epi 221: midterm exam
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
significant results
RR?
CI?
p-value?
RR: includes 1
CI: 95%, narrow
p-value: <0.05
environmental epi
effect on human health of physical, biologic, and chemical factors in environment
similar to nutritional epi
ecologic studies
at the population level, large sample size
observational/analytical
measured at group level (all other studies → individual level)
e.g., measuring exposure as % malnourished vs malnourished/not malnourished
e.g., measuring outcome as infant mortality rate vs infant deaths
nutritional epidemiology
relations between diet and health
defined by exposures
life course theory
what?
five principles?
three concepts?
three epi models?
explains health & disease patterns across populations over time
biological, behavioral, social, economic, environmental → disease
lifespan development: natural consequences
human agency: personal control, behavior, and social contexts (!!)
timing: when? how long? in what order? (e.g., critical/sensitive windows)
linked lives: social networks
historical time & place: period, cohort (e.g., great depression)
trajectories: substantial part of lifespan (e.g., alcohol consumption)
transitions: brief part of lifespan (e.g., parenting)
maintains/is within trajectory(s)turning point: redirection in situation/behavior (e.g., parenthood → decreased alcohol)
change in trajectory
latency: biological risk
exposure that manifests later in life (e.g., fetal exposure → adult disease)cumulative: accumulation risk
additive exposures that accumulate throughout life → outcome
sequence does not matter, can be any factor (social, biological, etc.)pathway: social risk
one exposure can result in multiple/different outcomes (e.g., school prep → poor vs good → dumb vs smart)
sequence matters
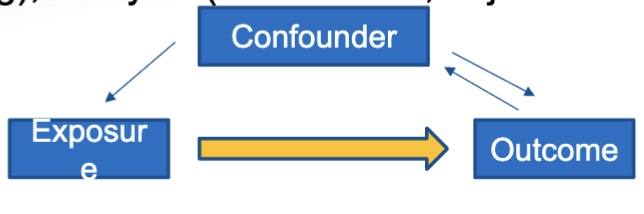
confounding
confounder: third variable, precedes exposure, related to outcome
confounding control:
design: randomization
analysis: stratification
infant mortality
death of a live-born child before the age of 1
maternal mortality
death of a woman while pregnant OR up to 6 weeks after birth
3 factors of MCH historical foundation
4 phases in US health policy for MCH
policy development for MCH: Phase 1
Characteristic:
Motivation:
Event:
policy development for MCH: Phase 2
Characteristic:
Motivation:
Event:
policy development for MCH: Phase 3
Characteristic:
Motivation:
Event:
policy development for MCH: Phase 4
Characteristic:
Motivation:
Event:
title V
Main source of MCH support from the government
Social Security Act
When: 1935
What:
Title IV:
Title V:
Title XVIII:
Title XIX:
OBRA
When: 1989
4 Initiatives
Healthy People 2020
What are the 4 Goals?
When: 2010 (by DHHS)
4 Goals
Healthy People 2030
What are the 5 objectives?
When: 2020
5 Objectives
public health
science of protecting and improving health of communities through health promotion, research, and [prevention, detection, & control of disease]
epidemiology
one of public health’s disciplines
study of distribution of determinants of health in the population & application to control health problems
distribution
what?
hypothesis?
studies?
descriptive epidemiology; describes time/person/place
no hypothesis/not tested
case/cross-sectional studies
determinants
what?
hypothesis?
studies?
analytical epidemiology; determines risk factor → outcome (hypothesis)
hypothesis/tested
observational/experiemntal studies
application
what?
4 intervention targets?
prevention epidemiology
when/where intervention is targeting
i.e., primordial, primary, secondary, tertiary
primordial
application → prevention → intervention
targets risk factor
e.g., exercise to prevent obesity in people who are not obese
primary
application → prevention → intervention
targets early disease
e.g., exercise to prevent early GDM in people who are obsese
secondary
application → prevention → intervention
targets late disease
e.g., screening/glucose monitoring to prevent late GDM in people who have early GDM
tertiary
application → prevention → intervention
targets disability
e.g., to prevent disability/complications of GDM in people who have late GDM
distribution study design
analytical study design
qualitative design
distribution
survey design
distribution
experimental
analytical
observational
analytical
case report
case series
qualitative (distribution)
cross-sectional
survey (distribution)
parallel
cross over
factorial
experimental (analytical)
cohort
case control
cross-sectional
observational (analytical)
incidence proportion (attach rate/risk)
# of new cases of disease (specified time)
/
population (at risk) at start of specified time
secondary attack rate
# of new cases among contacts
/
total # of contacts
incidence (person-time) rate
# new cases of disease (during time interval)
/
avg population during time interval
point prevalence
# current cases (present & past) (at point in time)
/
population (at same point in time)
period prevelance
# current cases (past & present) (over period of time)
/
avg population
prevalence
incidence rate # new cases/start population) x avg duration of disease
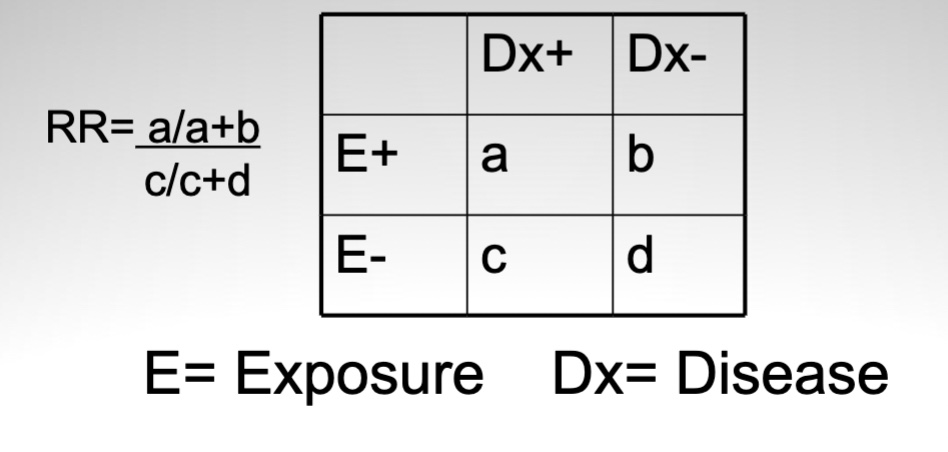
relative risk
relative change ratio in incidence (associated with presence of exposure)
risk of disease in exposed → risk of disease in unexposed
includes 1 = strong association
RR (relative risk equation)
RR <1?
RR >1?
= incidence of disease in exposed/unexposed
RR <1 = % exposed less than unexposed
RR >1 = % exposed greater than exposed
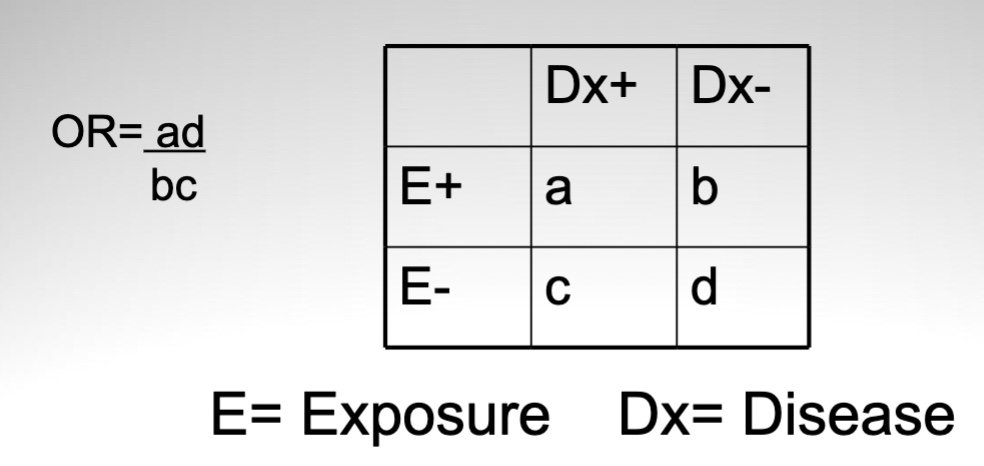
odds ratio
measure of association in which study type?
when interpreted as RR?
odds of disease exposed → odds of disease unexposed
measure of association in case-control studies
can be interpreted as RR if disease is rare (<10%)
inference by association
Inferred or observed?
observed! (not inferred!)
causal inference
Inferred or observed?
causal relationship: exposure as direct factor? exposure determines outcome?
what is required for causal relationship?
inferred! (not observed!)
exposure does not have to be a direct factor for causal relationship
exposure cannot determine an outcome as a causal relationship
Must use…
internal validity (NOT external)
specificity: E → O
temporality: E occurs before O
biologic gradient: proportion E increases compared to O
biological plausibility: amount E can be related to O
coherence: design similar to other studies
consistency: findings similar to other studies
analogy: outcome is similar to other studies
strength of associations
considers alt explanations
experimentation
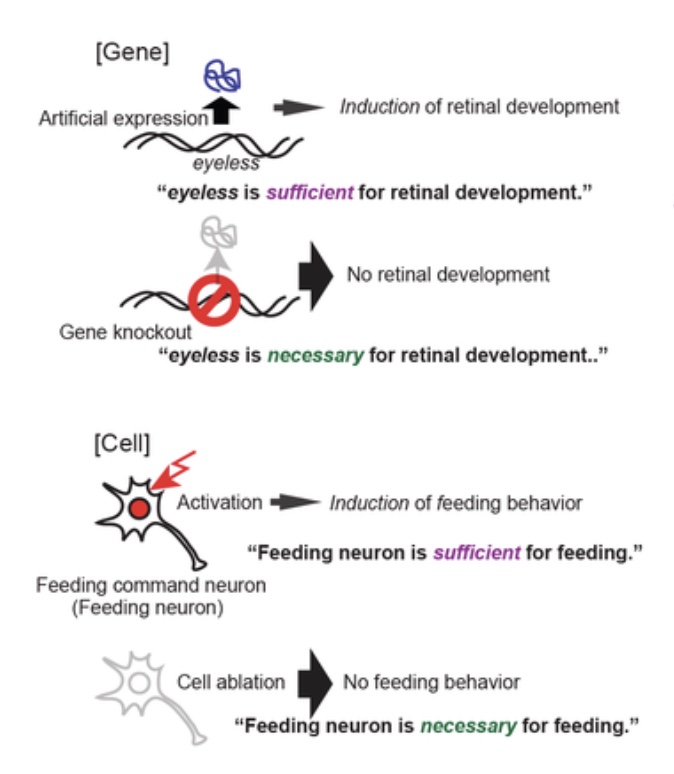
necessary vs sufficient exposure
necessary?
sufficient?
both?
neither?
necessary: required for outcome, cannot cause on its own
sufficient: not required for outcome, can cause on its own
both: is required for outcome, and can cause on its own
neither: not required for outcome, cannot cause on its own
internal validity
what is it?
3 factors?
established causal relationship
bias
selection bias: individuals not representative of target population
information bias: key factors inaccurately measured, reported, classified
confounding: third factor relating exposure & outcome
chance: i.e., statistics
information bias
misclassification?
prevented by?
types?
misclassification
differential: dependent on outcome/exposure, effect unknown
systematic, usually human error
effect unknown (worse T^T)
different between the two group
non-differential: not dependent on outcome/exposure, attenuation of associations
random, usually machine error
weakens associations
same between the two groups
→ prevented by: blinding!!
interviewer bias
recall bias
observer bias
laboratory error
chance
null hypothesis?
alt hypothesis?
p-value?
confidence interval?
null hypothesis (Ho): association due to chance
true = no association
alt hypothesis (Ha): association not due to chance
p-value: if Ho true, probability of strength of data against Ho
p-value <0.05 = strong evidence against Ho
confidence interval: interval that true value is likely found (95%)
→ more informative than p-values
wider: greater variability and/or small sample size
narrower: smaller variability and/or large sample size
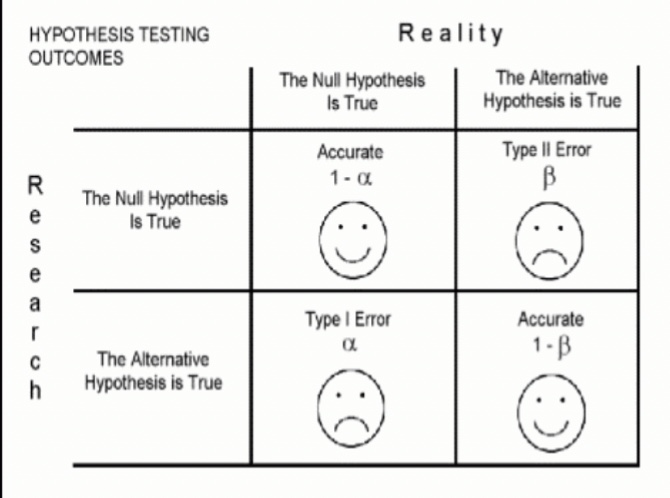
association testing: errors
type I?
type II?
type I: false positive
→ i.e., multiple testing
rejects Ho (wrong) → no association
accepts Ha (wrong) → association found
type II: false negative
→ i.e., small sample size, difference size, & significance level
accepts Ho (wrong) → there is association
rejects Ha (wrong) → association not found
external validity
what?
generalizability: inferences from one population can be extended to another
reproductive epidemiology
study of distribution and determinants of reproductive processes
defined by outcomes (fecundity & fertility)
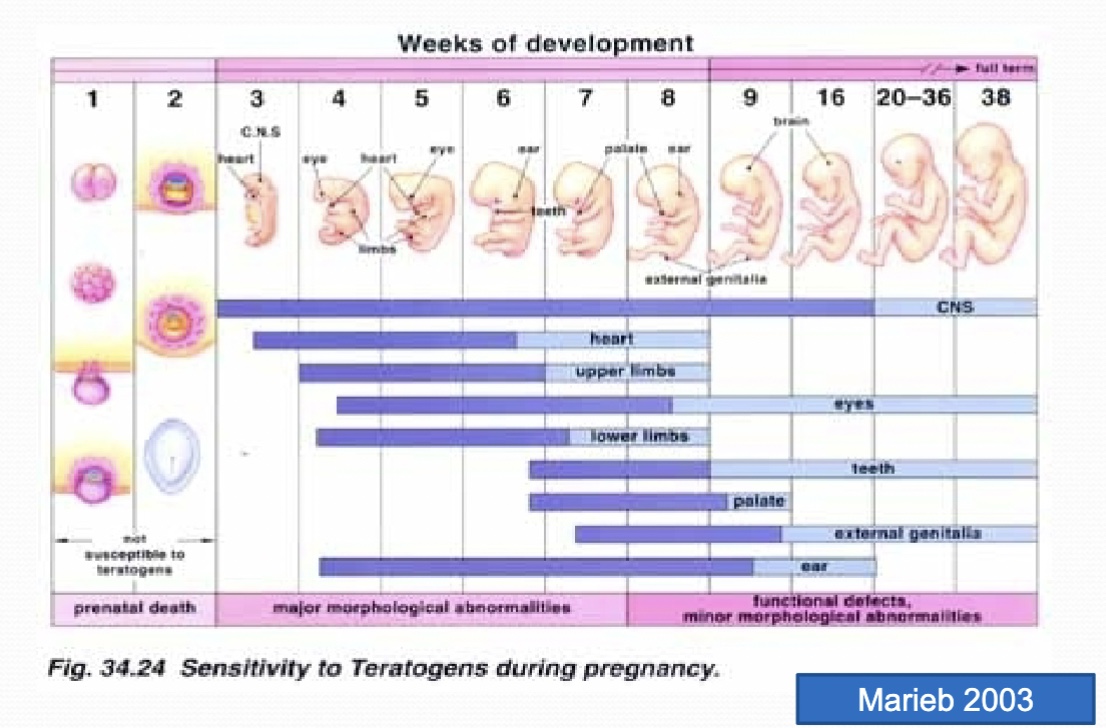
critical vs sensitive windows
critical: leads to structural defects
occurs in early pregnancy
increasing metabolic capabilities
cellular proliferation & development
sensitive: leads to functional defects
occurs in mid-late pregnancy
susceptible to non-structural defects
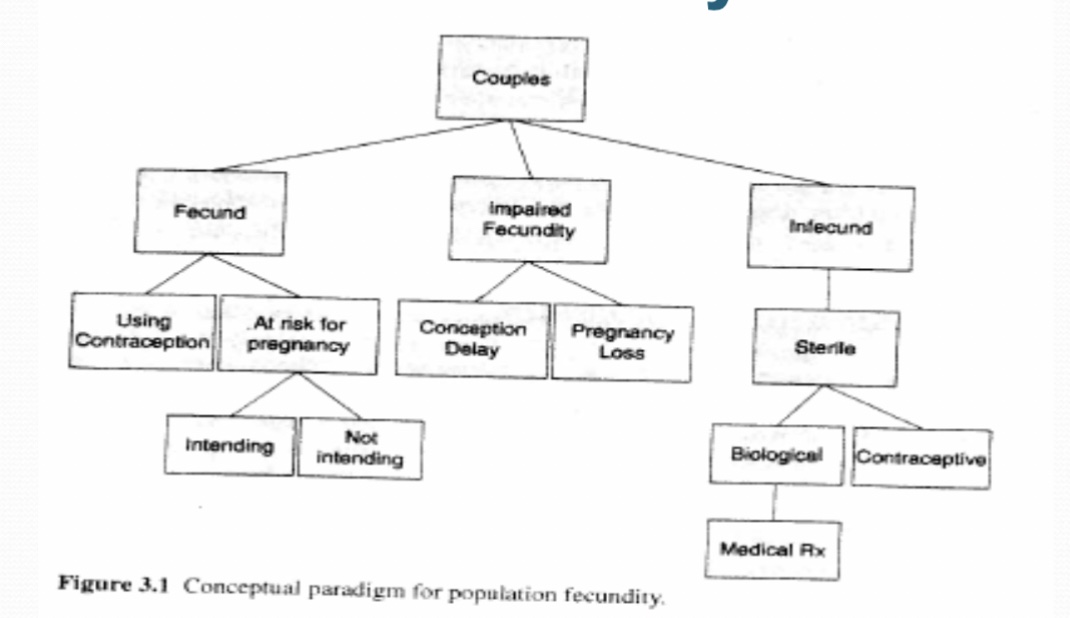
fecundity
what?
male vs female?
biological capacity of males and females for reproduction
male outcomes
puberty, libido/hormones
semen quality
urologic health
andropause
female outcomes
puberty, libido/hormones
menses & ovulation
gynecologic health
contraception
menopause
fertility
relation to fecundity?
primary vs secondary?
clinical classifications?
demonstrated fecundity
fecundity = necessary, insufficient → fertility
primary: no prior conceptions
secondary: at least one prior conception
fertile: <6 months
sub-fertile: 6-12 months
infertile: >2 months
general fertility rate
fertility
# live births per 1000 women
total (completed) fertility rate
fertility
# of births per woman
sex ratios (measuring fertility)
primary vs secondary?
fertility
primary: # conceptions, endogenous cases
secondary: # live births, exogenous cases
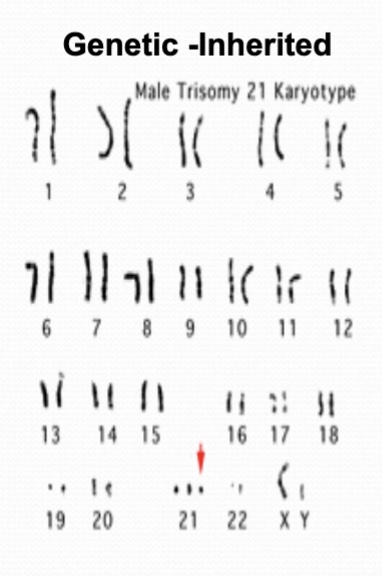
teratology
teratogens?
study of congenital malformations (structural birth defects)
teratogens: genetic
teratogens: environmental
infections (e.g., CMV, syphilis, rubella, HIV, EBV)
maternal toxic exposures (e.g., substance use, vitamin A, chemicals)
maternal conditions/environment (e.g., diabetes, obesity, fever, thyroid disorder, occupation)
congenital malformations
structural birth defects (present at birth)
developmental abnormalities
adverse environmental exposure: consequences
5 levels
no effect
least severefunctional defect
IUGR (growth abnormality)
structural defect
death
most severe