Sed Pet Week III
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
sedimentary structures, sandstone compositions
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
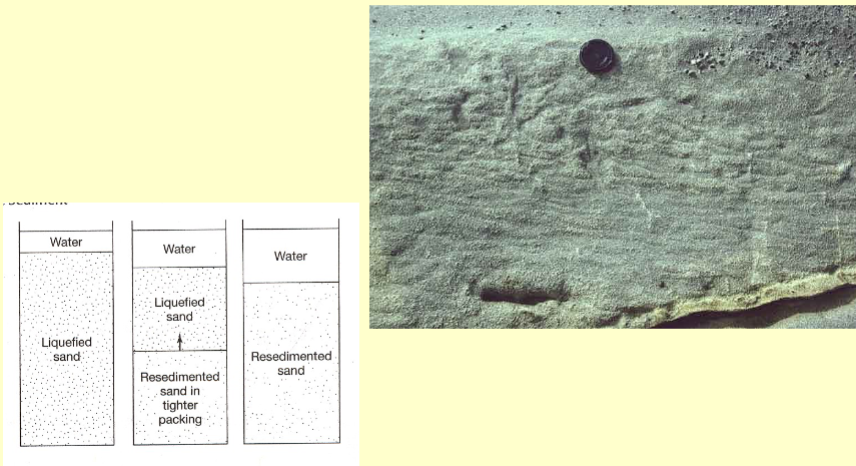
Liquefied flows
Very concentrated dispersions of grains in a fluid. Usually result from shock of granular sediment (earthquake). Grains kept in suspension by fluid pore pressure and upward movement of expelled fluid (grains continue to attempt downward moition)

Grain flows
Characterized by grain to grain collisions; little friction so they only occur on steep slopes where the angle of initial yield is exceeded

Debris flows
Slurry like flows in which large particles are set in fine-grained matrix. Matrix has yield strength that helps to support grains. It lubricates grain irregularities so debris flows can occur on gentle slopes. Coarser grains carried on top
seen commonly in continental margins (subaqueous)
Cohesive freezing
Internal cohesion causes a fluid to stop moving/move very slowly
Sandstone formation
Sed rock → pedogenesis (soil) → erosion → transport → deposition/burial
Mechanisms of transport
mechanical breakage, chemical weathering, authigenic input, hydraulic sorting, burial diagenesis
Goldich weathering series
Silicate minerals with higher polymerization tend to be most stable at earth’s surface (quartz, muscovite, feldspar). Those that form at higher temps and pressures are less stable and this more susceptible to weathering (olivine, pyroxenes)

Interference colors differ due to (retardation)
Birefringence * thickness of thin section. Light is split in different directions when entering a mineral
Sodium cobaltinitrite
stains potassium-bearing minerals yellow
Clay minerals
Formed through weathering of feldspar. Most are product of hydrolysis
Sandstone types
quartz-sandstones, feldspathic sandstones, lithic sandstones, muddy sandstones, mudstones
Greywacke
muddy sandstone that is grey in color (dirty sandstone)
Quartz subdivisions
Monocrystalline (single quartz crystal in a grain). Usually volcanic, not undulatory
Polycrystalline (multiple quartz crystals in a grain). Mature sandstones, undulatory
Foliated (quartz crystals are squashed and elongated). Seen in metamorphic grains, polycrystalline quartz
Chert (cryptocrystalline, very small crystals). Speckled appearance under microscope
generally optically clear, conchoidal
Feldspar subdivisions
Potassium feldspar (carlsbad twinning) orthoclase. Turns yellow with staining
Plagioclase feldspar (polysynthetic twinning) albite. Doesn’t turn yellow with staining
Unidentified (hard to tell)
usually have close to 90 degree cleavage in 2 directions
Zoning in plagioclase
Early plagioclase rich in calcium (anorthite)
Late plagioclase rich in sodium (albite). Show more zoning, center of grain is often more calcium-rich and fines outward to sodium rich
Lithic types
Sedimentary - (mudstone, siltstone, shale, sandstone, carbonate)
Metasedimentary - (foliated, massive)
Metamorphic (look for deformation)
Plutonic (granite, pyroxenes, porphyry)
Volcanic (basalt, feldspar)
Euhedral, subhedral, anhedral
How well formed crystal faces are; euhedral are well formed, anhedral are irregular and have few faces. subhedral are somewhere in between
Undulatory extinction
Because the c-axis of the grain is bent due to heavy deformation, the grain will go extinct at different times (quartz)
Optic axis (hexagonal and tetragonal)
Same as the c axis (vertical). When looking down this, the mineral will go extinct (no light splitting)
Controls on sandstone composition
Source composition (dependent on tectonic setting, eg. quartz varieties)
Modification during weathering (climate)
Modification during transport (sorting, compositional
stabilization)Modification during burial (introduction of cements,
deletion of labile grains)
Dolomite
rhomb, with warm, pale brown colors (high birefringence)
Quartz grades
Lower grade (lower metamorphic) quartz tends to be undulatory. Polycrystalline, less clear
Upper grade (upper metamorphic, volcanic) quartz tends to be less so. Monocrystalline, optically clear
Quartz and dolomite replacement
Quartz dissolves under basic conditions, precipitates in acidic conditions
Dolomite precipitates under basic conditions, dissolves in acidic conditions
dolomite replaces the quartz
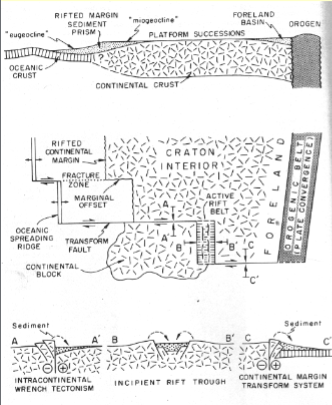
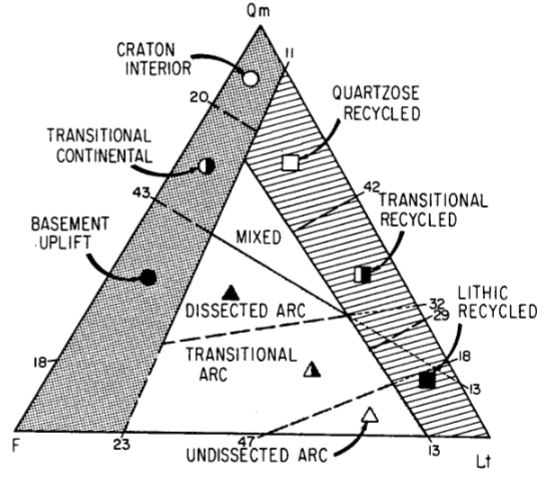
Stable craton provenance
Associated with little metamorphic activity; quartz rich. Few lithics and very little (if any) feldspar presence
seen in continental interiors and passive platforms
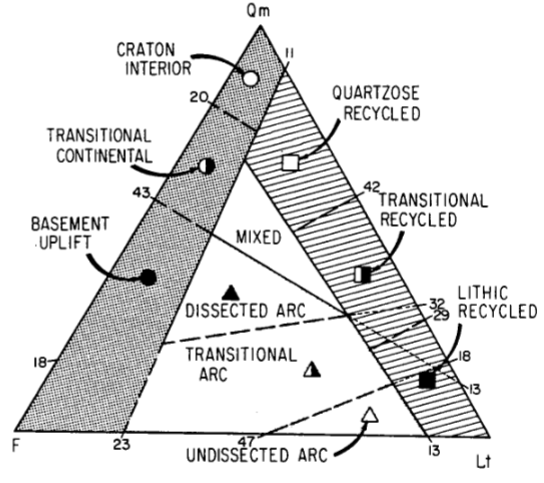
Continental block provenance
Chunk of continental crust (granite). Generally feldspar and quartz rich. Compositions similar to bedrock
Seen in rift-related settings (east Africa), and transform faults
Recycled orogen provenance
limestone and surface sedimentary rocks are visible and deformed, but basement metamorphic layers are rarely visible. Basal layers are not deformed, and so the sediment that is produced will be mainly sedimentary (sand-sized lithics and quartz; chert, flint, siltstone, sandstone, dolomite)
seen in foreland fold thrust belts and subduction zones
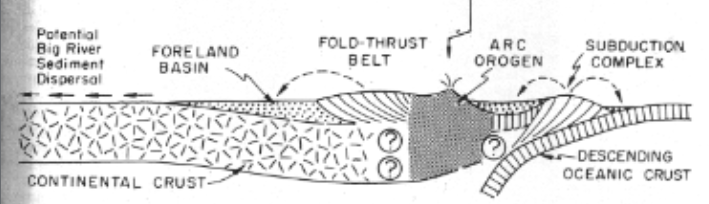
Magmatic arc provenance
Arc origin sources show mainly lithic-volcanics and feldspatholithics. Grains are dark in color and generally immature, not showing as much rounding/weathering as other provenances
seen in island arcs and continental arcs
Weathering in hot, moist climates
Hydrolysis happens faster because heat is a catalyst. Weathering happens much more quickly, chemically and physically. Polycrystalline quartz is broken down into monocrystalline grains, feldspar and lithics are removed
Weathering in cold, dry climates
Hydrolysis happens more slowly due to less heat. Weathering happens slowly because there are fewer catalysts to speed up the process. More feldspar and lithics survive in sandstones
Larger lithic grains are more likely to
Survive in transport. Smaller lithic grains are weaker and break into their constitutive parts. Finer sand grains also mean lower presence of feldspar (downstream fining)
Coarser sandstones have higher presence of
lithics than fine grained sandstones. It is important to collect sandstone with similar grain sizes when comparing them
Determining sandstone maturity
look at the fabric of the sample (matrix/grain support, grain contact, overgrowths, etc.)
look at grain texture (size, shape, sorting, rounding)
look at composition of framework grains
look at composition and nature of interstitial material (diagenetic contributions)
Overgrowths
layers of new quartz that form on top of existing sand grains during the diagenetic process. Remain in optical continuity with the original grain. Layers preserve the original rounded detrital quartz grain. Overgrowths can become abraded if sandstone is weathered
Textural anomalies
Irregularities in grain sorting that indicate the sediment must have undergone different processes before being deposited
ex:
well-rounded sand grains floating in silt or clay matrix
extremely well-sorted but very angular grains
finer grains better rounded than coarser grains
Types of cement in siliciclastic sandstones
Most common: carbonate, silicate (qtz), clay
less common: sulfate, halite, iron oxides
Types of authigenic grains in siliciclastic sandstones
feldspar, hematite, glauconite, zeolites (volcaniclastics)
How to determine siliciclastic type from quartz
see image

Feldspar varieties (complex)
see image

Lithic fragments are the most direct evidence of
provenance types (where the rock originated). However, they can be fine grained and hard to interpret
Factors influencing presence/type of lithics
– Source type
– Distance from source (e.g., schist fragments restricted to close to source)
– Generally more prevalent in coarser fractions
– Durability influenced by climate
– Some are highly susceptible to weathering and diagenesis (e.g. volcanic lithics)
– Intraclasts derived from within basin (mud chips)
Volcaniclastics
Very volumetrically important. Eruption type can be related to composition; silicic is indicative of explosive eruptions (felsic) while mafic is indicative of quiet eruptions
Tuff types
Vitric (glassy appearance; indicative of pumice, flow banding)
Crystal (crystals may be any volcanic material)
Lithic tuff (variety of lithic fragments can be incorporated, either during eruption or subsequent reworking of volcanic sand)
