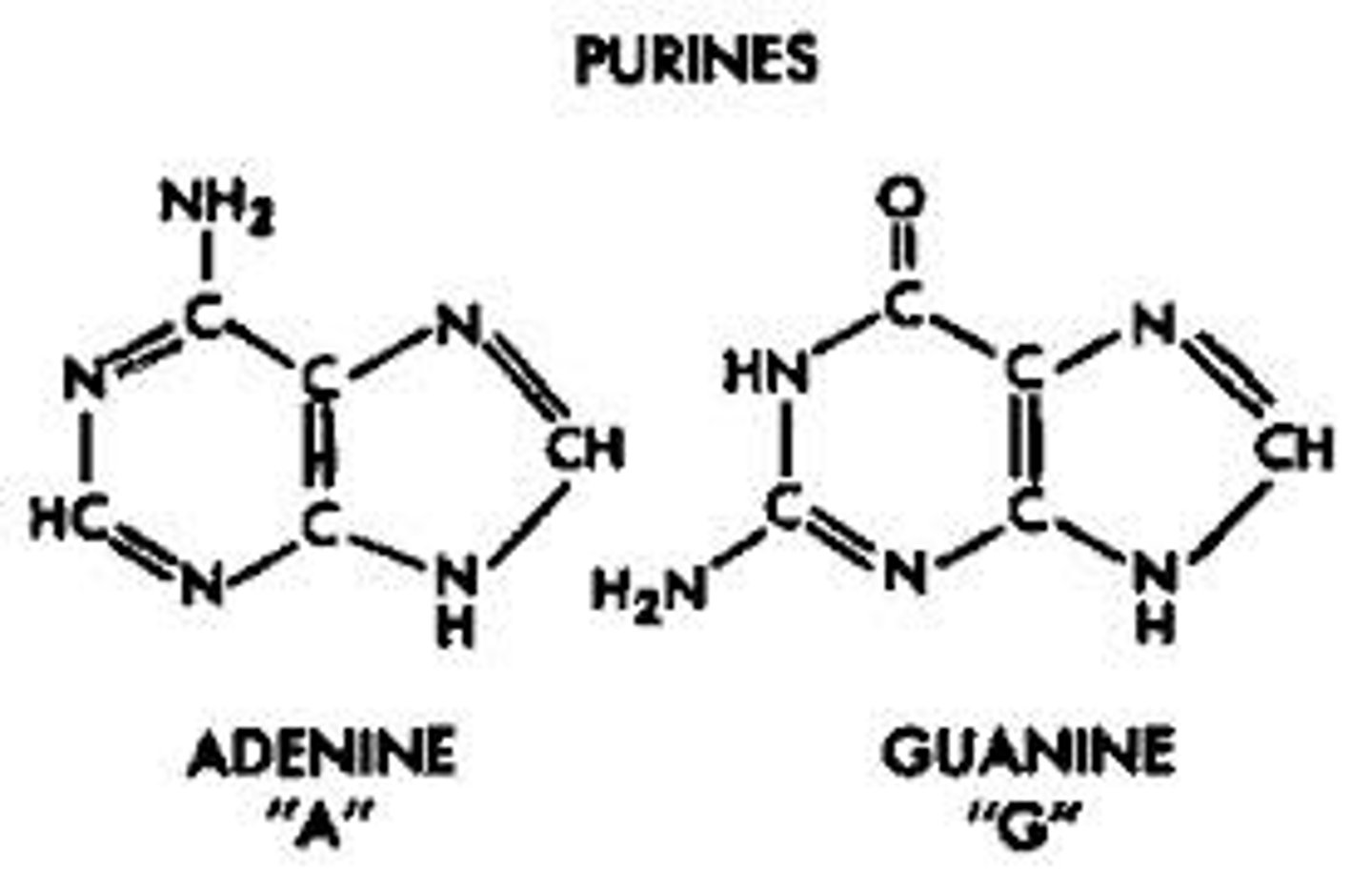
Purines
Double ring bases, adenine, guanine
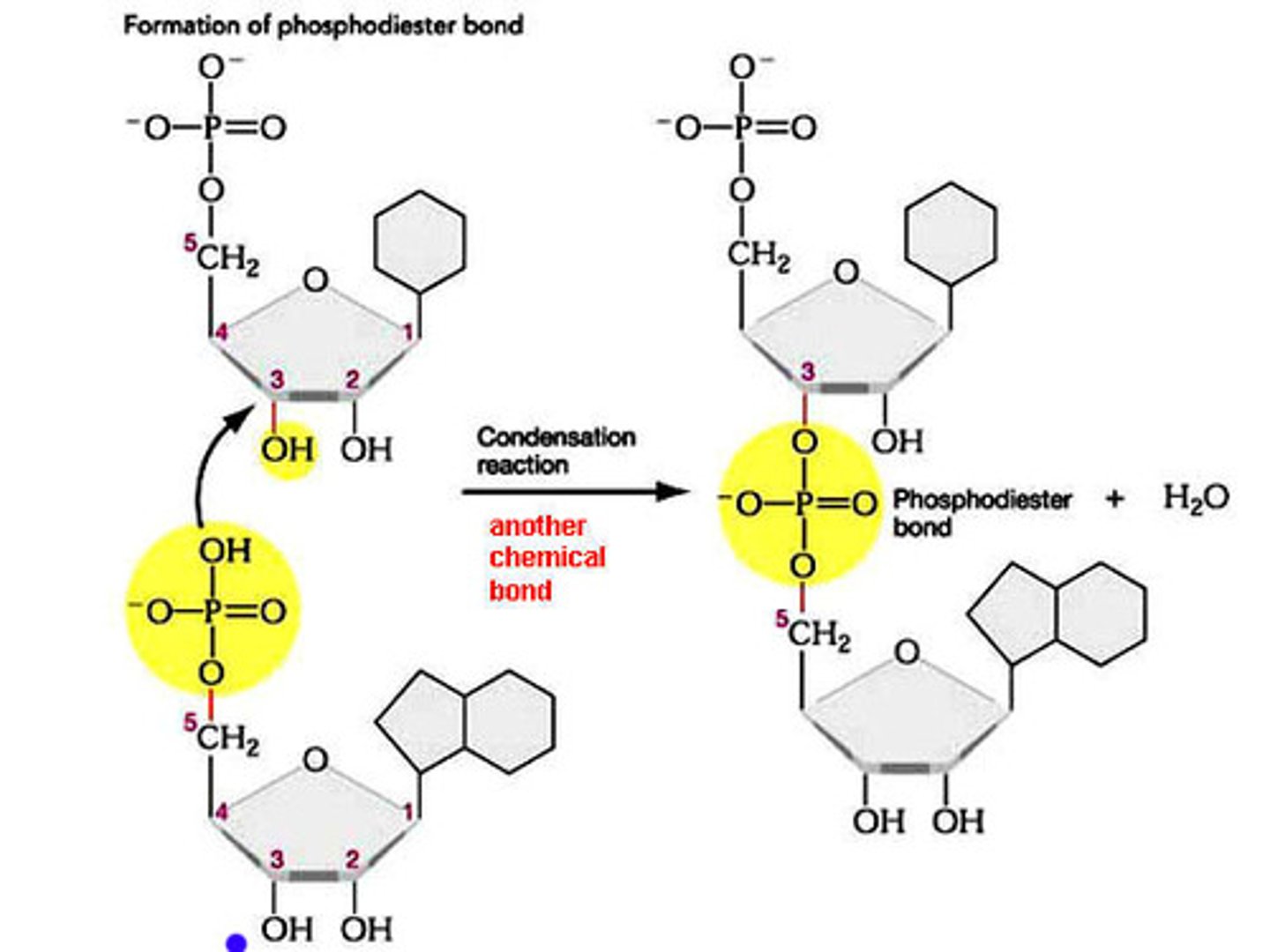
Phosphodiester Bond
phosphate group of 1 nucleotide connects to the 3' carbon of the next sugar. series of covalent bonds C-O-P-O-C
Carbohydrates
C,H,O in 1:2:1 ratio,
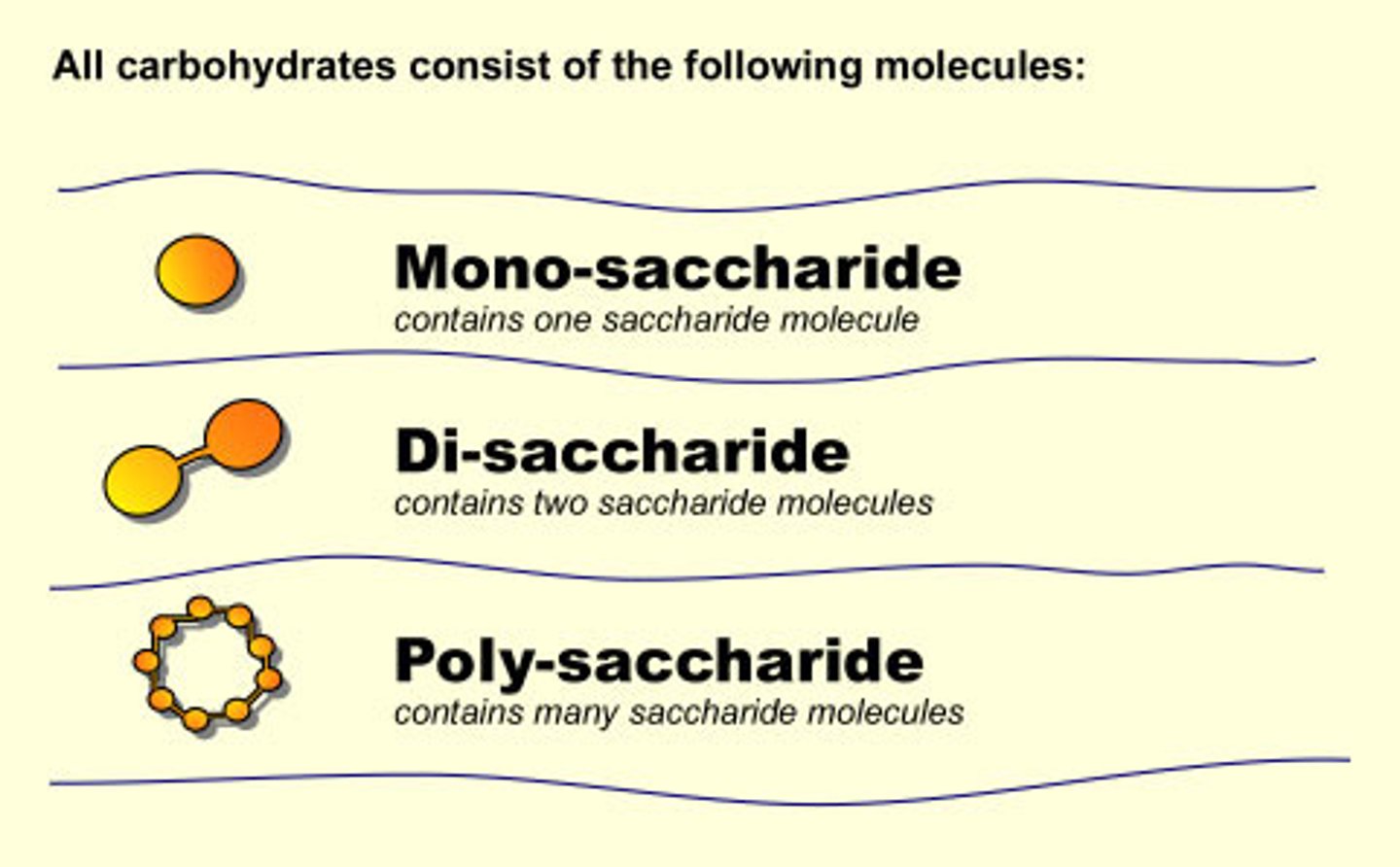
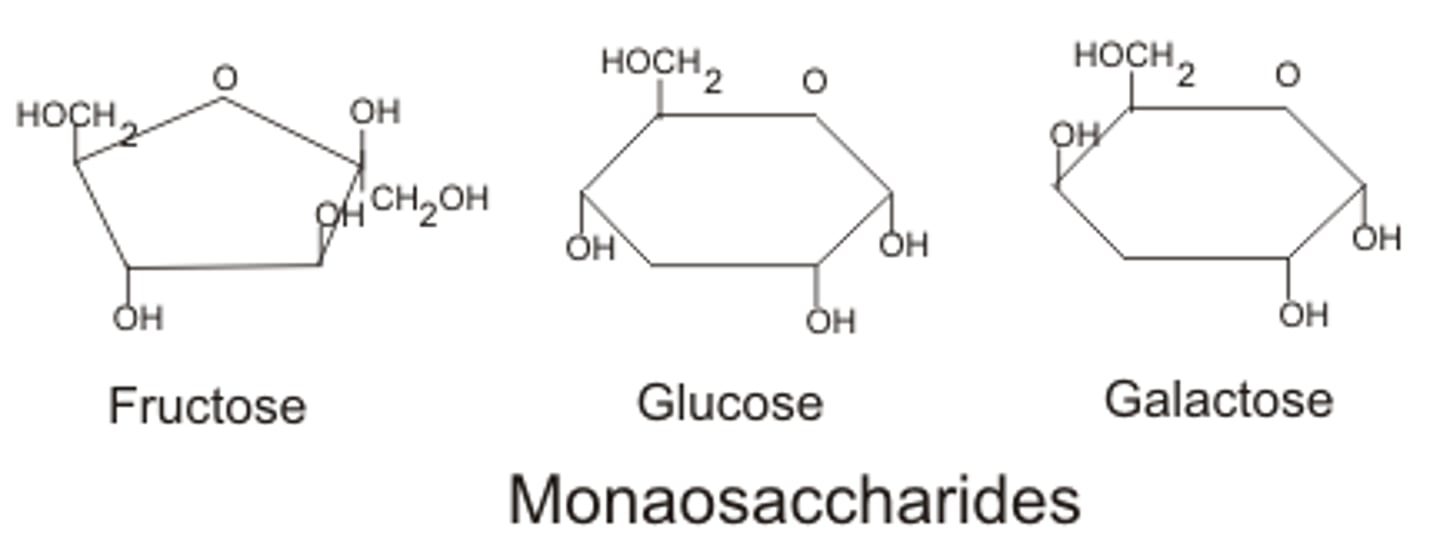
Monosaccharides
simplest sugar. unbranched carbon chains, form rings in aqueous solution
Polysaccharides
linked monosaccharides by covalent bonds
Lipids
contain lots of H & C. nonpolar molecules, insoluble in water, HYDROPHOBIC
Fats
Energy storage, structural support. Made from fatty acids and glycerol
Steriods
cholesterol and steroid hormones. 4 interconnected C rings

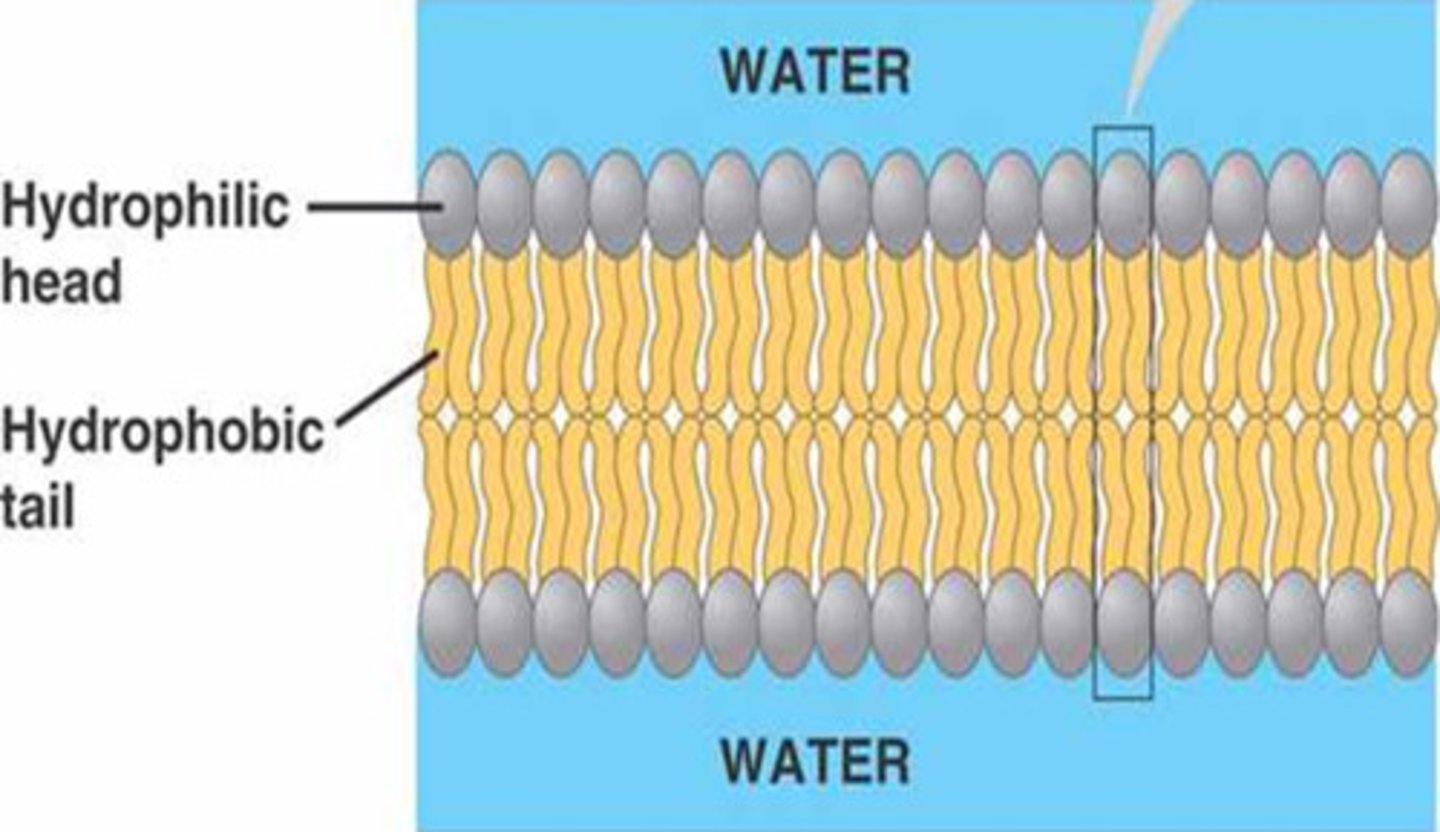
Phospholipids
form cell membranes. a charged nitrogen containing molecule, a phosphate group, a glycerol & 2 fatty acids
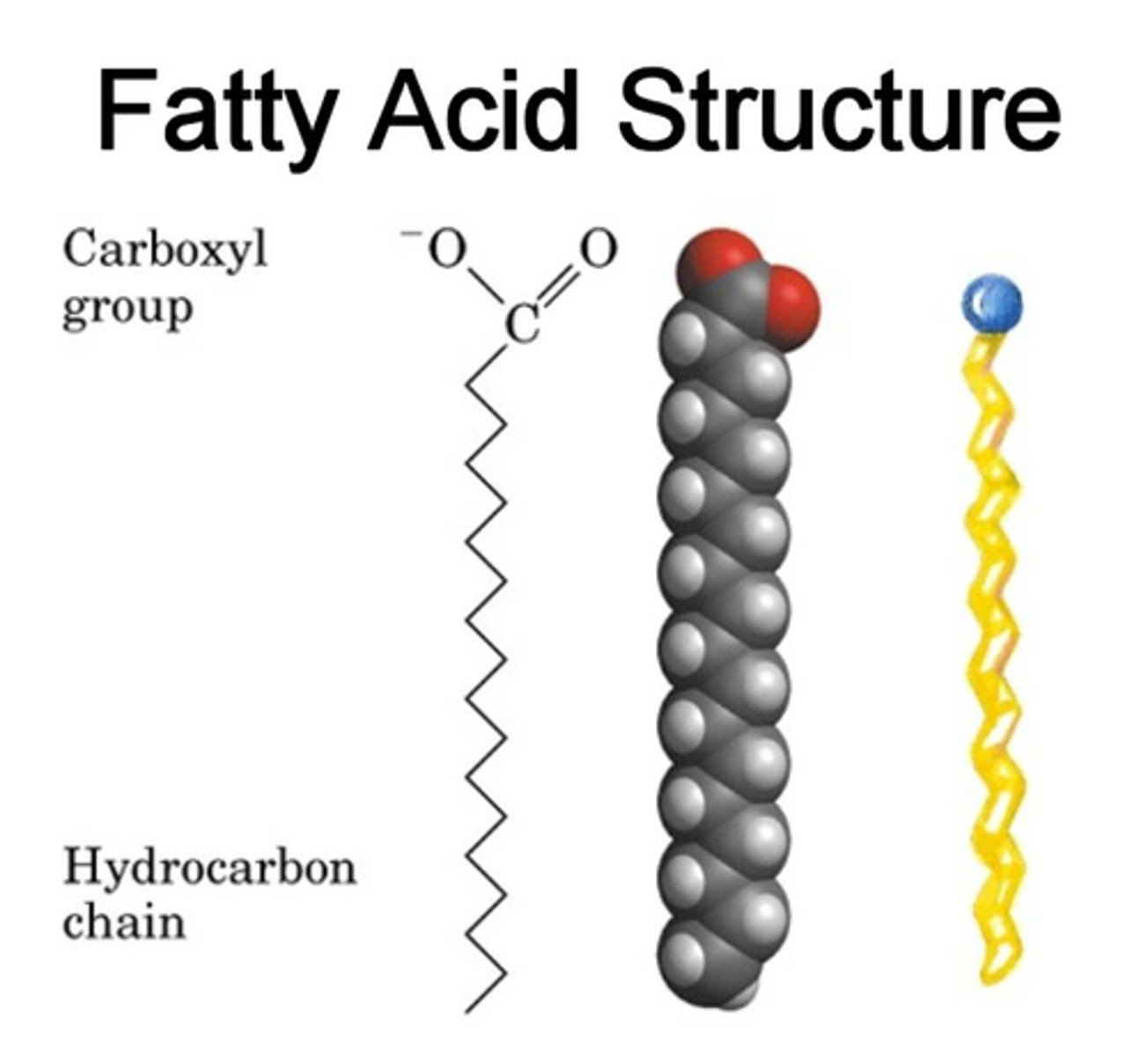
Fatty Acids
long chains of C & H with a carboxyl group at the end. Released an H+ in water
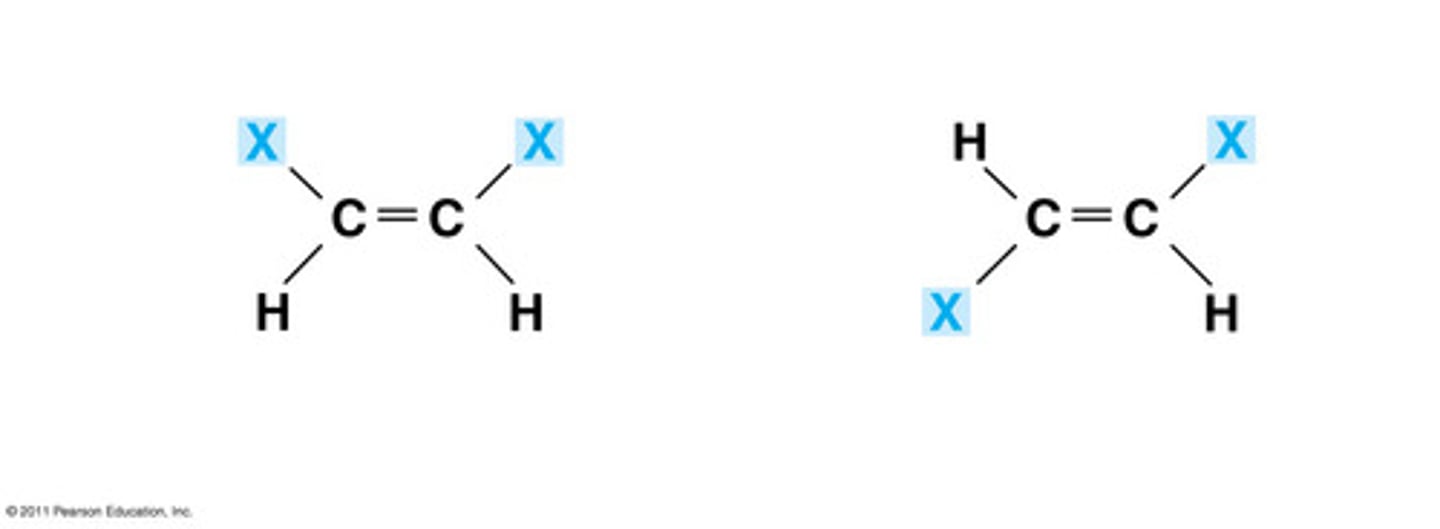
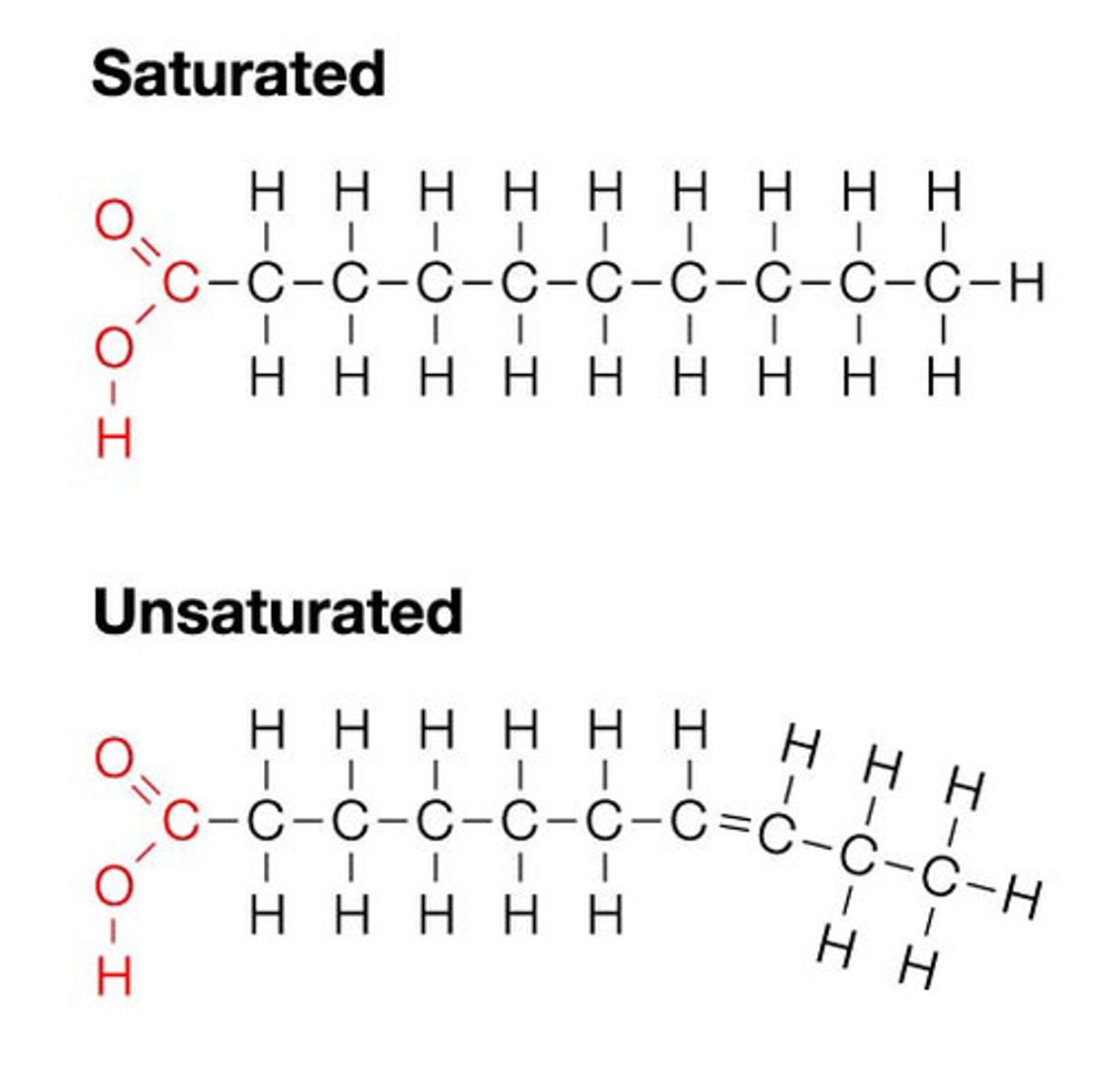
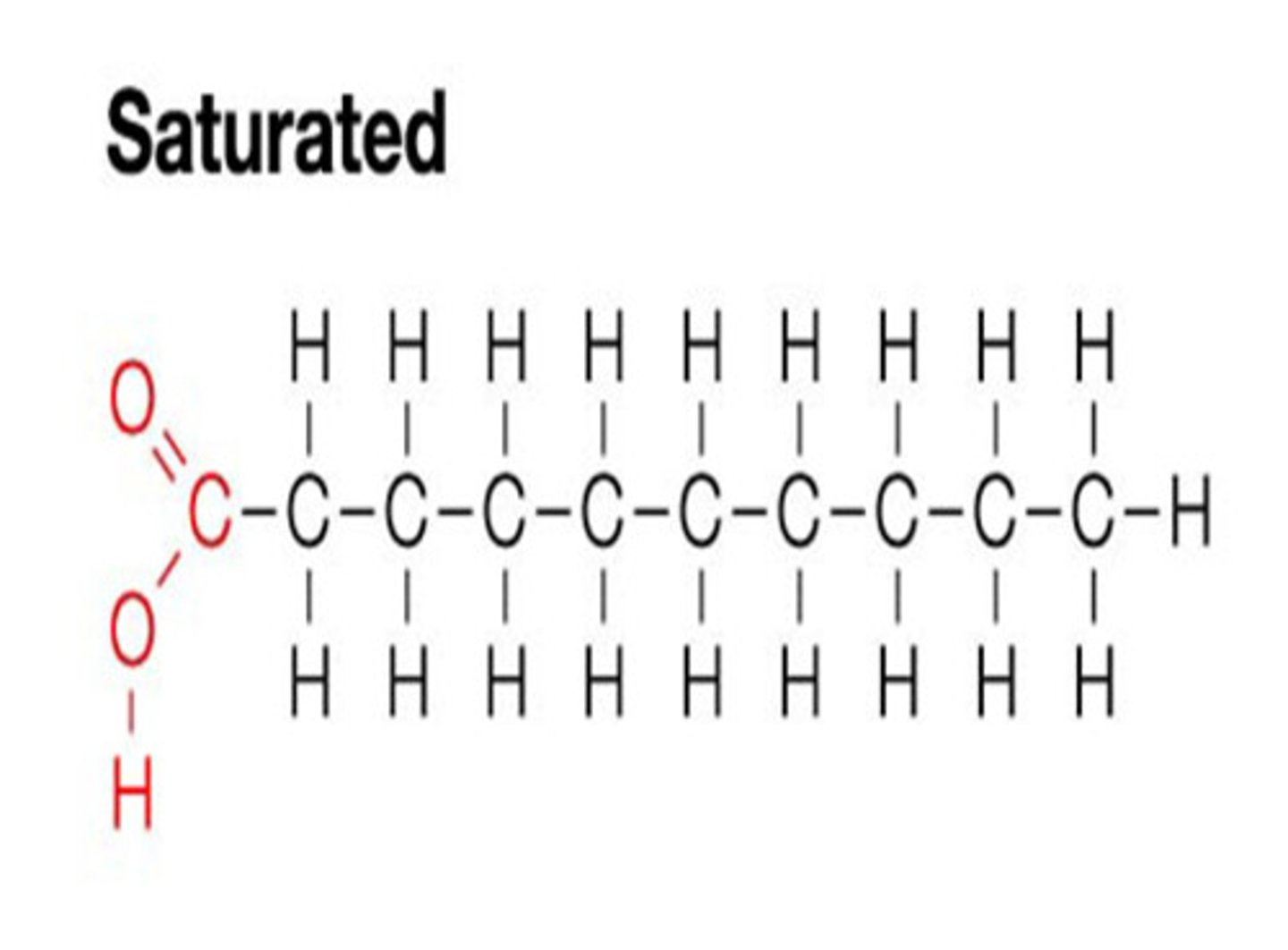
Saturated
Carbons linked by single covalent bonds. saturated with hydrogen. Solid at room temperature.
Unsaturated
one or more double bonds linked Carbons. Liquid at room temperature. Not saturated with hydrogen
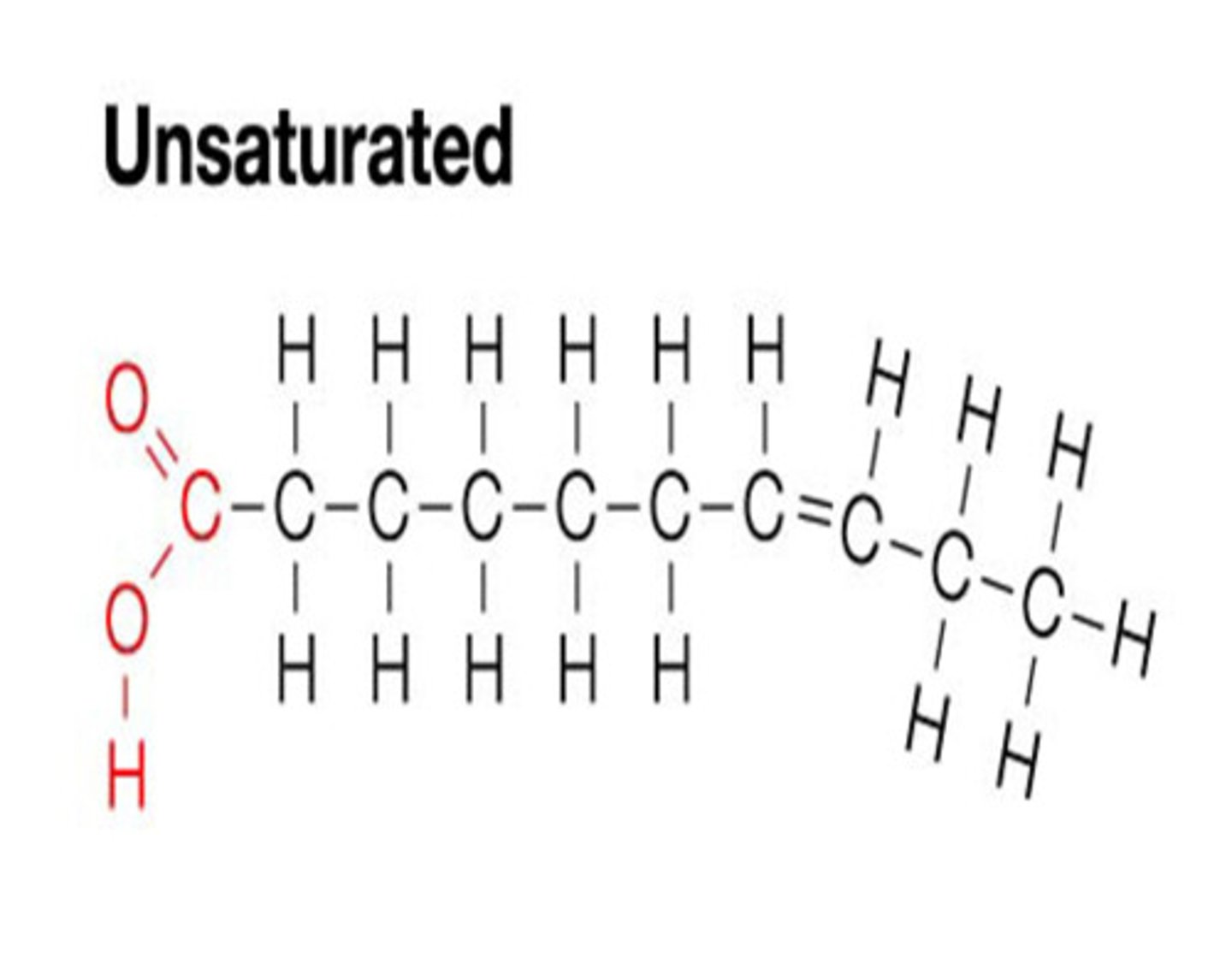
Energy Storage for Plants & Animals
plants store energy as carbs. Animals store energy as fats
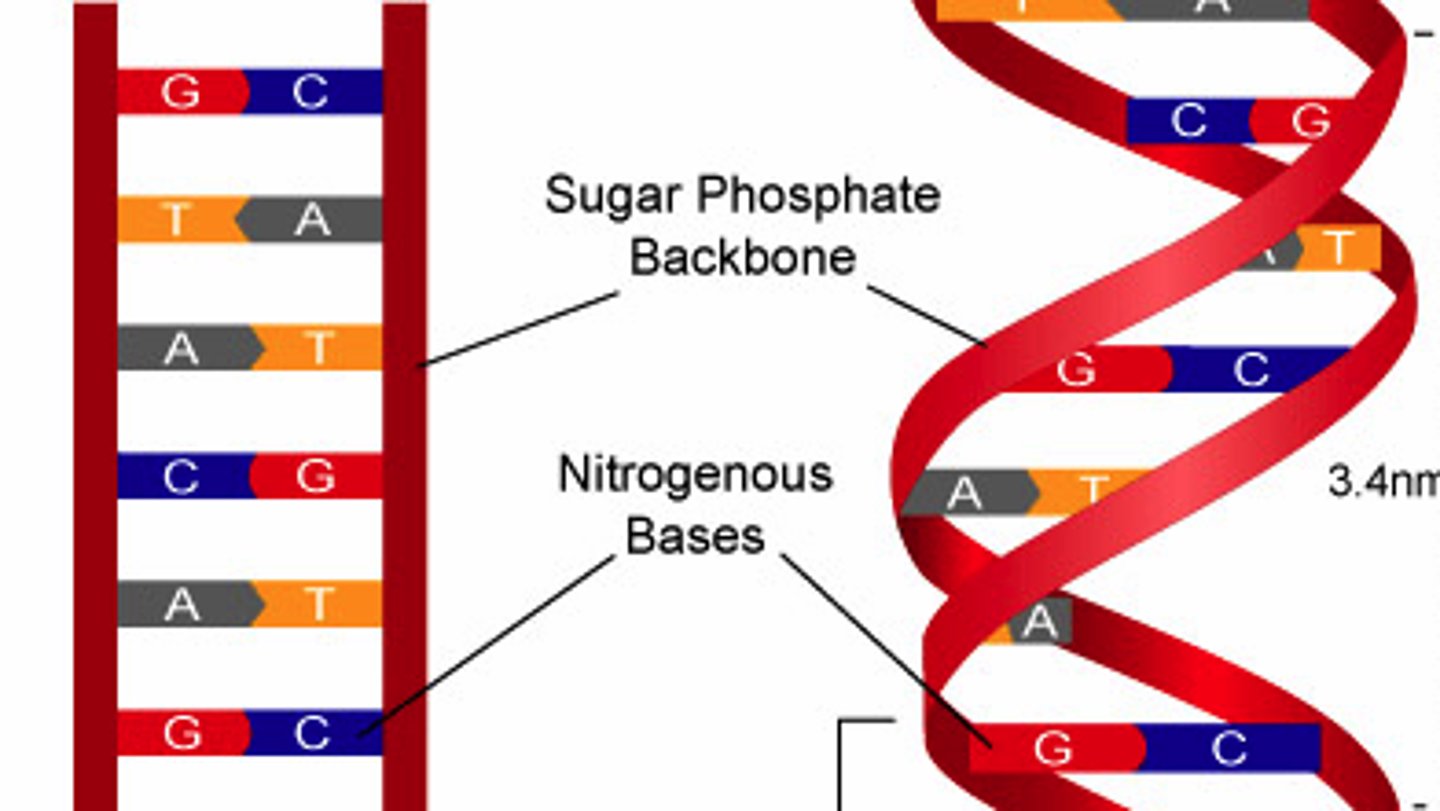
DNA Backbone
alternates phosphates and sugars
the nonvariable part of DNA
negatively charged
Nucleoside
Sugar and base. NO PHOSPHATE
DNA
2 antiparallel strands in a double helix. strands interact by H bonds forming between complementary bases. Phosphate group interact with water on the outside
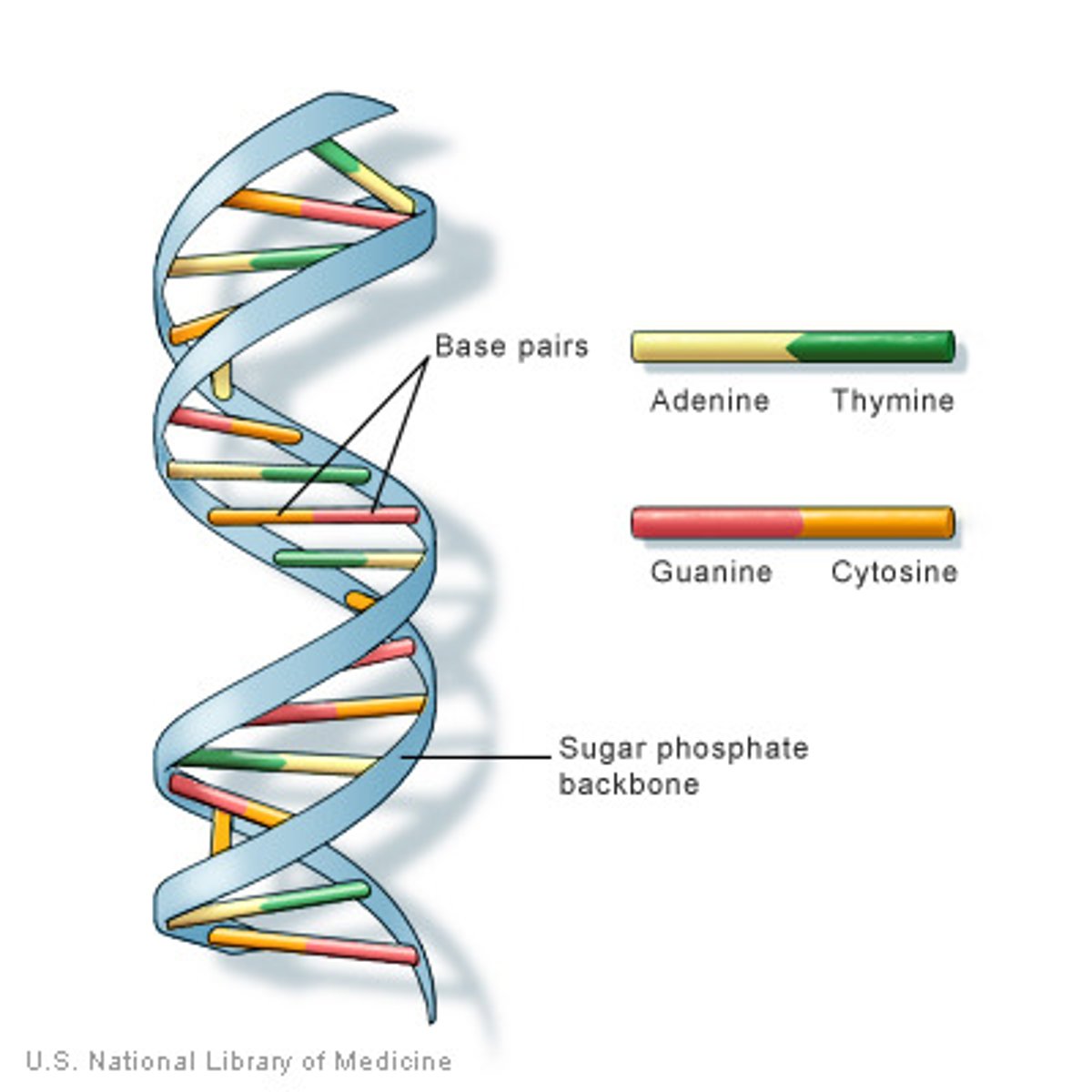
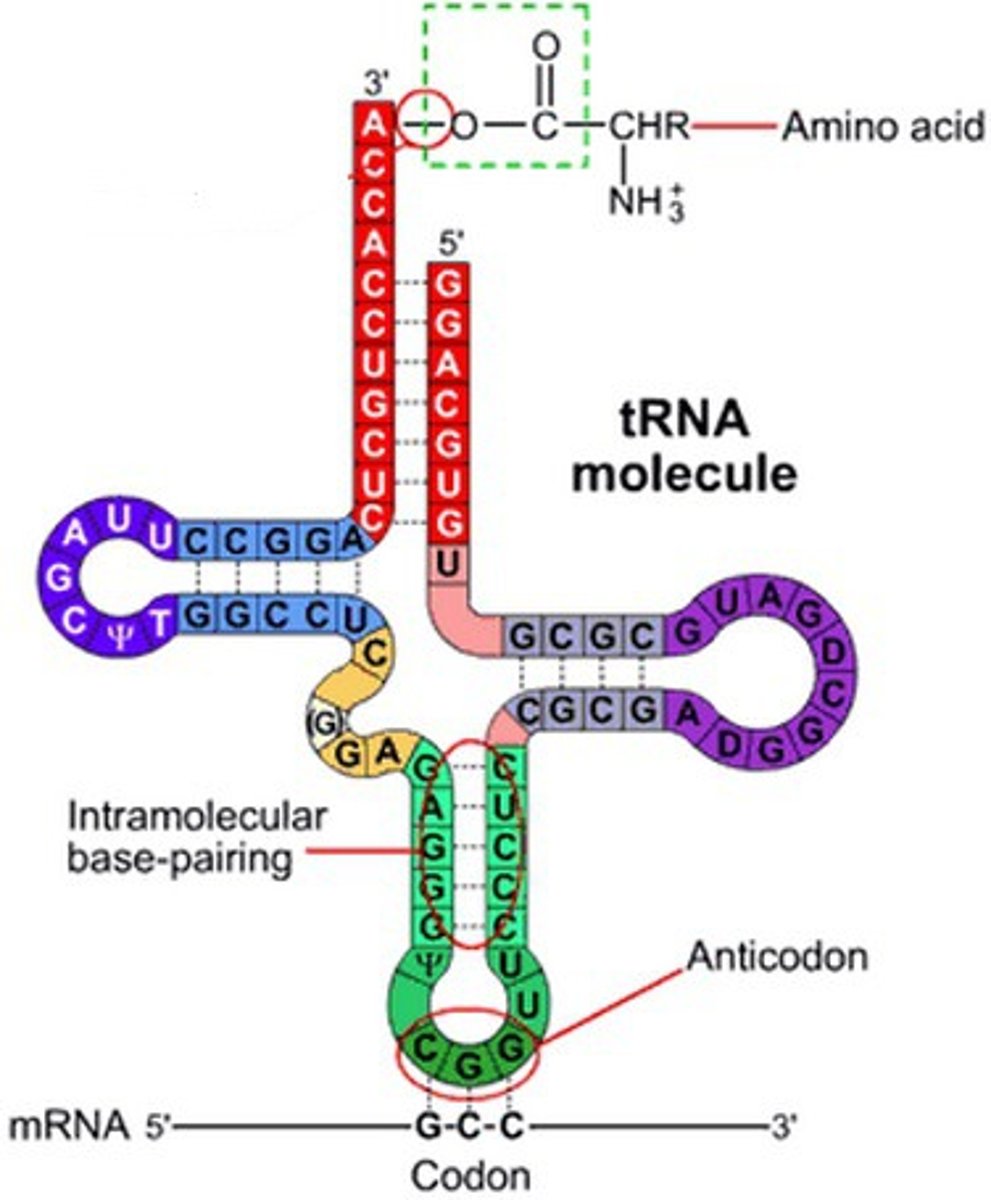
Base Pairing
A + T, C+ G- keeps DNA width consistent, keeps geometry the same
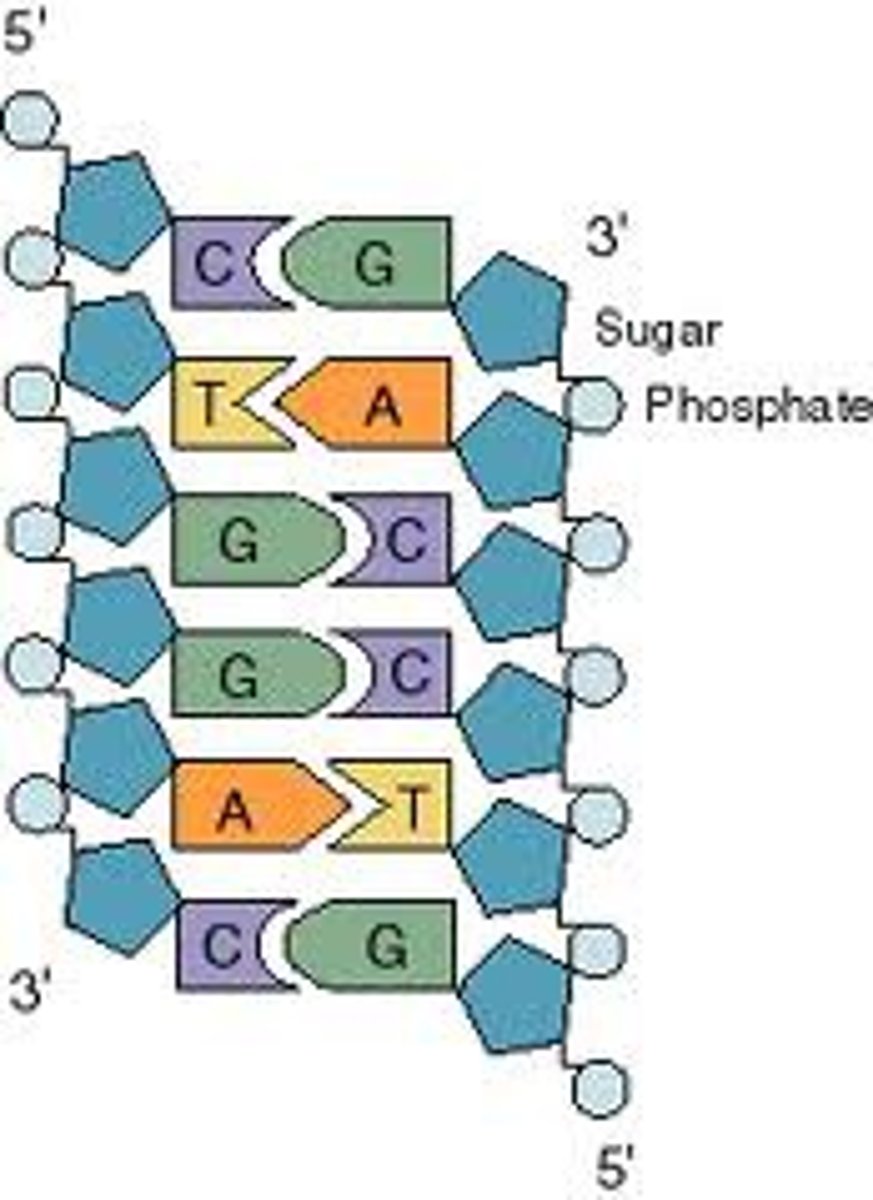
Base Stacking
Bases interact noncovalently with each other and stack or tightly group, which stabilizes the helix
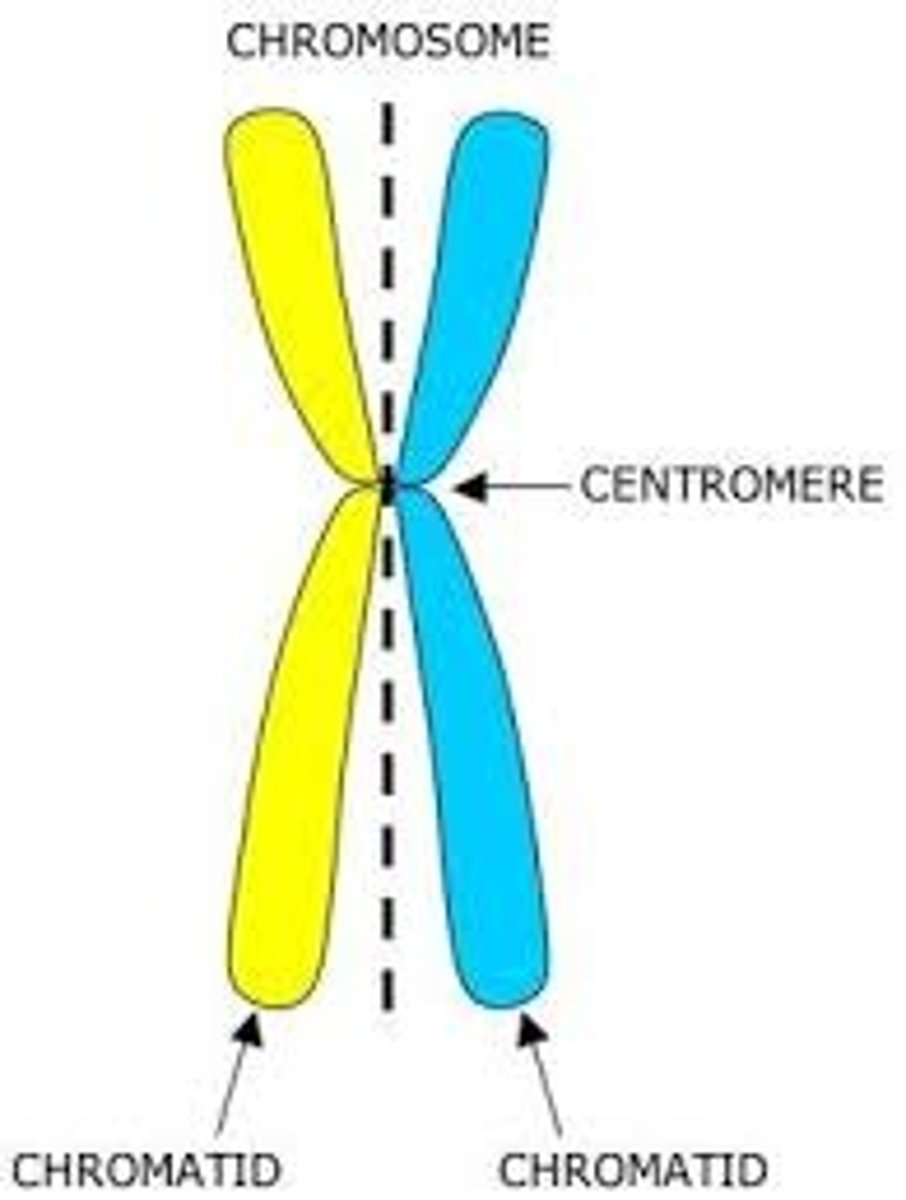
Chromatin
DNA coiled and packaged with proteins
Gene
a sequence of DNA that codes for a product and its associated control regions
Enhancer Sequences
A DNA sequence that regulates gene expression by acting as a binding site for proteins that increase the ability of RNA polymerase to transcribe a specific protein
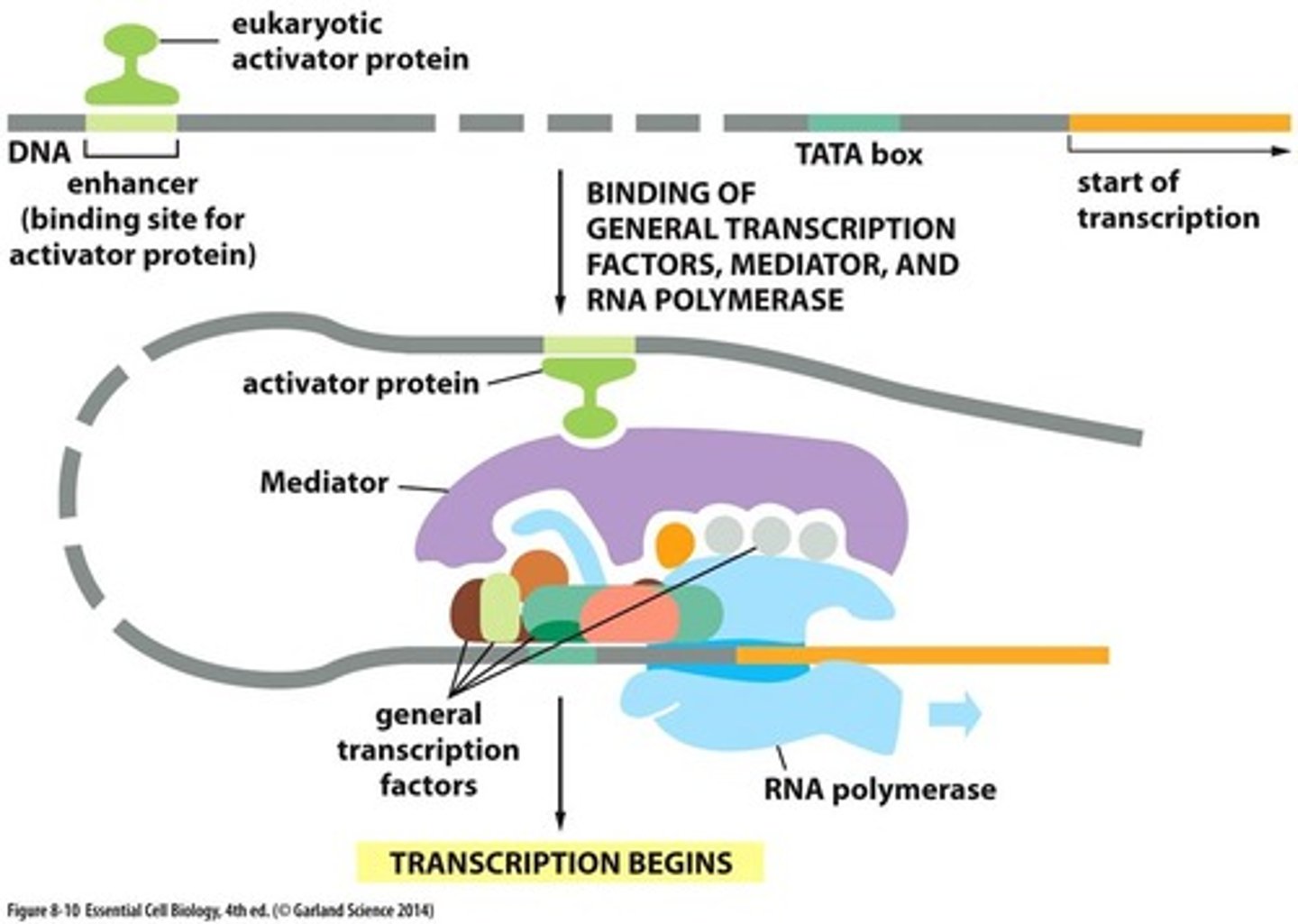
Promoter
general transcription factors bind here (TF)
Terminator
End transcription
Transcription
a process. Product- Transcript. Can use either DNA strand as a template strand. DNA strand transcribed from 3' to 5' direction. RNA strand made 5' to 3'
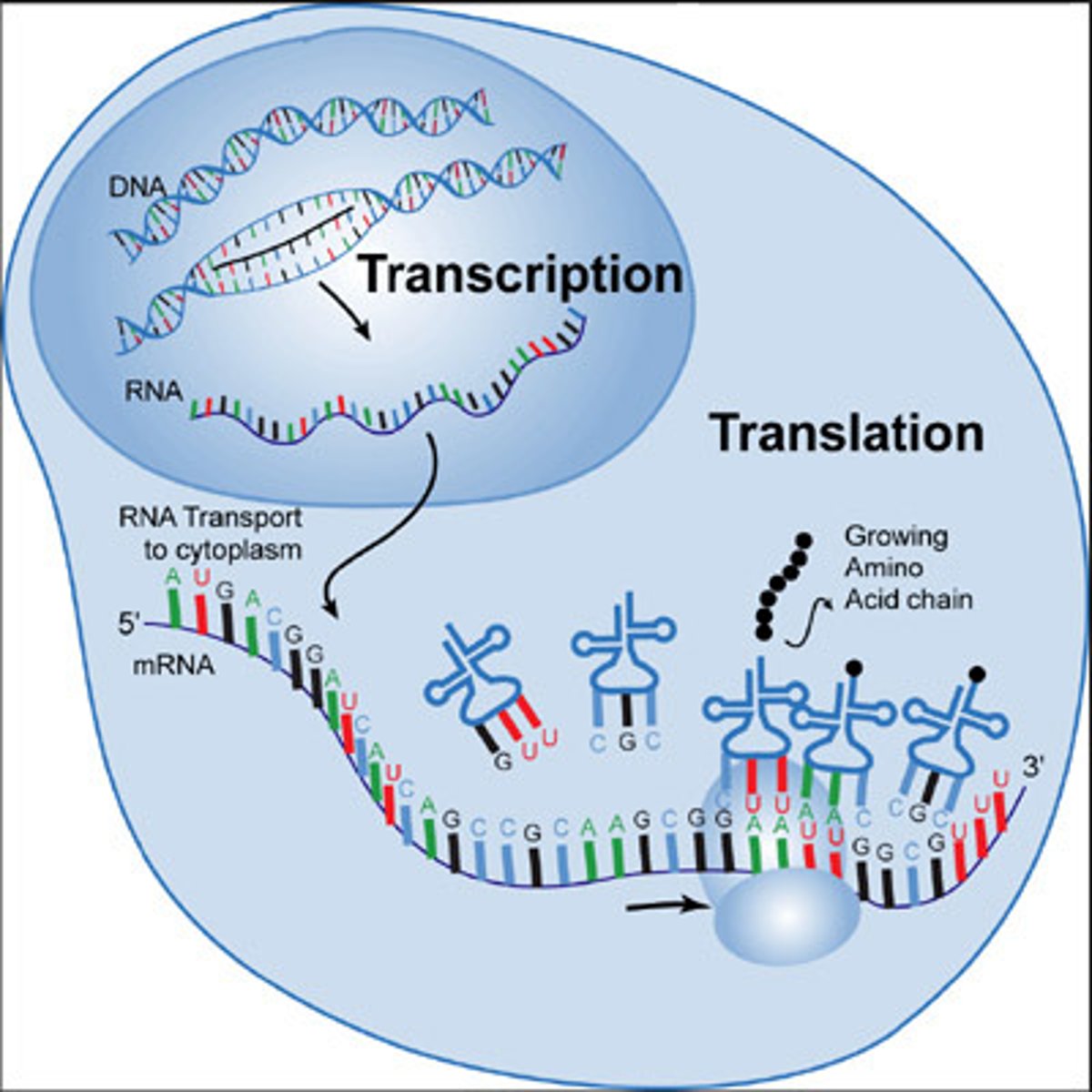
RNA Polymerase Complex
separates the DNA strands to form the "transcription bubble"
Transcript
complementary and antiparallel to the template. Built from its 5' to its 3' direction
RNA Polymerase
checks for correct base pairing & catalyzes pyrophosphate release & phosphodiester bond formation inside the RNA polymerase
mRNA
transcript that contains information to build a protein
Prokaryotes & mRNA
can immediately used their mRNA to build proteins
Eukaryotes & mRNA
process their mRNA because some of the Primary transcript isn't useful
Eukaryote mRNA Processing
1) add a special nucleotide to the 5' end (5' cap)
2) add a bunch of adenine to the 3' end (Poly A Tail)
3) remove introns and covalently bond exons together
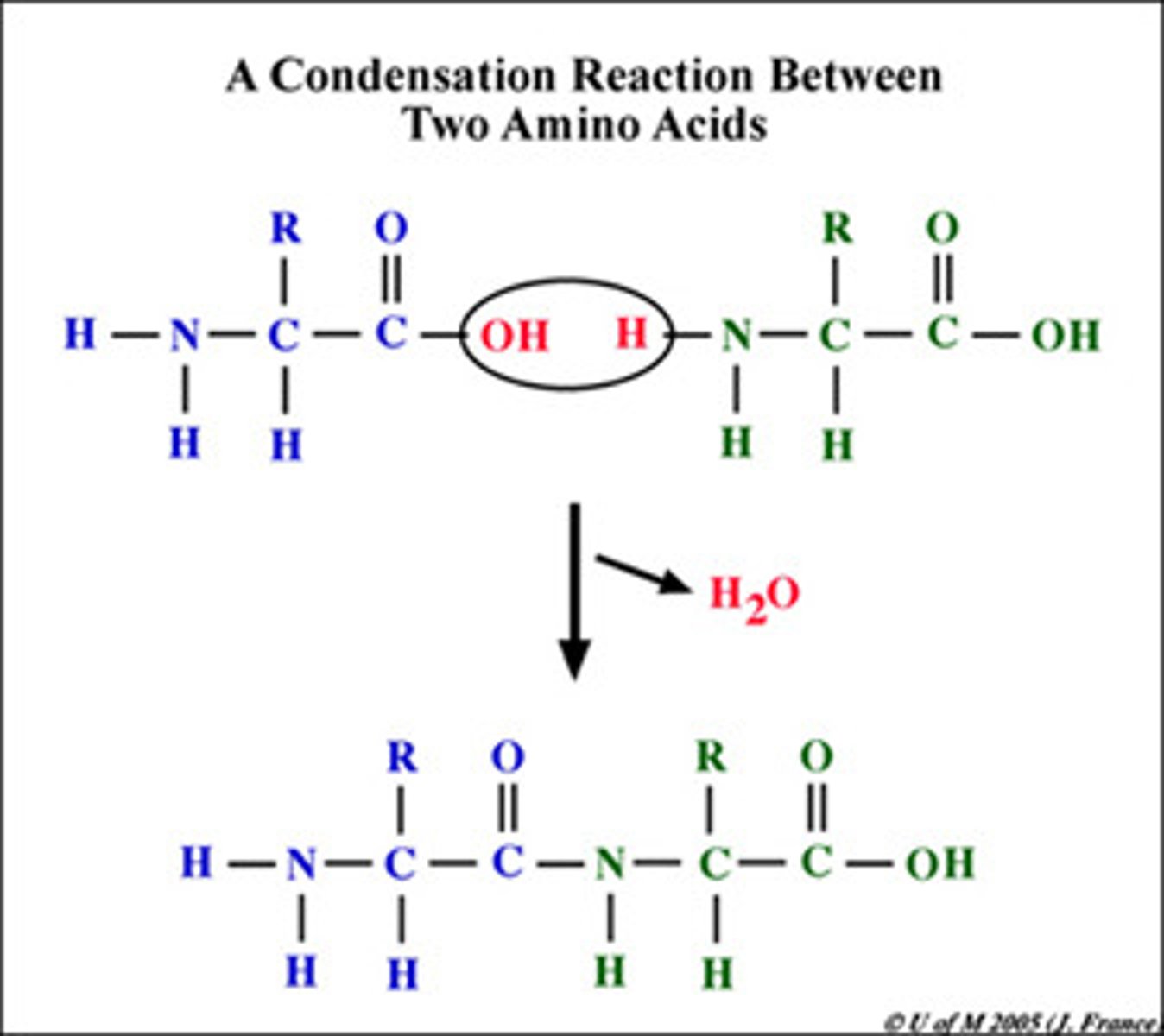
Peptide Bond
links amino acids
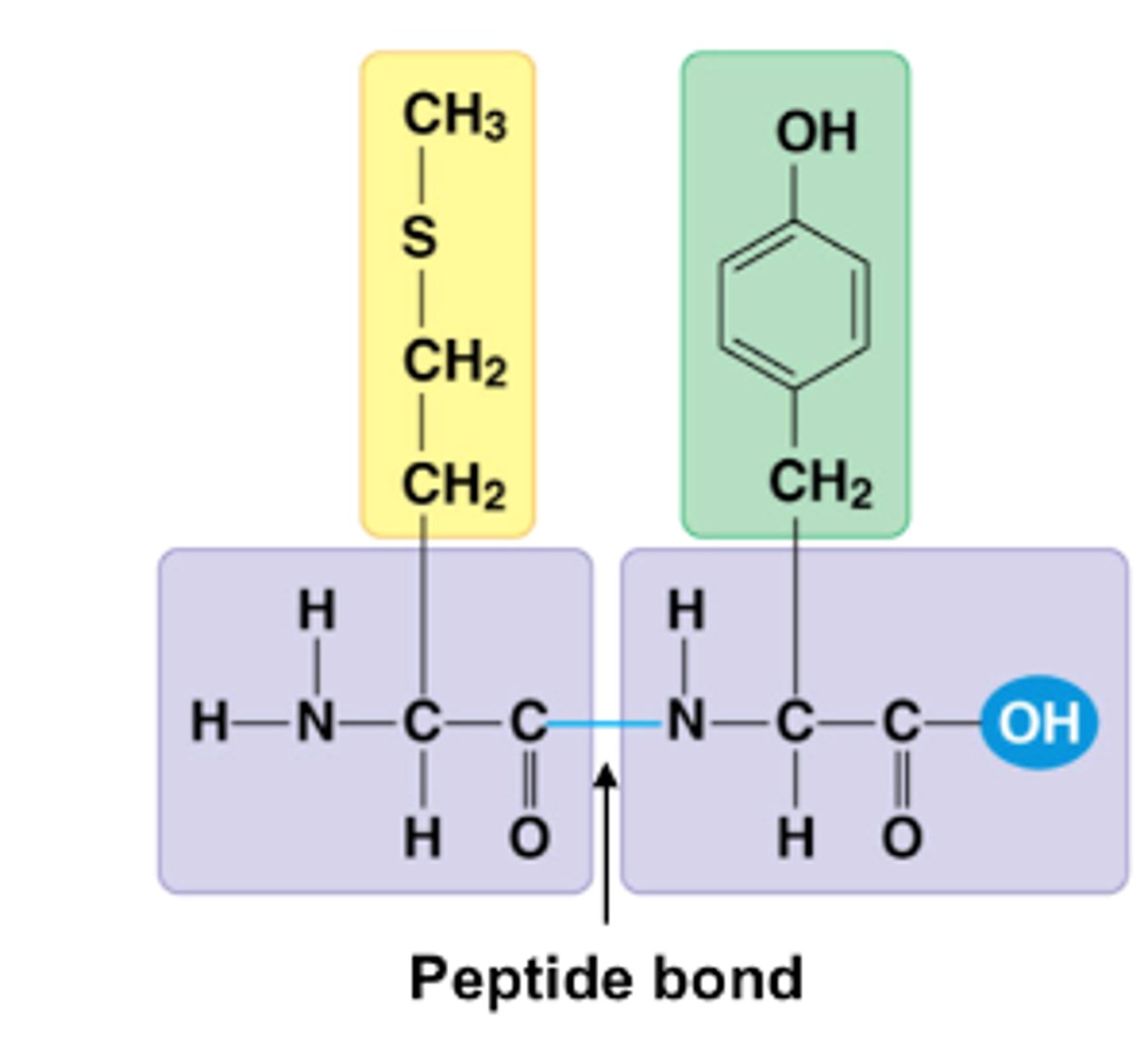
Dehydration process
removes water to form peptide bond
Carbonyl Group
C=O
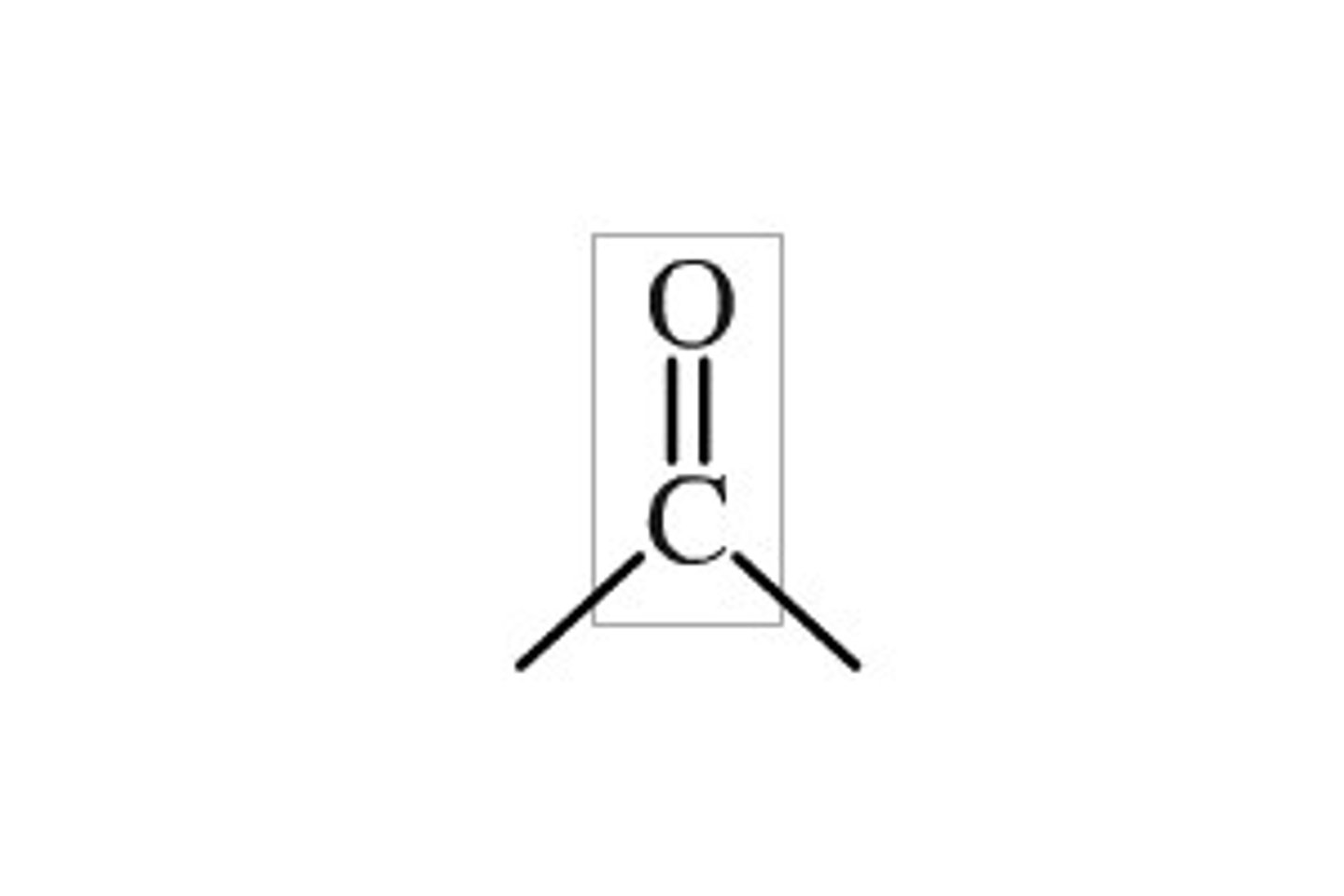
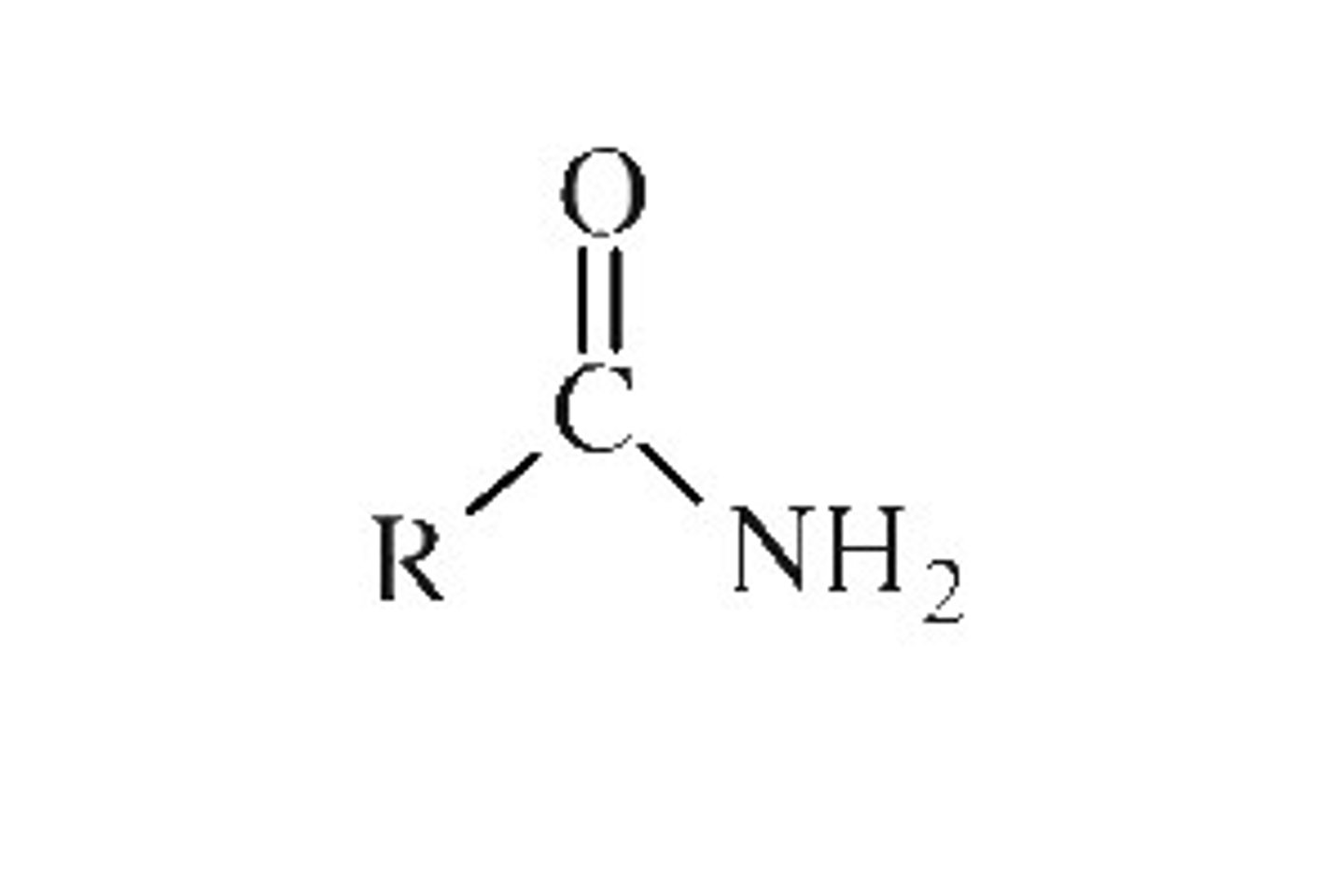
Amide Group
N-H
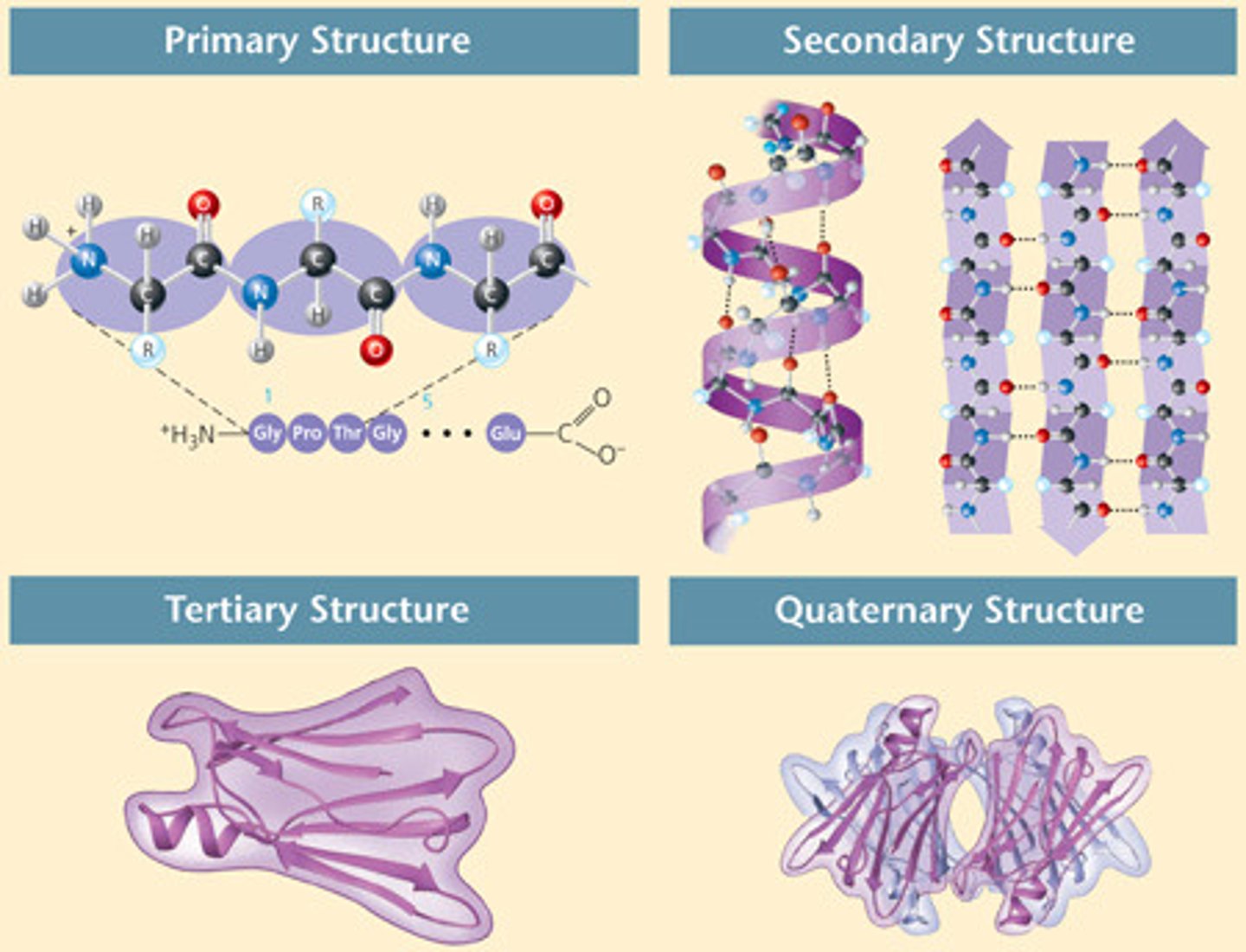
Primary Structure
the sequence of amino acids
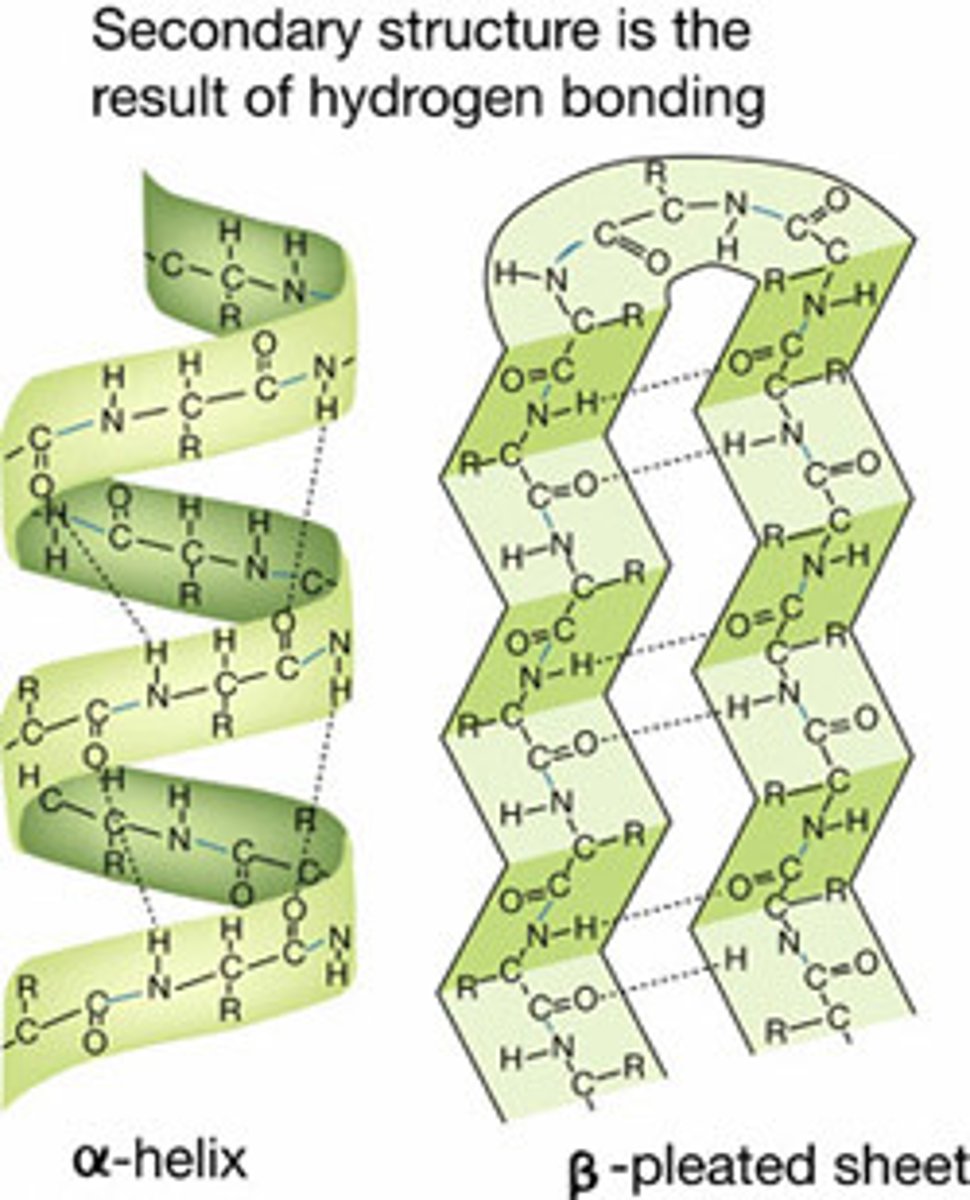
Secondary Structure
repeating folding patterns stabilized by H bonds b/t carbonyl group of 1 amino acid and the amide group of another nonadjacent amino acid
R Groups
aren't involved in the H bond formation but their shape and charge make 2 degree structures more or less likely in any particular polypeptide
Alpha Helix
each carbonyl group H bonds with an amide group 4 amino acids ahead in the chain
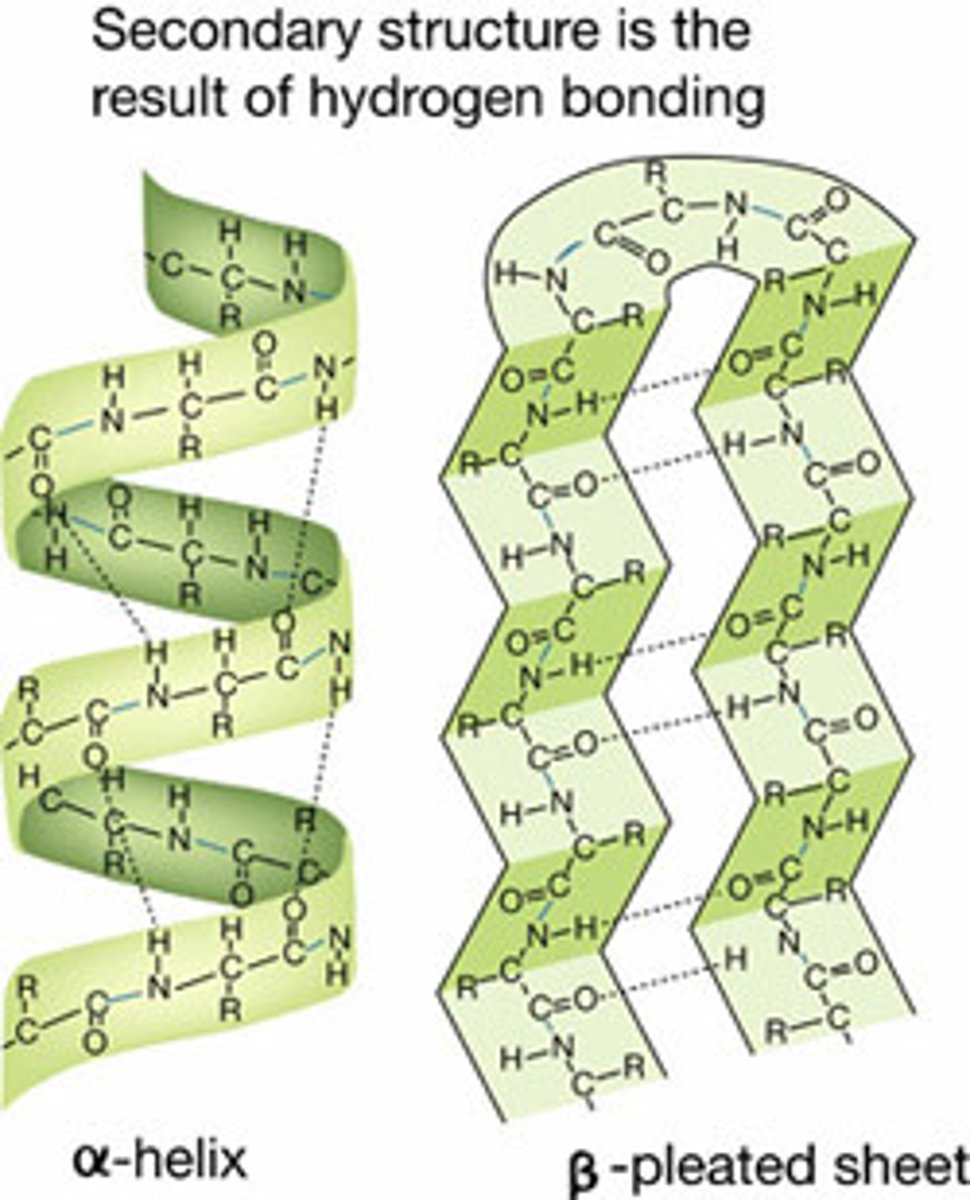
Beta (Pleated) Sheet
the polypeptide fold backs on itself and H bonds form b/t carbonyl groups in 1 chain and amide groups in another chain
Tertiary Structure
polypeptide folds into a 3D shape because of R group interactions. may be the final level of structure for a protein
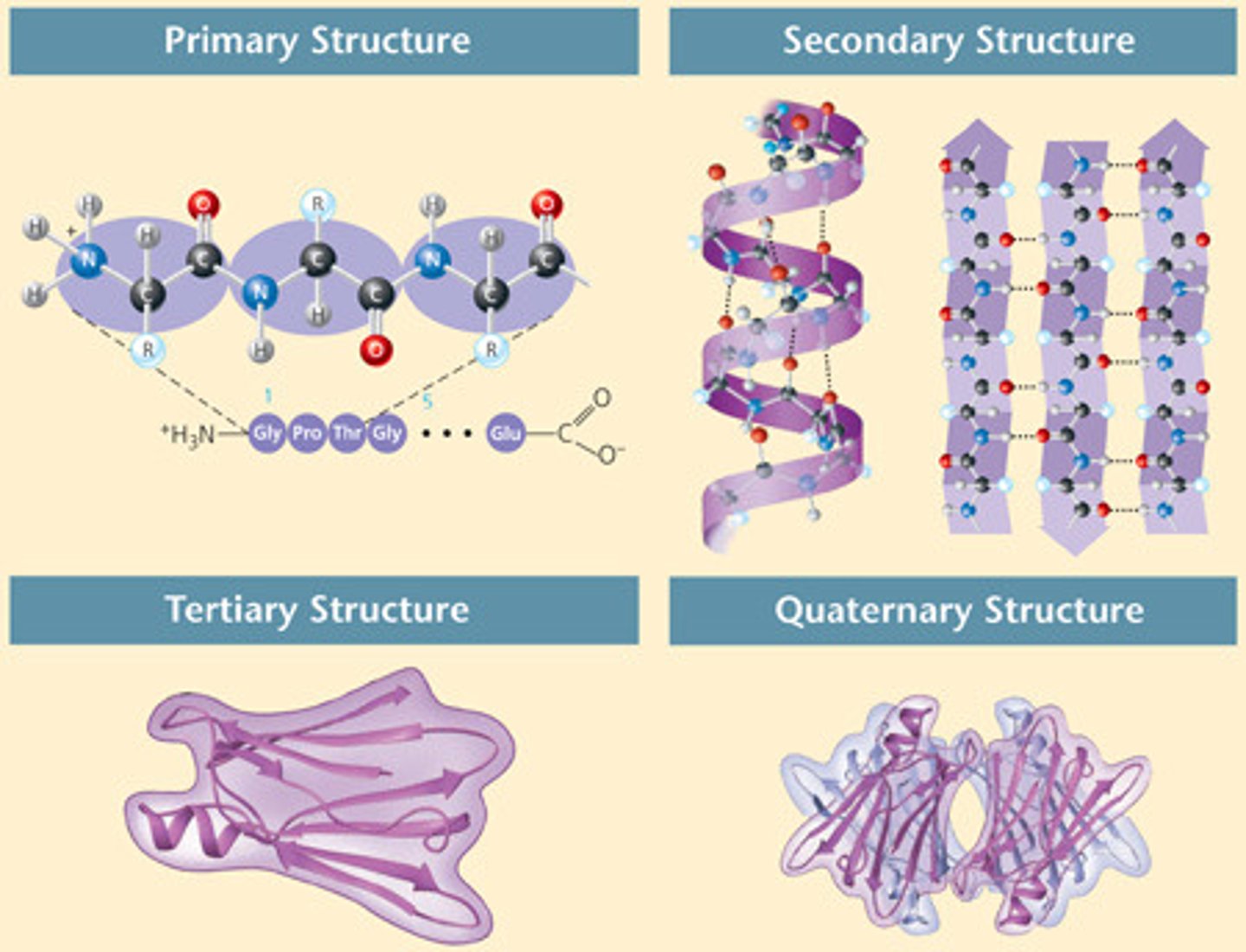
Quaternary Structure
2 or more polypeptides associated to form a functional multimeric protein
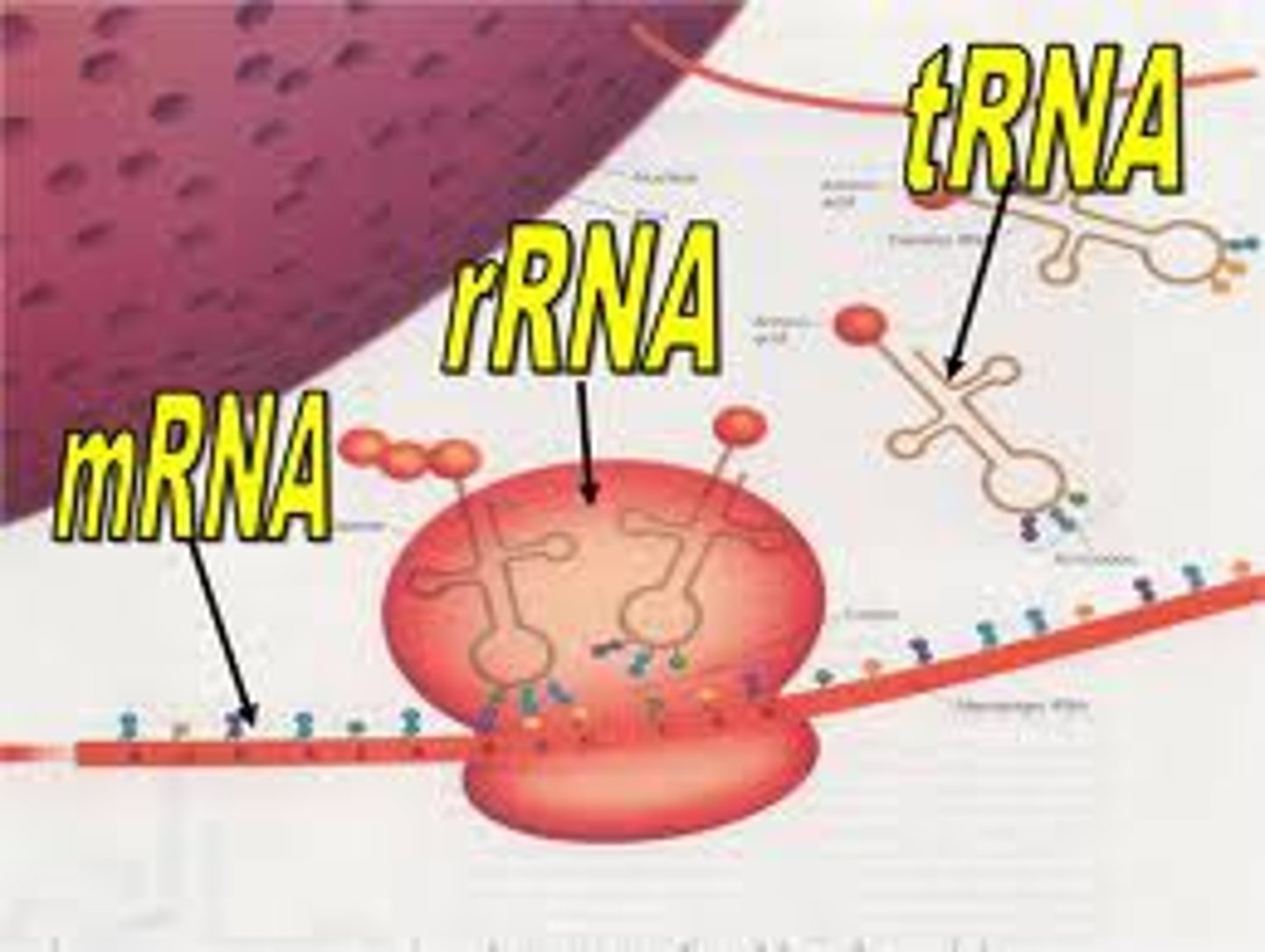
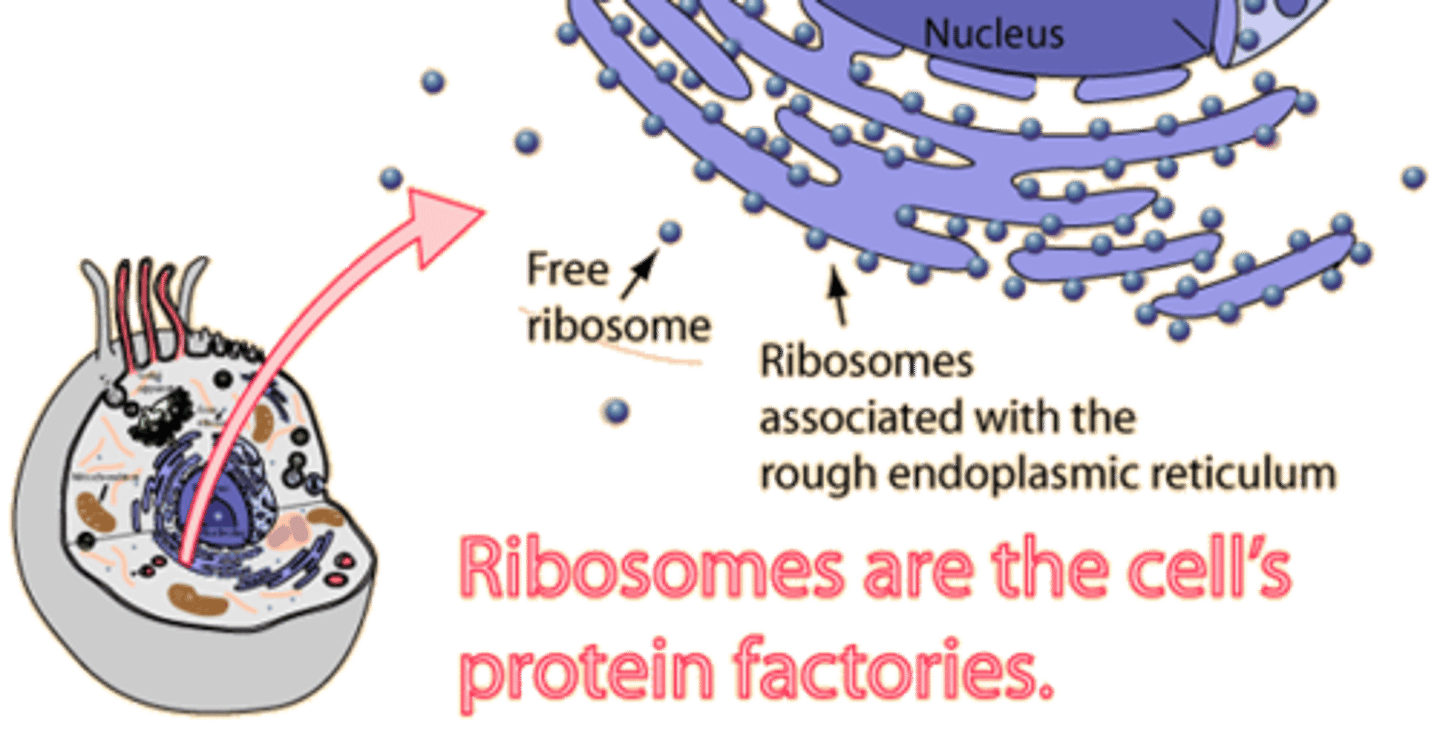
Ribosomes
complexes of protein and rRNA that form the environment for translation. a large and a small subunit
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
each type brings a specific amino acid to the ribosome
Initiation
initiaion factors bring the equipment for translation together
Elongation
ribosomes move the mRNA as amino acids are added to the polypeptide
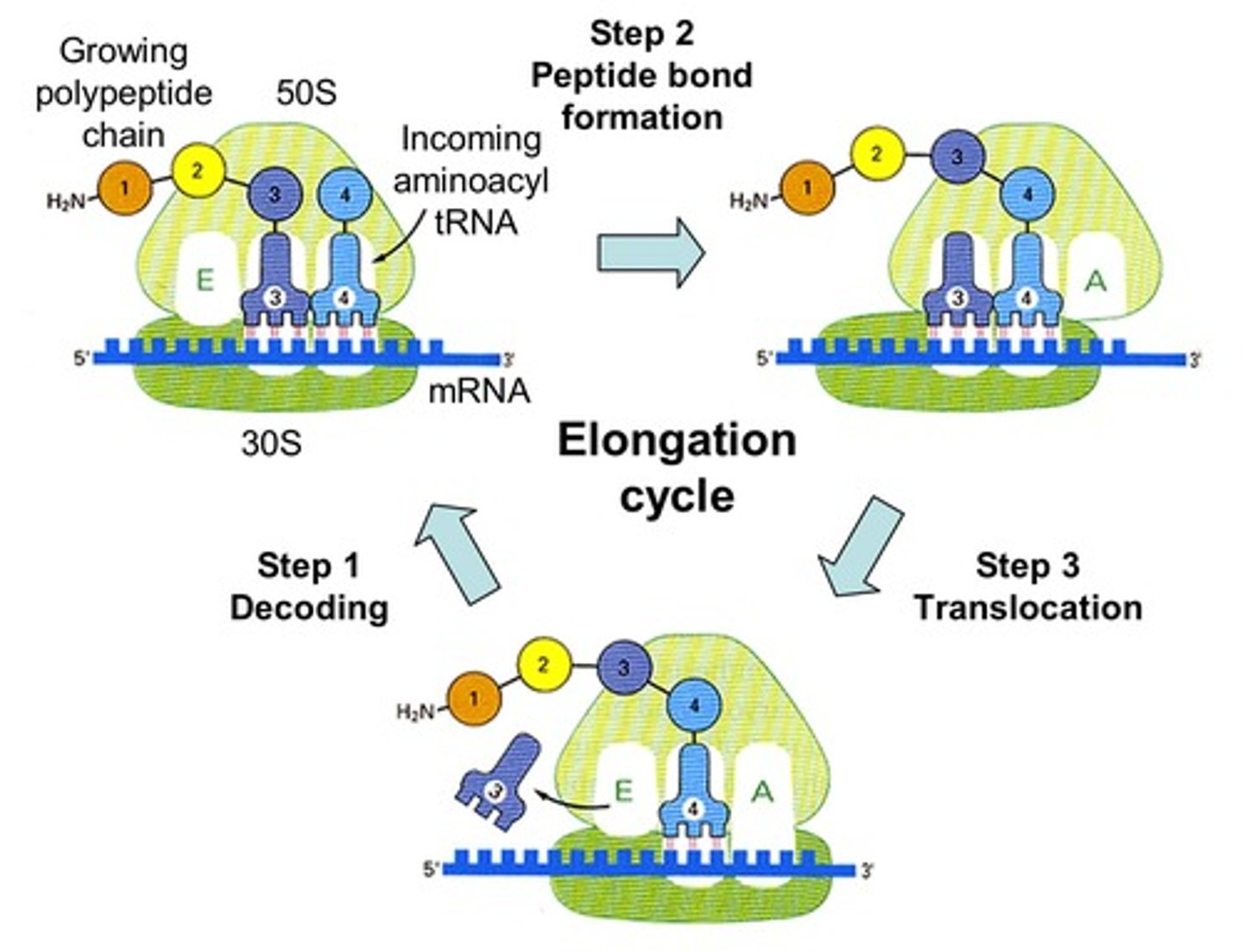
Termination
at a stop codon, a protein release factor binds to the ribosome, breaking the bond between the last tRNA and the polypeptide
Gene Expression
making a product from a gene.
Genes that code for RNA products: run transcription
Genes that code for proteins: run transcription then translation
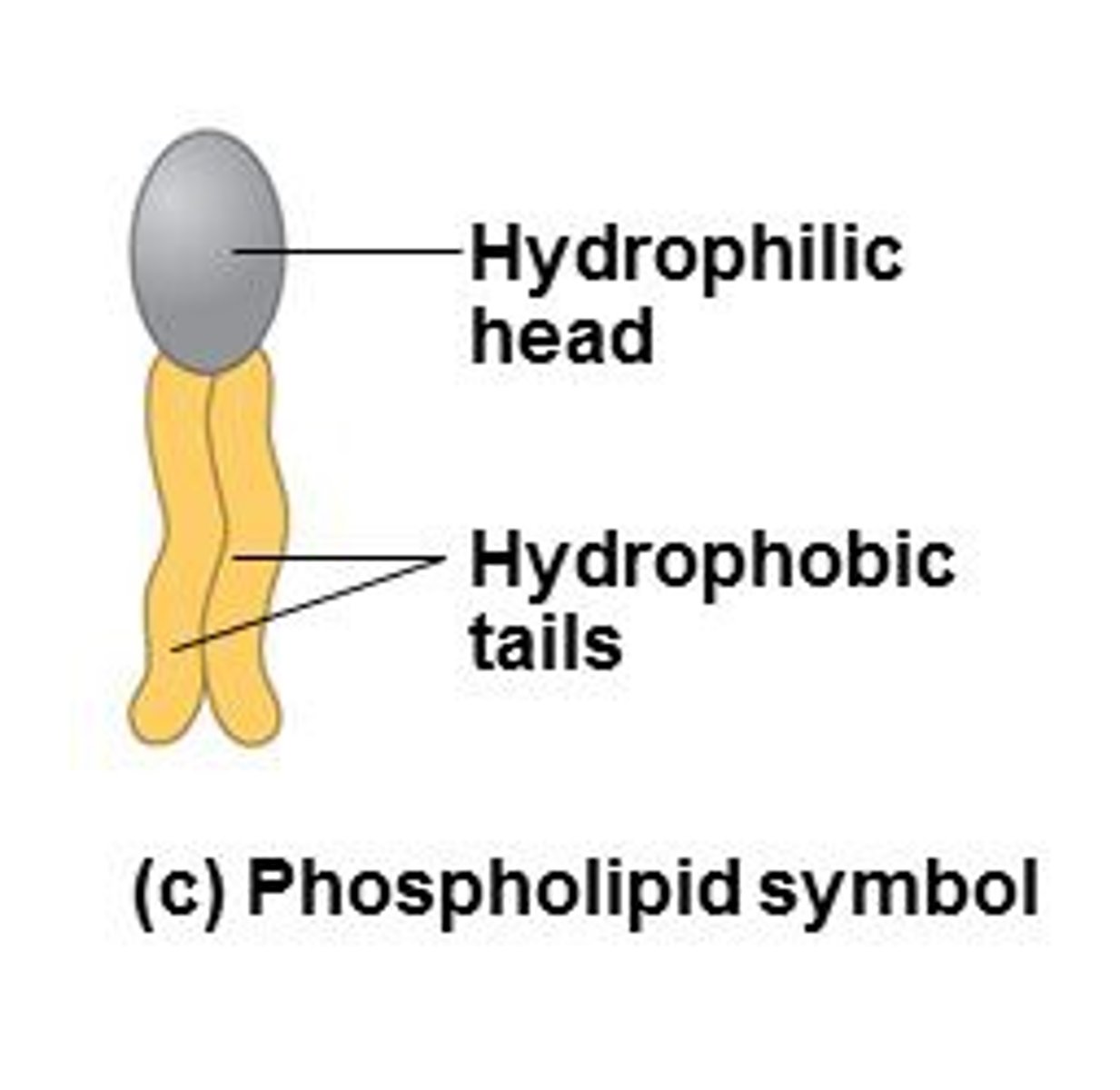
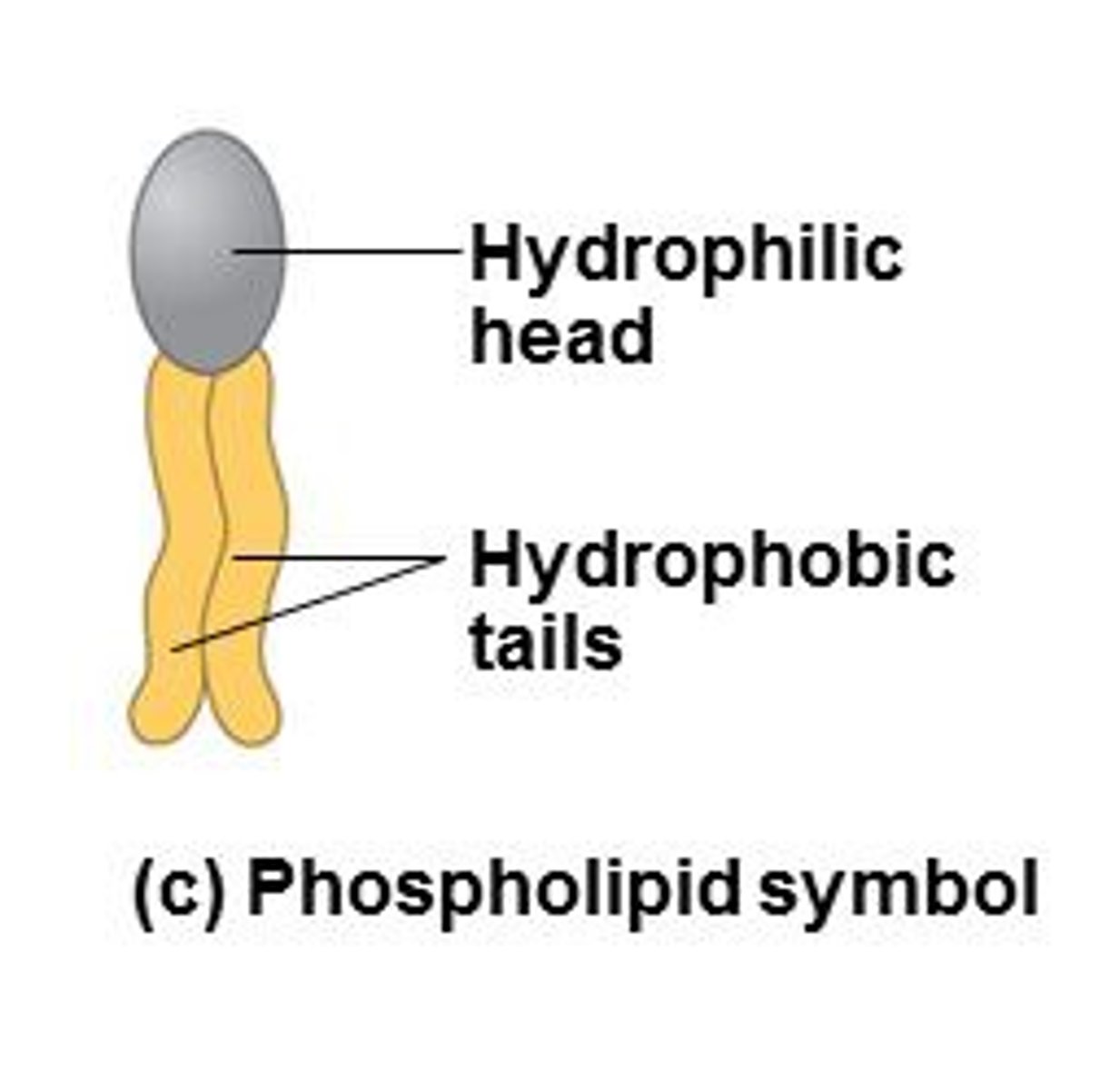
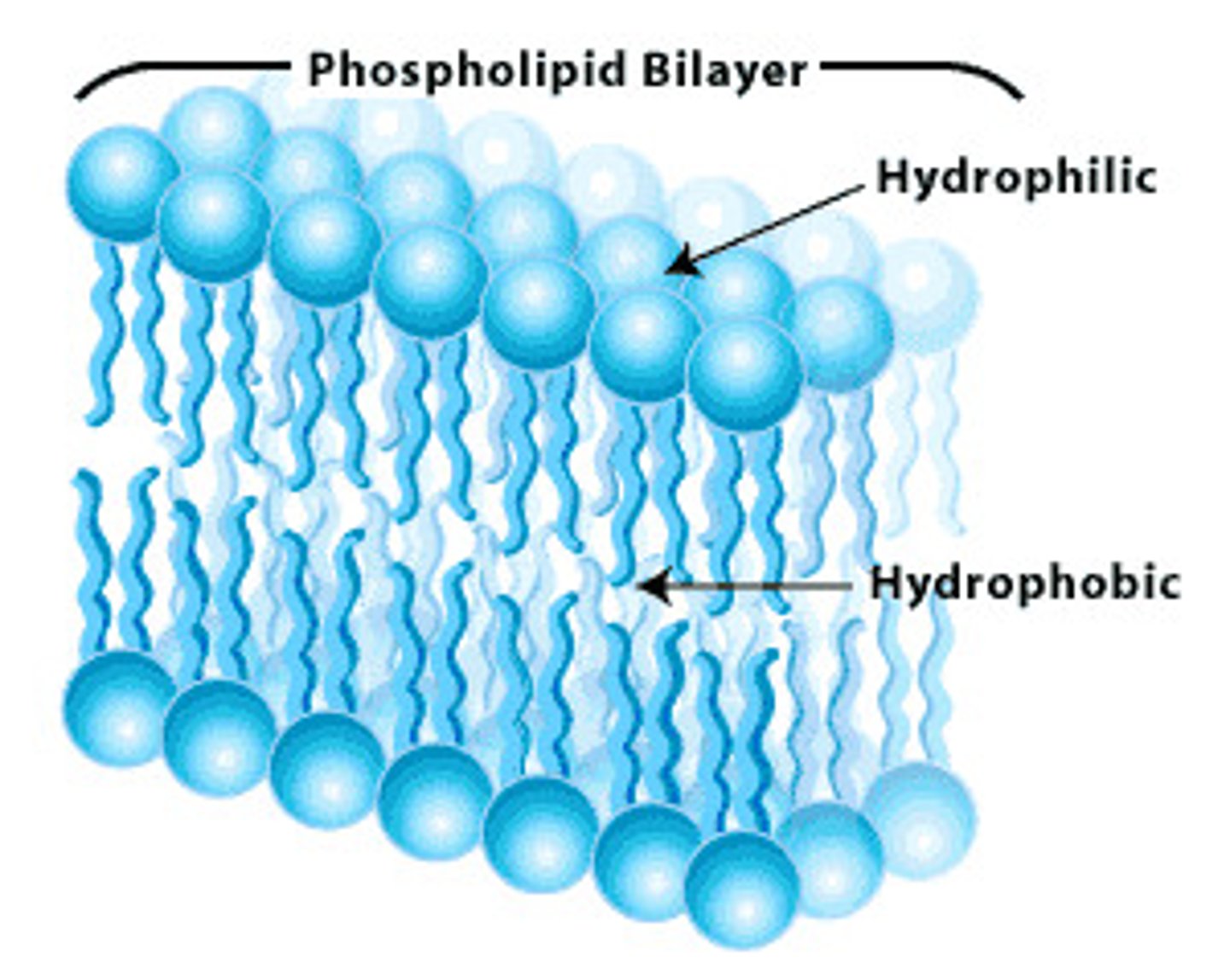
Phospholipid Strucutre
most common lipid. Hydrophilic head, hydrophobic tails. pH=7. Polar heads-interact with water. Nonpolar tails- orient to interact with each other. Differ in saturation
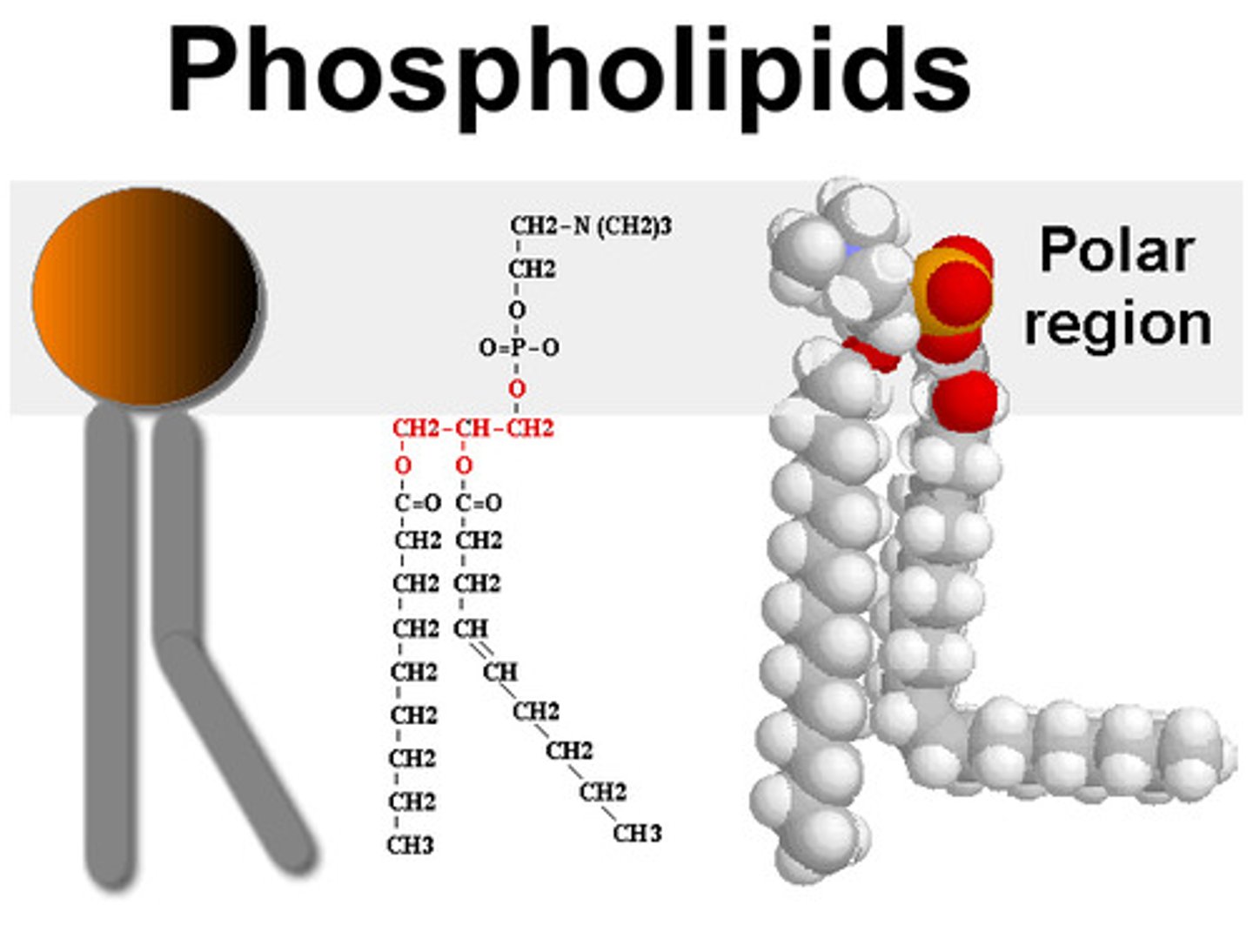
Amphipathic
having hydrophilic & hydrophobic regions (ex. phospholipid)