Science 8: Mechanical Systems MS1 & MS2
MS1: Describe various simple machines and use mathematical formulas to calculate
Simple machines use mathematical formulas to calculate:
- Work (Force x distance)
- Force (work / distance)
- Mechanical Advantage (Force output / Force input)
- Efficiency (work output / work input x 100)
- Speed Ratio (#teeth driver / #teeth follower)
- Pressure (Force/area)
MS1.1: Calculate Work
Force: is a push or pull, has magnitude and direction, is measured in Newtons (N)
Work: is the transfer of energy through motion, requires a force and distance, is measured in joules (J)
MS1.2: Simple Machines
A machine is a device used for multiplying forces or changing the direction of a force. Machines can increase the speed with which work is done.
Types of Simple Machines:
Levers
- A simple machine that changes the amount of force you must exert in order to move an object
- 3 parts of a lever:
- Fulcrum: the pivot point of a lever
- Load: the mass of the object being moved
- Effort Force: the force used to operate a lever
- FLE (fulcrum, load, effort), 123
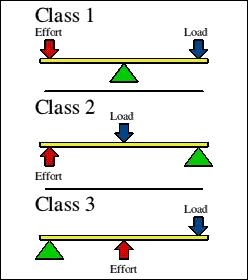
- Class 1 Lever
- Fulcrum is between the effort force and the load
- Teetor totter, scissors, etc.
- Class 2 Lever
- Load is between the fulcrum and the effort force
- Nutcracker, wheelbarrow, etc.
- Class 3 Lever
- Effort force is between the fulcrum and the load
- Baseball bat, golf club, etc.
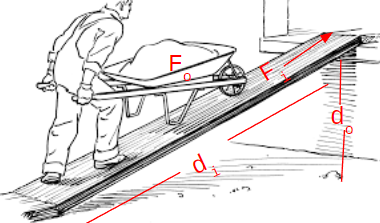
Inclined Plane
- A simple machine that is a ramp or a slope
- Always Force advantages because the effort force is decreased by increasing distance
Wedge
- A simple machine that is a triangular tool
- Portable inclinced plane
- Used to seperate two objects or pieces, hold objects in place, and/or lift
Pulley
- A simple machine that has a grooved wheel that carries a rope
- Used to change the direction of the effort force and/or to lift objects with less effort (FA)
Wheel and Axle
- A simple machine with two wheels of different diameters that turn together
- Can produce distance or Force advantage
- Effort on wheel = Force advantage
- Effort on axle = S/d advantage
Screw
- A simple machine that is a cylinder wrapped with an inclined plane
- Force advantage
- It turns rotational motion into linear motion
MS1.3: Mechanical Advantage of Simple Machines
Mechanical advantage is a value that indicates how much a machine multiples force or distance.
- MA>1 Force advantage (Less force needed)
- Trade off is speed or distance
- MA<1 Speed or Distance advantage
- Trade off is force
- MA=1 Change of direction only
Mechanical Advantage and Levers
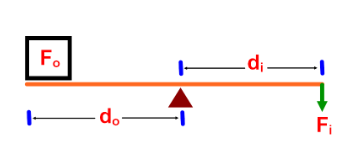
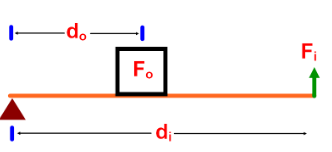
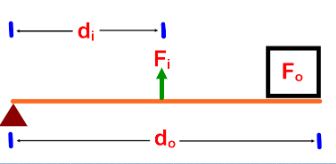
- Fo is always the load
- Fi is the effort force
Changing the length of the arms affects the MA of the lever.
Ma of a Class 1 Lever: 3 different ways
- MA=1 Change of direction: Fulcrum exactly in the middle
- MA<1 Speed/distance advantage: Fulcrum closer to the effort force
- MA>1 Force advantage: Fulcrum is closer to the load
MA of a Class 2 Lever: Force advantage (MA >1)
MA of a Class 3 Lever: Speed/distance advantage (MA <1)
Mechanical Advanatage and Pulleys
- Fixed pulleys have a MA=1 and only provide a change of direction
- Moveable pulleys have a MA>1 and provide a force advantage
- Block and tackle pulleys are made up of multiple pulleys working together, used to lift a large load, provide a force advantage, and the force can be in any direction
- The amount of ropes is the MA
Mechanical Advanatage and Pulleys
Fo is the load, and Fi is the force to push the load up the ramp.
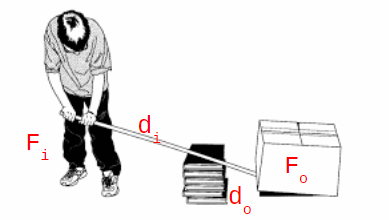
MS1.4: Calculate Work Input and Work Output
When you do work on a machine, the machine does work on the load.
The work you do is WORK INPUT
The work the machine does it WORK OUTPUT
W=F x d, Wi=Fi x di, Wo=Fo x do
MS1.5: Energy, Friction & Efficiency
- Energy: The ability to do work; work is done whenever a force causes an object to move; when work is done, energy is transferred or transformed
- Kinetic Energy:
- The energy of motion
- Thermal energy is kinetic energy
- Roller coasters, pulleys, levers, etc.
- Potential Energy:
- Stored energy
- Chemical potential energy (batteries)
- Gravitational potential energy
- Elastic potential energy
The Law of Conservation of Energy: Energy cannot be created, or destryoed, only changed in form. Work is the conversion of potential energy to kinetic energy!
- Friction: A force that resists movement
- Anywhere 2 surfaces rub against each other
- Results in loss of energy due to heat/friction
- Can be prevented by using lubricants (oil)
- Efficiency: A value indicating how much energy is lost due to friction or heat
- E.x. 80% effiencient, 20% of work is lost to friction
MS1.6: Gears
- Gears are rotating wheel-like objects with teeth cut into the rim
- Gears work together in groups called gear trains
- Motion is transferred from one gear to another
- Changes the direction of a force
- Force input is applied to the driver gear, and the force output is the follower gear
- The gear between the driver and the follower is called the idler gear, and its purpose is to allow the driver and follower gear to turn in the same direction
Parallel Gear:
- Driver and follower gear are the same size
- Change of direction only (MA=1)
Multiplying Gear:
- Large driver and smaller follower
- Speed advantage (MA<1)
Reducing Gear:
- Small driver and larger follower
- Force advantage (MA>1)
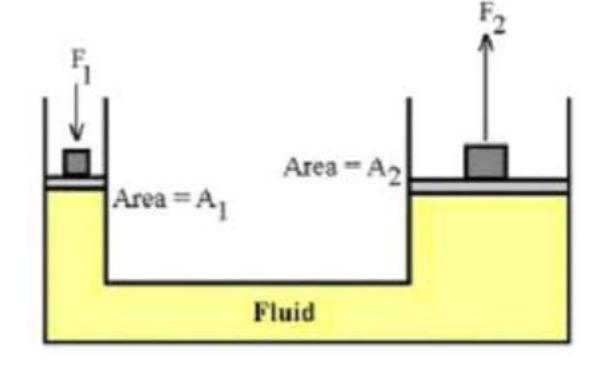
MS2: Pascal’s Law and Pressure
MS2.1: Pascal’s Law and Pressure
Pressure is a measurement of the amount of force acting over a certain area.
Pascal’s Law:
- Pressure exerted on a contained fluid is:
- Transmitted, undiminished in all directions
- Perpendicular to the walls of the container
- If you apply pressure to a fluid in a closed container, the fluid will transmit that same amount of pressure in all direction
Hydraulic systems are a mechanical system that uses liquids under pressure, in a closed system to do its work.
- Uses pistons of different sizes to create a force advantage
- Pressure is the same throughout the container
- A small amount of force can be applied to the small piston, which means a large amount of force will be applied on the large piston because pressure stays the same throughout the system.