Chapter 3: Chromosomes and Inheritance
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
chromosomes are best defined as
the structures within living cells that contain the genetic material
the units of inheritance that code for proteins
genes
mitosis results in
two daughter cells containing the same number and type of chromosomes as the original parent cell
a typical human cell has ____ pairs of chromosomes for a total of ___
23; 46
meiosis produces cells that contain
half the number of chromosomes found in other cells within the same organism
the ___________ of eukaryotic cells is the organelle that primarily contains the genetic information
nucleus
most human somatic cells have a total of _____ chromosomes
46 (23 pairs, each containing 2 chromosomes)
a diploid cell is defined as a cell that has
two sets of chromosomes
a nucleus is
an organelle found in eukaryotic cells that contains the hereditary material
what does a haploid cell contain?
a single set of chromosomes
the structures within all living cells that contain the genetic material are called
chromosomes
a haploid cell is represented by n and a diploid cell by 2n. the n refers to______
a set of chromosomes
the kind of nuclear division followed by cell division that results in two daughter cells containing the same number and type of chromosomes as the original parent cell is called______
mitosis
after replication, each chromosome consists of two copies called ____, that are attached by a centromere
sister chromatids
in eukaryotes, ______ is the type of cell division that is responsible for the production of gametes
meiosis
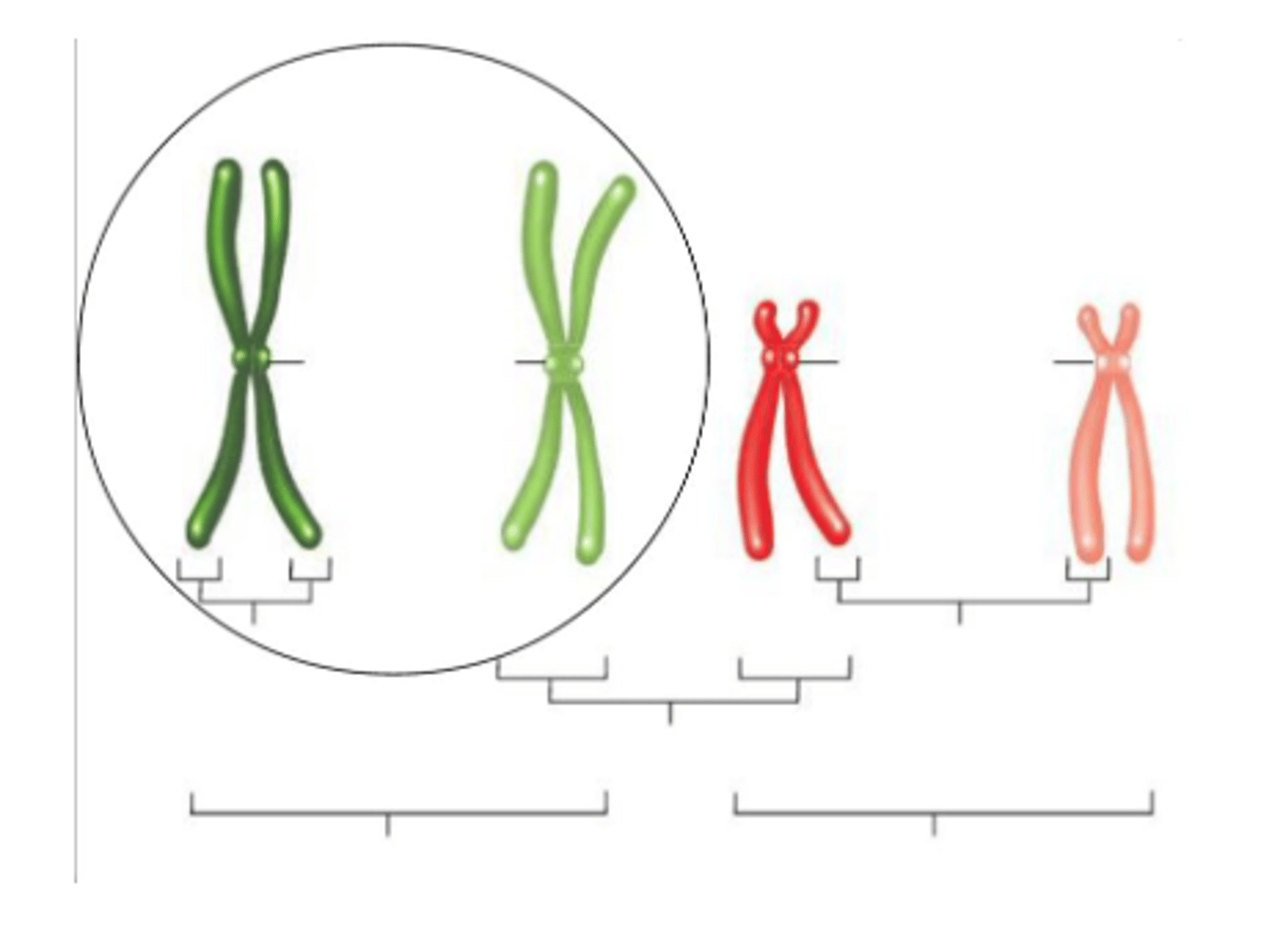
in this picture the circled chromosomes are
homologous chromosomes
in a _____ cell, each type of chromosome is a member of a pair
diploid
a(n) _____ cell has a single set of chromosomes
haploid
in a diploid cell, each member of a pair of chromosomes is called a(n)
homolog
in humans, a diploid cell contains two sets of chromosomes, for a total of ________ chromosomes. In contrast, a gamete (sperm or egg cell) contains only a single set, consisting of ____ chromosomes
46; 23
what is the name for the diffuse complex of DNA and proteins in a eukaryotic cell?
chromatin
the two copies of a replicated chromosome are called ____
sister chromatids
during the G1 phase of interphase, ____
cells grow in size
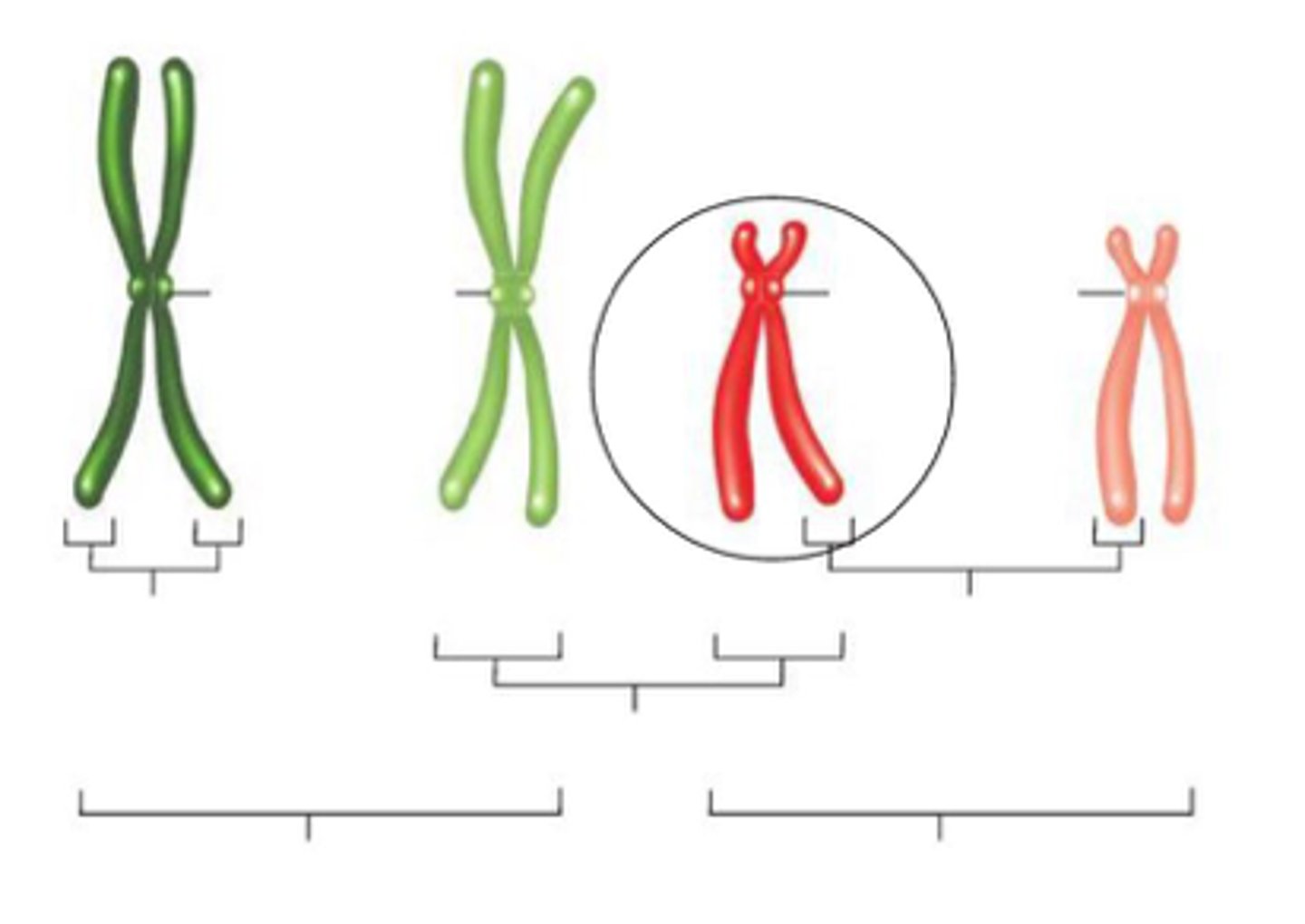
in this picture the circled chromosome is composed of two
sister chromatids
during prophase of mitosis, chromosomes _______ into discrete structures. Furthermore, the two _______ separate moving towards the moles and the mitotic _______ begins to form
condense, centrosomes, spindle
select the events that occur during prometaphase
chromosomes attach to the microtubules through the kinetochore
the nuclear envelope completely breaks down
chromosomes inherited from each parent that match in size, shape, and banding are called
homologs or homologous
the mitotic spindle of an animal cell has two poles, which originate from the two ______
centrosomes
what. is chromatin?
a complex between DNA and proteins that is found in eukaryotic cells
during which part of interphase do cells achieve the majority of their growth?
G1
during ____ of mitosis, chromosomes are aligned along the equatorial plate, or the center of the cell
metaphase
select the events that occur during prophase of mitosis
the nucleolus becomes less visible
the centrosomes move apart
the chromatin condenses into more compact structures
During ______, pairs of sister chromatids become attached to kinetochore microtubules which emanate from opposite poles of the cell.
prometaphase
the mitotic ______ contains three types of microtubules: axial, polar, and kinetochore microtubules
spindle
what event occurs during metaphase of mitosis?
pairs of sister chromatids become organized in a single row
which of the following events occurs during anaphase of mitosis?
sister chromatids separate from each other and head to opposite poles
if the original diploid mother cell had eight chromosomes, a cell in telophase of mitosis would have _____ nuclei, each with ____ chromosomes
two; eight
which of the following best describes the outcome of mitosis and cytokinesis in human somatic cells?
2n --> 2n
what ensures that cell cycle events occur in the proper sequence?
checkpoints
cells that are destined to undergo meiosis and produce gametes are called ______ cells
germ or germ-line
during anaphase, each chromatid moves towards the pole to which it is attached. this movement is caused by the shortening of the
kinetochore microtubules
all of the following events occur during telophase except that the
pairs of sister chromatids begin to separate from each other (this occurs in anaphase)
mitosis and cytokinesis result in the formation of ____
two genetically identical daughter cells
synapsis is the process by which _____
homologous chromosomes recognize each other and begin to align themselves in prophase I
when a cell evaluated the results of previous steps, this is called a(n)
checkpoint
during the zygotene stage of meiosis I, the _____ complex aligns homologous chromosomes
synaptonemal
a _____ cell is any cell of the body that is not a gamete or precursor to a gamete
somatic
a bivalent, or tetrad, consists of ____
two pairs of sister chromatids of homologs
during which of the following phases are tetrads organized along a plate in the center of the cell?
metaphase of meiosis I
during prophase of meiosis I, homologous chromosomes recognize and begin to align with each other via a process called _____
synapsis
consider an organism that has four pairs of chromosomes (2n = 8). at the end of meiosis I, each cell would have _____ chromosomes and _____ chromatids
four; eight
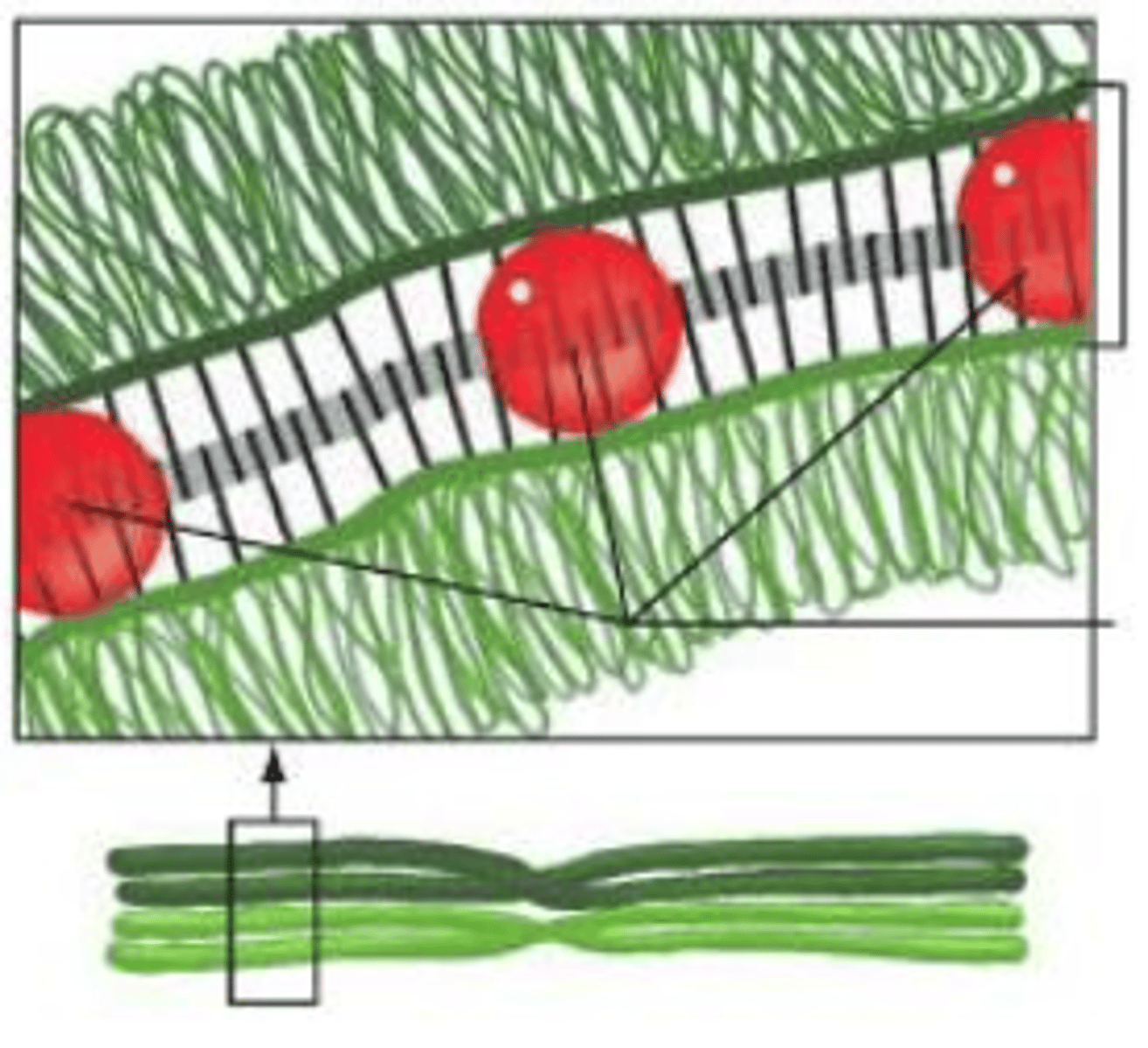
the zipper like structure in the center of this picture represents ____
the synaptonemal complex
During what stage of meiosis II does the nuclear envelope break down?
prophase II
A bivalent is also called a ______ because it is composed of four chromatids.
tetrad
select the aspects of meiosis that contribute to genetic diversity in a population
independent assortment
crossing-over
in _____of meiosis, the bivalents (which are also termed tetrads) are aligned along the center of the cell
metaphase I
select the events that occur during mitosis
sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles
chromosomes condense, and nuclear envelope breaks down
kinetochores begin attaching to spindle fibers
in 1903, Walter Sutton suggested that chromosomes carry Mendel's hereditary units. Select the reasons he gave for this proposal.
in all cells derived from a fertilized egg, half of the chromosomes and genes have maternal origin, and half have paternal origin
both chromosomes and alleles of unrelated genes assort independently
during meiosis, homologous chromosomes and alternative alleles of a gene pair then separate to different gametes
every cell has two copies of each chromosome, and there are two copies of each kind of gene
which of the following best describes the outcomes of meiosis I in humans?
2n --> 1n
Mendel's law of ______ can be explained by the homologous pairing and separation of chromosomes during meiosis
segregation
if the chromosomes decondense during the preceding interphase, they recondense during ______ II of meiosis
prophase
meiosis increases genetic diversity in a population through crossing-over and by _________ assortment of parental chromosomes
independent
the random arrangement of homologs along the metaphase plate in meiosis I is consistent with Mendel's law of _____ ____
independent assortment
which of the following statements about mitosis and meiosis of humans is true?
mitosis produced two diploid daughter cells, while meiosis produces four haploid daughter cells
in 1902-1903, Walter Sutton proposed that _____ contain genes
chromosomes
the behavior of chromosomes during meiosis explains Mendel's law of segregation. Specifically, a gamete contains only one copy of each type of chromosome because of which of the following?
the homologs segregate during meiosis I and the sister chromatids during meiosis II
which aspect of chromosome behavior is consistent with Mendel's law of independent assortment?
independent alignment of different homologous pairs along the metaphase I plate