Carbohydrates, Lipids, Nucleic Acids and Proteins
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/41
Last updated 8:54 PM on 2/3/26
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
1
New cards
Identify the properties shared by all lipids
Hydrophobic, nonpolar, not polymers, do not dissolve in water
2
New cards
Identify the three types of lipids and their roles in an organism
Triglycerides provide energy storage, insulation and cushioning of organs. Phospholipids are a major component of the cellular membrane. Steroids are hormones.
3
New cards
Explain the difference between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids.
Saturated fats are composed of all single covalent bonds, and are solid at room temp. Unsaturated fats contain a double bond halfway through, and are liquid at room temp.
4
New cards
Why are saturated fats solid at room temp while unsaturated fats are liquid at room temp.
Saturated fats have a high melting point due to closely packed molecules, while unsaturated fats have a low melting point due to their double bonds that prevent close packing.
5
New cards
Identify the components of a phospholipids
composed of Glycerol, 2 fatty acids and a phosphate
6
New cards
define the term amphipathic
a region is hydrophilic in a region and hydrophobic in another. For example phospholipids have hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails.
7
New cards
Identify the three groups of molecules that are considered carbohydrates
monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides.
8
New cards
Write the general molecular formula for a monosaccaride
C6H12O6
9
New cards
List two functional groups in sugar
Hydroxyl, and carbonyl
10
New cards
List three monosaccharides and explain how they are similar and different.
Sucrose, fructose and galactose. They are isomers but they have different shapes.
11
New cards
list 3 common disaccharides and their role. How are they formed from monosaccharides.
Sucrose transports sugar in plants. Lactose is milk sugar in mammals. Maltose breakdown products of starch. They are formed by dehydration synthesis.
12
New cards
Difference between alpha ring structure and beta ring structure.
Alpha OH is on the bottom. Beta OH is on the top
13
New cards
Full names of DNA and RNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid and ribonucleic acid
14
New cards
Identify the type of chemical reaction that joins nucleotides to make a polynucleotide.
Dehydration
15
New cards
what type of fat is worst for heart, blood and body
Trans fat
16
New cards
why are trans fat harmful
we do not contain the enzymes to break them down
17
New cards
Shape of a steroid
(lipid) 3 hexagon and a dog house.
18
New cards
what is fiber
a carbohydrate
19
New cards
what is the monomer in the nucleic acid
nucleotide
20
New cards
3 components of Nucleic acids
Phosphate ground, sugar, nitrogen containing base
21
New cards
Explain the difference between DNA and RNA
Function, DNA is the genetic material that contains instructions, and RNA carries information from DNA to cell.
Nitrogenous, DNA AGCT, RNA AGCU
Shape, DNA double helix, RNA single stranded
Sugar, DNA deoxyribose, RNA Ribose
Nitrogenous, DNA AGCT, RNA AGCU
Shape, DNA double helix, RNA single stranded
Sugar, DNA deoxyribose, RNA Ribose
22
New cards
Explain what is meant by the term complementary when discussing nucleic acids. Explain which pairs of nitrogenous bases are complementary, the type of interaction between complementary bases, and how this interaction holds the double bond helix together in double-stranded DNA
Complentary means that each is a predictable counterpart of the other. A is complentary to T, G is complentary to C (both vise versa). The pairing is always the same making the double helix hold.
23
New cards
Discuss the role of DNA in reproduction and explain how the structure of the DNA molecule allows for production of two indenitical DNA molecules during DNA replication
DNA provides directions for its own replication. DNA is able to replicate due to the complentary base pairing
24
New cards
Describe how DNA and RNA work together to express the info encoded in a gene.
First the DNA is transcribed into RNA then transcription of info goes from DNA to RNA then the RNA molecules interact with proteins building of a cell. This is how DNA and RNA work together to read info
25
New cards
Describe the 4 parts of DNA
Phosphate, Deoxyribose, Nitrogen base, and hydrogen bonds
26
New cards
What parts make up the nucleotide
Phosphate, Deoxyribose, Nitrogen base
27
New cards
Draw the structural formula for an amino acid. Identify the functional groups of the A.A
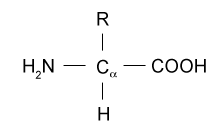
28
New cards
Explain how the 20 amino acids are similar and different to each other
They are similar as they contain a central carbon, and they contain an amino and carboxyl group. They are different as they each have a different R group
29
New cards
How to identify if the R group is charged, Hydrophobic or polar.
If it is charged than it will have a charge, Hydrophobic interactions are nonpolar, such as CH3, Polar groups such as OH... Polar will win over Nonpolar
30
New cards
Define Primary structure
a chain of amino acids connected and stabilized by peptide bonds
31
New cards
Define secondary structure
The secondary structures is a regular, repeating pattern of folding of a polypeptide chain, these structures are stabilized by hydrogen bonds between backbone atoms
32
New cards
Define Tertiary structure
irregular folding of a polypeptide chain, held together by interactions between R groups such as Hydrogen, Ionic and Disulfide bonds and hydrophobic interactions
33
New cards
Define Quaternary structures
polypeptides interact with each other to form a multi subunit proteins. They are stabilized with interactions between R groups (same as tertiary structure stabilizers)
34
New cards
Identify which bonds break when a protein is denatured by heat.
Peptide bonds do not break but all other levels are lost but hydrophobic break first
35
New cards
Identify which bonds break when a protein is denatured by PH
Peptide bonds do not break but all other levels are lost but ionic bonds break first
36
New cards
Explain why the specific shape of a protein is important
The specific shape of a protein is important as it determines the function of that protein
37
New cards
Explain why there is a large variety of possible proteins structures
There are 20 different amino acids, meaning there is a large number of possibilities where they could be arranged. This large number of possible arrangements leads to an even bigger number of possibilities for protein structures. These arrangements can also be bonded differently
38
New cards
carbohydrates function
Energy and energy storage
39
New cards
Elements of Carbohydrates
C, H, O
40
New cards
Lipids function
energy storage, and phospholipids make up cell membrane
41
New cards
Proteins function
Made up up C, H, O, N, P, S; involved in everything a cell does
42
New cards
Nucleic Acids fucntion
Store and tranmit infromation; made up from C H O N P; DNA and RNA