422 exam2 last minute notes
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
Distributed as powders
B-lactams
epoxides with N
peptides
Allergic/immunogenic reactions
Epoxides
Aziridines
B-lactams
Quinones
Aromatic Criteria
Planar
Fully conjugated
4n + 2
Common aromatic rings
Rings that are not aromatic
5 and 6 membered rings
7 membered rings
Faster metabolism
Lower resonance energy
Amide bonds have partial double-bond character (resonance) —>
planar, trans preferred, restricted rotation
Low stability and low solubility
Planar (sp2)
Rigid
pi-pi stacking (aromatic)
Low Fsp3
Rigid
Low solubility
Lipophilic
High Solubility
Flexible (sp3)
Disrupt packing
High Fsp3
High solubility
Small LogP
Lower brain penetration
More polar (hydrophilic)
Poor permeability
Good solubility
Oral
Large LogP
High brain penetration
More lipophilic
Good permeability
Poor solubility
Topical
Good BBB permeability
LogP 2-4
Small
Nonpolar
Low PSA
Few HBD/HBA
Bad BBB permeability
Large
Polar
Charged
High PSA
Lipinski: Good oral absorption
MW < 500
LogP < 5
HBD < 5
HBA < 10
Lipinski: Poor oral absorption (topical)
MW > 500
LogP > 5
HBD > 5
HBD > 10
Quartenary ammonium compounds
Veber Good bioavailability
< 10 rotatable bonds
PSA < 140
Veber Poor bioavailability
Many rotatble bonds
High PSA
Epoxide
Enthalpy driven
ΔH
Entropy driven
−TΔS
Smaller Entropy Penalty
Few RB
Larger Entropy Penalty
Many RB
Increase binding affinity
Rigid, fused rings
High Plasma Protein Binding
Planar
Lipophilic
Bioavailability decreases when taken with milk/Mg2+/Ca2+
Carboxylic acids
-floxacin
-tetracycline
Few RB
Less entropic penalty
Better oral bioavailability
Structure determinants
Bond length
Bond angle
Conformation
Hybridization
Conformers differ by
rotation not connectivity
Trans conformers are generally lower energy than
gauche
Synperiplanar =
Synclinal =
Antiperiplanar
0
60
180
Rate the strength of attractions
Charge–charge (ionic) > HB > dipole > VDW
Bioavailability will drop with citric acid due to
Altered ionization/chelation, not transporter inhibition
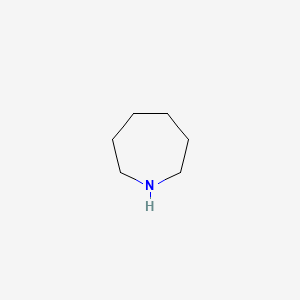
Azepan
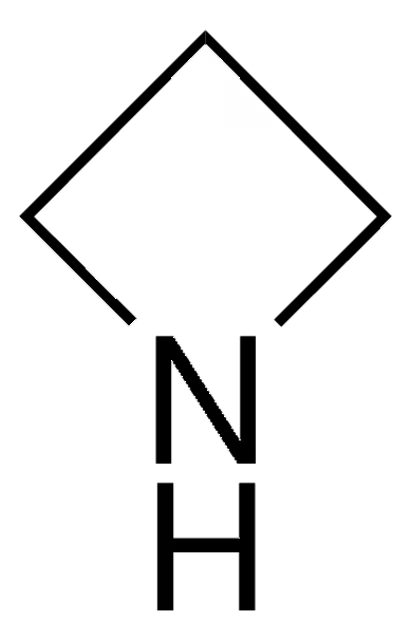
Azetidine
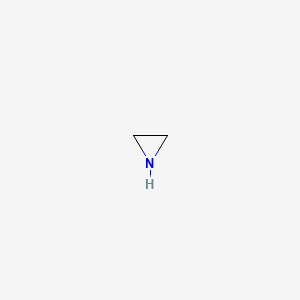
Aziridine
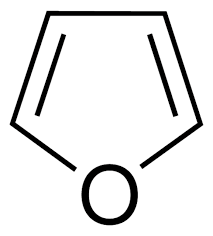
Furan
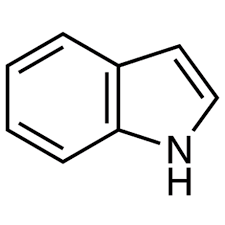
Indole
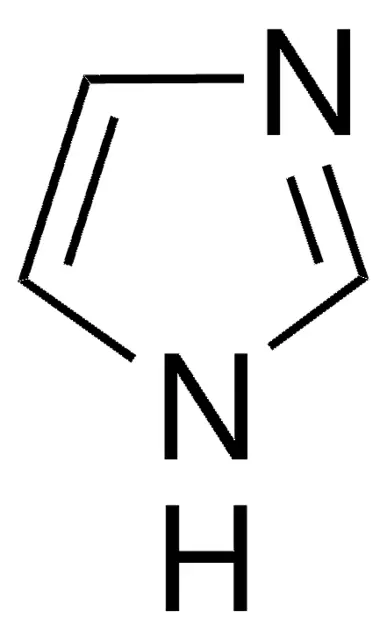
Imidazole
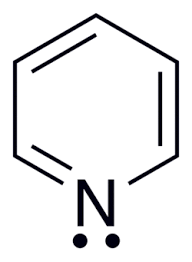
Pyridine
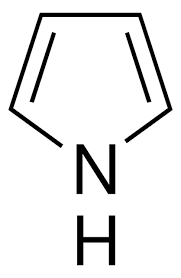
Pyrrole
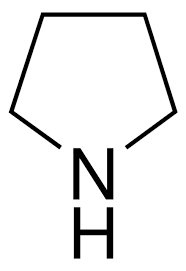
Pyrrolidine
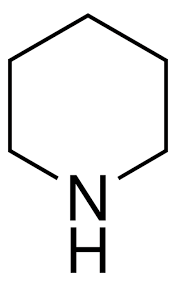
Piperidine
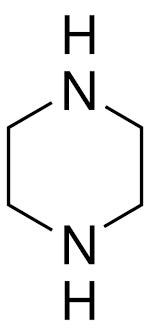
Piperazine
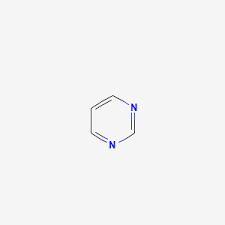
Pyrimidine
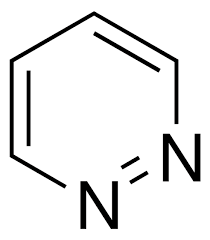
Pyridazine
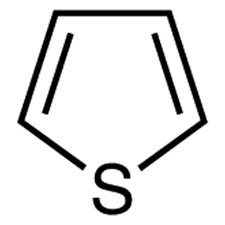
Thiophene
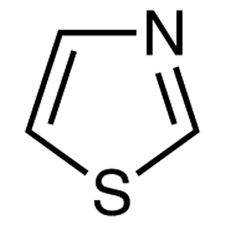
Thiazole
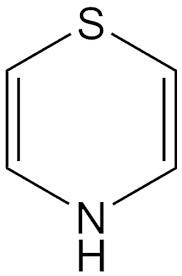
Thiazine
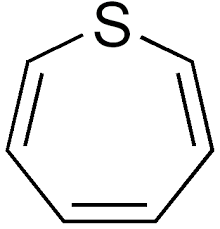
Thiepine
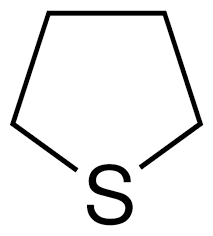
Tetrahydrothiophene
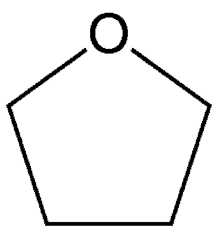
Tetrahydrofuran
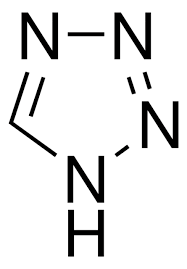
Tetrazole
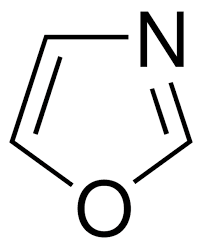
Oxazole
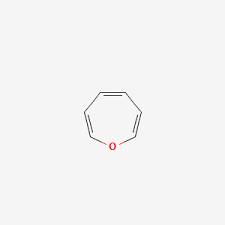
Oxepine
High tPSA
Poor BBB
Small RE
Fastest metabolism
Low logP
Best for oral medications
Large logP
Poor oral absorption
Good topical use
High plasma binding
Large MW
Poor oral absorption
NH Groups
pka=10
pH < pka → protonated (positive)
Carboxyl groups
pka=5
pH > pka → deprotonated (negative)
pH < pka
pH > pka
protonated (positive)
deprotonated (negative)
What cannot be a HBA
Sulfur/Pyrrole
Increase concentration of drug in brain (fatty tissue) and decrease plasma
thiophene
Decrease concentration of drug in brain (fatty tissue)
Pyrrolidine
Trans is more
energetically favorable
PEPT1/PEPT2
LAT1
Large, neutral amino acid
OATPs
more than one carboxylic acid
Passive Diffusion
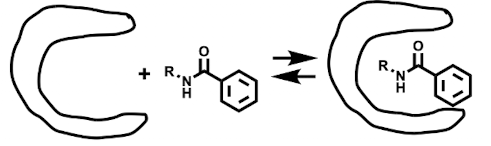
Non-covalent binding
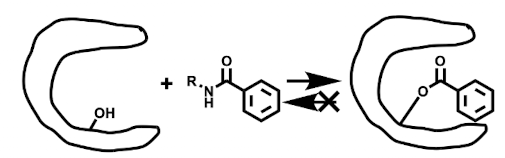
Irreversible binding
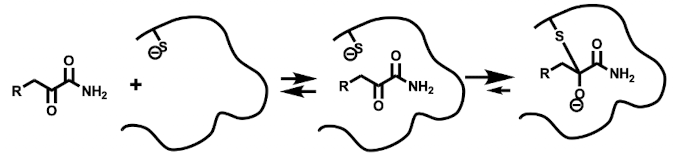
Covalent Reversible binding
same constitution
same molecular formula
same order of atomic connections (connectivity)
same configuration
same 3D arrangement of atoms and the same connectivity
(R vs S)
enantiomers
non-superimposable mirror images (left hand and right hand)
diastereomers
stereoisomers that are not mirror images and cannot be superimposed.
must have the same molecular formula and connectivity, but at least two stereocenters with different configurations
Racemate is composed of
2 non-superimposable mirror images
Newman
Fisher
R and S
D and L
Epimers
Only one chiral center is different