GENET 390: Topic 2.3 - Denaturing + Renaturing DNA + Calculating Tm
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
What bonds are being broken during denaturing of DNA?
H-Bonds between base pairs
What is the easiest way to denature DNA
Heating it
***At what temp is all DNA fully denatured?
90 degrees Celsius
What occurs during the process of renaturation/annealing?
Reformation of H-Bonds
How do you reanneal DNA?
REMOVE the thing that is causing the breaking of bonds
eg. Lower temp
eg. Neutralize base (seen with mini prep)
Define annealing temp
Temp at which a particular sequence reanneals
How does High Annealing temp affect stringency? define stringency
High Stringency = High specificity in base pairing
Higher annealing temp = Higher base pair specificity
reduces non-specific binding
Why does Higher temps lead to increased stringency?
Mismatches will fall apart at lower temperatures
What is a Hyperchromicity curve? How does it relate to denaturation/renaturation
Measures Absorbance at 260nm
Measure DNA denaturation by spectrophotometric measurements
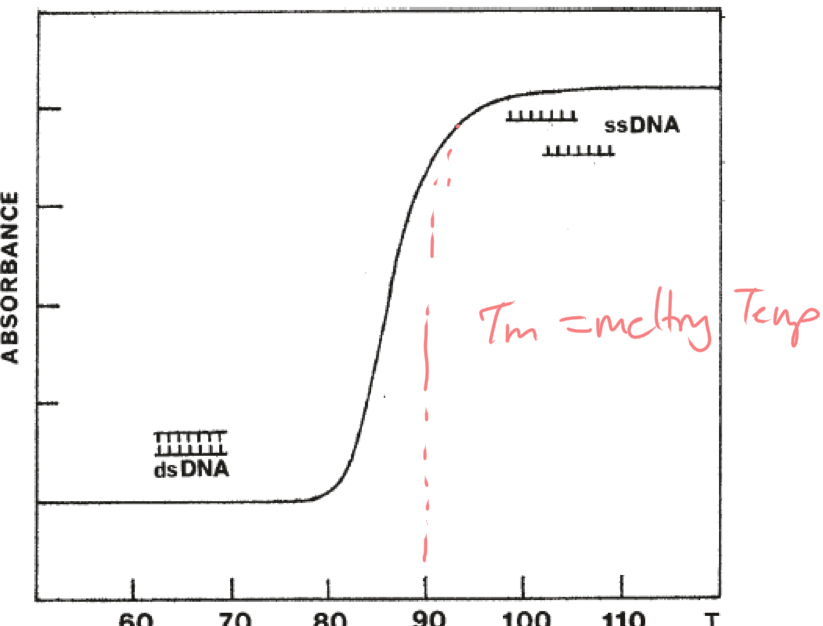
****How does ABSORBANCE change as DNA denatures?
Absorbance INCREASES as dsDNA —> ssDNA
ssDNA absorbs more
What is Tm?
Melting temp. Temp at which DNA denatures
At what point along the hyperchromicity curve is Tm measured at?
MIDPOINT
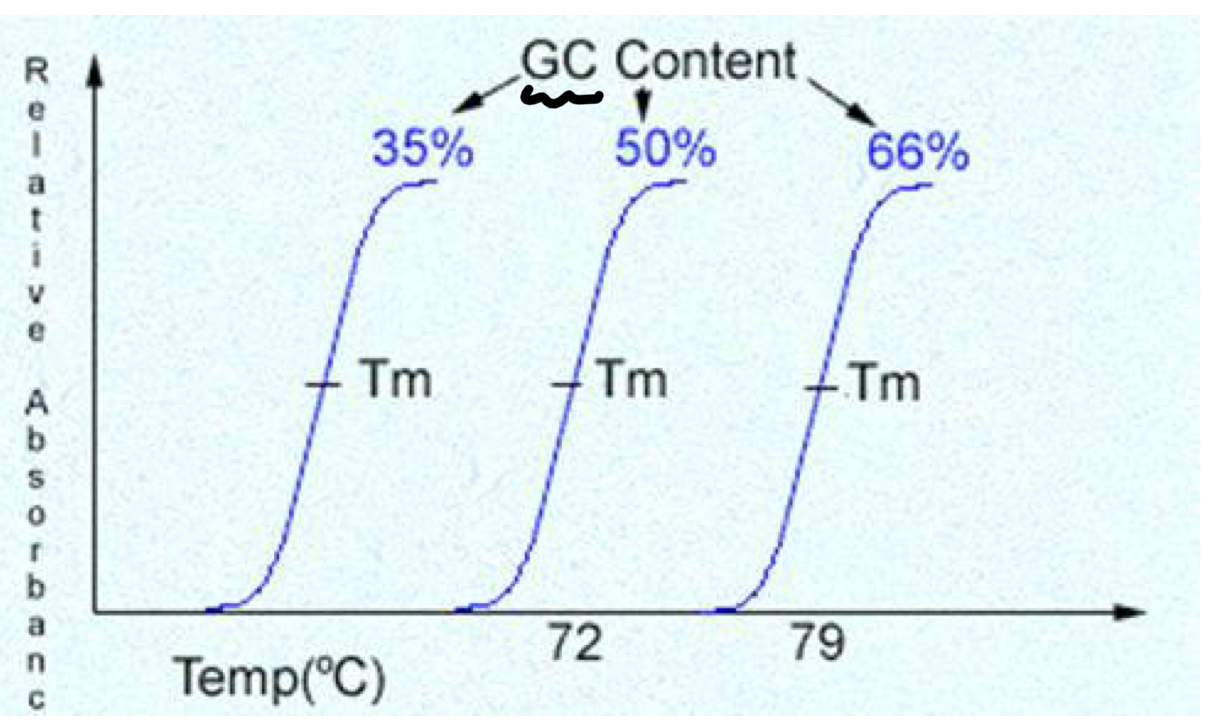
TRUE or FALSE: Base composition does not affect denaturation
FALSE
G-C bp = more stable at higher temps
Why are GC pairs more stable?
BASE stacking (driving force)
also a little bit to do with H-bond #
How does Tm change as GC content increases?
Tm Increases
***Although DNA fully denatures at 90 degrees Celsius, what temp do we practically use to ensure all dsDNA is denatured?
94 degrees Celsius
to accommodate for GC content effects
***What is the restriction on DNA size (bp) for 94 degrees denaturation?
not too sure on this 100bp thing
100 bp = minimum
***Why not use temps higher than 94?
Any higher = Increase risk of breaking Phosphodiester bonds
heat breaks all bonds
Weaker bonds are just easier to break at lower temps
*****What are the 6 FACTORS that influence Tm besides the GC content?
Sequence length
Presence of Salts
Presence of Organic solvents
pH
Nucleic acid type (DNA vs. RNA)
Sequence homology
How does sequence length affect Tm?
Does Tm become more dependent on composition in SHORTER or LONGER sequences?
More dependent on composition in Shorter Sequences = Much more variable in Tm
VERY dependent on GC content
Longer sequences = less affected by CG content
Around how many bp is Tm only slightly affected by composition?
greater than 1000
How does Salt affect Tm
Presence of salt INCREASES Tm
How does salt increase Tm
Ionic strength (presence of salt) stabilizes DNA duplex as part of the HYDRATION SHELL
Shields the repulsion of phosphates in the backbone
How does Ion concentration affect Tm?
Increase [ion] = increase stability = Increase Tm
***Are DIVALENT or MONOVALENT cations preferred for salt stabilizing effects on DNA?
DIVALENT
eg. Mg 2+
How do Organic Solvents Effect Tm?
Decreases Tm
**How/why do Organic solvents Decrease Tm?
Some can act as COMPETITIVE DENATURANTS
Molecules contain functional groups that can compete with base stacking interactions = Destabilize double helix
Disrupts the H-Bonds
Not all organic solvents disrupt Base stacking: what are some that do? (4)
Urea
Formaldehyde
Formamide
DMSO
How does pH affect Tm?
Both low + high pH = Decreases Tm
saw in miniprep with basic solutions
How do Basic solution decrease the Tm?
OH from base denatures DNA by removing the H+ of the H-bond forming the Base Pairing = Break bond
IONIZE NITROGENOUS BASES
BASE = STRONG H-ACCEPTOR
pH greater than 9
How does Type of nucleic acid affect Tm?
Higher Tm
RNA:RNA
RNA:DNA
DNA:DNA
Lower Tm
Why is Tm RNA:RNA > RNA:DNA > DNA:DNA? (2 reasons)
RNA = Capable of forming 2x’s the H-BONDS between H2O + Backbone
due to 2’ OH = More stable double helix when in H2O
2’OH = Stiffens the Helix = Strengthen double Helix
How does Sequence Homology affect Tm? DEFINE SEQUENCE HOMOLOGY
Definition: Amount of similarity between sequences/ amount of correctly matched based pairs
Low Homology (any MISMATCH) = SUBTANTIAL DECREASE in Tm
eg. 1 mismatch in DNA:DANA duplex = drop Tm by 20 degrees
Are there times where we will tolerate mismatches?
Yes
Finding relative sequences in southern
Why is the DNA melting curve so steep?
Once you get it started its a lot easier to pull apart
Why is it a lot easier to pull apart DNA after its started?
The initial pulling apart Weakens neighboring Base Pairs
Which regions melt first?
A/T rich
***Is Melting dependent on DNA CONCENTRATION? Why or why not?
YES!
High Concentrations = favor DUPLEX FORMATION = Increases Tm
Duplex formation is ssDNA —> dsDNA
higher concentration = more likely to find match to reanneal???
Why does Complete Denaturation of Genomic DNA require incubation at 94 degrees Celsius?
94 will denature a sequence that is 100% G/C pairs
Safe temp to ensure complete denaturation WITHOUT strand breakage
What occurs if you set up annealing conditions incorrectly?
Mismatches in annealed duplex
How many STEPS are required for Renaturing?
2
What are the 2 STEPS of renaturation
Nucleation
Zippering
Which of these 2 steps = the rate limiting step? WHY?
Nucleation
Its the hardest to START/ takes a long time
once you get it started the process = quick
****What is Nucleation?
RANDOM short complementary sequence formations
***How do these short complementary bp sequences form?
BROWNIAN MOTION
Random collision between sequences
***What is the required minimum length of bp needed to start zippering?
3 base pairs
Define Zippering
Rapid base pairing
When does Zippering occur?
if Bases ADJACENT TO the 3 bp are ALSO COMPLEMENTARY
What occurs if the Adjacent base pairs are not complementary?
Zippering does not occur + base pairing dissociates
**True or False: Only one nucleation event occurs and then zippering occurs immediately in succession
FALSE
MANY are require
TRIAL + ERROR over and over until the 3 bp are matched to allow zippering + zippering = possible
Is/Should Zippering be VERY sequence specific?
Yes
However specificity Depends on conditions
What are the conditions for Renaturation?
OPPOSITE of DENATURATION
What are the opposite conditions (4)
Low temp (below Tm)
HIGH formaldehyde/formamide
Some salt
High DNA concentrations
****What are the optimal Reannealing Temp?
20-25 degrees below Tm
Lower temps = allow Toleration of Mismatch
****What temps Ensure STRINGENCY/SPECIFICITY?
Close to Tm
Higher temps
How does salt help with reannealing?
Prevent electrostatic repulsion between backbones
increase stability of duplex
How does High [DNA] help with reannealing?
2 molecules are required for rate limiting nucleation step = reannealing is concentration dependent
higher [ ] more likely for random motion to result in correct bp
Can DNA [ ] ever be too high? Why or why not?
Yes
Too high = form Concatemers
Define Concatemers
Multiple sequences all annealed
***High stringency is always desired: What 3 conditions promote high stringency?
Higher temps closer to Tm (Still has to be below)
Keep salt concentration low
High formaldehyde/formamide
Compare the speed of reannealing to denaturation?
Slow compared to denaturation
several hours under lab conditions
***What type of DNA reanneals faster? (what characteristics)?
SHORTER or HIGHLY REPETITIVE reanneals faster than Long, non-repetitive DNA
Finish the Sentence: Using the rate of reannealing you can measure the frequency of _____
specific base sequences
What are 4 examples of where we use reannealing (not sure how important)
Southern + Northern (use probes)
PCR (Primers)
Cloning (variety)
****What is one example for when it is important to CALCULATE Tm?
Tm = important consideration for Primer design
normally calculated by software though
What are the 2 main ways to calculate Tm?
Basic
Nearest Neighbors
What are the 2 equations used in BASIC calculations? What type of sequences are they each applied to? (not sure how important)
Marmur: SHORT less than 14 bp =
Tm = 4xGC + 2xAT -7
Wallace: LONGER more than 14 bp
The above applies to DNA:DNA + DNA:RNA duplexes. WHAT ABOUT RNA:RNA duplexes Are the same calculations applicable? Why or Why not?
NO - RNA:RNA = stronger association = Stronger duplex
Calculations of Tm = DIFFERENT depending on NUCLEIC ACID TYPE