Biological Molecules and nucleotides
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
What are the common elements in a biological system?
the common elements are Nitogen, Sulfur, Phosphorus, Carbon, Oxygen, and Hydrogen
What defines a monomer? What are the monomers of life?
A monomer is a molecule that can be covalently bonded to other identical or similar molecules to form a polymer.
Amino acids, monosaccharides, and nucleotides
What molecule is not a monomer but can form supramolecular structures? Why is it not a monomer?
Lipids. They cant be called monomers since they do not covalently bond to one another to form chains of repeating similar molecules.
What are the 4 major biomolecules?
Amino acids, lipids, nucleotides, and carbohydrates
what colours are used to represent the common biological elements?
Sulfur = yellow
Nitrogen = blue
Hydrogen = white
Carbon = black/gray
Phosphorous = orange
Oxygen = red
What are trace elements and name one important one?
Elements found in very small amounts biologically. Iron is an important one for oxygen transport and ETCs.
What is another name to describe carbohydrates? Generally, what is the ratio of C, H, and Os?
Polyhydroxy aldehydes and ketones.
CnH2nOn. each carbon except for one has a hydroxyl group
-NH2 and -NH3+
What is the name of this functional group?
What is a molecule containing this group called?
This is an amino group
a molecule containing it is an amine.
-SH What is this group called?
What is R-SH called?
A sulfhydryl group
A thiol
Compare ethers and esters
Ethers have a carbon flanking an oxygen on either side while esters are a carbonyl group where the carbon is attached to another oxygen and that oxygen is attached to an R group
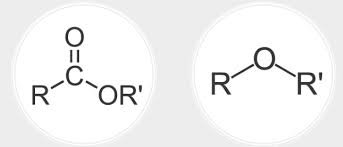
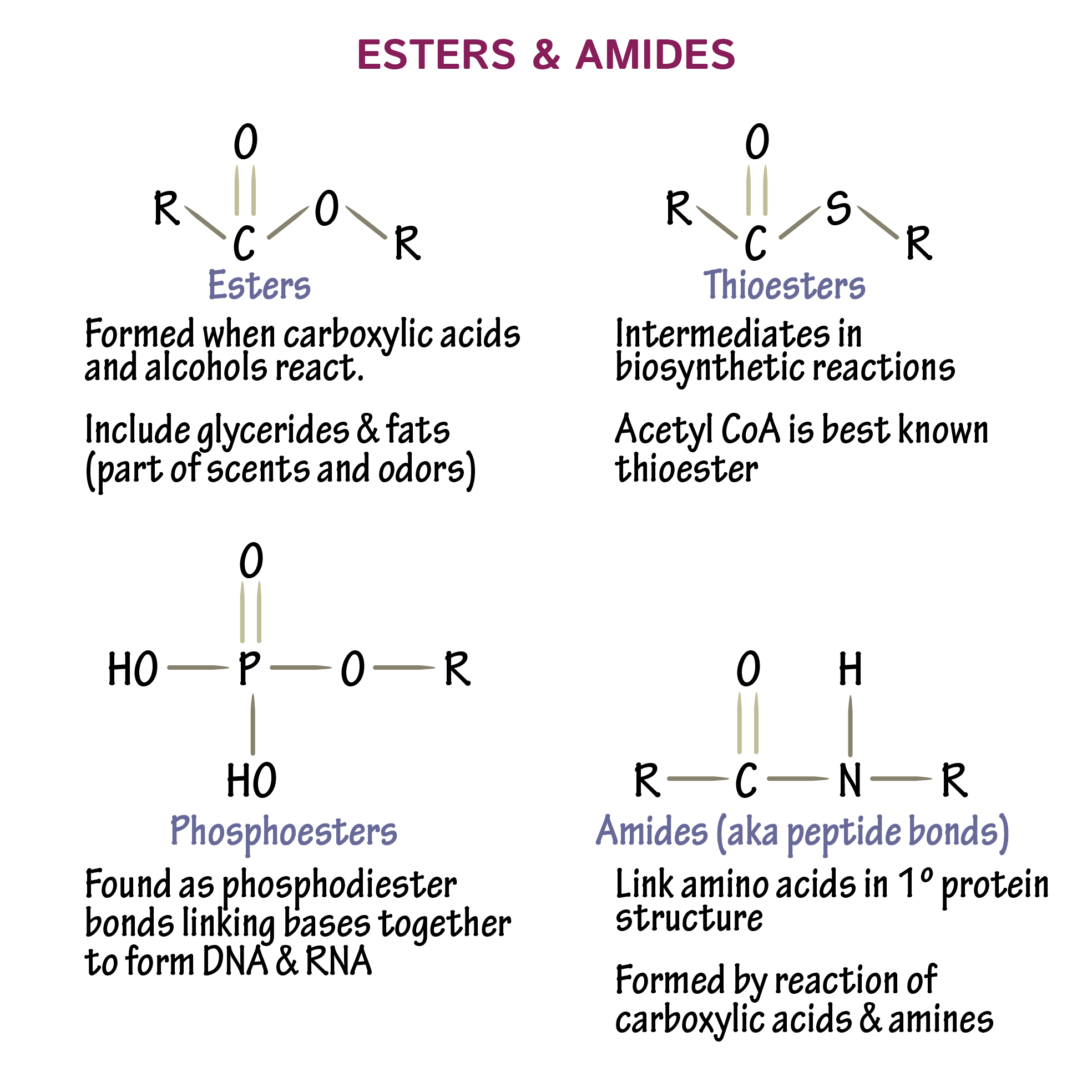
What is a thiosester? A phosphoester?
A thiosester is an ester where the carbonyl carbon is attached to an S instead of oxygen
A phosphoester does not have a carbonyl. The double bond is between P and O.
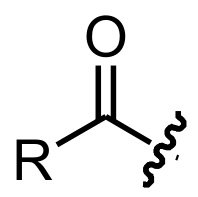
What is an Acyl group?
An acyl group is essentially a carboxylic acid group minus the OH.
What does it mean that polymers have directionality?
Their bonds all run in the same direction and their ends are geometrically distinct.
What bonds form between monosaccharides? Amino acids?
Glycosidic linkages. Peptide bonds
What is the electron geometry of H2O?
How many H-bonds can H2O theoretically form as a liquid? In ice?
tetrahedral
A maximum of 4 are possible, 2 as a donor and 2 as an acceptor.
There are 4 in ice and 3 in water.
What is a hydrogen bond? What type of interaction?
What are longer in water, covalent or H-bonds?
A hydrogen bond is a type of electrostatic interaction between partial charges. A single hydrogen is involved: it is covalently bonded to an electronegative atom in one molecule, and interacts with the electronegative atom of another molecule. (EN atoms = O,N, or S. no fluorine in biological scenarios)
H bonds are about 2x longer than the covalent bonds in water
What are the 4 types of non-covalent bonds? Describe each.
Ionic interactions - between a full positive and full negative charge. Weaker in aqueous environments
Hydrogen bonds - an electrostatic interaction between partial charges involving a Hydrogen donor and a hydrogen acceptor
Van der Waals forces - Dipole-Dipole interactions between 2 polar molecules and London dispersion forces between nonpolar molecules. LDFs include temporary distortions of electron clouds and are present in all substances.
Hydrophobic effect - the tendency of water to minimize its contact with non-polar substances, causing the hydrophobic substances to aggregate and disrupt the normal hydrogen bonding pattern of water.
What are the 3 electrostatic forces in order of strongest to weakest?
Ionic interactions
Hydrogen bond
Van der Waals
Why is the hydrophobic effect spontaneous?
It is entropically favourable because the amount of water in an ordered state is less than if the hydrophobic substances were not aggregated.
What is an amphipathic molecule? What molecules form a Micelle?
Why do phospholipids form a bilayer?
A molecule that is both hydrophobic and hydrophilic (polar and non-polar regions)
Lipids with one fatty acid tail since their conical shape allows a monolayer. Phospholipids are more bulky/”rectangular” therefore to form a sphere they must be arranged in a bilayer.
What experiment proved that DNA stores genetic information using T2 bacteriophages?
The Hershey and chase experiment
Steps = Infection, blending, centrifuge.
What are some functions of nucleotides and nucleic acids?
Enzymes (RNA)
Store genetic information
Electron carriers
Energy transfer (ATP—>ADP)
Decoding
What are purines? pyrimidines?
Purines are a six membered ring attached to a five membered ring. Each ring is heterocyclic since it contains carbons and nitrogens. Purines = A and G
Pyrimidines are a single 6-membered ring with 2 nitrogens. Purines = C, U, T
At what positions in a pyrimidine ring are the nitrogens? What about purine rings?
Pyrimidine = 1 and 3
Purines = 1, 3, 7, 9
What is the difference between a ribose and deoxyribose sugar?
A base + a sugar = what?
Ribose has a 2’ hydroxyl group
a nucleoside
what carbon in a sugar ring is linked to the base in a nucleoside?
What are the name conventions for nucleosides?
the 1’ carbon
Purines become “osines”
Pyrimidines become “idines”
How is a phosphate linked to the 5’ carbon of a sugar of a nucleoside?
does the phosphate or sugar lose an OH group?
by a phosphoester bond
The phosphate loses an OH group and the sugar loses an H
What is ribothymidine?
A thymine base bonded to a ribose sugar
What stabilizes the primary structure of nucleotides? What is the primary structure?
3’ to 5’ Phosphodiester bonds. The primary structure is the sequence of nucleotide residues.
What is the 5’ end of a nucleic acid? 3’ end?
The 5’ end has a 5’ carbon that is not involved in a Phosphodiester bond.
The 3’ end has a 3’ carbon that is not involved in a Phosphodiester bond.
Both may have other things attached but as long as there is no phosphodiester bond, then it is the end.
The overall nucleic acid runs _______, and the bonds run _______?
5’ to 3’ _ 3’ to 5’
What is the charge of the DNA backbone?
Uniformly negatively charged
Why is RNA more soluble than ssDNA?
RNA can form 3 extra hydrogen bonds per residue due to its 2’ hydroxyl group
What is released in the formation of a phosphodiester bond?
a pyrophposphate (PP)
What enzyme hydrolyzes phosphodiester bonds? At what position does it do this normally? what happens if it occurs the abnormal way?
Phosphodiesterase; closer to the 3’ end (bond between P and O)
This creates normal ends but if it occurs closer to the 5’ end, then the products will have a phosphate at the 3’ end and an OH at the 5’ end.
Why does non-enzymatic alkaline hydrolysis only occur for RNA?
What are the products?
because a 2’ hydroxyl group is required
Products are a nucleoside and a cyclic intermediate that has a 50:50 chance of becoming a 3’,5’ bisphosphate nucleotide or a 2’,5’ bisphosphate nucleotide
what is a nucleotide with no 3’ or 2’ OH group called?
dideoxynucleotide
What are some properties of the bases in nucleic acids?
hydrophobic/poorly soluble but can form H-bonds
heterocyclic and aromatic
Planar
Absorb UV at 260nm
What does the 260/280 ratio inform you? What is the ratio ideally?
It tells u about the purity of a DNA sample. The ideal ratio is 1.8-1.95. Lower indicates protein contamination.
Which absorbs UV better: ssDNA or dsDNA?
What is a hypochromic shift? What is a hyperchromic shift?
ssDNA
A hypochromic shift is a shift from high to low absorbtion which would be equivalent to a renaturation (ss to dsDNA)
A hyperchromic shift is from low to high absorbtion equivalent to denaturation
Compare Z, B, and A DNA
Z = left handed
B = right handed (Normal)
A = compressed
What is secondary structure of DNA? What is the major stabilizing force? Minor force?
It is the double helix of DNA (when two strands come together)
Major stabilizing force = base stacking interactions which include hydrophobic and van der Waals forces.
Minor = Hydrogen bonds
What are chargaff’s rules? what do they apply to?
Chargaffs rule supply only to double-stranded DNA.
They are A = T, C = G, and (A+C)/(G+T) = 1
When 2 strands of DNA come together and H-bond, the overall polarity of the DNA ________.
decreases
why is DNA still soluble if bases are largely hydrophobic/insoluble?
Because the backbone, which is exposed to H2O, is polar and charged.
Being complementary is the ability to ____________?
H-bond when antiparallel
Describe denaturation/DNA melting? What conditions favour denaturation? How is it different that degradation?
Denaturation is the reversible breaking of non-covalent bonds in DNA (base stacking interactions and H-bonds).
Conditions that favour this are a high pH, low salt, and high temperature.
Degradation is breaking the covalent bonds and is not reversible.
What is Tm on a DNA melting curve? is Tm higher or lower when %G/C decreases?
Tm Is temperature at which half the DNA in a sample is single stranded and half is still double stranded (midway point).
Tm is lower when %G/C decreases.
What are the steps of DNA renaturation? What conditions favour renaturation?
Nucleation (slow step and must cool sample slowly)
Zippering (fast step, helix completion)
Favourable conditions: Low temperature, High salts, Low pH (below ~9.5)
Why is a G-C pair “stronger” than a A-T pair?
It has stronger base-stacking interactions
compare pKa and pH
pKa is the strength of an acid while pH is a measure of protons in solution.
If pH > pKa, then the acid will be protonated or deprotonated?
deprotonated
What occurs when pKa = pH?
the concentration of conjugate base is equal to the concentration of the acid in a solution
Increasing pH for DNA changes Tm, but increasing pH for RNA causes _____?
Alkaline hydrolysis
Why is RNA melting possible?
Yes because RNA can have intrastrand base pairing
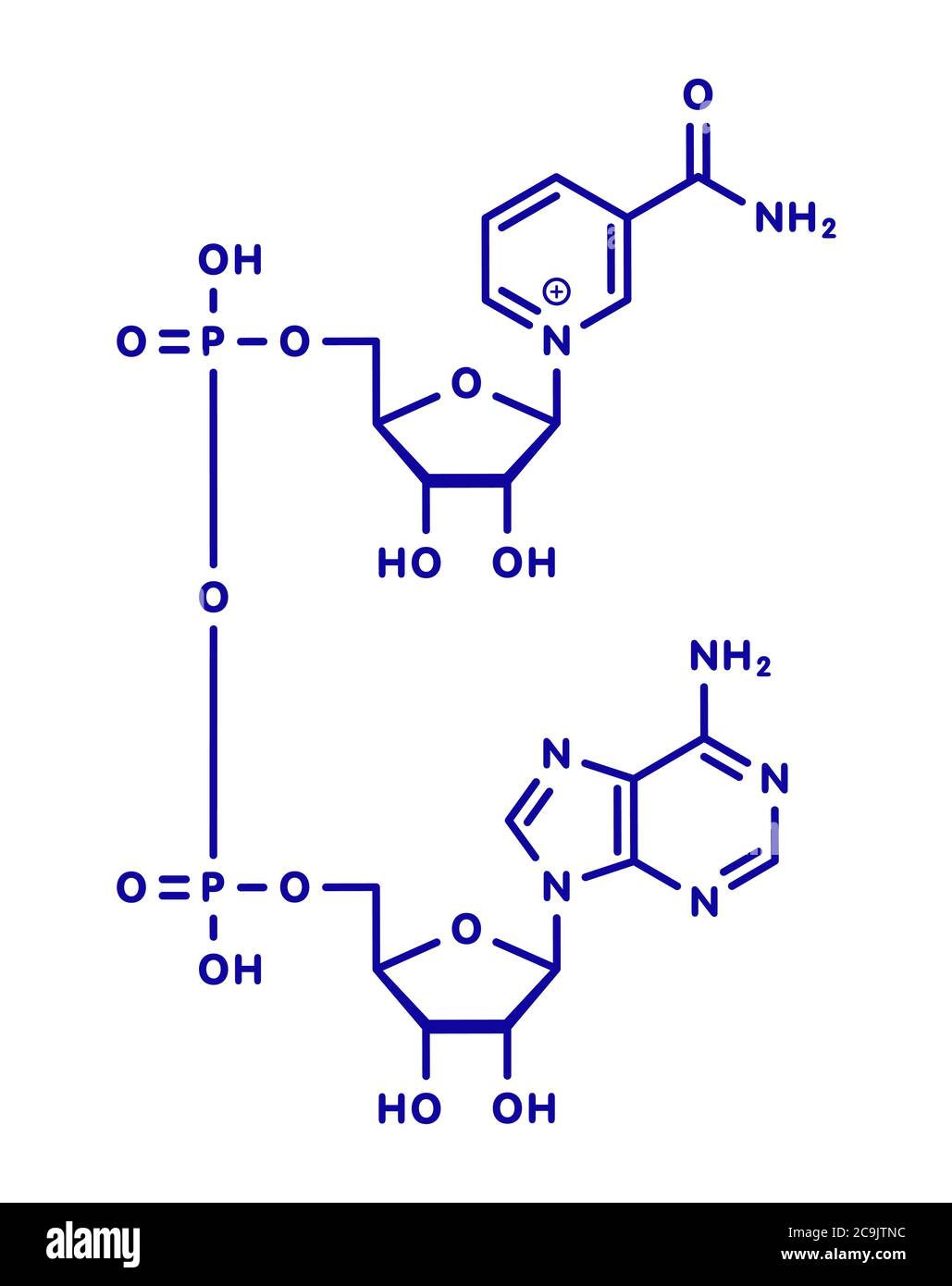
What are the 2 bases in this molecule? what is the molecule? what bond connects the 2 monomers? Is this the oxidized or reduced form of the molecule?
Top = Nicotinamide base
Bottom = adenine
The bases are connected by a phosphoanhydride bond
This is NADH in its oxidized form (NAD+)