Genetic Chapter 2
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Character/Trait ?
Attribute if individual members of a species for which various heritable differences can be defined
What is gene discovery ?
Find a set of genes affecting some biological process of inheritance by the single gene inheritance patterns of their mutant alleles or by genomic analysis
Heritable variants?
Individual’s who inherit a trait that expresses differently from some standard form
Wild Type?
Most common form
Are mutants rare to wild type?
Yes
Phenotypes?
Form taken by some character in a specific individual
Detectable outward manifestations of a specific genotype
What are the 4 steps of analyzing traits ?
Amass mutants affecting the trait
Cross mutant to wild-type
Deduce functions of the gene at the molecular level
Identify how the gene interacts with the other to produce the trait in question
Genetic dissection ?
use of recombination and mutation to piece various components of a given biological function
Forward genetics?
Genes are first identified by mutant alleles and phenotypes
Later cloned and subjected to the molecular analysis
Reverse genetics ?
Begin with the cloned segment of DNA/protein sequence
What does reverse genetics introduce ?
Programmed mutations back into the genome to investigate
Mendel’s pioneering experiment ?
Garden Pea, Pisum Sativam- 3:1 ratio
Why did Mendel choose Garden pea?
Easy to grow and breed
What was Mendel interested in ?
The way which the hereditary unit that influenced traits from generation to the other
What are the 7 traits that Mendel investigated ?
Colour
Shape
pod colour
pod shape
flower colour
plant height
Position of flowering
What is a pure line ?
Pop, all bearing the identical fully homozygous genotype
Self-pollination ?
Fertilize eggs with sperms from the same individual
Parental generation?
Start of genetic breeding
F1?
From 2 homozygous diploid lines
F2?
From F1 generation 1:2:1
Gene ?
Fundamental physical and functional unit of heredity
Allele ?
Different form of a gene that can exist at a single locus
Dominant ?
Phenotype shown by a heterozygote
Is the dominant allele expressed even when heterozygous with recessive allele?
Yes
Recessive ?
Phenotypic affect is not expressed in a heterozygote
Heritable factors?
Genes that are located on chromosomes
Somatic cell division ?
Division of body cell into two daughter cells
Does mitosis produce exact copies of the parent cell?
yes
Where does meiosis take place?
meiocyte
Sexual cell division ?
division of a meiocyte that produce sex cells
what does meiosis produce ?
Sperm and eggs in plants/animals or sexual pores in fungi/algae
Does meiosis have one-half of the genetic material of the original cell ?
true
n ?
the number of chromosomes in the genome
2 genomes per chromosomes sets per adult cell
Diploid ?
cell having two chromosomes sets
Haploid ?
cell having one chromosome set
List 3 main concepts of Mitosis ?
Can take place in diploid or haploid cells
progenitor cell becomes two genetically identical cells
somatic cell division and the accompanying nuclear
Meiosis ?
Sexual cell division two sequential divisions take place along with two nuclear divisions
Does meiosis happen only in diploid cells?
True
What are the resulting gametes of meiosis ?
Haploid, 4 cells are produced
Tetrad ?
group of haploid cells
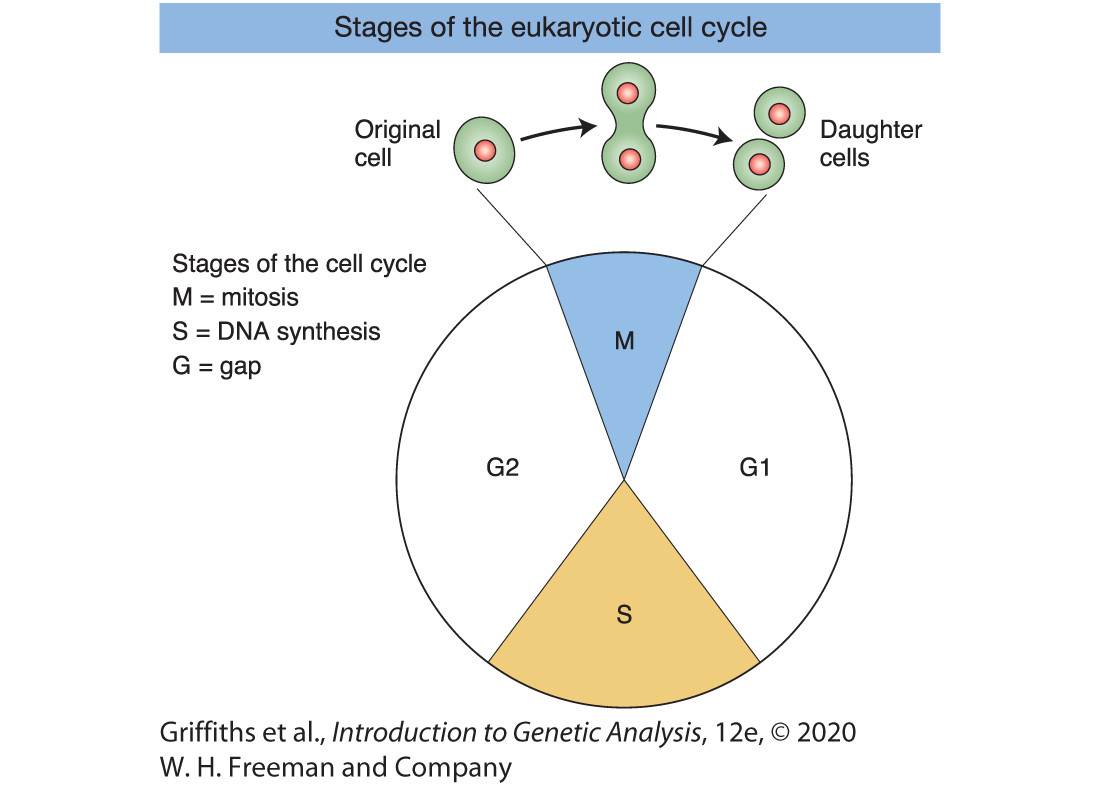
Stages of eukaryotic cell cycle ?
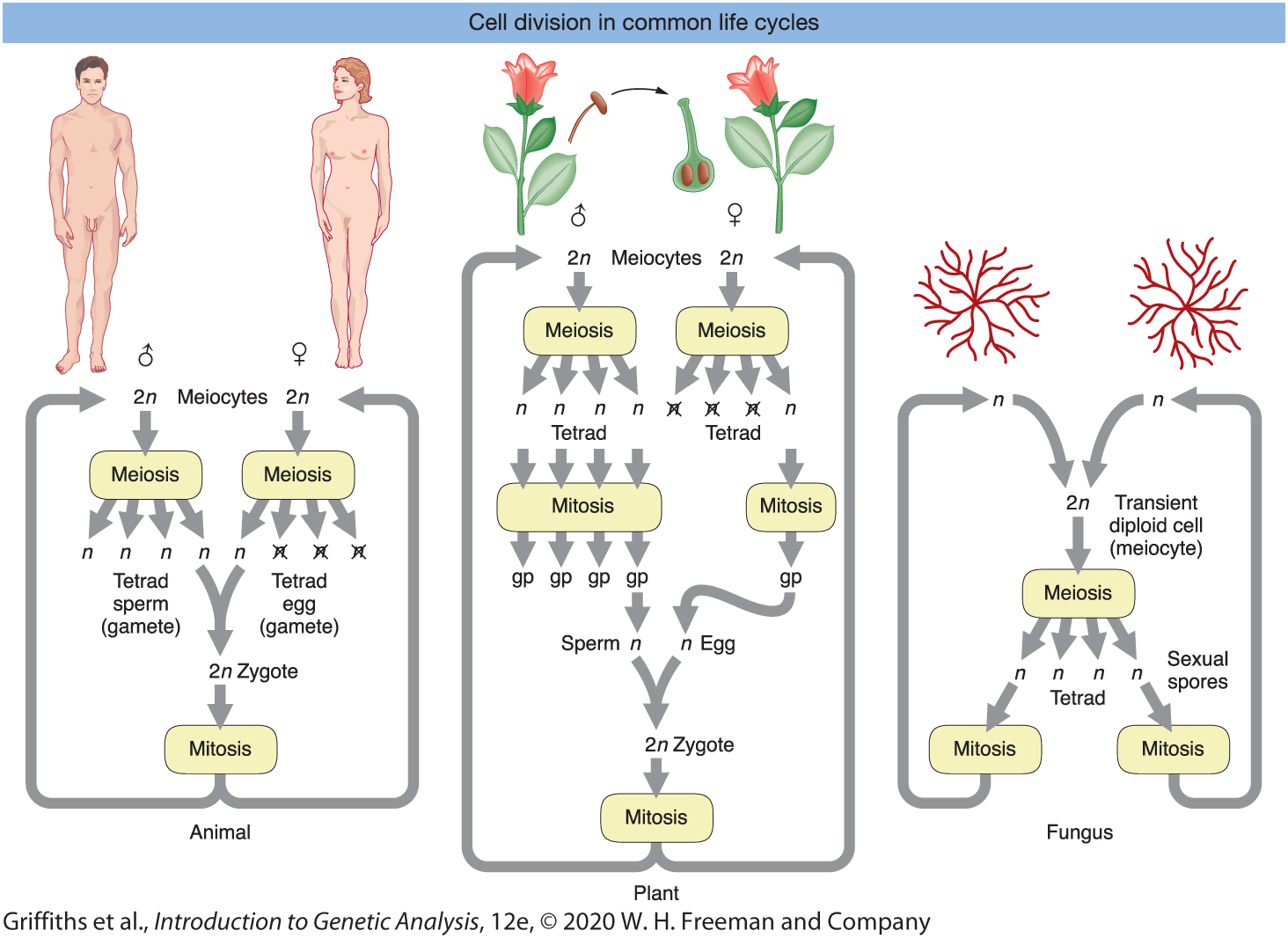
Cell division in common life cycles ?
How does chromosome become shorter?
condense by coiling
chromatids ?
one of the two side-by-side replicase produced by chromosome division